Proton Pump Inhibitors
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
ECL cell activation mechanisms
3 main mechanisms
Vagal stimulation → ACh→ M1 maChR activation _> increase in histamine
gastrin release → cholecystokinin B (CCK-B) receptor activation → increased histamine
D-cell activation → SST → SST-2 receptor activation → decreased histamine
Erosive esophagitis
A condition where the lining of the esophagus becomes inflamed
Symptoms: difficulty swallowing, pain, bleeding
Persistent inflammation of the esophageal tissue. Also results in thinning over time
Suppression of stomach acid levels can contribute to healing of the esophageal lining
Irreversible inhibition of parietal cell proton pumps
Parietal cell proton pumps (H+/K+ ATPases) are responsible for the increase in gastric acidity
A drug that can selectively and irreversibly inhibit these H+/K+ATPases would allow symptom relief for extended periods
Irreversible inhibition can only be reversed through the expression of new H+/K+ ATPases, so short-term drug exposure can cause long-term effect
PPI design challenges
H+/K+ ATPases are not unique to the stomach; renal medulla also has them (important for potassium reabsorption)
H+/K+ ATPases are structurally similar to Na+/K+ ATPases and Ca2+ ATPases found in the heart and nerves, which may also be affected by PPIs
Successful PPIs must be able to
Survive the stomach conditions
Penetrate the membranes to reach its destination
Remain at the target tissue once delivered
General structure of PPIs
Several critical properties for success:
Acid trapping
Ability to cross the stomach membrane
Conversion into irreversible suicide inhibitors
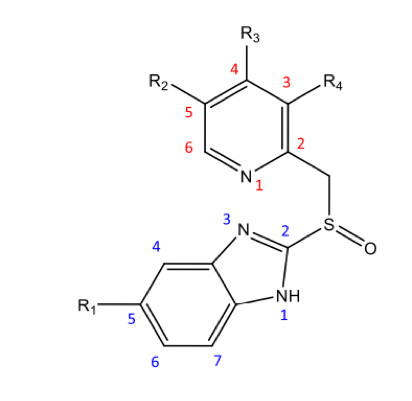
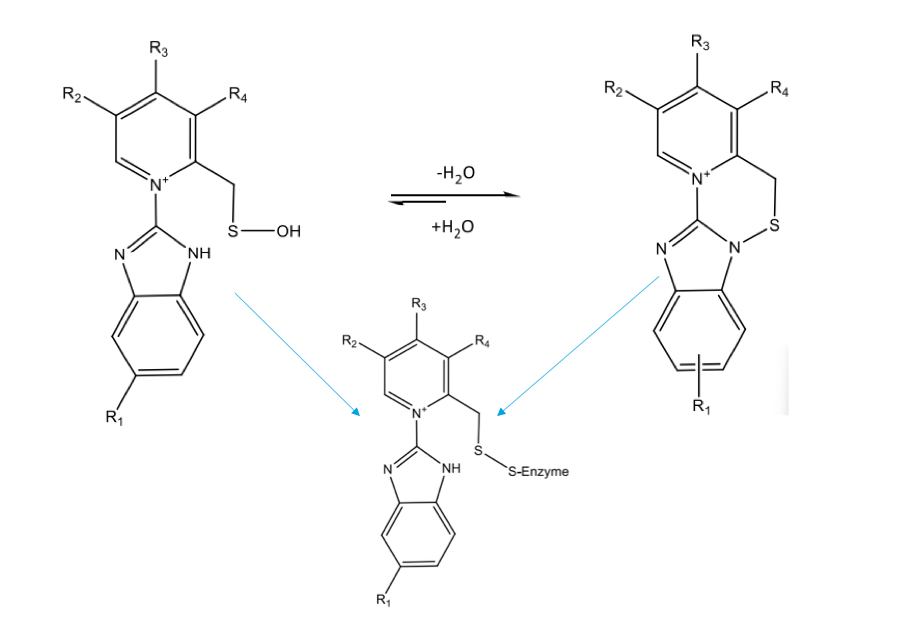
PPI activation: entry into the gastric cannula
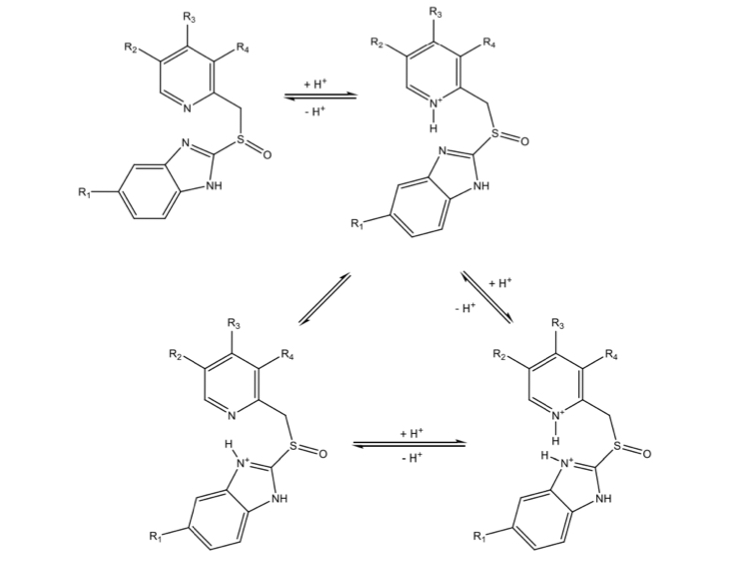
PPI activation: warhead activation
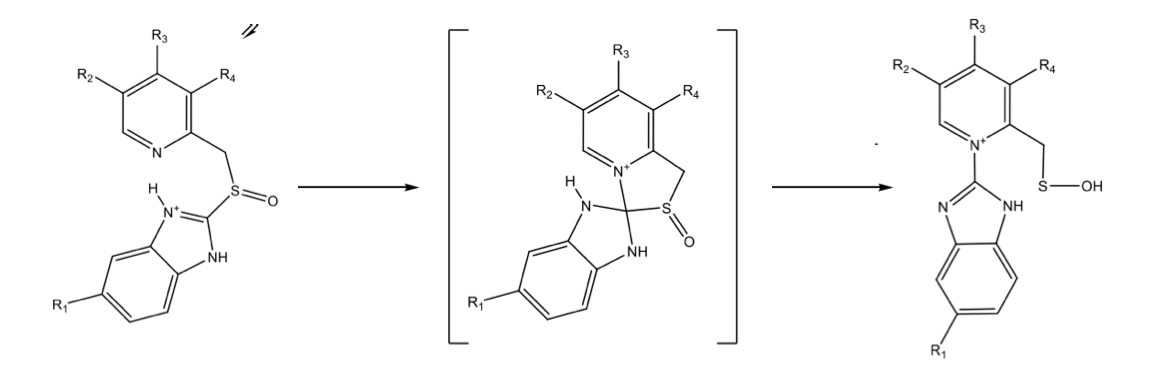
Acid trapping
pH of the stomach causes protonation of the molecule that causes it to be able to stay at its site once it makes it there - basically traps it in the gastric cannula
This does not happen in the renal medulla or other sites
PPI activation: irreversible inhibition
Enteric coating in PPIs
EC: a polymer barrier applied to oral medication. To prevent it from dissolving in the gastric environment(Can be used to bypass the harsh acidity of the gastric environment to prevent degredation)
Enteric coating considerations
Since coated molecules are absorbed at the intestines, onset is typically delayed by 2-3h (compare with H2RAs and antacids)
Food delays PPI absorption,so taking these drugs 30-60min before a meal allows maximal absorption and optimal inhibition → adherence issues
Crushing or chewing will destroy the protection provided by coating →must be taken whole
PPIs with alternative delivery mechanisms were also developed to address these shortcomings → will cover in the next lecture
Timoprazole
The first PPI, developed in 1975
Selective and irreversible inhibitor of parietal cell H+/K+. ATPases
Despite its short half-life, timoprazole was able to provide extended relief (1-2 days) in clinical studies
Acted as a goitrogen (interfered with thyroid fxn) due to benzimidazole functional group through thyroid peroxidase inhibition - never made it FDA approval