Engineering Graphics Midterm
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are the A,B,C,D,E standard sheet size measurements:
A 8.5x11 inch
B 11x17inch
C 17x22 inch
D 22x34 inch
The primary metric unit used in engineering drawings is the
SI unit
The primary U.S. customary unit used in engineering drawings is the:
US customary units
Most hand-drawn lettering is done at a height of:
3mm or 1/8 inch high
Sheet scale for object 2x larger than actual size:
2:1
When lettering text, space the letters so that the space between the letters is always equal. True or False
TRUE
How many views must be drawn for each part drawing?
As many as needed
What is an oblique surface and how many projection planes is it perpendicular to
None
What is an inclined surface and how many projection planes is it perpendicular to:
1; principal projection planes
What is the order of line preferences:
Visible lines
Hidden lines
Cutting lines
Centerlines
Phantom lines
What is the difference between and thick and thin line:
Thick lines: Used to represent the most important features in a drawing, such as visible edges or boundaries of objects.
Thin: Less important details (centerlines)
What is the standard thickness of a thick line:
0.6 mm
What is the standard thickness of a thin line:
0.25 mm
Phantom Line
thin line of alternating long and short dashes
Cutting-plane
section or plane where material is to be removed
Short-break
Thick freehand or freely drawn using CAD
Centerlines
Dark and thin lines
dimesntion line
Thin line with arrowheads at each end that indicates size
Symmetry line
Thin horizontal line parallel with vertical lines
hidden line
dark and thin dashes
section line
thin line (used for ‘shading’)
Sans serif means:
Lettering with no serifs (simple and minimalistic)
All word lettering in a drawing should start with a capital letter followed by lowercase letters. True or False
false
Which line types should be drawn thick:
Visible lines, cutting plane lines, and short-break lines
Which line types should be drawn thin:
dimension lines, extension lines, centerlines, hidden lines, phantom lines, and leader lines
Three purposes of technical drawings are:
Visualization
Communication
Documentation
Know what 1st angle and 3rd angle projection are and what we use here in the U.S.:
3rd angle: The views are produced as is the observer is outside lookig in (US uses this one)
1st angle: The observer looks the object to the planes of projection
Know all uses of centerlines:
Shows axis of symmetry for a feature or part
Indicates a path of motion
Shows the location for the bolt-hole circles and other circular pattern
Axis
Imaginary line that runs through the center of a thread screw
Pitch
The distance between the same points on adjacent threads of a screw
root
Bottom of the groove between two sides of a thread
Crest
highest point on a thread
side
also called flank
Minor Diameter:
smallest diameter of the thread
Major diameter
largest diameter of the thread
Pitch diameter
diameter of an imaginary cylinder that passes through the thread profile
Depth
Distance between the base and the crest of the thread, measured perpendicular to the axis
Which line type may be used to show a repetition of a series of identical features?
Phantom lines
What is a common intersection of three or more surfaces:
vertices
What is a common intersection of two surfaces:
Edge
Whenever possible, what type of line should extension lines dimension to:
Visible lines
Centerlines in some cases to showcase diameters
The right-side view shows which dimensions:
Depth and height
The top view shows which dimensions:
Depths and width
The front view shows which dimensions:
Height and width
What is the minimum distance between the part and the first dimension?
1.5 mm
Crossing dimension lines is acceptable?
YES
The three basic applications of screw threads are:
To hold parts together
To provide for adjustment between parts
To transmit power
What is the symbol for reference
( )
What is the symbol for countersink

What is the symbol for counterbore
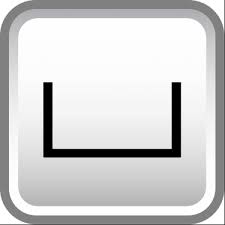
What is the symbol for depth
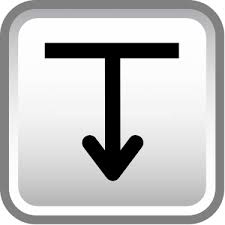
What is the symbol for spot face

Know all parts of a thread call out in a drawing both inch and metric:
Threads per inch: 13 TPI/ 1.5 mm
Thread series: UNC,UNF,UNEF/ No series needed
Tolerance class: 2A, 3B/ 6H 6g
Pitch: 0.06 inch/ 1.5 mm
Major diameter: 0.5 inches/ 10 mm
Know proper dimensioning:
Use logical placement
Make is legible and easy to read
Know what are possible types of information that can be found in the title block:
Title, scale, date, author, approval blocks
What are the stages of the design process:
Problem identification
Ideation
Refinement/analysis
Implementation/ documentation