Plant Pigments and Photoreceptors
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Pigment Definition
molecules colored because they absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect others.
Photoreceptor Definition
molecules that perceive specific wavelengths of light to control a plant response.
What are the main pigments in plants?
chlorophyll, carotenoids, anthocyanins, betalins
Chlorophyll
Function: absorption of light aiding in photosynthesis
Absorbs: red and blue
Reflects: greens and yellows (think leaves and grass)

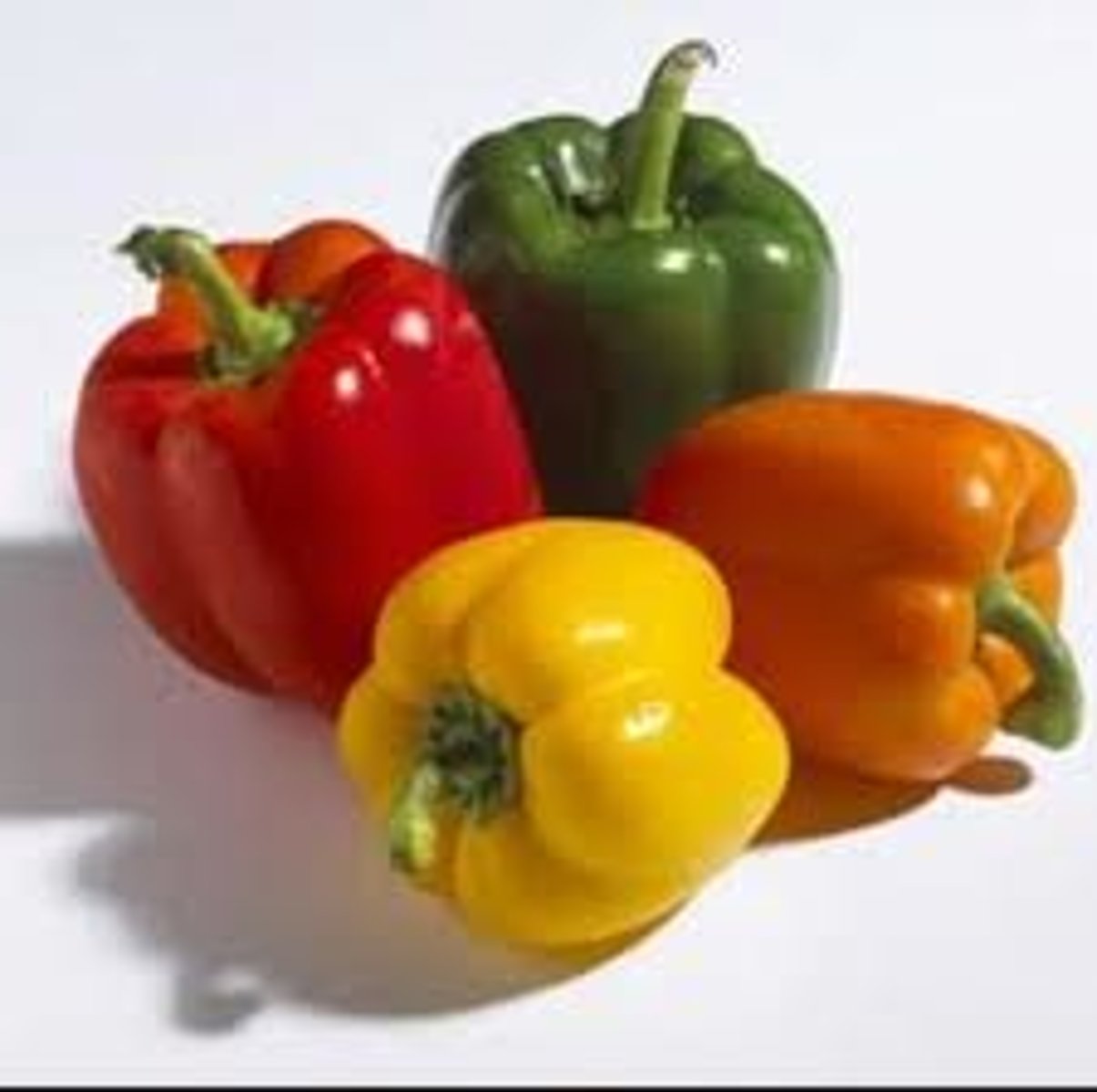
Carotenoids
Function: controls hormone functions, light trapping, and protection of DNA
Absorbs: blues and greens
Reflects: reds, yellows, and oranges (think bell peppers)

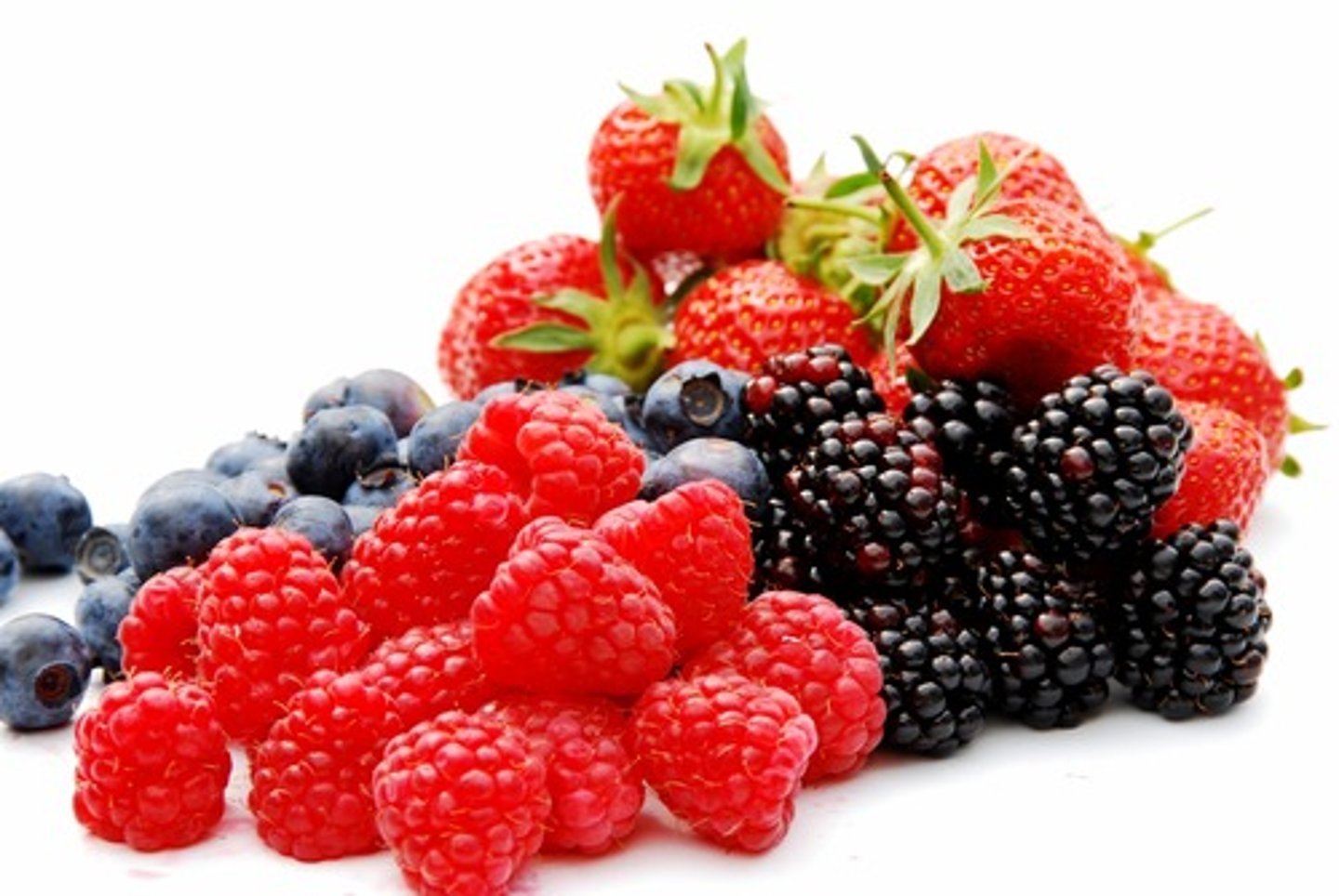
Anthocyanins
Function: "natures sunscreen" - protects from UV damage. can also help attract pollinators, though not it's main function.
Absorbs: blues and greens.
Reflects: reds, blues, and purples - depending on pH levels (think berries)

Betalins
Function: attract pollinators to aid in dispersing seeds
Absorbs: greens and yellows
Reflects: red, violet, yellow, orange (think flowers)

Cryptochromes
Function: keep track of circadian clock, regulates growth and development
Wavelengths Perceived: blue light
Phototropins
Function: controls phototropism which optimizes growth. controls chloroplast movement, leaf expansion (not growth), and light induced stomatal openings
Wavelengths Perceived: blue light

UVR8
Function: DNA repair, production of sunscreen (anthocyanins)
Wavelengths Perceived: 280 nm - 250 nm (UVB light)
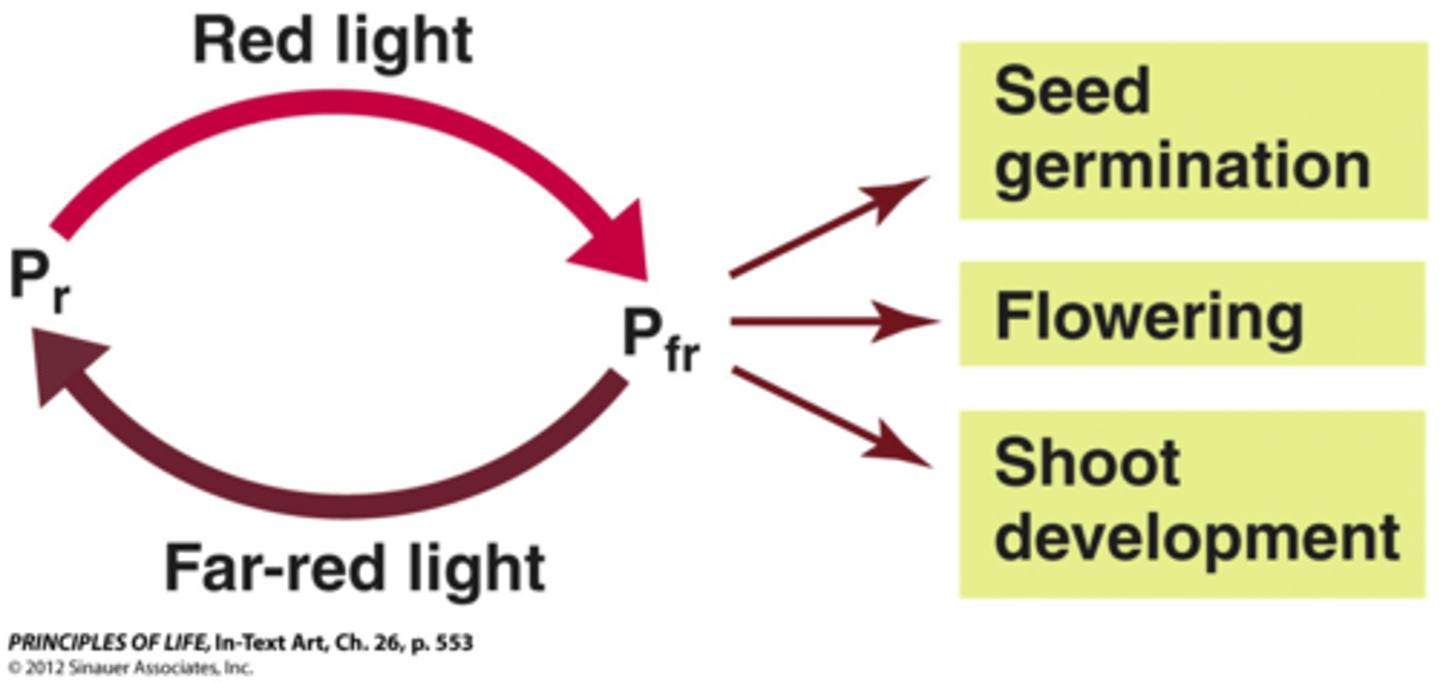
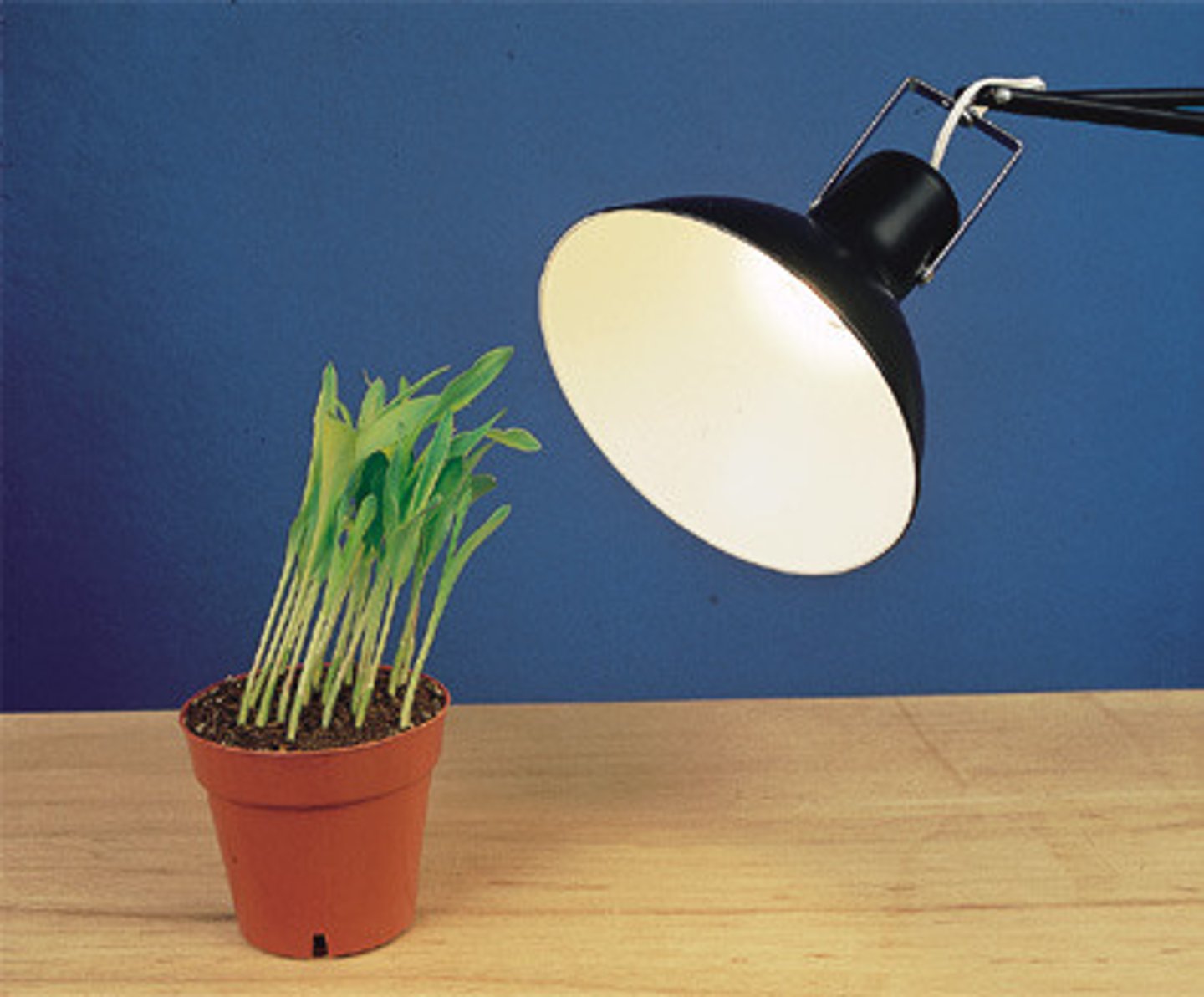
Phytochromes
Function: regulates light induced responses like seed germination, senescence, and flowering time. able to change shape based on wavelengths perceived (shade adjustment).
Wavelengths Perceived: red light and far red light.
How do phytochromes used red light and far red light to control seed germination, flowering, and senescence?
Far red light is high in the shade. Red light is high in the sunlight. Phytochromes can change shape based on which version of red light they are perceiving.
Whenever a plant is in the shade, phytochromes are in the Pr state (inactive) which doesn't give the plant a sign to flower/germinate. As the plant gets exposed to sunlight, the phytochromes switch to the active form, which is Pfr. This signals to the plant that flowering is able to take place.