Covalent Bonding !!
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
a bond formed when two positive nuclei are held together by their common attraction for a shared pair of electrons
What type of elements form covalent bonds?
nonmetals
Covalent bonds are __________ bonds
strong
Why do elements form covalent bonds?
in order to have a full outer shell of electrons
What is shared in a covalent bond?
electrons
What do covalent bonds form?
molecules
What is a molecule?
group of atoms held together by covalent bonds
What is a diatomic molecule?
a molecule that contains only two atoms
What is a diatomic element?
elements that exist as a diatomic molecule
What are the 7 diatomic elements?
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine
More than one bond can be formed, what does this lead to?
double and triple bonds
What do the shape of covalent molecules depend on?
the number of bonds and the orientation of these bonds around the central atom
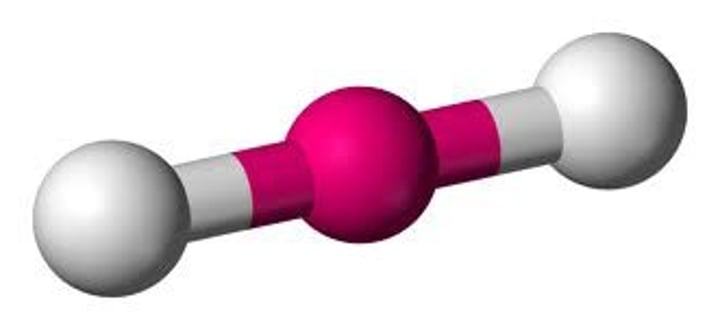
The shape of a molecule that has two covalent single bonds and no lone pairs on the central atom is
linear
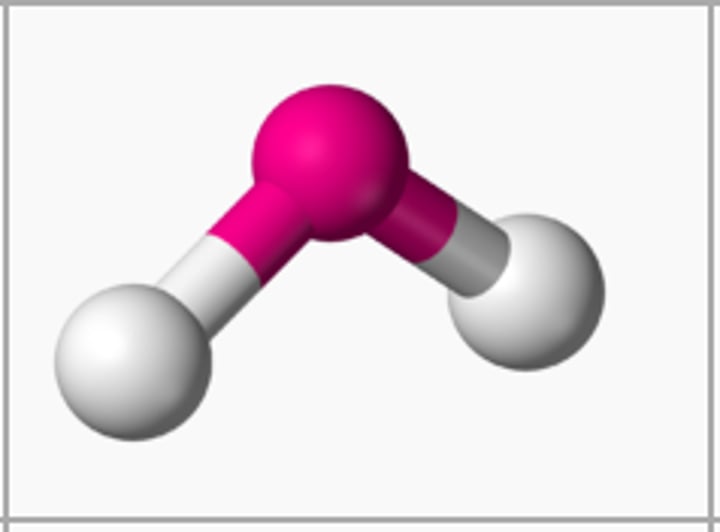
The shape of a molecule that has two covalent single bonds and two lone pairs on the central atom is
angular
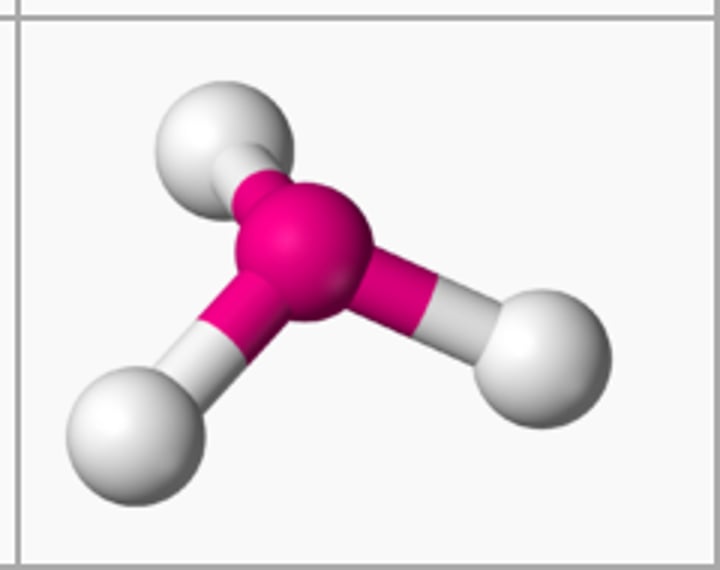
The shape of a molecule that has three single covalent bonds and one lone pair on the central atom is
trigonal pyramidal
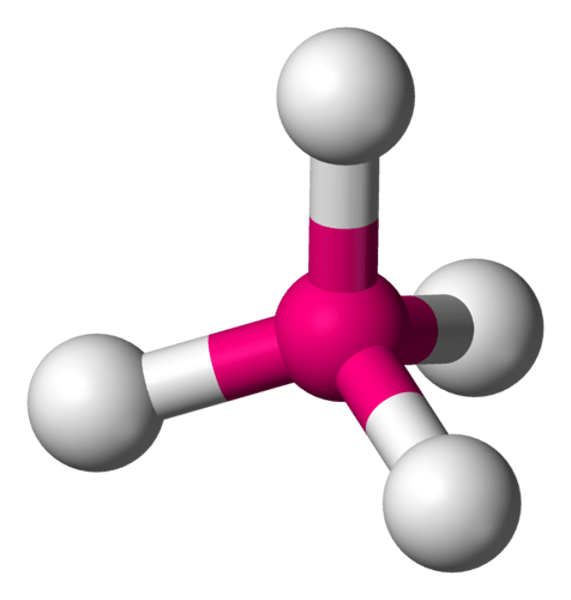
The shape of a molecule whose central atom has four pairs of bonding electrons is
tetrahedral
Covalent substances can form either
discrete molecular or giant network structures
What is a covalent molecular substance?
simple molecules held together by weak forces of attraction
Examples of covalent molecular
water,ammonia,iodine
What state is a covalent molecular substance?
solids,liquids or gases at room temperature
Covalent molecular substances have ______________ within the molecules and only ______________ between the molecules
strong covalent bonds, weak attractions
Why do covalent molecular substances have ___ melting and boiling points?
low, because only little energy is needed to separate the weak attraction between the molecules
Why do covalent molecular substances not conduct electricity?
because they do not have charged particles which are free to move
Covalent molecular substances which are insoluble in water may _______________
dissolve in other solvents
What is a covalent network substance?
A giant structure where atoms are covalently bonded together
Examples of covalent networks
Diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide
What state is a covalent network substance?
solid
Covalent network structures have a _____________ within one ___________
network of strong covalent bonds,giant structure
Why do covalent network substances have ____ melting and boiling points?
high, because the network of strong covalent bonds is not easily broken
Why do covalent network substance not conduct electricity?
because they do not have charged particles which are free to move
Why can graphite conduct electricity?
because of the delocalised electrons along its layers.
covalent networks ______ dissolve
do not