ORGCHEM REVIEWER
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is Catenation?
When carbon atoms can form long chains or rings by bonding with other carbon atoms.
Carbon bond strength and stability
Carbon-Carbon (C-C) and Carbon-Hydrogen (C-H) are very stable. This is because their bond strength is high and durable under a wide range of conditions.
What is tetravalency?
It is the property of carbons to bond their 4 valence electrons with four other atoms in the outermost shell. This allows for more diverse bonding possibilities.
What is hybridization?
Where carbons allows carbon to form different types of bonds by mixing its s and p orbitals into new hybrid orbitals.
What are organic compounds made of?
CARBON bonded to Nitrogen, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Sulfur, and other nonmetals
What type of bonding do organic compounds have?
Covalent Bonding - When electrons are SHARED between atoms not transferred.
What is the melting & boiling point of organic compounds?
They have a low melting and boiling point and weak intermolecular forces.
The boiling point lowers as branches increase. This is due to their molecular structure, which often includes long chains or rings that reduce the efficiency of intermolecular interactions.
What is the solubility of organic compounds?
They are SOLUBLE in non-polar (molecules with no electrical or partial charges) solvents and INSOLUBLE in water. However, functional groups such as hydroxyl in alcohols increase solubility in polar solvents because hydroxyl groups are water-loving.
What is their diversity in structure?
Vast range of structure
What is the electrical conductivity of organic compounds?
They are poor conductors of electricity.
What are Aromatic Compounds?
Under the Homocyclic ring structure. They have alternative sinlge and double bonds.
Characterized by their resonance and stability to the structure
What are Alkanes?
A type of hydrocarbon that consists only of single bonds between carbon atoms. They are saturated compounds.
What is a hydrocarbon?
An organic compound made ONLY of hydrogen and carbon.
What are Alkenes?
They contain at least one double carbon-carbon bond. They are unsaturated
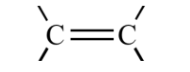
What are alkynes?
Alkynes are hydrocarbons with at least one triple carbon bond.They are also unsaturated compounds.
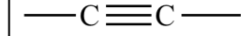
What are Alcohols?
It is a functional group that:
One or more hydroxyl groups (-OH)
They are polar because of the hydroxyl group (-OH) where oxygen is electronegative.
They are highly soluble in water due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds.
Used for ethanol, in alcoholic beverages, and as a biofuel.
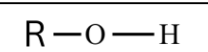
What are Thiols?
Functional groups that:
Contain sulfhydryl groups (-SH)
They are slightly polar
Less soluble in water than alcohols but can dissolve weakly
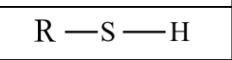
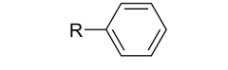
What are Arenes?
Functional groups that:
Are aromatic hydrocarbons that contain one or more benzene rings.
They are characterized by their stability and unique chemical properties due to resonance.
What are Ethers?
Functional groups that:
Consist of an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups.
They are generally nonpolar and insoluble in water.
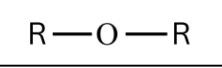
What are Alkyl Halides?
Functional groups that are:
Polar
Slightly soluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
They consist of an alkyl group bonded to a halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I).
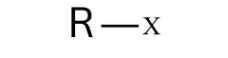
What is an alkyl group?
A molecular fragment derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom.
What is an aliphatic/acylic hydrocarbon?
They are hydrocarbons that have straight or branched chains only. No rings. They can either be:
Saturated (Single bonds)
Unsaturated (Double or Triple bonds)
What are alicyclic hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons that form a ring structure. They can either be heterocyclic (The ring has a non-carbon atom), or homocyclic (made of carbon atoms only). Under homocyclic:
Aromatic: Conjugated system
Non - Aromatic: No conjugation, no special ability.
Anti-romatic: Highly unstable and reactive
Tetravalency
Carbons have four valence electrons in its outer shell which allow for bonding.
Catenation
The ability for carbon to bond and create chains with other carbon atoms
Isomerism
Carbons can have the same molecular formula with different structures
What happens to the boiling point of alcohols as the carbon chain length increases?
The boiling point increases due to van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding.
The solubility of alcohols in water __________ as the carbon chain length increases.
decreases; short chains are highly soluble.
What are the products of oxidizing primary alcohols?
Primary alcohols oxidize to aldehydes and further to carboxylic acids.
Describe a primary alcohol.
An alcohol where -OH is bonded to a carbon attached to one other carbon.
What type of alcohol is oxidized to form ketones?
Secondary alcohols.
Why are tertiary alcohols resistant to oxidation?
Due to steric hindrance.
How does the boiling point of ethers compare to that of alcohols of similar molar mass?
Ethers have a lower boiling point than alcohols of similar molar mass.
What is the solubility of short chain ethers in water?
Slightly soluble.
Describe the polarity of alkyl halides.
Alkyl halides are polar molecules with a δ+ charge on carbon and δ- charge on halogen.
What happens to the boiling point of alkyl halides as the size of the halogen increases?
The boiling point increases due to dipole-dipole interactions.
Are alkyl halides soluble in water?
No, they are insoluble in water; soluble in non-polar organic solvents.
Describe a secondary alkyl halide.
An alkyl halide where the carbon bonded to the halogen is attached to two other carbons.
What is the primary characteristic of thiols compared to alcohols?
The S-H bond in thiols is less polar than the O-H bond in alcohols.
How does the boiling point of thiols compare to that of alcohols?
Thiols have a lower boiling point due to weaker hydrogen bonding.
What happens to the solubility of longer chain thiols in water?
They are generally insoluble.
Describe the polarity of thiols.
Thiols are weakly polar.
What is the result of the complete combustion of alkanes?
Produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), yielding maximum energy efficiency.
Complete combustion of alkanes formula
CnH_{2n+2} + (1.5n + 0.5)O_2 → nCO_2 + (n+1)H_2O
What occurs during incomplete combustion of alkanes?
Forms carbon monoxide (CO) or elemental carbon (C) along with water (H₂O), leading to reduced energy output and toxic byproducts.
Types of unsaturated hydrocarbons
Alkenes, Alkynes, Aromatic Compounds.
Alkenes formula
CnH2n; they contain at least one double bond and are used in synthesis.
Alkynes formula
CnH2n-2; they contain at least one triple bond and are utilized in complex molecule synthesis.
What are aromatic compounds?
Compounds that feature benzene rings, widely present in natural and synthetic materials.
Why do alkenes have higher reactivity than alkanes?
Due to the presence of double or triple bonds, which participate in addition reactions.
What is hydrogenation in addition reactions of alkenes?
An alkene reacts with H₂ in the presence of a metal catalyst (e.g., Pt, Pd, Ni), converting the double bond into a single bond.
What is halogenation in addition reactions of alkenes?
A reaction with halogens (Cl₂, Br₂) that forms dihalides.
Describe hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
A reaction with hydrogen halides (e.g., HCl, HBr, HI), following Markovnikov's rule.
What type of reaction is hydration in alkenes?
Addition of H₂O, often forming alcohols.
Constitutional isomers
Isomers that have the same molecular formula but different atom connectivity.
Stereoisomers
Isomers that have the same connectivity but different spatial arrangements (e.g., cis-trans isomers).