USE PHYSICAL CARDS ib economics chapter 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Last updated 1:44 AM on 11/8/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
Positive Statement
a statement regarding something that is, was or will be (true or false)
2
New cards
Normative Statement
a statement regarding something that is out to be (judgement)
3
New cards
Ceteris Paribus
to isolate the effect of one variable as a result of a change in another variable
4
New cards
Scarcity
Insufficient resources to satisfy all needs and wants, therefore scarcity of resources causes scarcity of goods and services (in factors of production: land, labour, capital, and enterprise)
5
New cards
Resource allocation
Overallocation: too many resources assigned to the production of particular goods and services
Under allocation: too few resources assigned to the production of particular goods and services
Leads to ⇨ reallocation of resources or misallocation of resources
Under allocation: too few resources assigned to the production of particular goods and services
Leads to ⇨ reallocation of resources or misallocation of resources
6
New cards
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity Cost: Results from the condition of scarcity that forces a choice between competing alternatives where the value of the next best alternative foregone to obtain something else
Scarcity ⇨ Choice ⇨ Opportunity Cost
Scarcity ⇨ Choice ⇨ Opportunity Cost
7
New cards
Factors of Production
Factors of Production: the inputs that are used in production of goods or services in the attempt to make an economic profit (land, labour, capital, and enterprise)
• CAPITAL- wealth formed for the purpose of investing in a company/thing
• Physical Capital- machinery, tools, and buildings
• Human Capital- skills, attitude, and knowledge
• Natural Capital- expanded meaning of land
• Enterprise- the combination of all factors of production to earn an economic profit
• CAPITAL- wealth formed for the purpose of investing in a company/thing
• Physical Capital- machinery, tools, and buildings
• Human Capital- skills, attitude, and knowledge
• Natural Capital- expanded meaning of land
• Enterprise- the combination of all factors of production to earn an economic profit
8
New cards
Production Possibility Curve (PPC)
A visual representation of all possible combinations of two types of goods that can be produced with given factors of production
• Assumed that quality and quantity of resources remain the same
• Assumed that the state of technology remains the same
• For PPC to be achieved, all resources must be fully employed and used efficiently
• However, output is always below frontier in real world due to unemployment of resources (higher unemployment= further away from point)
• Scarcity, choice and opportunity cost are always taken into account
• Assumed that quality and quantity of resources remain the same
• Assumed that the state of technology remains the same
• For PPC to be achieved, all resources must be fully employed and used efficiently
• However, output is always below frontier in real world due to unemployment of resources (higher unemployment= further away from point)
• Scarcity, choice and opportunity cost are always taken into account
9
New cards
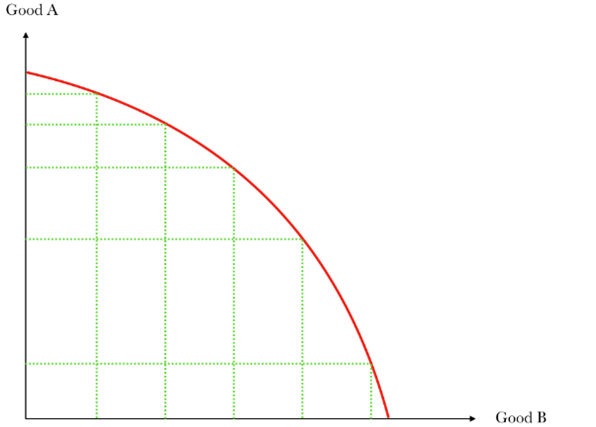
PPC Graph
o Curve shows maximum resources that can be utilised
o PPC displays the law of increasing opportunity cost (the more produced of one thing, the more of the other thing that needs to be forgone)
o Further down the curve, one thing is benefitted more than the other
o Shape of PPC displays opportunity cost of producing goods and services
o Various combinations, e.g. gives up laptops for phones
o PPC displays the law of increasing opportunity cost (the more produced of one thing, the more of the other thing that needs to be forgone)
o Further down the curve, one thing is benefitted more than the other
o Shape of PPC displays opportunity cost of producing goods and services
o Various combinations, e.g. gives up laptops for phones
10
New cards
Economic Efficiency
6 Types of Economic Efficiency: (don’t need to learn all of them yet)
1. Allocative Efficiency
2. Productive Efficiency
3. X-inefficiency
4. Pareto Optimality
5. Dynamic Efficiency
6. Social Efficiency
1. Allocative Efficiency
2. Productive Efficiency
3. X-inefficiency
4. Pareto Optimality
5. Dynamic Efficiency
6. Social Efficiency
11
New cards
Allocative Efficiency
(1) Allocative Efficiency: when firms are producing the combination of goods and services that are most wanted by consumers
o Both consumers and producers are satisfied
o Allocation the right amount of resources to the right amount of products and no waste
o P=MC (price = marginal cost (cost of producing one additional unit of output))
o As allocative efficiency is a “combination” of goods and services, it will reach the most ideal point for consumer demand
o Both consumers and producers are satisfied
o Allocation the right amount of resources to the right amount of products and no waste
o P=MC (price = marginal cost (cost of producing one additional unit of output))
o As allocative efficiency is a “combination” of goods and services, it will reach the most ideal point for consumer demand
12
New cards
Productive Efficiency
(2) Productive Efficiency: when firms are producing at the lowest cost possible
o When maximum number of goods and services are produced with a given amount of inputs
o Impossible to produce more goods without producing less services
o Curve can’t move outwards anymore because all resources are exhausted (without growth)
o When maximum number of goods and services are produced with a given amount of inputs
o Impossible to produce more goods without producing less services
o Curve can’t move outwards anymore because all resources are exhausted (without growth)
13
New cards
Types of Economic Systems
3 Types:
1. Free Market Economy
2. Command/Planned Economy
3. Mixed Economy
1. Free Market Economy
2. Command/Planned Economy
3. Mixed Economy

14
New cards
Free Market Economy

15
New cards
Command/Planned Economy

16
New cards
Mixed Economy

17
New cards
Transition Economy
