Biol 2325: Abdomen (part 1: muscles, abdominal body wall vessels, and nerves)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is the abdomen?
The area from below the diaphragm to
the pelvic inlet
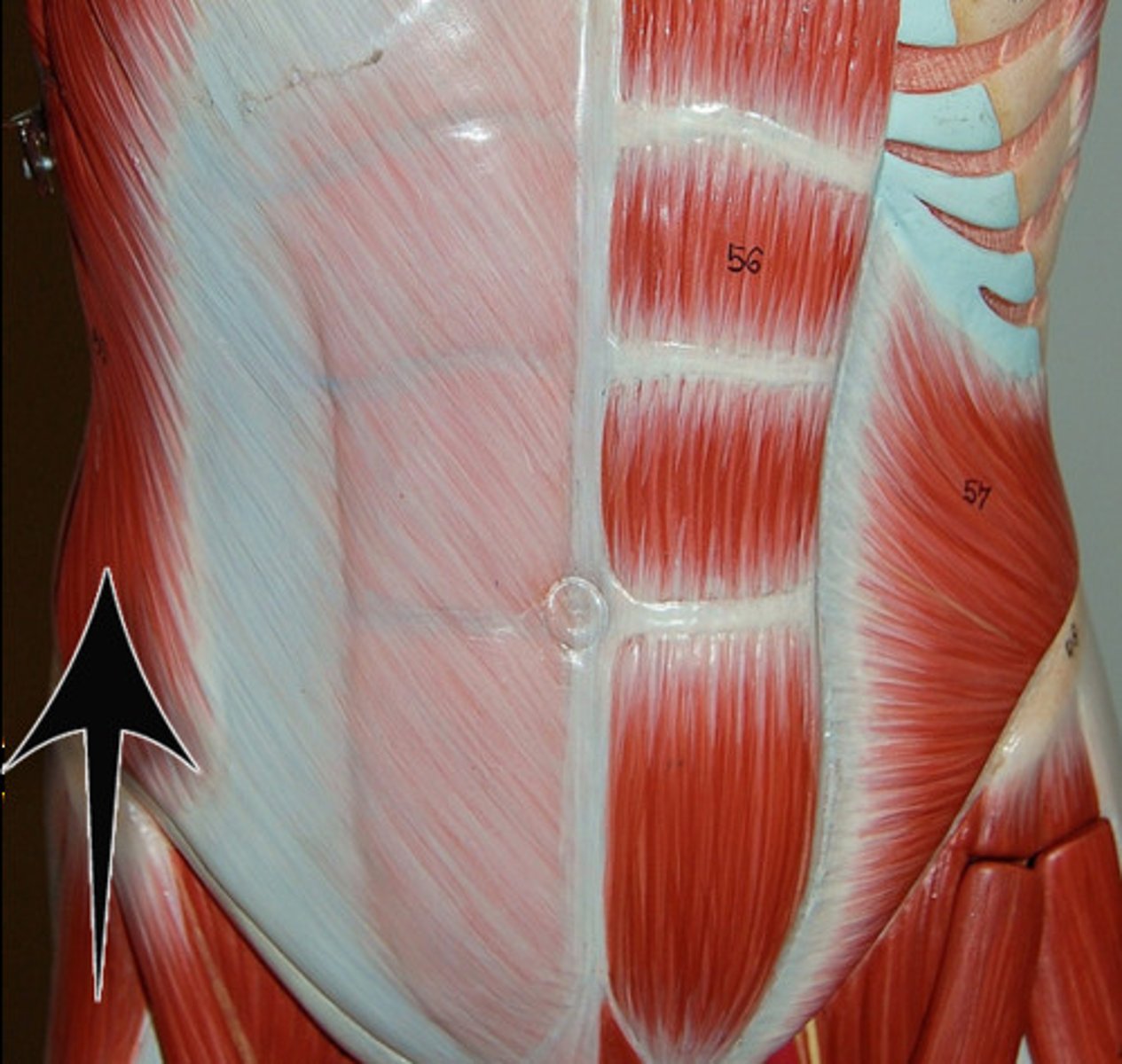
rectus abdominis
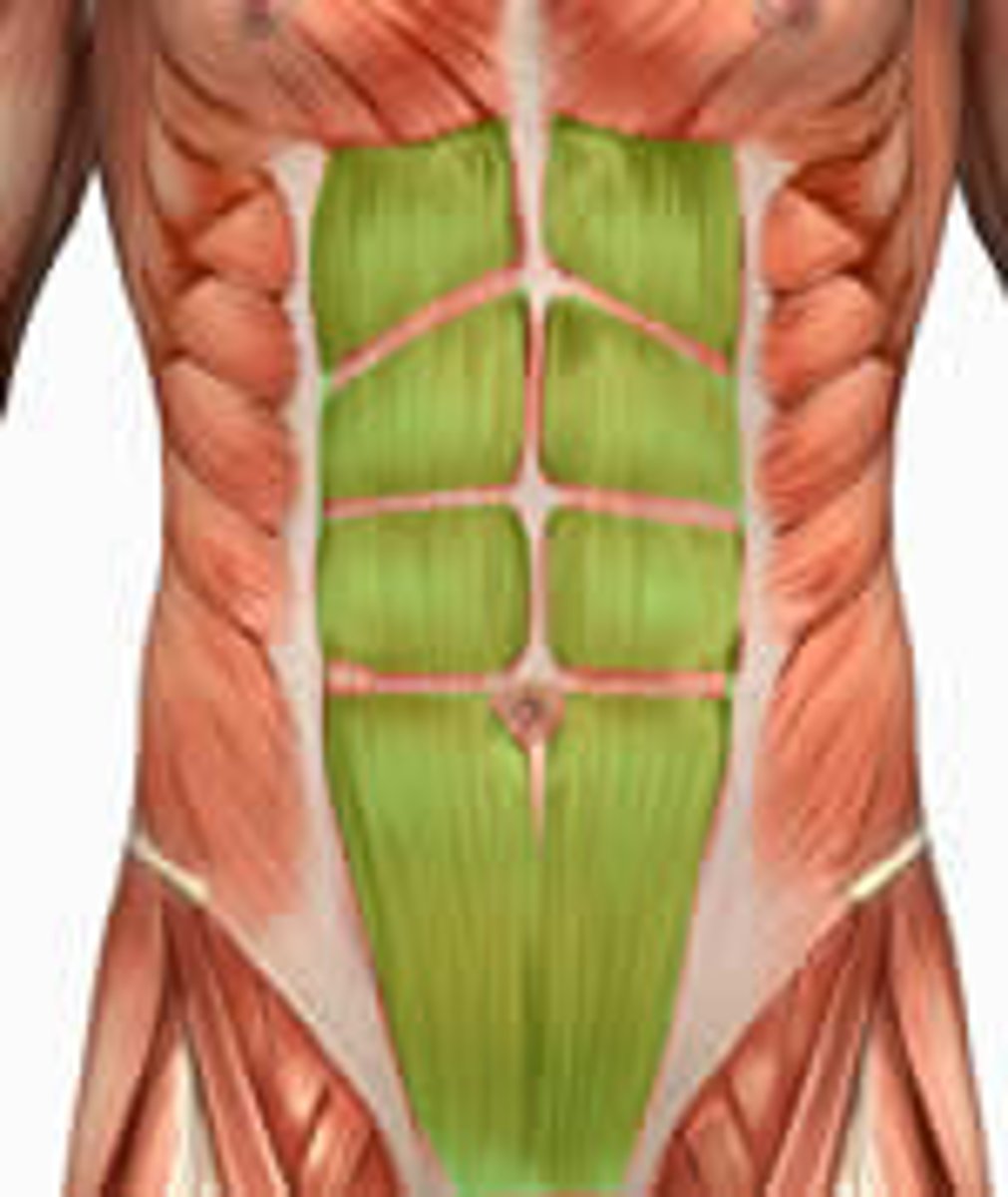
tendonous intersections
Function of tendonous intersections
Allows the use of specific segments of the rectus abdominis instead of having one huge muscle
Linea alba
midline tendinous seam joining the abdominal muscles
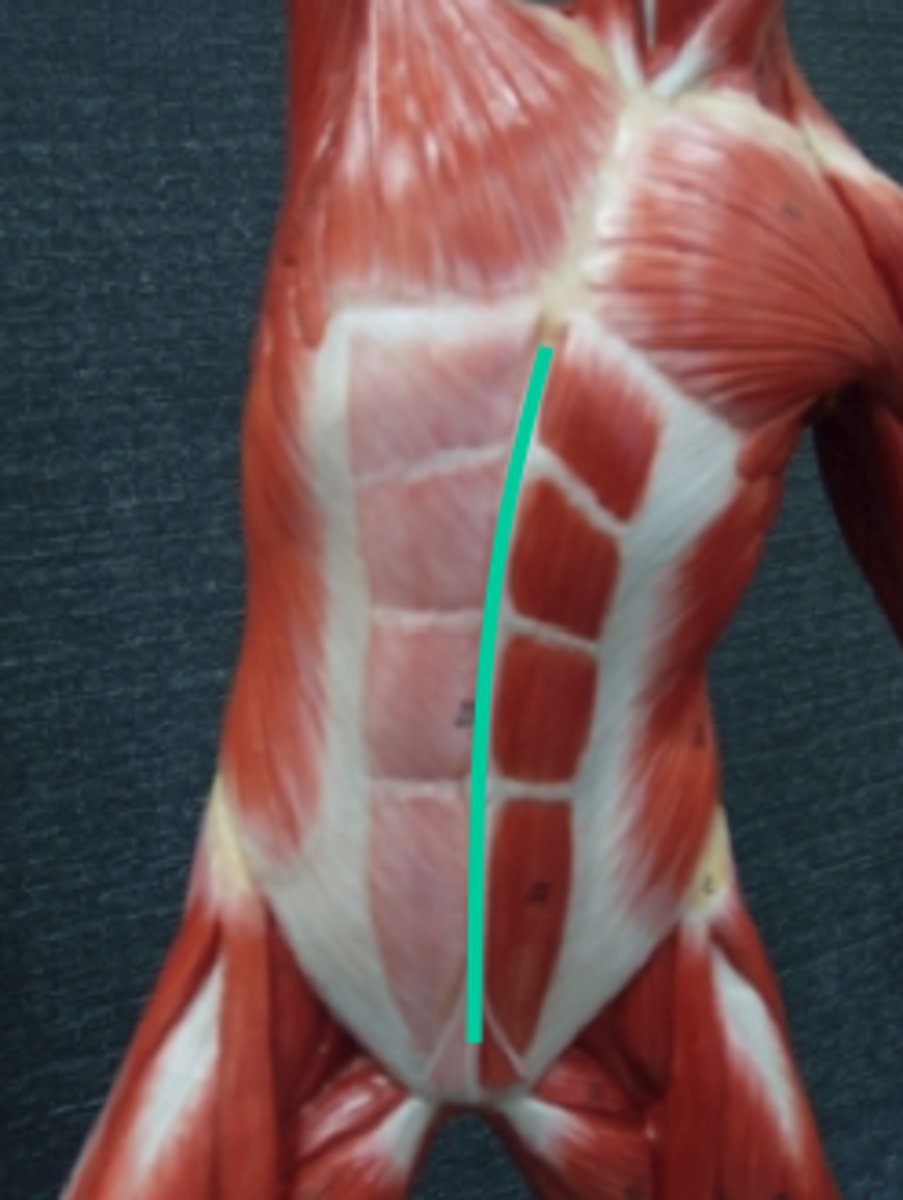
What is the most anterior abdominal muscle?
rectus abdominis muscle
Function of the rectus abdominis
Pulls the ribs down for forced breathing (exhalation), helps compress the abdominal cavity
What part of the musculature pattern is the rectus abdominis?
Ventral musculature
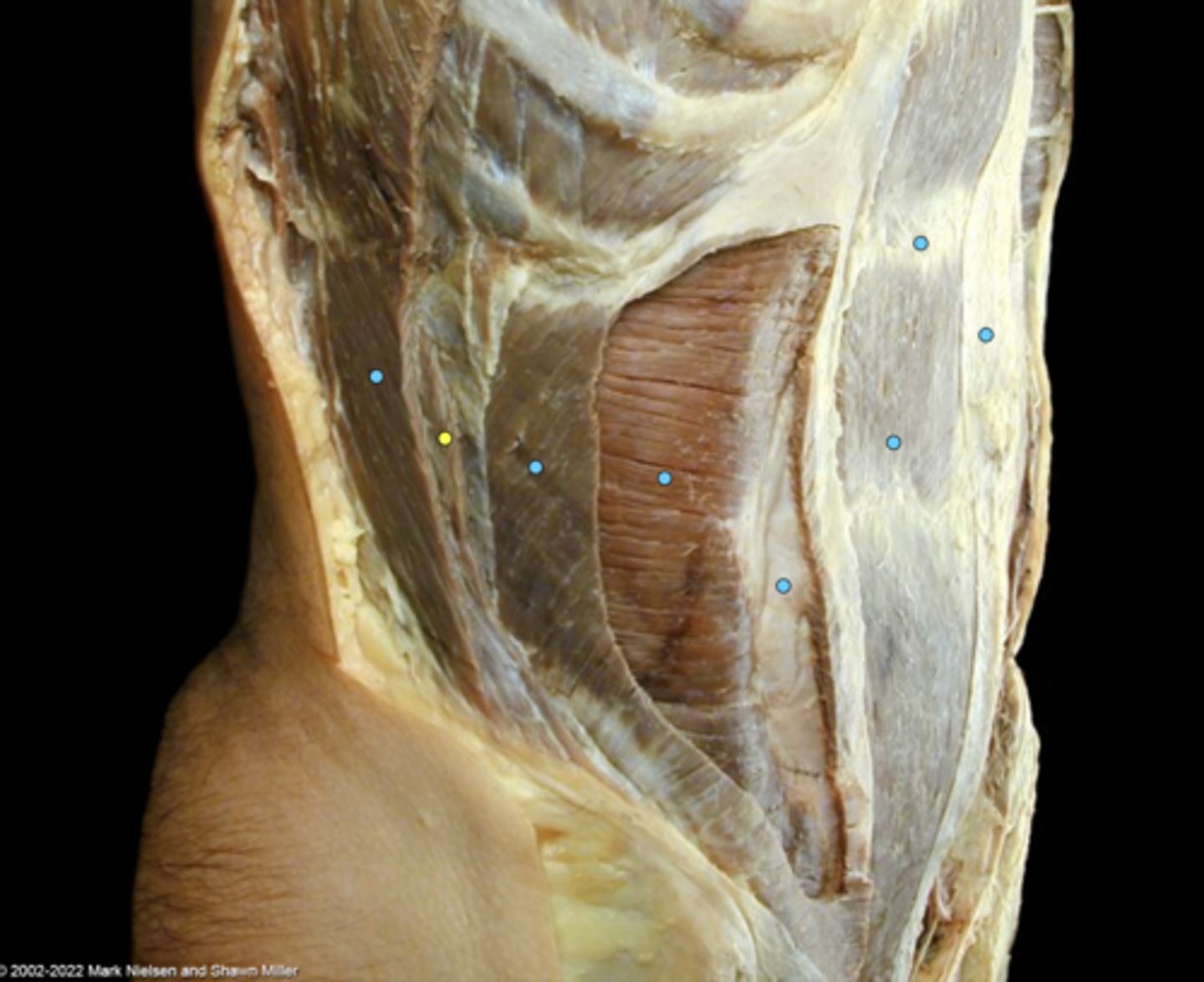
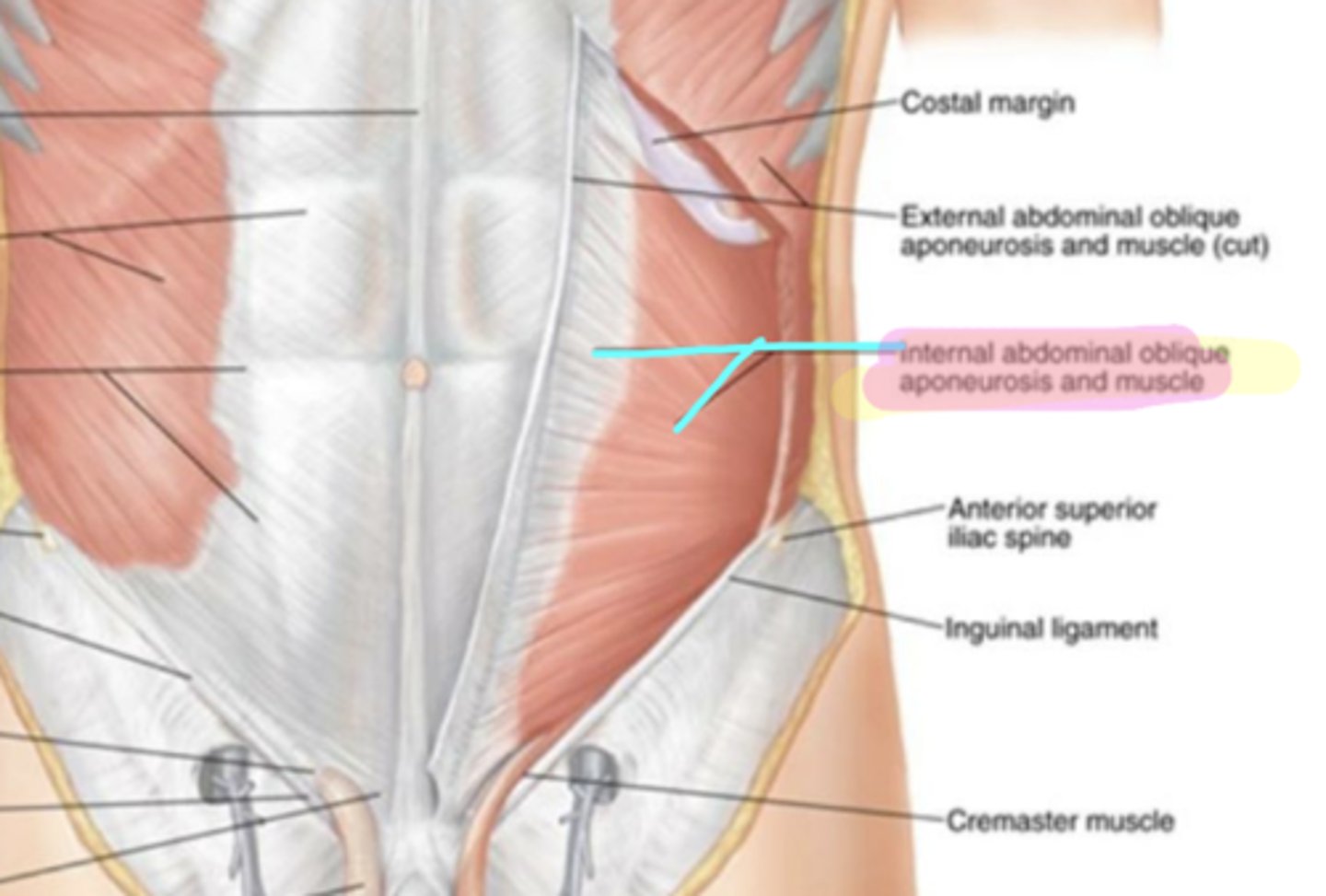
External oblique muscle
What are the two laminae of the external oblique
Superficial lamina and the deep lamina
External oblique muscle- superficial lamina
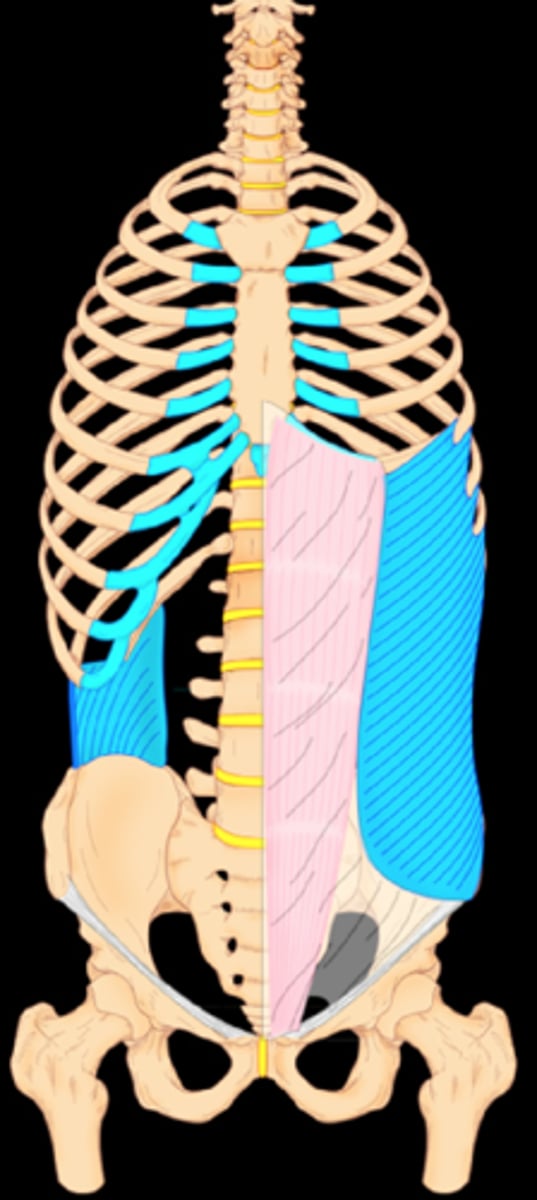
aponeurosis of external oblique
(The pink on the image)
What is the fiber orientation of the external oblique?
Medially and inferiorly ("ex" to "sex")
Inguinal ligament
Thickened part of the bottom of the external oblique aponeurosis
Function of the external oblique
Contralateral rotation, compresses the abdominal cavity, flex the trunk (when using both sides of the muscle)
External oblique deep lamina
What musculature layer is the external oblique muscle superficial lamina?
Lateral supracostal or lateral outermost muscle layer
What musculature layer (of the muscle pattern) is the external oblique deep lamina?
Lateral external musculature layer
Internal oblique muscle
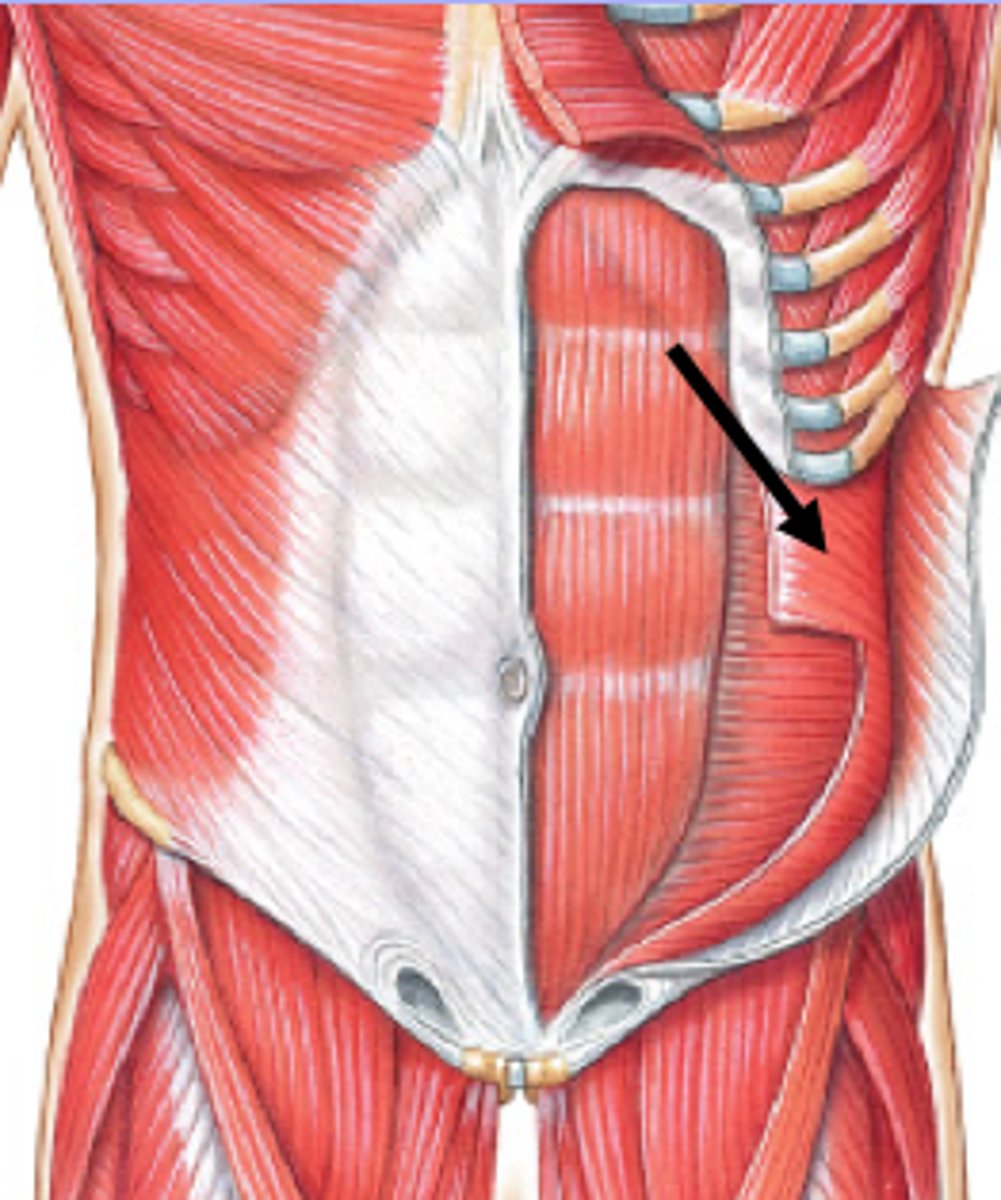
What is the fiber orientation of the internal oblique muscles?
Superiormedially, meaning they run upwards and inwards
Internal oblique muscle aponeurosis
Does the internal oblique muscle aponeurosis cover the ribs?
No
how does the internal oblique Aponeurosis change in relation to the rectus abdominis?
Part of the internal oblique aponeurosis runs infront of the rectus abdominis while part runs behind
Function or the internal oblique muscles
Ipsilateral rotation and flexion of the trunk
What muscle pattern layer is the internal oblique muscle?
Lateral middle muscle layer
transversus abdominis muscle
Anteriolateral muscle of the internal muscle layer
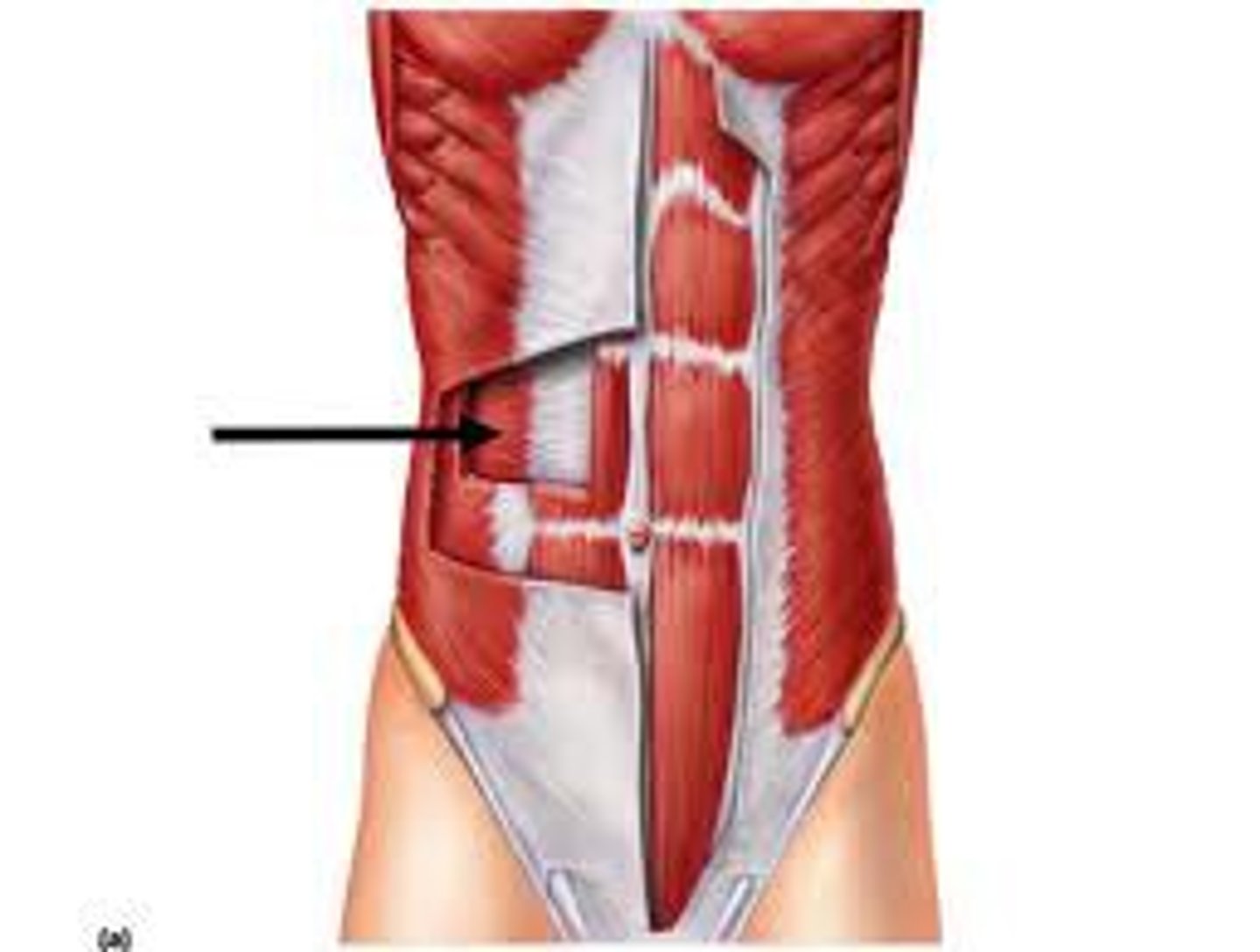
is the transversus abdominis anterior or posterior to the rectus abdominis?
Posterior
What is fiber orientation of the transversus abdominis?
Horizontally, or "transversely"
Function of the transversus abdominis muscle
Increase interabdominal pressure
What muscle layer (of the muscle pattern) is the transversus abdominis?
Lateral internal muscle layer
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
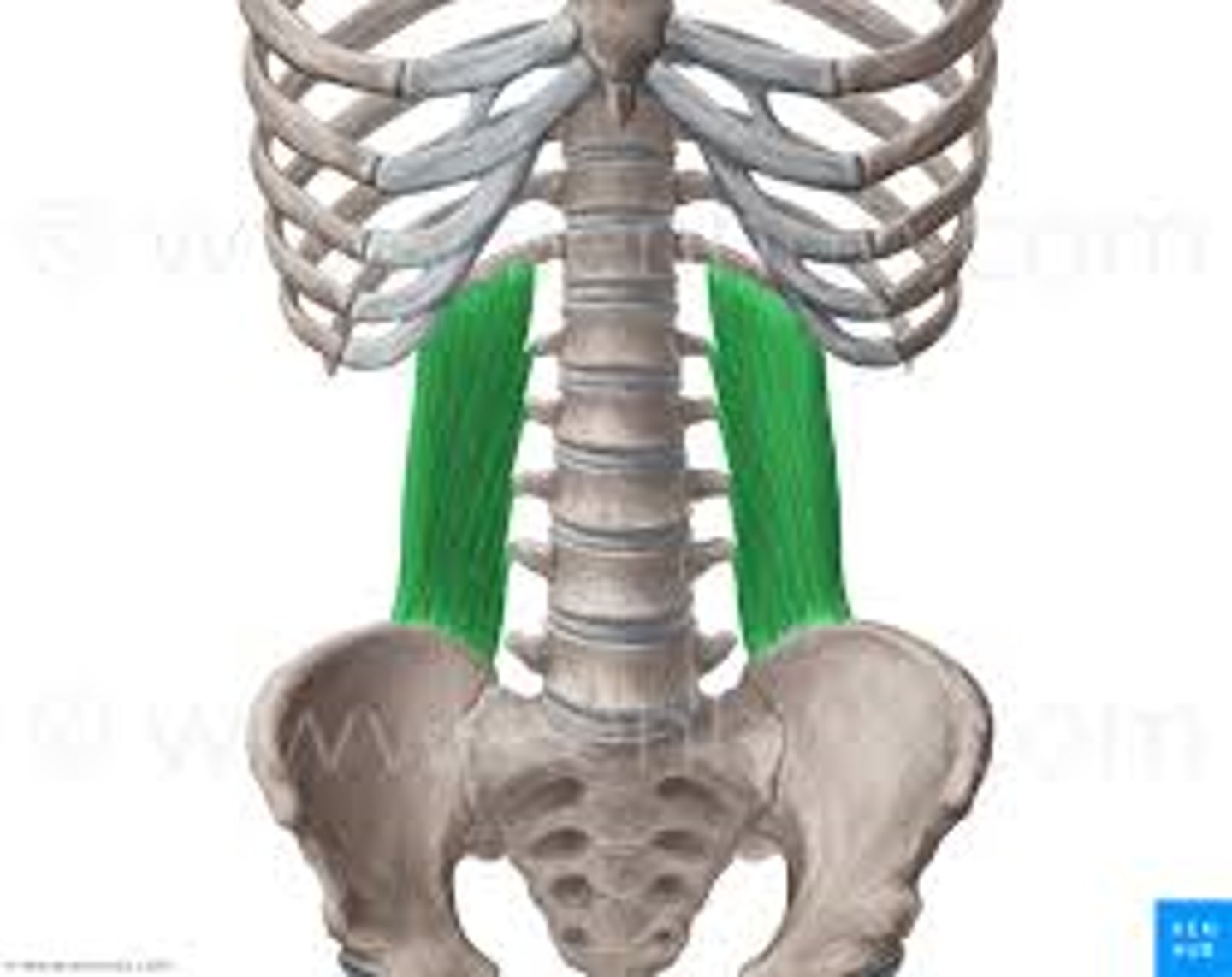
Structure of the quadratus lumborum
Muscle that attaches to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae
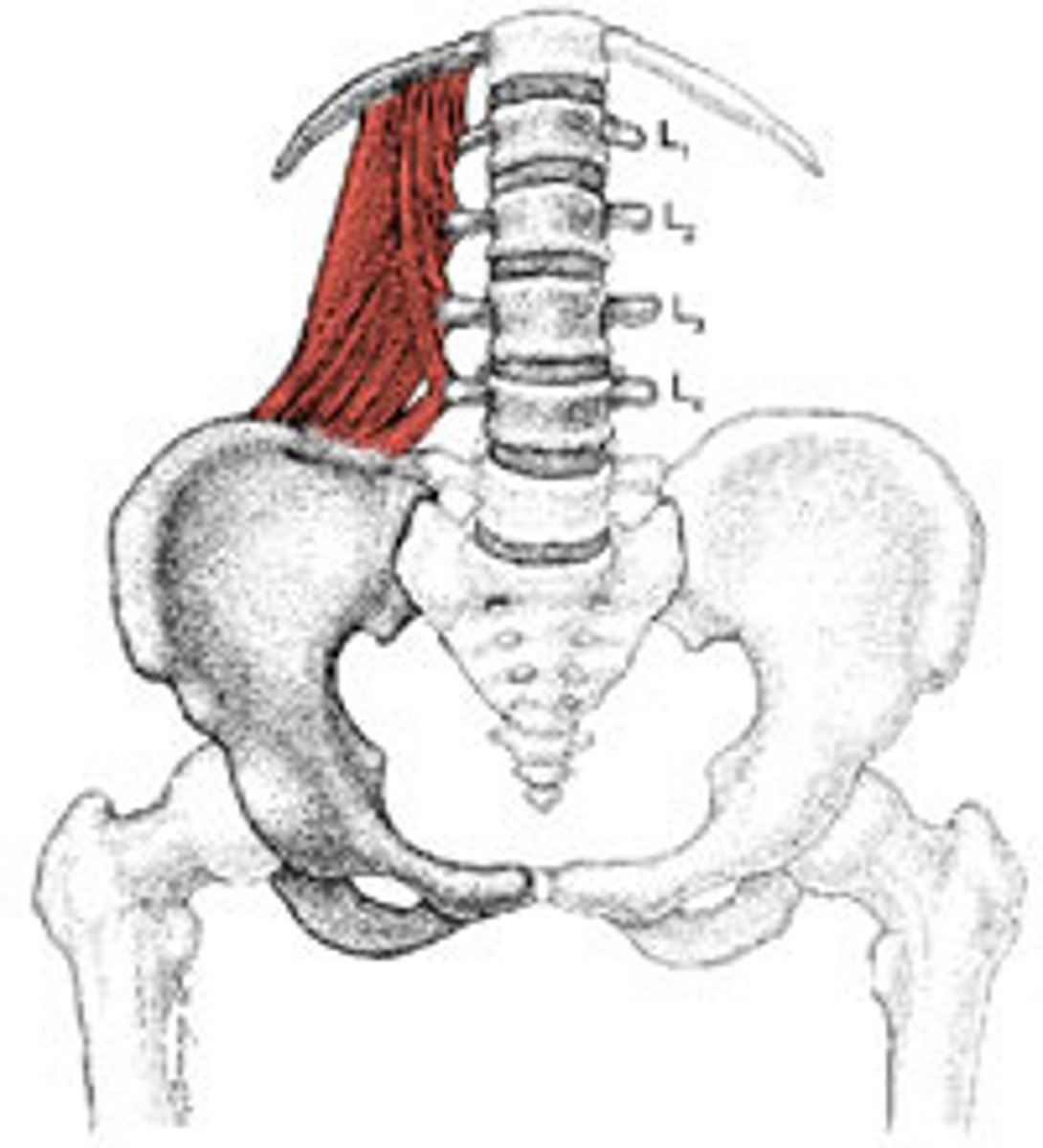
Function of the quadratus lumborum muscle
Stabilize the lumbar curvature of the spine and ipsilaterally flex the trunk
What muscle layer is the quadratus lumborum in respect to the muscle pattern?
Lateral internal muscle layer
What two abdominal muscles are in the lateral internal layer of the abdomen?
Transversus abdominis and quadratus lumborum muscles
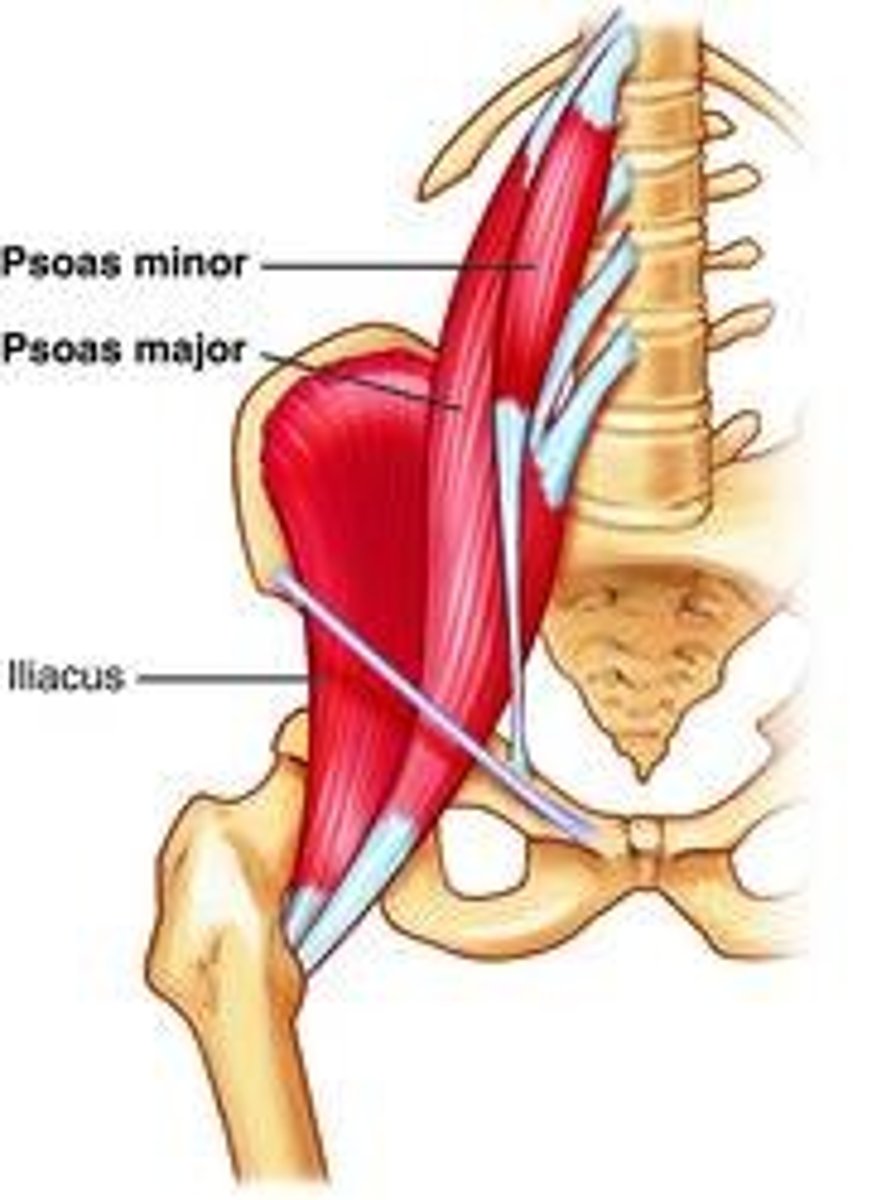
Psoas major muscle
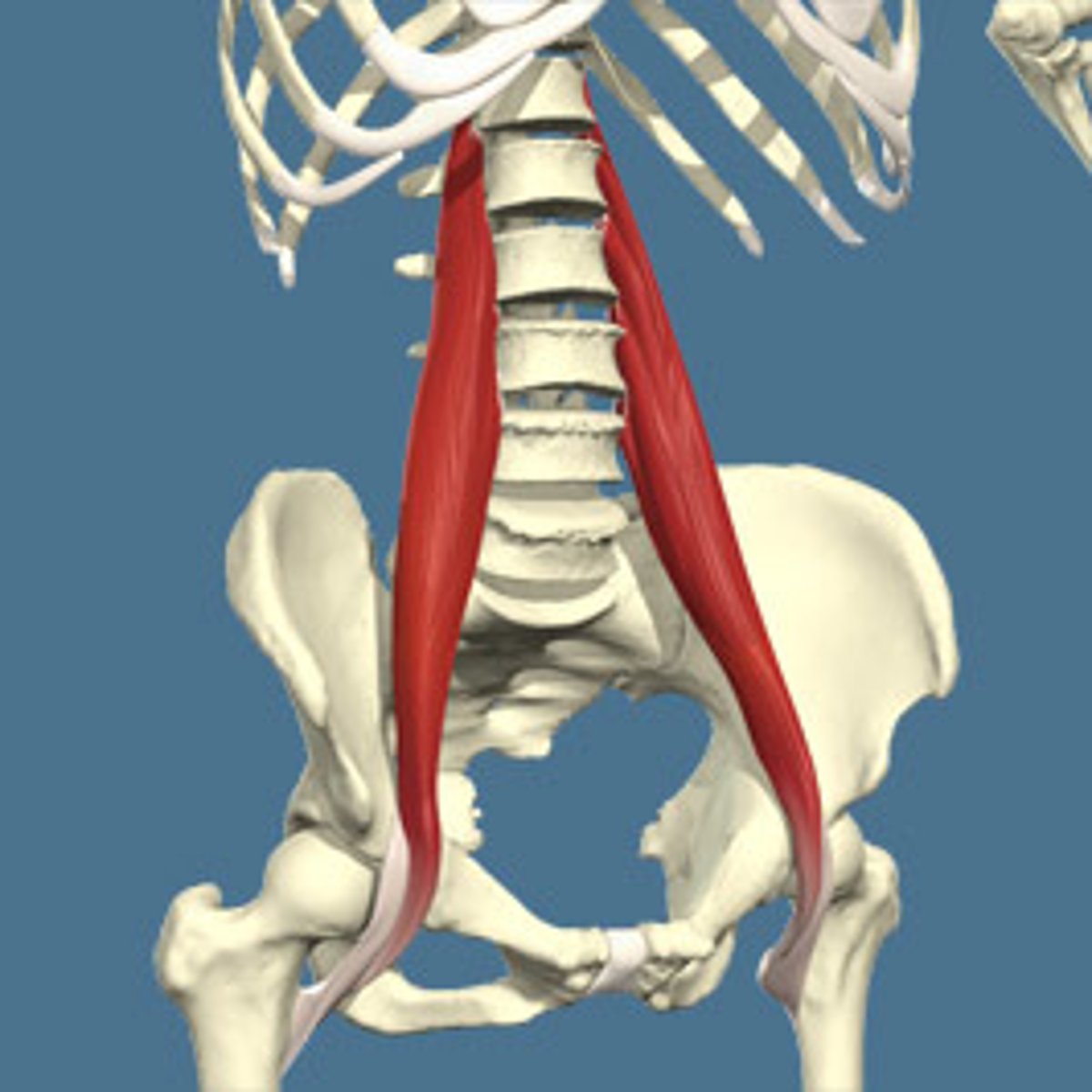
Structure of the psoas major muscle
"S" shaped muscle that attaches to the transverse processes and front of the vertebral bodies of the lumbar spine
Function of the psoas major
Stabalize the lordotic curve (along with the quadratus lumborum), also ipsilaterally flexes the abdomen and flex the hip
Main function of the psoas major
flexion at hip
What mucle layer is the psoas major?
Subvertebral
Psoas minor muscle
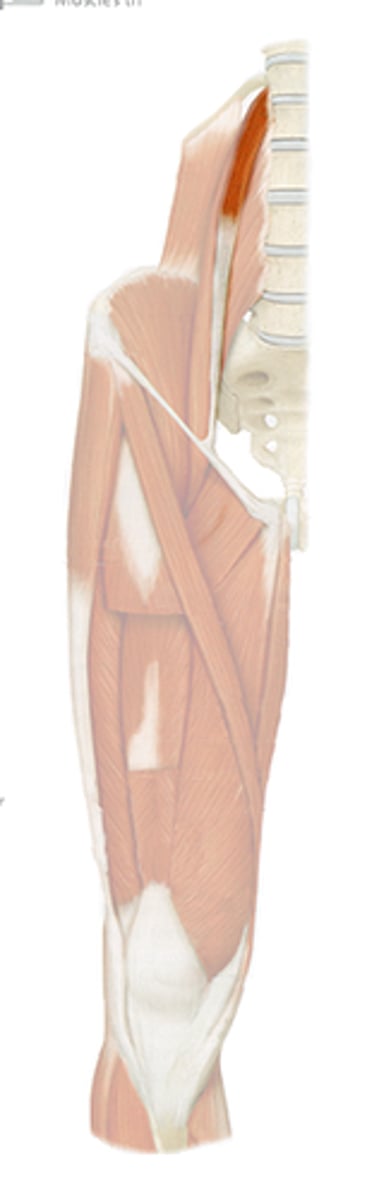
Is the psoas minor in front or behind the psoas major?
In front
Function of psoas minor
flexion of lumbar vertebral column
What muscle layer is the psoas minor?
Subvertebral
Functional significance of abdominal body wall
Protect internal organs while allowing more dynamics that bone would. Its a "dynamic retaining wall"
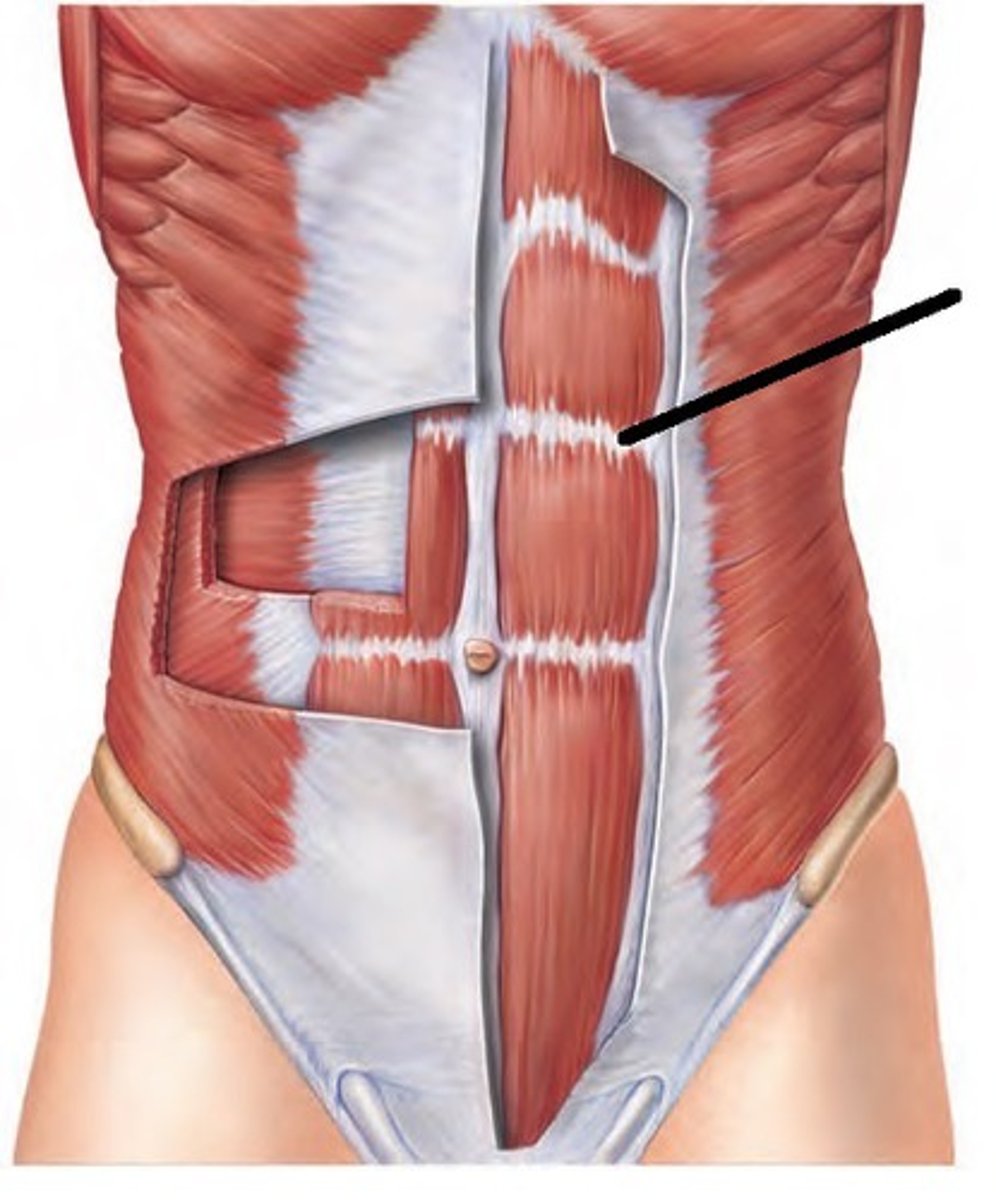
What are the aponeurosis of the internal oblique, external oblique, and transversus abdominis doing ABOVE the belly button?
They wrap the rectus abdominis. the aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis running behind the rectus abdominis with the other two running in front
What happens to the internal/external oblique and transversus abdominis aponeurosis below the belly button?
All the aponeurosis are in front of the rectus abdominis
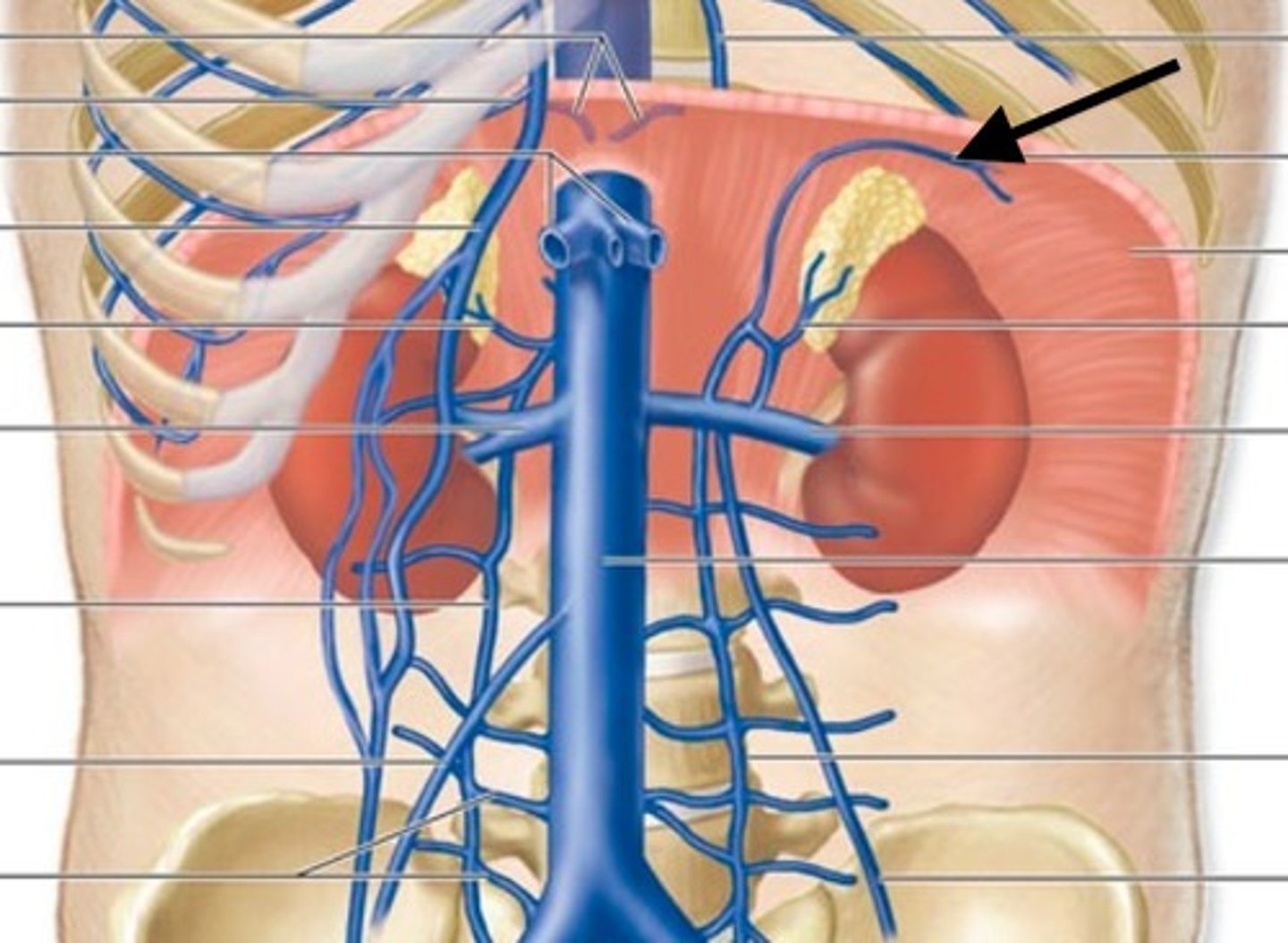
inferior phrenic arteries
supply the inferior surface of diaphragm
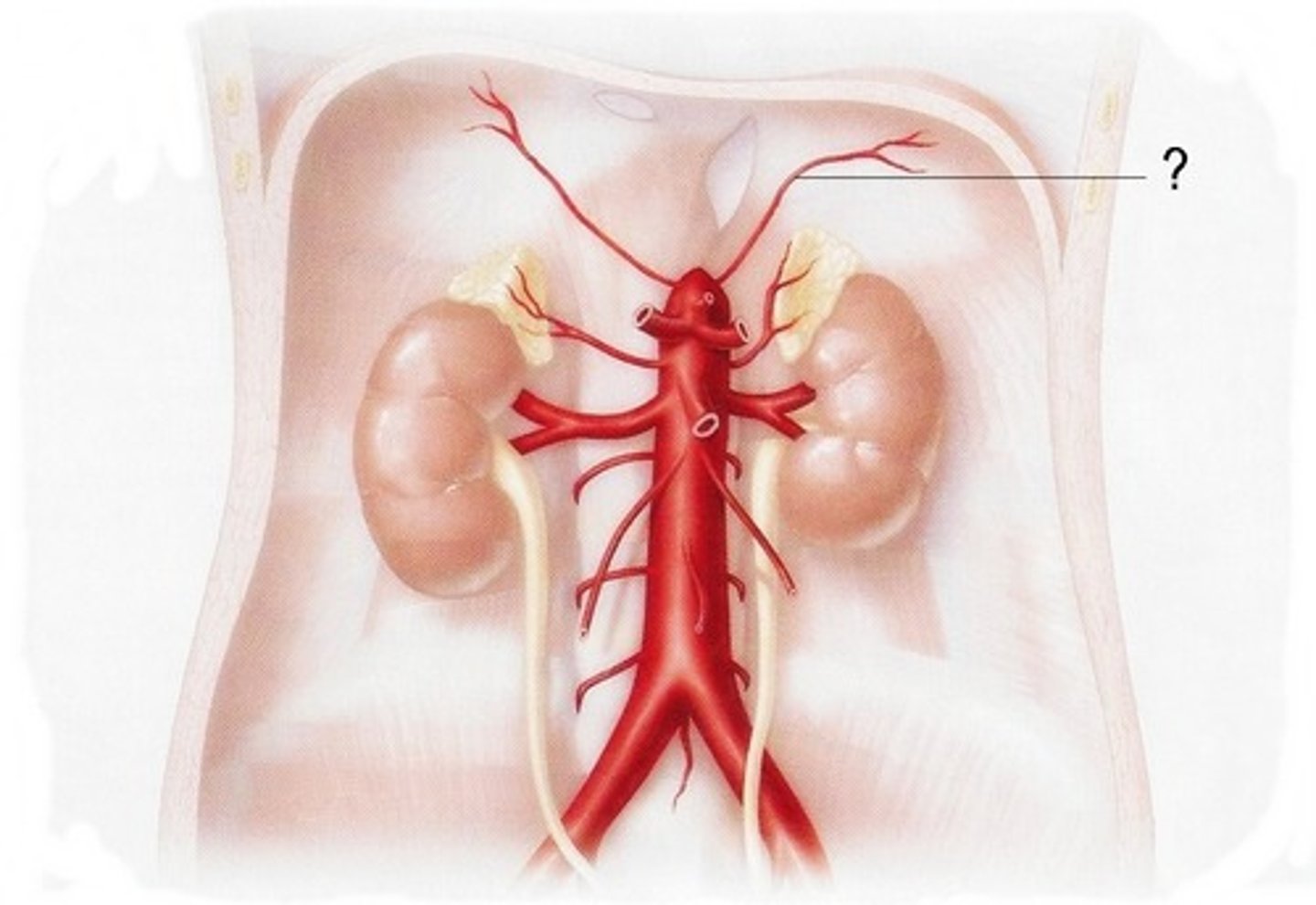
What do inferior phrenic arteries branch from?
Directly off the aorta
lumbar arteries
small, paired blood vessels that originate from the abdominal aorta and supply the POSTERIOR abdominal wall. They are similar to the intercostal arteries in the abdomen.
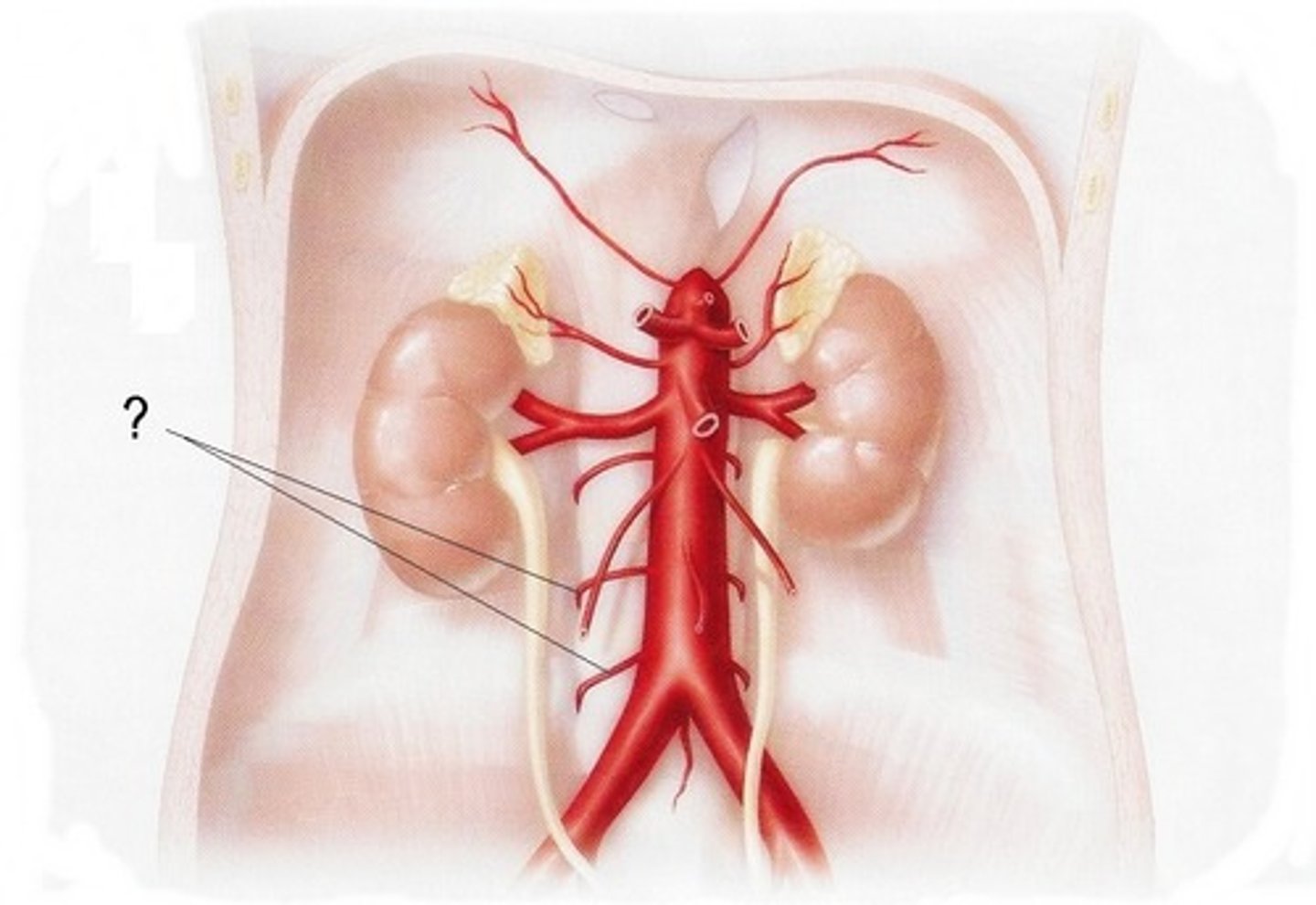
Are the inferior phrenic arteries and lumbar arteries posterior or anterior body wall supply arteries?
Posterior
superior epigastric artery
branch of internal thoracic artery that supplies the upper anterior abdominal wall
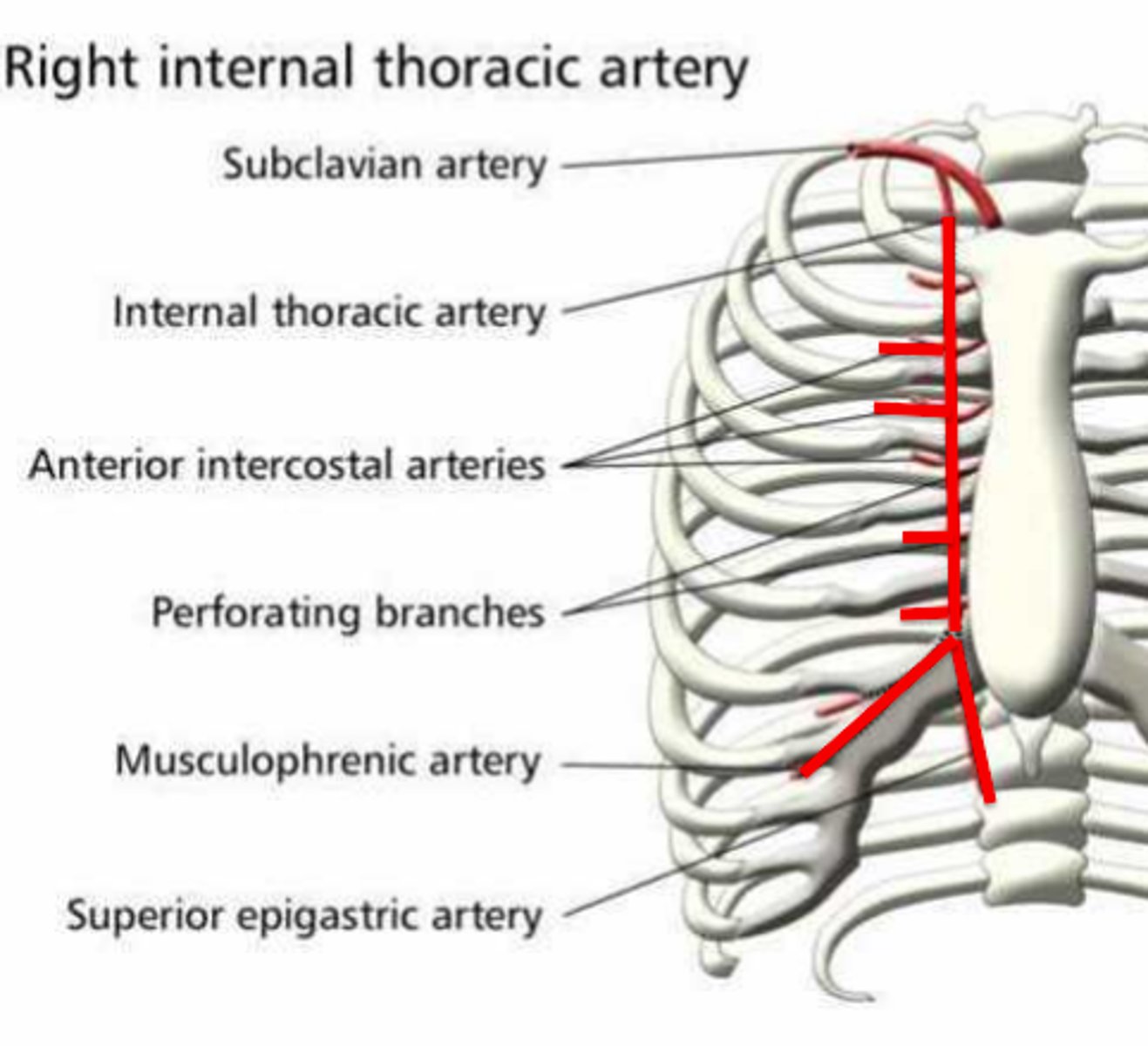
What muscle is supplied by the superior epigastric artery?
Rectus abdominis
What forms a collateral circuit with the superior epigastric artery
Inferior epigastric artery
inferior epigastric artery
A lower anterior supply artery.
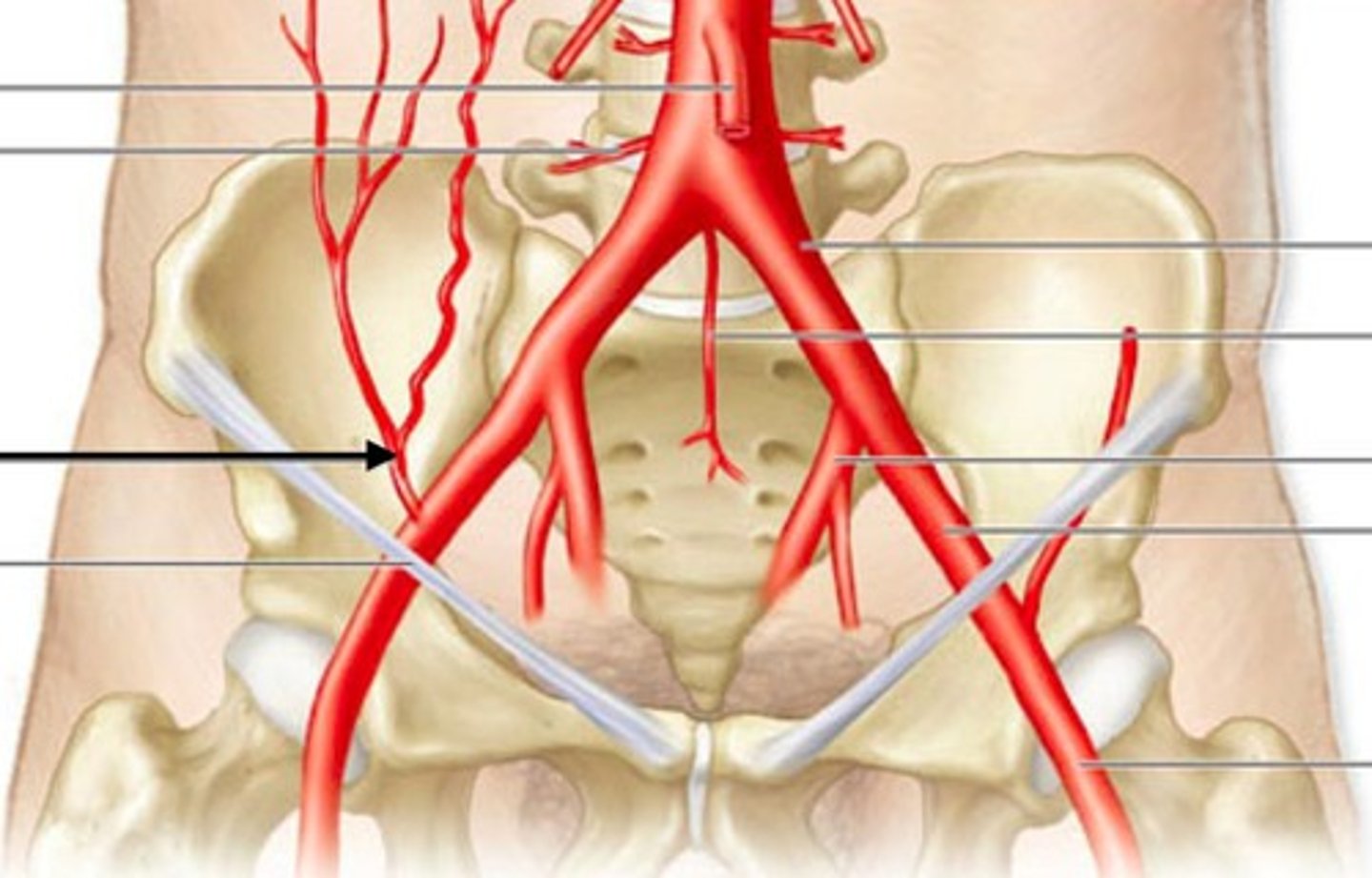
From which artery does the inferior epigastric artery branch?
The external iliac artery.
In which direction does the inferior epigastric artery travel?
Superiorly into the abdominal body wall.
Lumbar veins
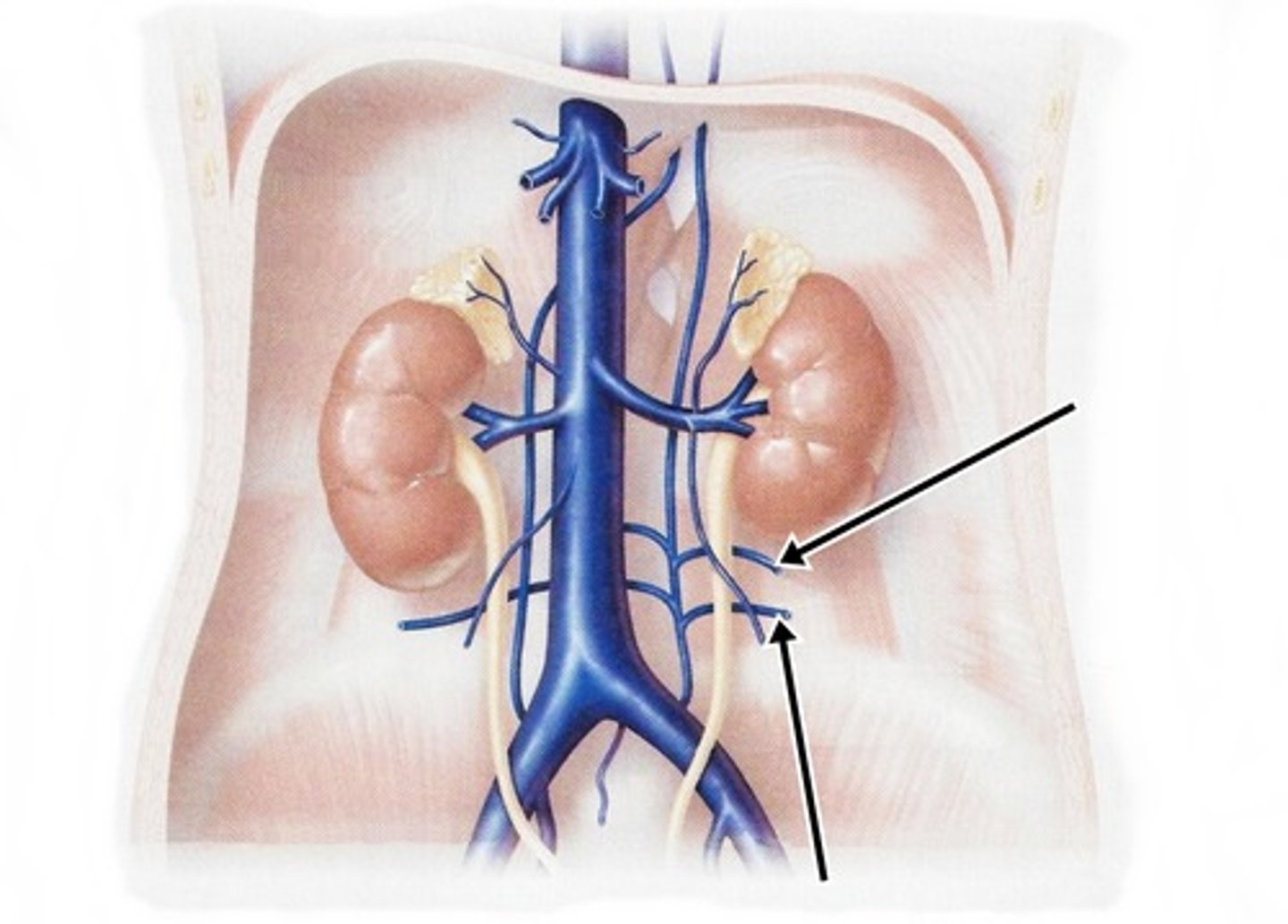
Inferior phrenic veins
drain the inferior surface of the diaphragm into the inferior vena cava
Ascending lumbar veins
Branches off the common iliac vein that receive blood from the lumbar veins
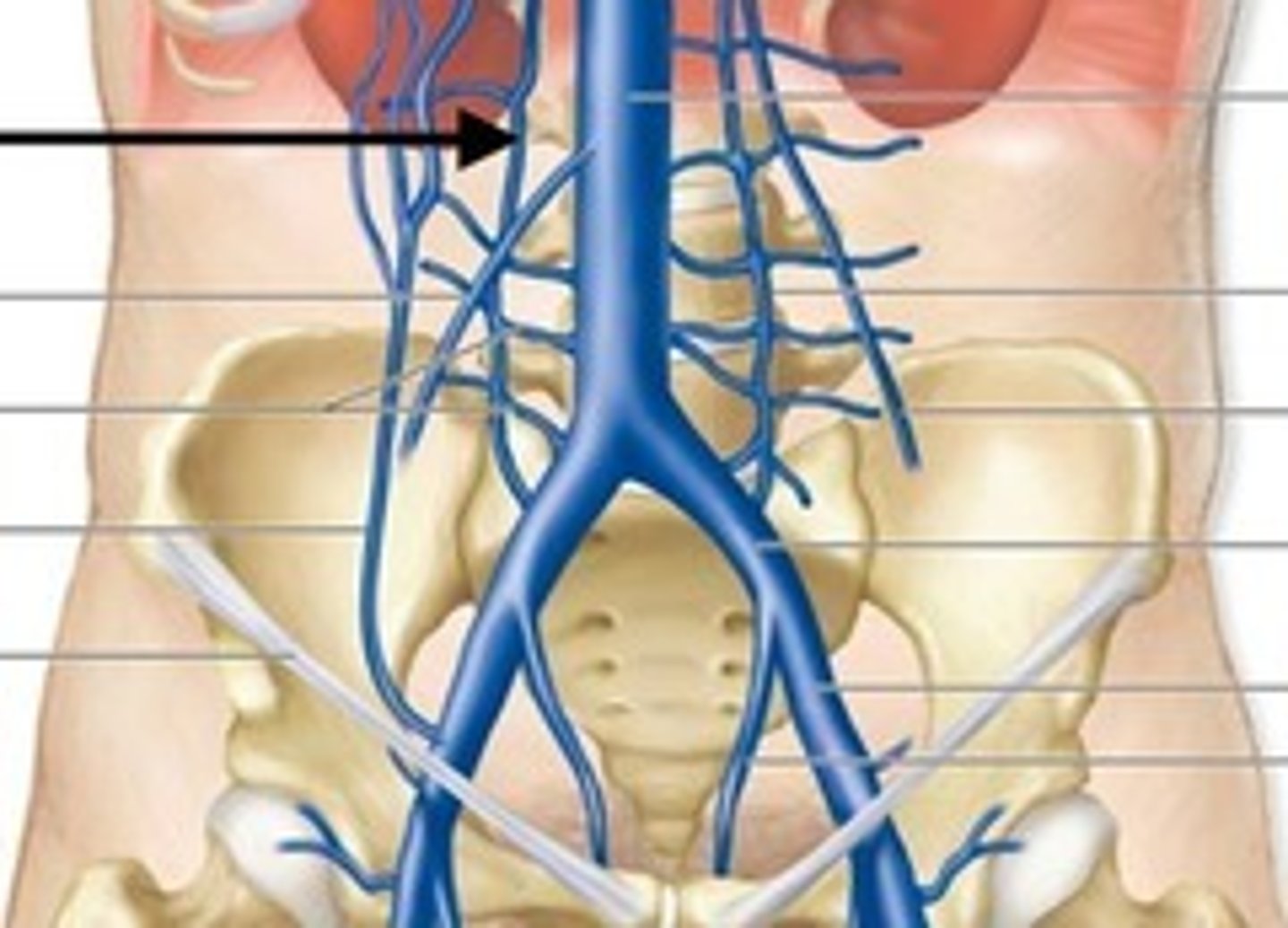
Where do the right ascending lumbar veins go?
The azygos vein
Where do the left ascending lumbar veins go?
The hemiazygos vein
Why do we have more veins than arteries?
There is more volume of blood coming back to the heart than leaving it. Act as a blood reservoir
Are the lumbar and inferior phrenic arteries posterior or anterior supply vessels?
Posterior supply vessels
Superior epigastric veins
Upper anterior drainage veins into the internal thoracic veins
Inferior epigastric vein
LOWER anterior drainage veins into the external iliac veins
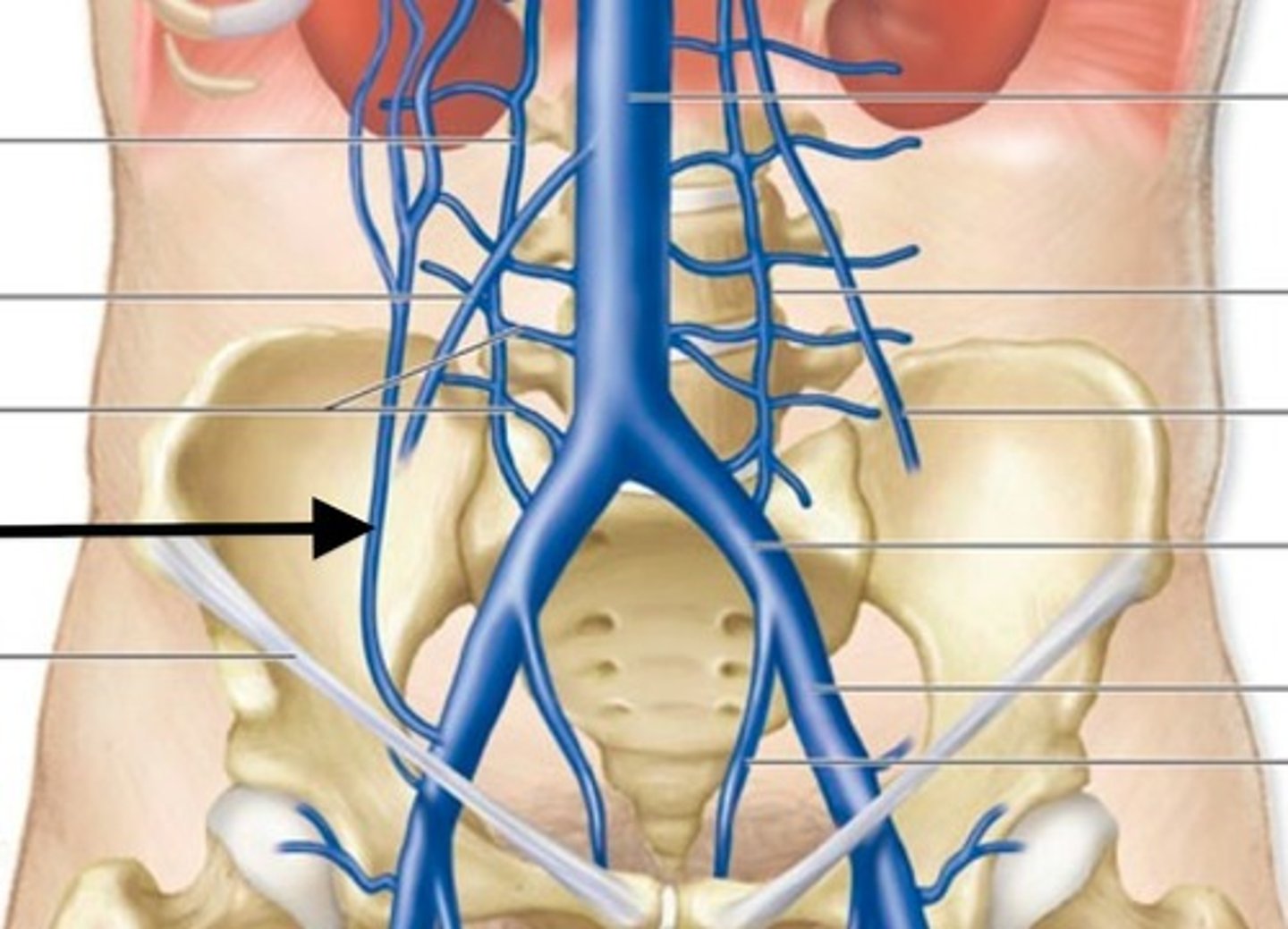
When does the right ascending lumbar vein become named the azygos vein?
When it exits the top of the diaphragm
What is the abdominal wall from T7-T11 innervated by?
Intercostal nerves
What is the abdominal wall at level T12 innervated by?
Thoracis spinal nerve T12 called "subcostal nerve" because its below the last rib
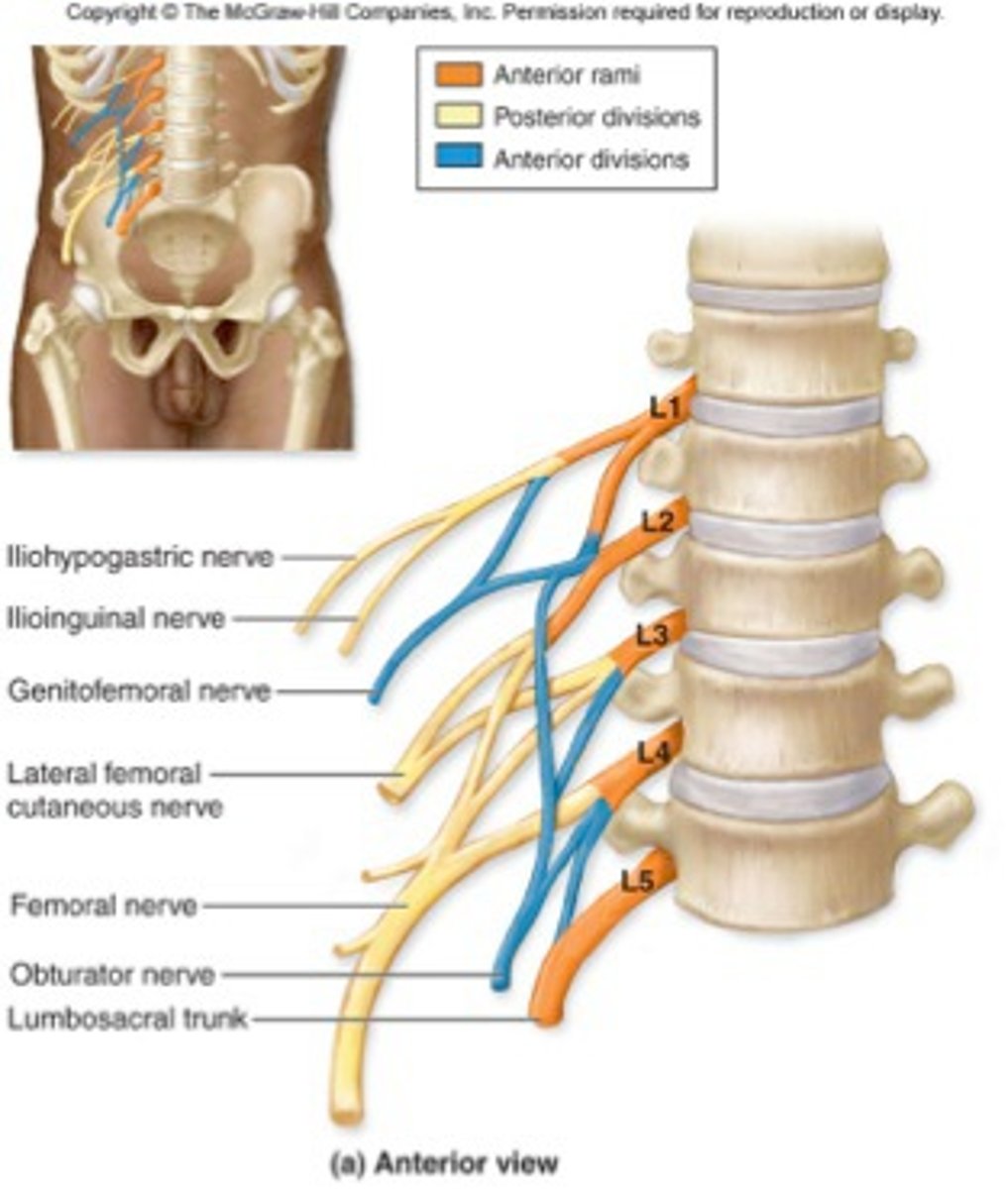
What are the three lumbar spinal nerves?
Iliohypogastric nerve, ilioinguinal nerve, genitofemoral nerve
iliohypogastric nerve
Lumbar spinal nerve L1 superficial to quadratus lumborum
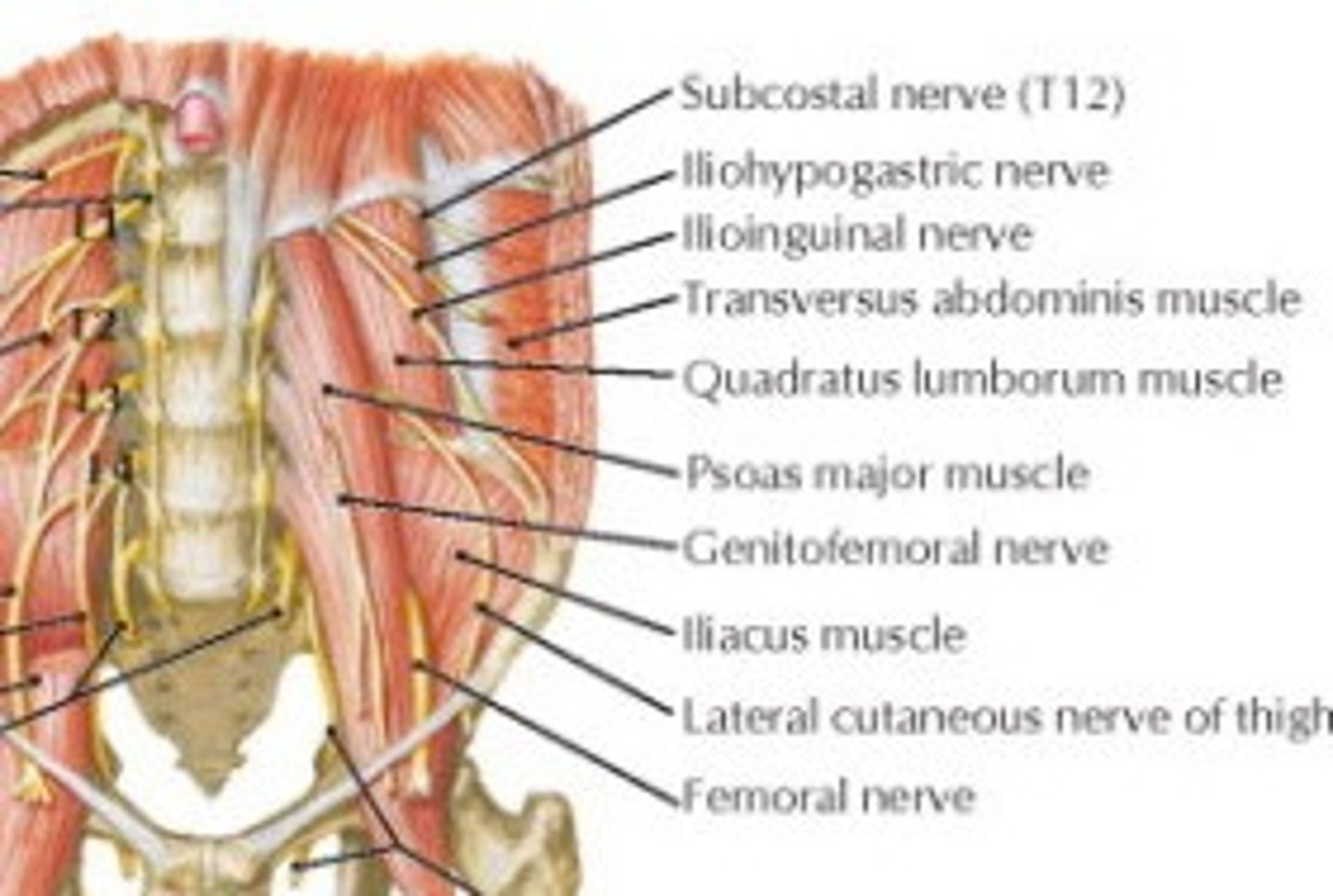
Where is the iliohypogastric nerve relative to the ilioinguinal nerve?
It is superior to the ilioinguinal nerve
Does the Iliohypogastric nerve have a lateral cutaneous branch?
Yes
function of iliohypogastric nerve
provides sensation to the skin of the lower abdomen and gluteal region
Ilioinguinal nerve
branch of the L1 spinal nerve
Does the inguinal nerve have lateral cutaneous branches?
No
Does the ilioinguinal nerve have an anterior cutaneous branch?
Yes
function of ilioinguinal nerve
innervates lower abdominal muscles, skin over superior/medial thigh and portions of external genitalia
genitofemoral nerve
Lumbar spinal nerve L2
Function on the genitofemoral nerve
provides sensation to the skin of the upper anterior thigh, the scrotum (in males), and the mons pubis (in females)