25: composition of the earth
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
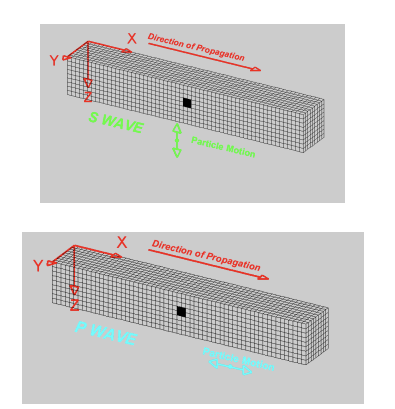
p-waves
seismic waves that move through liquids and solids
s-waves
seismic waves that do not move through liquids.

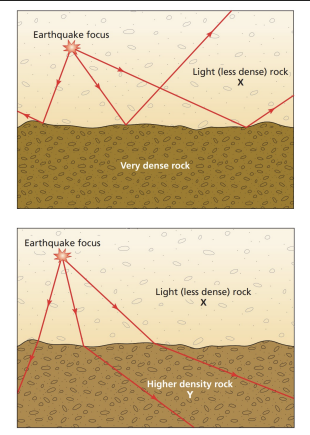
seismic wave behavior
speed changes with rock density; soft layers absorb waves; waves refract at density differences.
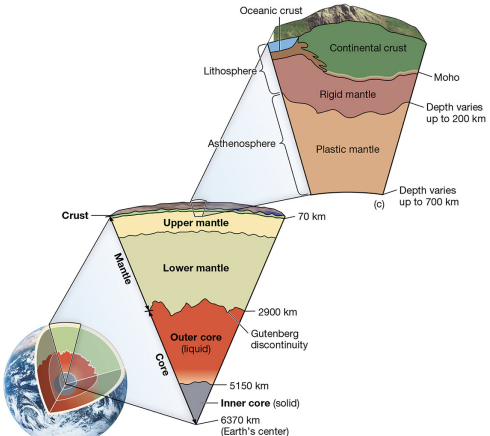
lithosphere
strong, brittle uppermost layer.
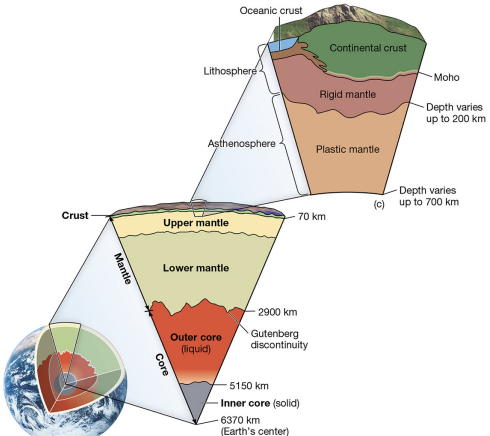
asthenosphere
plastically deformable mantle layer.
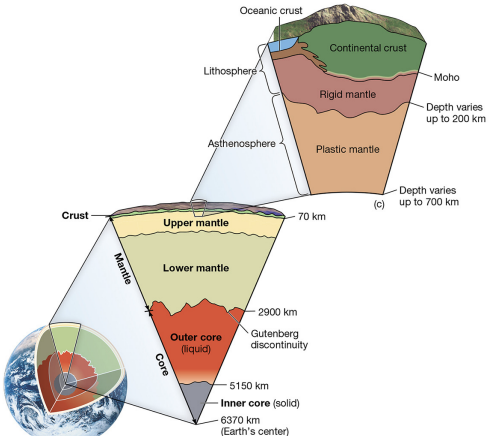
mantle
includes upper and lower mantle.
core
liquid outer core, solid inner core.

magnetic field source
moving liquid rock in outer core, produces north and south poles
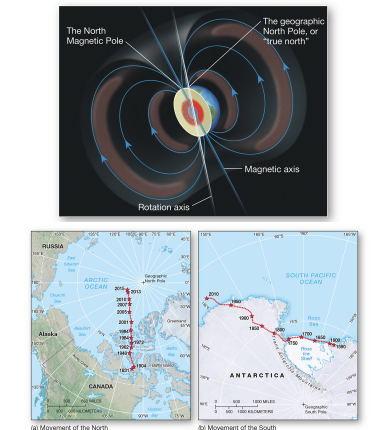
geomagnetic reversals
common polarity flips in earth’s history.
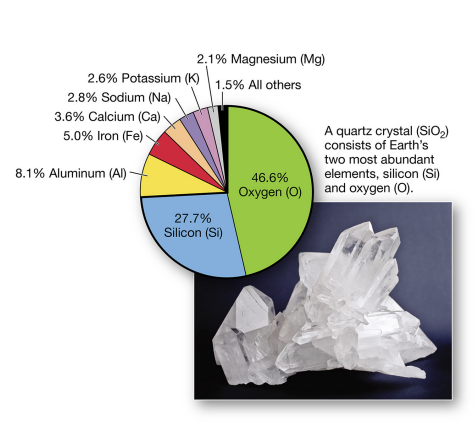
crust elements
oxygen abundant, 46.6%
silicon abundant 27.7%
crust contains lighter elements.
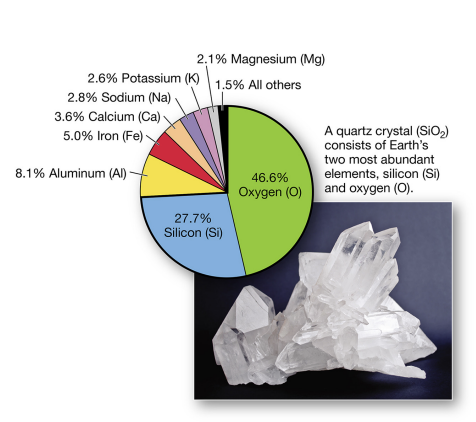
crust vs mantle
crust - aluminum and silicon
mantle - iron and magnesium

igneous rock formation
solidifies and crystallizes from magma or lava.

intrusive (plutonic)
cools within earth.
extrusive (volcanic)
forms on the surface.

mafic
high in iron/magnesium; dark and dense. (gabbro)

felsic
high in silica; light and less dense. (granite)
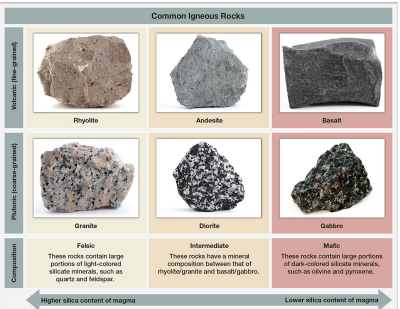
igneous combinations
any combo of intrusive/extrusive with mafic/felsic.
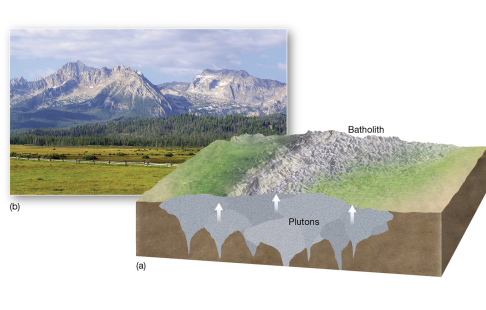
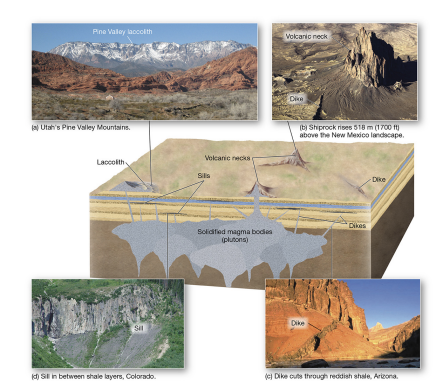
pluton
igneous body cooled below surface; exposed over time.
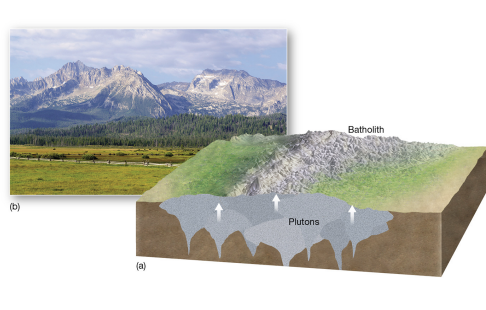
batholith / laccolith / volcanic neck / sills / dikes
igneous features that create iconic landscapes.
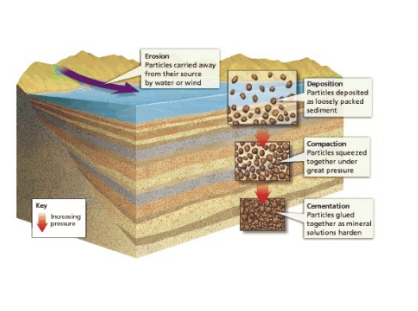
sedimentary processes
transport in high energy,
deposition in low energy
compaction and cementation.
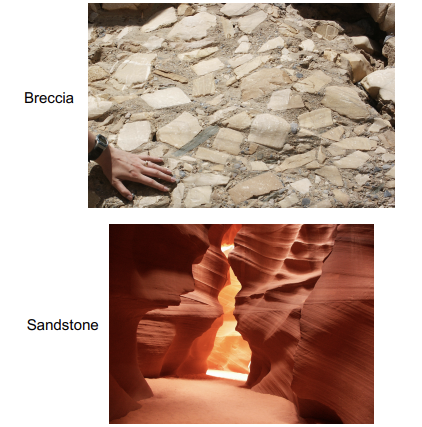

clastic
sediment compacted and cemented by overlying weight.
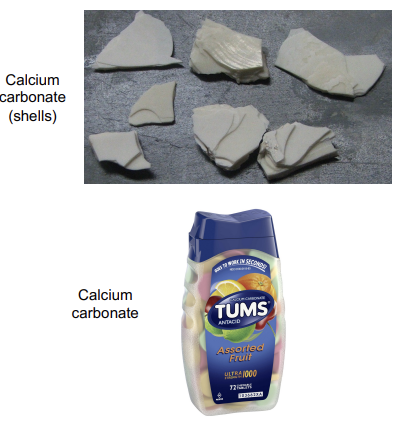

chemical
precipitation of dissolved chemicals.

evaporites
crystallized salt deposits from evaporating water.
examples of sedimentary rocks
sandstone, shale, conglomoerate
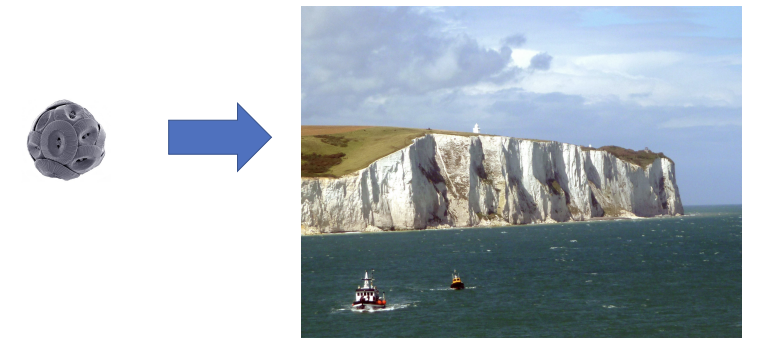
white cliffs of dover
composed of calcium carbonate.
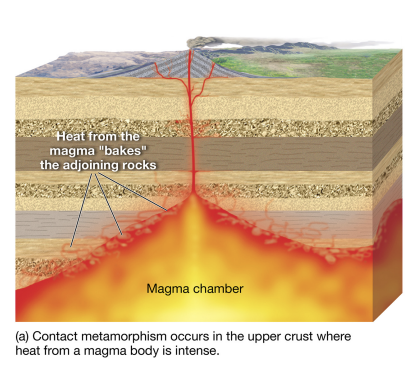
metamorphism causes
heating, pressure, both, or compression/shear.
contact metamorphism
magma heats adjacent rock, changing minerals.
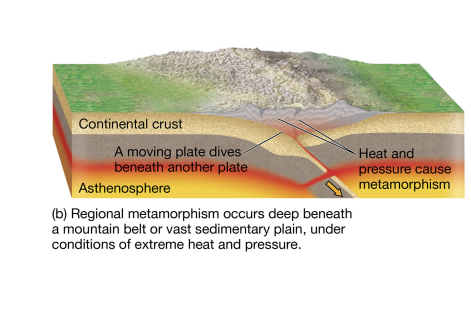
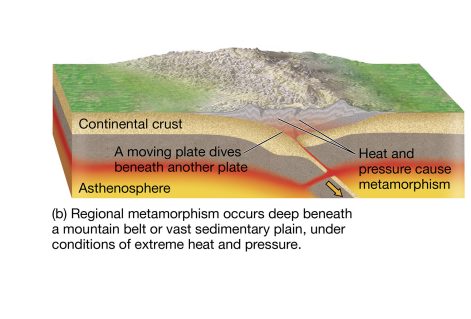
regional metamorphism
pressure from overlying rock alters minerals.
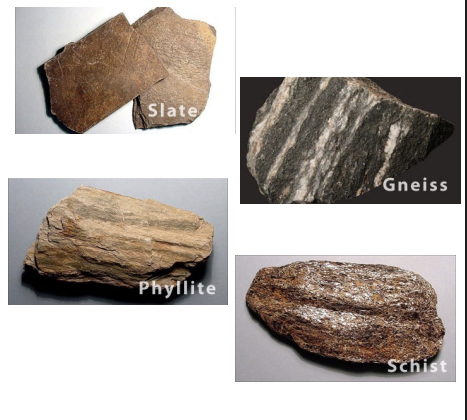

foliated
aligned crystals due to unequal pressure and shearing.
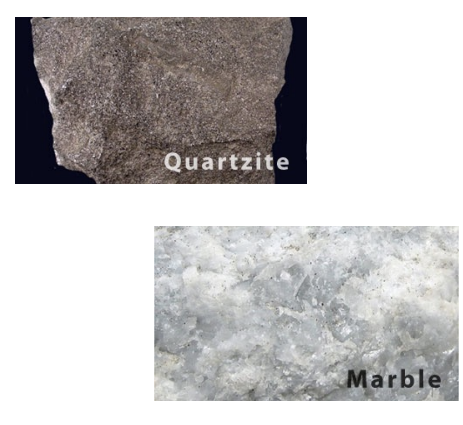

nonfoliated
no alignment; forms without shear; recrystallization increases density.
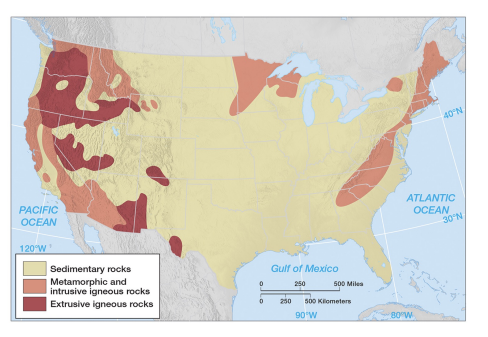
surface rocks on earth
sedimentary is the most common surface rock on earth
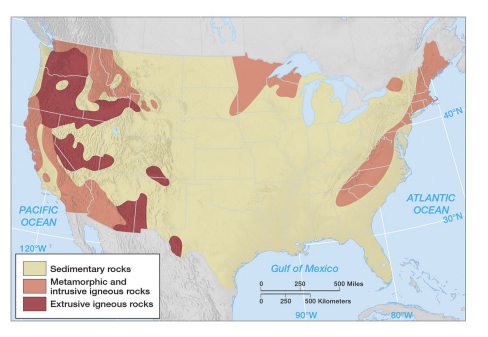
earth crust composition
96% igneous crust
75% exposed rocks are sedimentary.
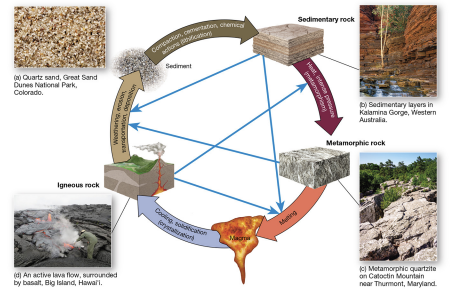
rock cycle
rocks are continually created, eroded, modified.
operates at the surface, operates at the subsurface
surface = hydrologic cycle
subsurface = tectonic cycle
wegener proposal
continents move; proposed in 1912.
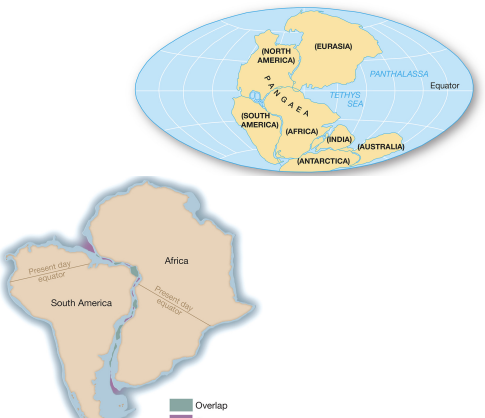
evidence: matching coastlines
continents fit like puzzle pieces.
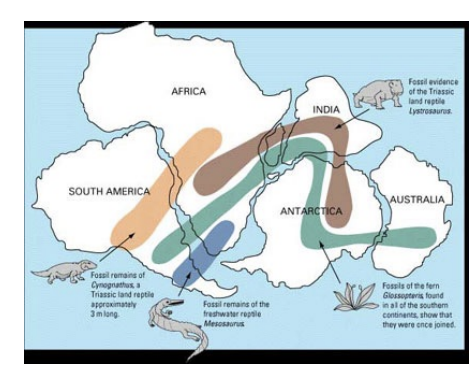
evidence: fossils
similar fossils found on distant continents.
similar plants on 3
freshwater reptiles on 2
small reptiles across many
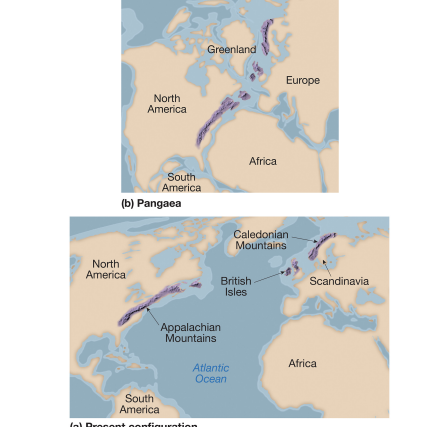
evidence: rocks
similar rocks on distant continents
appalachian and caledonian mountains share geology.
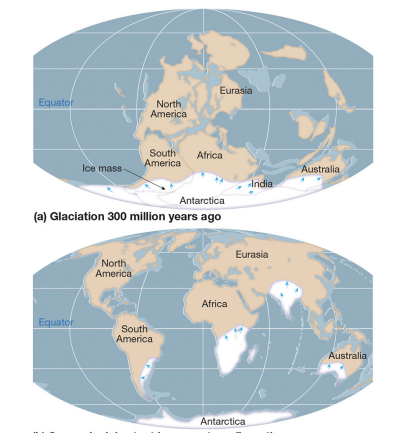
evidence: glacial deposits
similar flow patterns across continents.

evidence: species
related species appear on multiple continents.
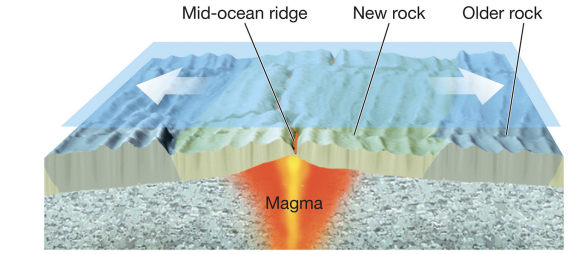
seafloor spreading process
magma rises through cracks in thin ocean crust, cools, forms new ocean floor with ridge shape.
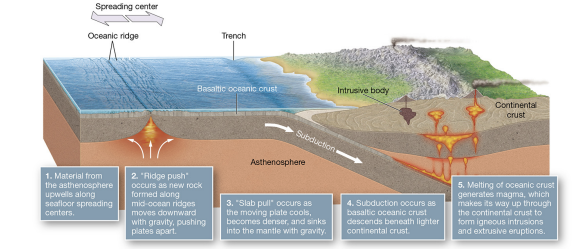
seafloor density contrast
continental crust ~2.7 g/cm³ - less dense
oceanic ~3.0 g/cm³ - more dense
denser oceanic crust subducts.
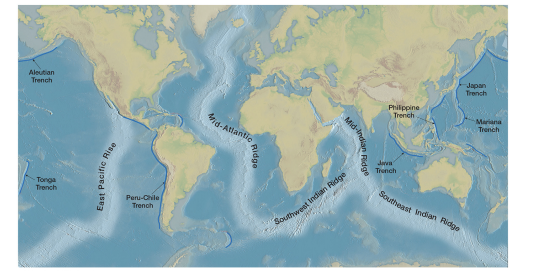
earthquake evidence
quakes common along ridges and trenches.

paleomagnetism
rocks record magnetic field orientation as they cool;
reversals preserved symmetrically around ridges.

age of crust
youngest crust at ridges
oldest near subduction zones.
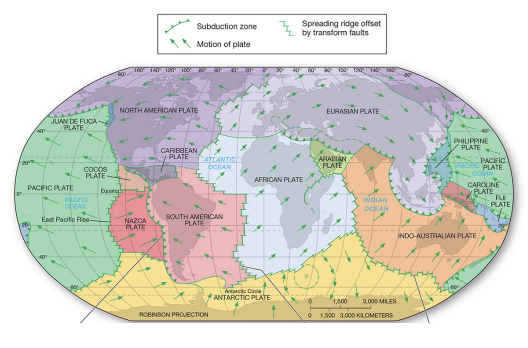
lithosphere plates
earth’s lithosphere is divided into moving plates.
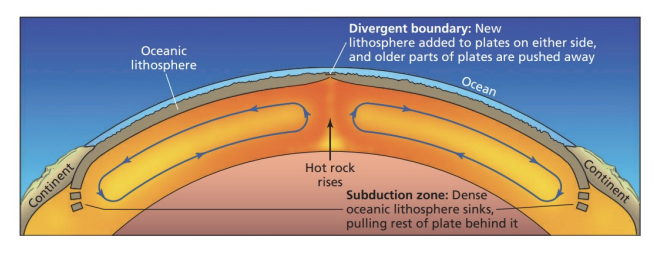
isostasy
continents float flexibly on denser mantle.
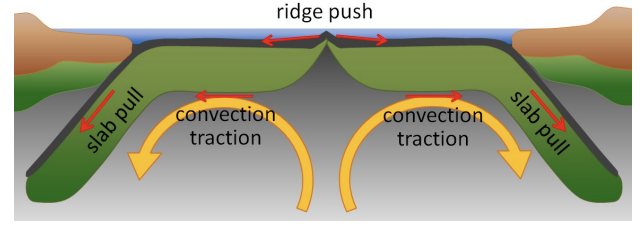
slab-pull model
convection drives motion; slab pull at subduction zones; ridge push from new crust.
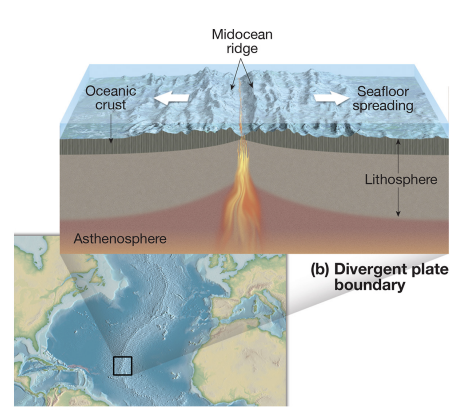
divergent boundary
plates move apart.
divergent oceanic-oceanic
forms midocean ridges.
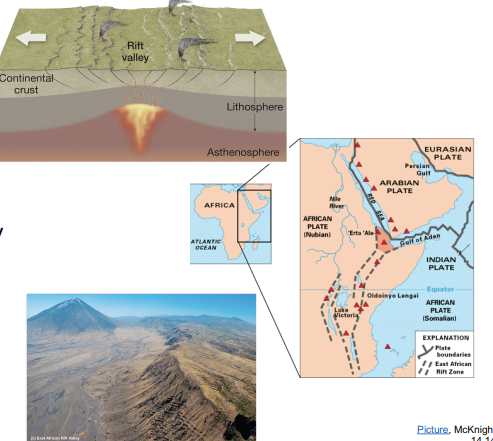
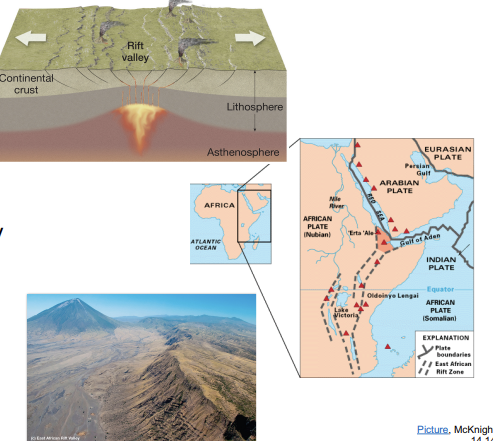
divergent continental
forms rift valleys.

east african rift
active divergent rift; forming a future ocean basin.
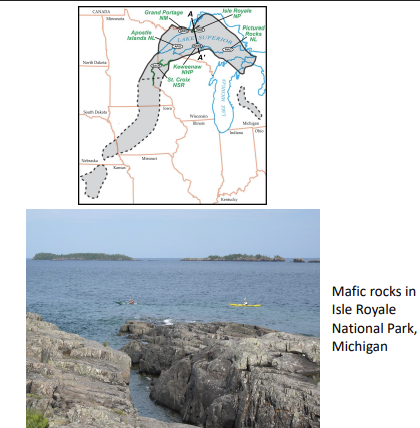
keweenawan rift
ancient failed divergent rift in north america; formed lake superior.
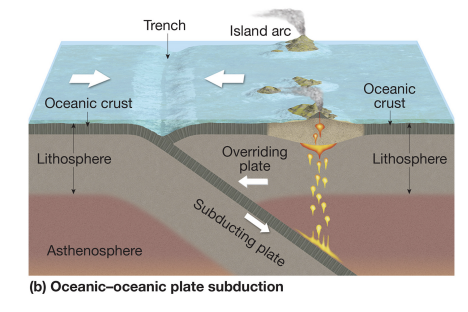
convergent boundary
plates collide.
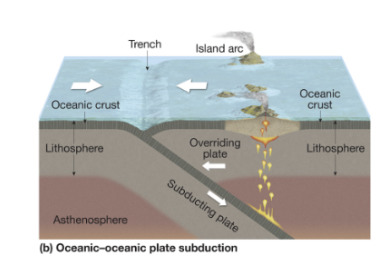
convergent oceanic-oceanic
denser plate subducts; trench + island arcs form
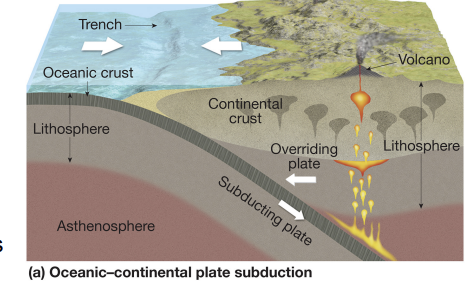
convergent oceanic-continental
oceanic plate subducts; volcanic arc form + metamorphism.
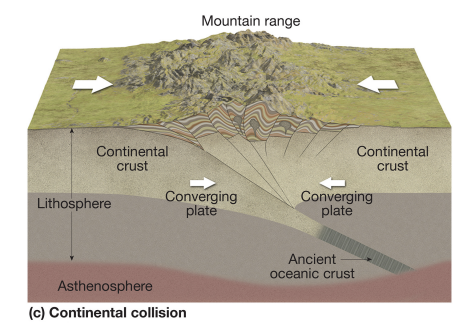
convergent continental-continental
no subduction; mountains build.
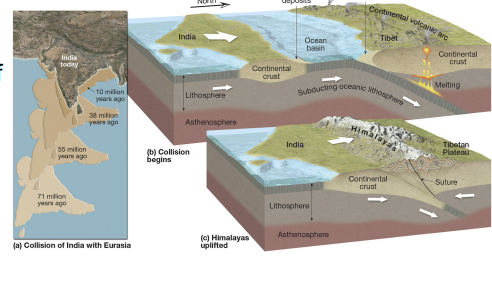
himalayan uplift
convergent: india collided with eurasia; formed himalayas; affected global climate.
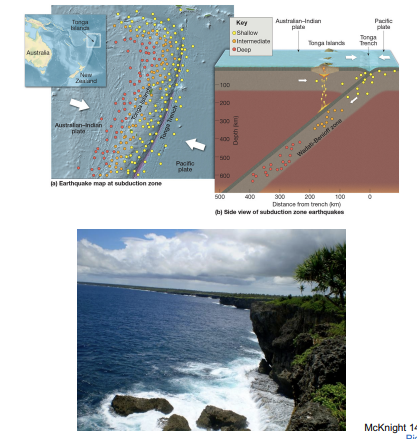
tonga volcanic arc
convergent: collision of australian-indian and pacific plates; wadati-benioff zone present.
flat subduction (laramide orogeny)
shallow subduction forming sierra nevada and rockies.
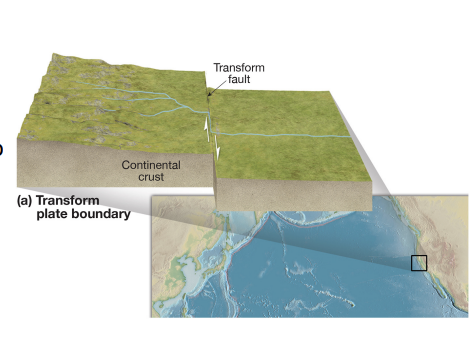
transform boundary
plates slide past each other; shallow earthquakes.

san andreas fault
transform: pacific vs north american plate; loma prieta 1989; san francisco 1906.