TEST: experiments, sampling methods, sampling bias
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
quantitative research
objectively collects + analyses numerical data to describe/predict/control variables
goal → test causal relationships between variables. predict + generalise results to larger population
operates w/ variables (= characteristic objectively quantified)
researchers aim to establish general laws of behaviour across diff. contexts
research ultimately support/rejects the theory being tested
hypotheses
researchers first read thru research available on their RQ (= literature review)
after aim → hypothesis (prediction of how IV affects DV)
experimental hypothesis predicts causal relationship between IV DV (want to support)
null hypothesis states IV has no effect on DV (want to reject)
clearly state IV DV + operationalise (clearly define how it will be manipulated/measured)
experimental and control group
psych. research never proves → supports experimental or fails to reject null hypothesis
experiment — key characteristics
quantitative research method. yields quantitative data (allows for stats)
goal → determine whether causal relation between variables exists (simplest has 1 IV, 1 DV)
findings → context-bound (few applications irl)
variables must be operationalised (expressed in terms of observable behaviour)
true experiment
aim → establish causality between IV and DV.
Ps randomly assigned to conditions
other variables controlled to establish causality
standardised procedure to allow replication + ensure reliability
often use deception to avoid demand characteristics
independent samples/repeated measures design
often have high internal validity (setting may lower external validity)
4 types of experiments
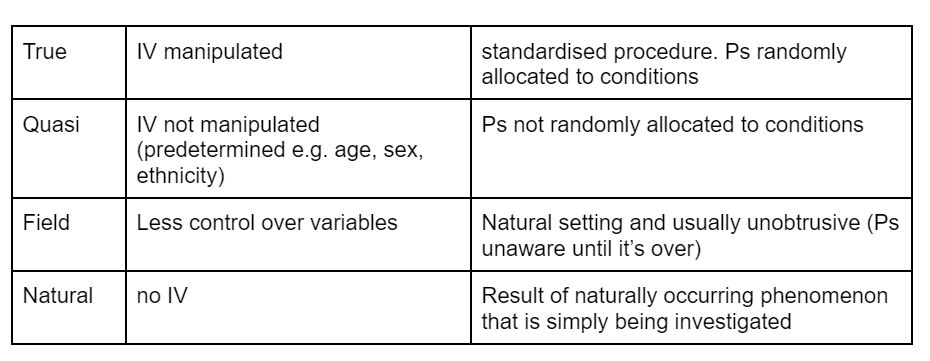
4 types of variables
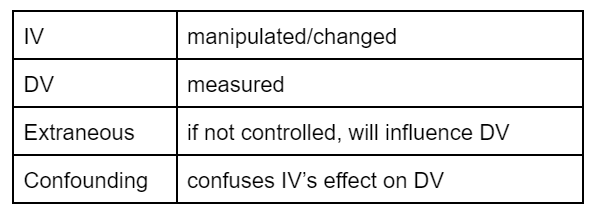
participants in research
people taking part = participants
psychologists define target population (group of interest for study)
sample → Ps chosen from target population
sample should be representative of population (may lack population validity otherwise)
bigger = better
sampling techniques and sampling bias
opportunity → Ps selected based on naturally occurring groups
random → each member of target population has equal chance of being selected
self-selected → Ps volunteer (based on ad/internet)
snowball → Ps recruit other Ps for study
stratified → sample matches makeup of population. Ps from various subgroups randomly selected
Sampling Bias → when non random sampling technique used (P variables in sample may not be representative and may influence outcome)
psych is WEIRD (western, educated, industrialised, rich, democratic)