Bio - Unit 2 Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:23 AM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
aerobic respiration
the usage of the air to breathe
2
New cards
anaerobic respiration
organisms that don't need air to breathe
3
New cards
monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
4
New cards
polymer
a molecular structure consisting of many monomers
5
New cards
dehydration synthesis
the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers where a water molecule is released.
6
New cards
hydrolysis
use water to breakdown polymers into monomers
7
New cards
photoautotroph
organisms that make their own food by using the sunlight
8
New cards
chemoautotroph
organisms that make their own food by using chemicals
9
New cards
heterotroph
organisms that get food by eating other organisms
10
New cards
panspermia
theory that life was formed by the "seeds" of life coming from space and the spread across the earth
11
New cards
abiogensis
theory that life was formed spontaneously from inorganic molecules on earth recreating primordial soup
12
New cards
carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
- immediate energy, energy storage, and structure
- immediate energy, energy storage, and structure
13
New cards
lipids
hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and sometimes phosphorus
long term energy storage, cushions organs, insulates body, growth and development, reproduction, cell communication, cell membrane, and waxes
long term energy storage, cushions organs, insulates body, growth and development, reproduction, cell communication, cell membrane, and waxes
14
New cards
proteins
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sometimes sulfur
enzymes, structural support, transportation, cell communication, controls growth and cell differentiation, defense, movement, storage
enzymes, structural support, transportation, cell communication, controls growth and cell differentiation, defense, movement, storage
15
New cards
nucleic acids
phosphorous, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
form genetic material, useable energy in all cells
form genetic material, useable energy in all cells
16
New cards
amino acids
monomer for proteins
17
New cards
nucleotides
monomer of nucleic acids
18
New cards
endosymbiosis
eukaryotic developed by engulfing chloroplasts and mitochondria
19
New cards
chloroplast
during photosynthesis, uses sun's energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce sugars and oxygen
20
New cards
mitochondria
power house of the cell, uses cellular respiration in sugar to produce ATP
21
New cards
enzymes
speed up the chemical reactions of the cell to biologically useful rates
22
New cards
denaturing
changing the molecular conformation of a protein (enzyme)
23
New cards
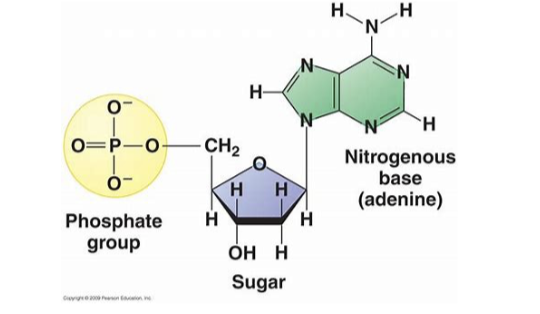
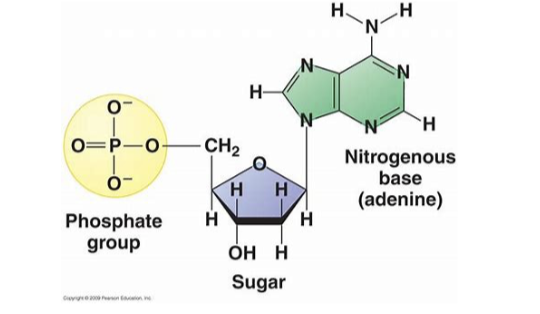
nucleic acids
24
New cards
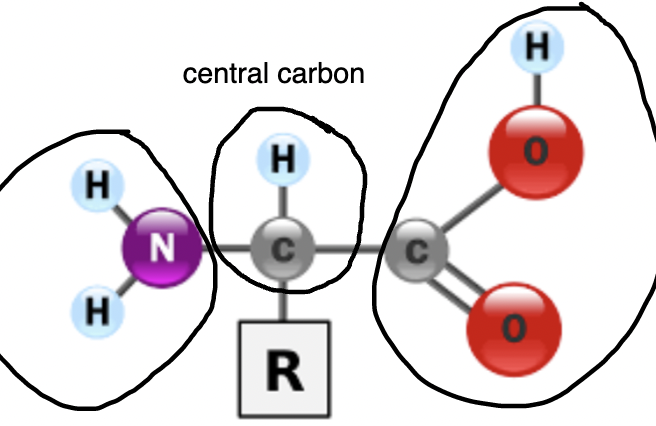
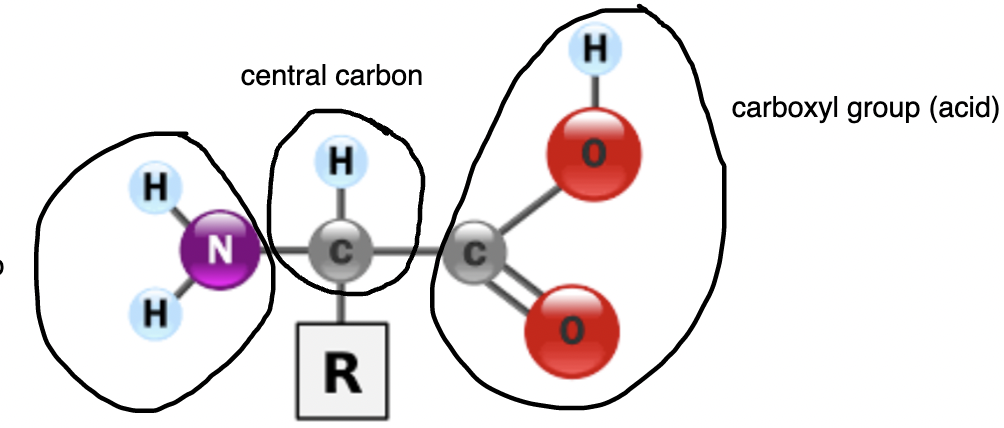
proteins
25
New cards
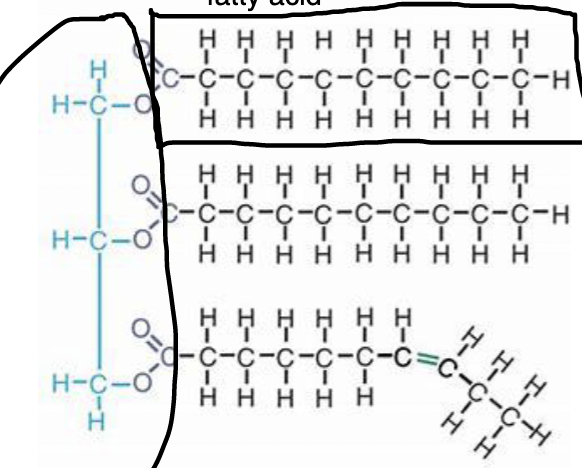
lipids
26
New cards
carbohydrates
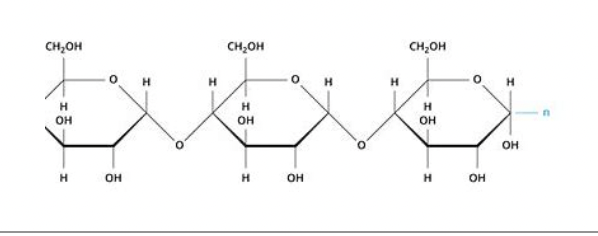
27
New cards
glycogen
the stored form of glucose that's made up of many connected glucose molecules - carbohydrates
28
New cards
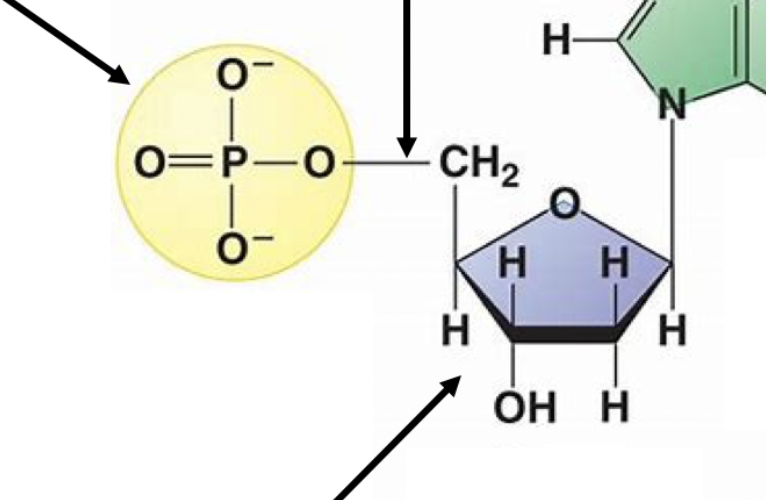
phosphodiester bond
bond between phosphate and sugars in nucleic acids
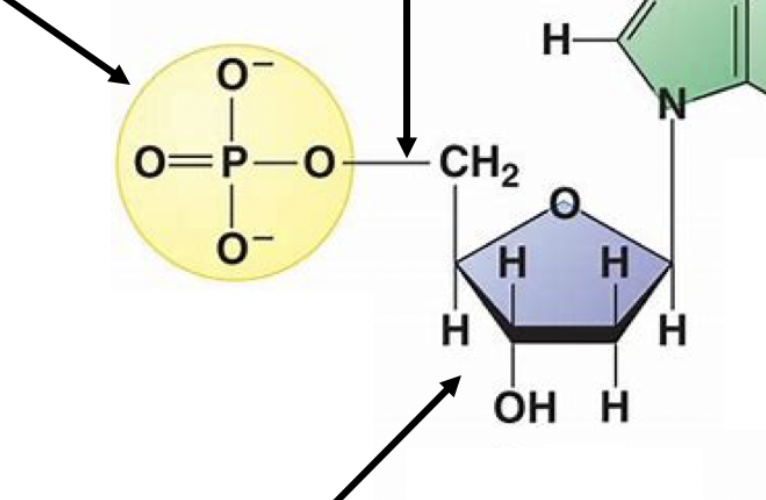
29
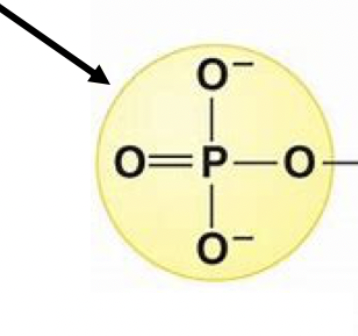
New cards
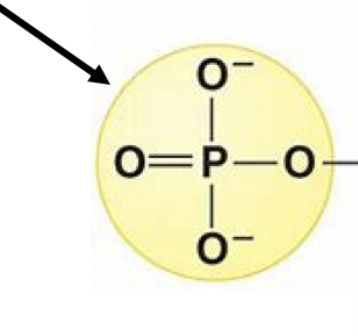
phosphate group
this group in nucleic acids
30
New cards
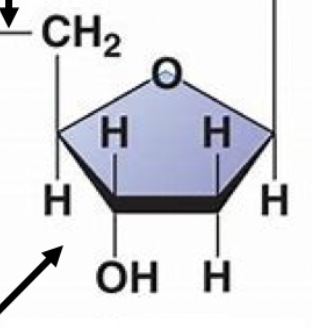
sugar
this group in nucleic acids
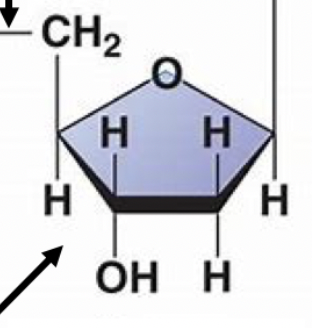
31
New cards
nitrogenous base
this group in nucleic acids
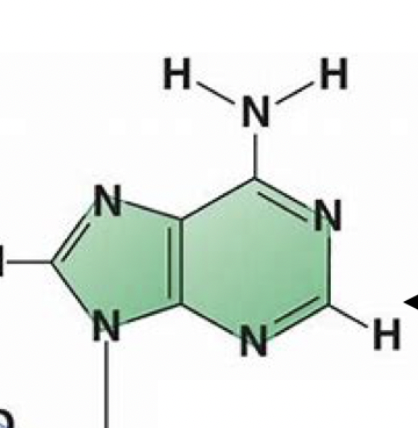
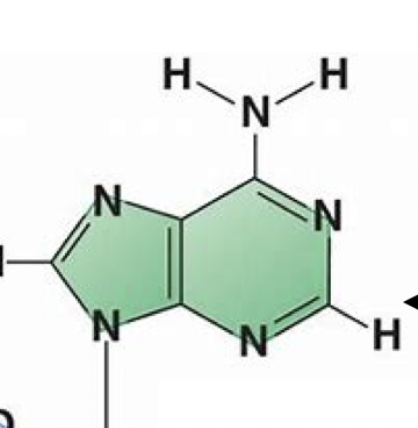
32
New cards
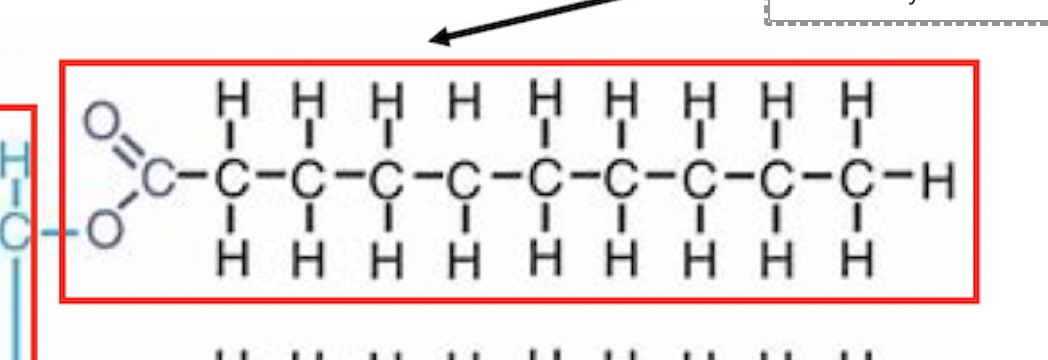
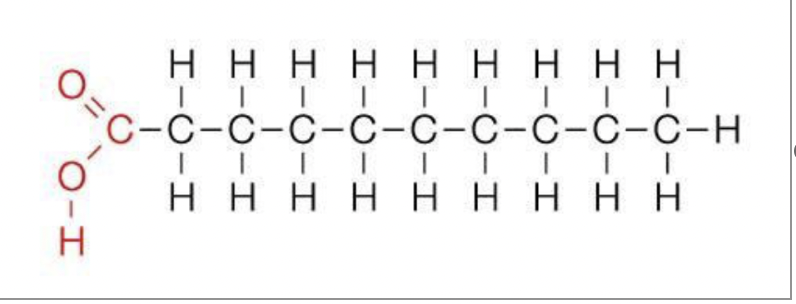
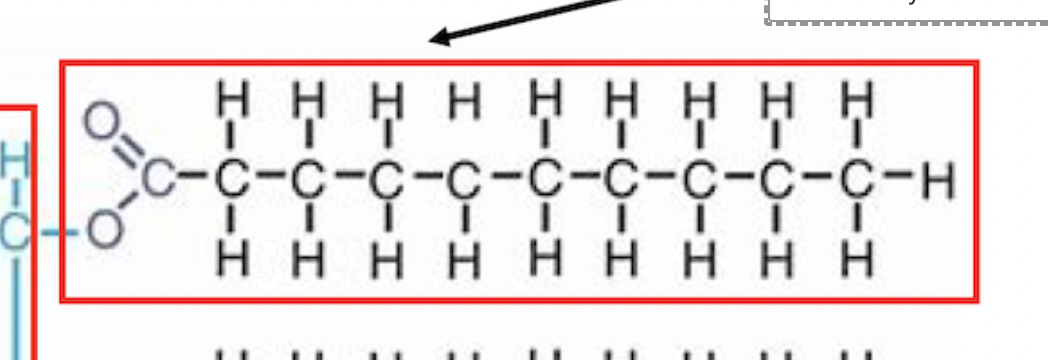
fatty acid
this group in lipids
33
New cards
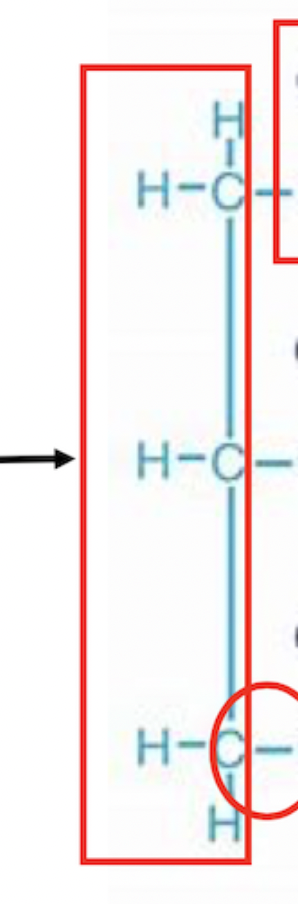
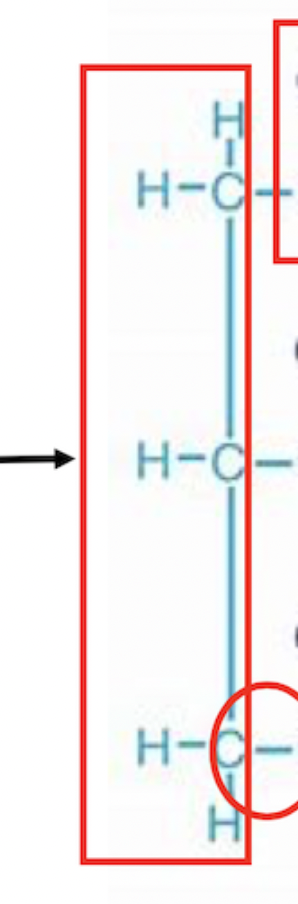
glycerol
this group in lipids
34
New cards
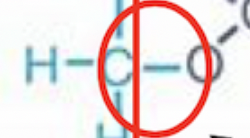
ester linkage
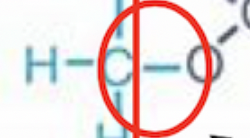
this bond in lipids
35
New cards
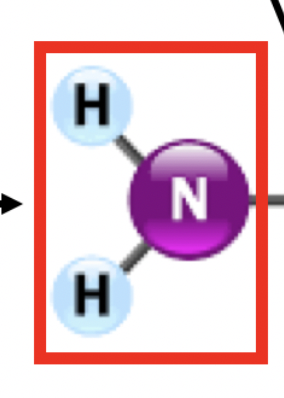
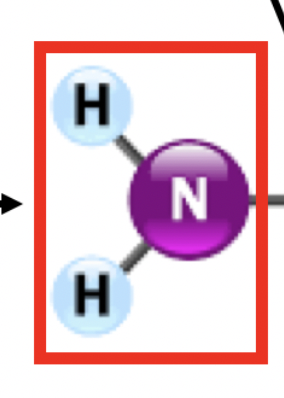
amino group
this group in proteins
36
New cards
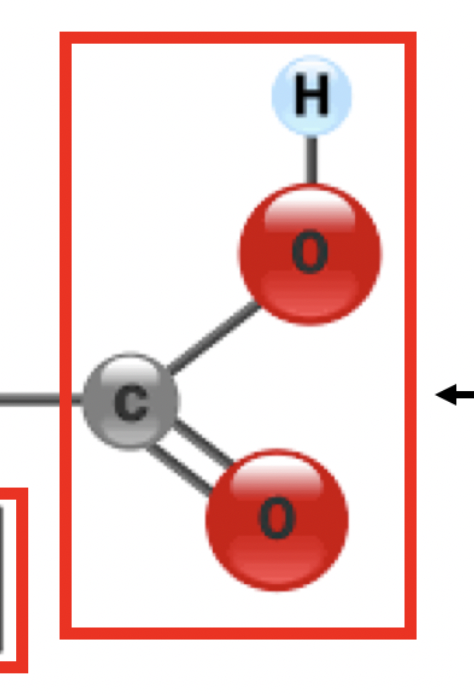
carboxyl group (acids)
this group in proteins
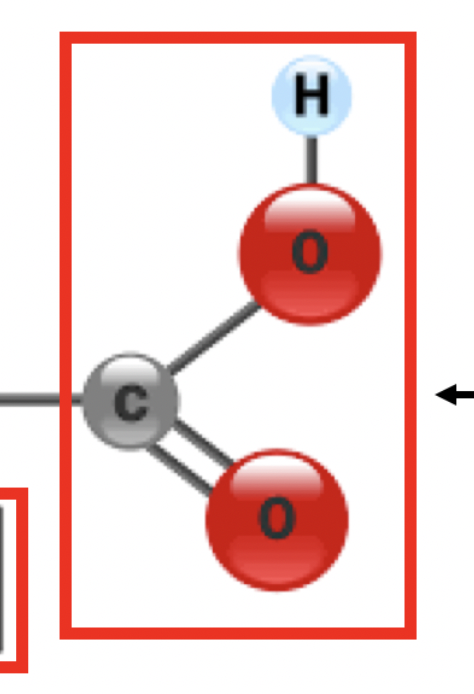
37
New cards
glycosidic linkages
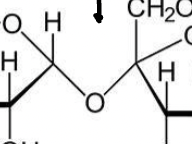
this bond in carbohydrates
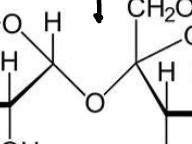
38
New cards
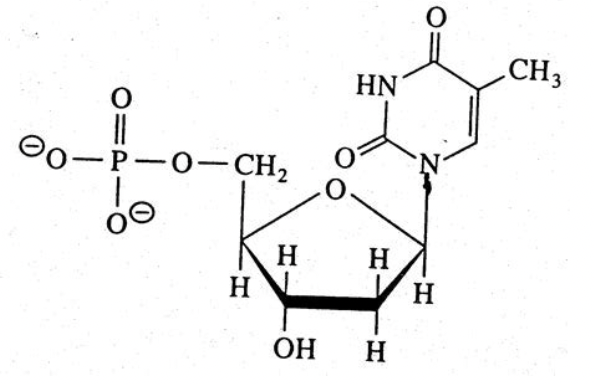
nucleic acid
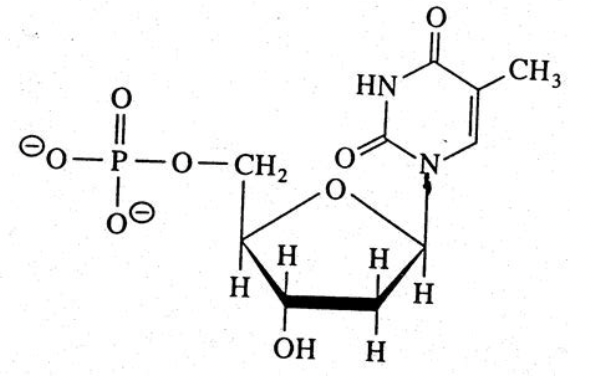
39
New cards
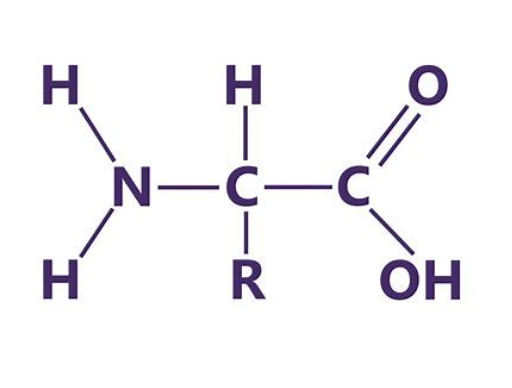
proteins
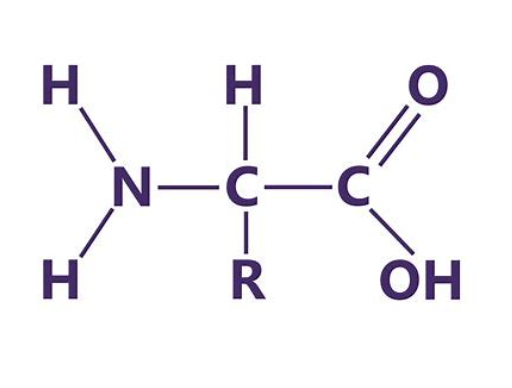
40
New cards
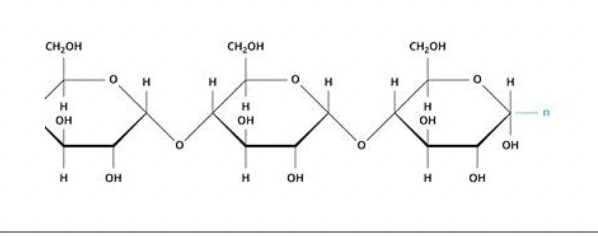
carbohydrates
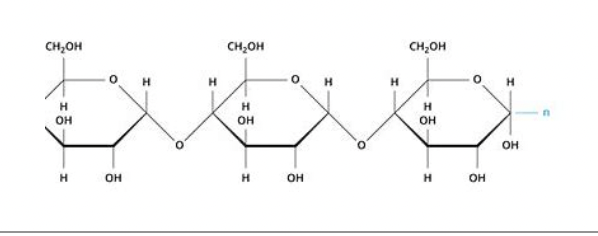
41
New cards
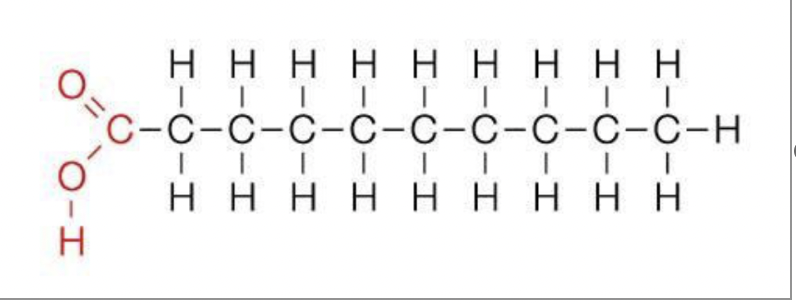
lipids
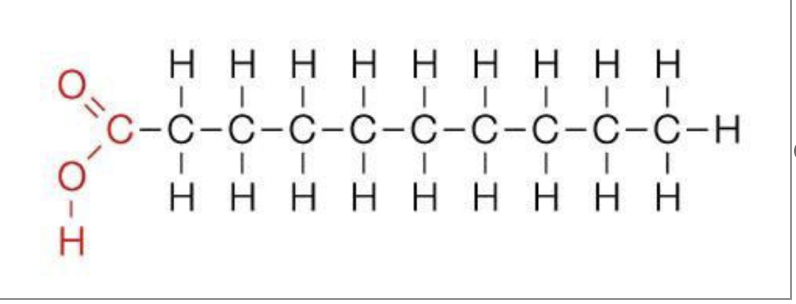
42
New cards
proteins
This macromolecule is responsible for building the majority of your structural components, like hair, skin, teeth and bones
43
New cards
the substance on which an enzyme acts
substrate