Science Year 9 Semester 1 - Earth Science
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is pressure?
The amount of force applied over a certain area
What is the crust?
The outermost layer of the Earth, composed of solid rock, which includes both continental and oceanic crust.
Which type of crust is thicker?
Continental crust is thicker.
Which type of crust is denser?
Oceanic crust is denser.
What is the mantle?
The thickest layer, located beneath the crust, made up of semi-solid rock that flows slowly over time. The flowing of rocks can cause movements in the crust.
Divided into upper and lower mantle.
What is the outer core?
The layer of the Earth located beneath the mantle, composed of liquid iron and nickel. It is responsible for generating Earth's magnetic field through its movement.
What is the inner core?
A solid ball of iron and nickel at the very centre of the earth. Despite extreme temperature, it remains solid due to immense pressure.
What is the lithosphere made of?
The crust and the rigid upper layer of the mantle, and id divided into tectonic plates.
What is a plate boundary?
The region where two plates meet. The plates can interact in different ways. It is the common cause of earthquakes and volcanoes.
What is a divergent boundary?
Two tectonic plates move away from each other.
What happens when two oceanic plates diverge?
Magma rises to form new oceanic crust, creating mid-ocean ridges. This process is called sea floor spreading.
What happens when an oceanic and continental plate diverge?
A depression is formed, known as a rift valley. It allows magma to rise from the mantle, forming volcanoes.
What is a convergent boundary?
Two tectonic plates move into each other.
What happens when continental and oceanic plates converge?
The denser oceanic crust us pushed underneath the lighter continental crust. This is called subduction and causes trenches to be formed.
What happens when two oceanic plates converge?
The denser material is pushed downwards and causes a deep trench on the seafloor
What happens when two continental plates converge?
The lighter material is pushed upwards and forms mountain ranges
What is a transform boundary?
Two tectonic plates slide across each other
What are the characteristics of a transform boundary?
These plates aren’t completely straight and when these “sticking points” are forced to move, the pressure build up can become too strong and cause earthquakes.
What is a fault?
The line at which two transform boundaries meet
In summary, what do CONVERGENT boundaries form?
Oceanic Trench, Volcanoes, Mountain Ranges
In summary, what do DIVERGENT boundaires form?
Mid Ocean Ridges, Rift Valleys, Volcanoes
In summary, what do TRANSFORM boundaries form?
Fault Lines, Earthquakes
What is Pangaea?
A supercontinent that had all the land mass joined together, around 280 million years ago
What is the continental drift theory?
According to Alfred Wegener, Pangaea broke up into several smaller continents over millions of years to their current positions
What are some evidence of the continental drift theory?
The continents appear to fit like a puzzle
Fossils of land animals and plants of the same age have been found on different continents
Similar rock types and mountain chains line up between different continents
New evidence shows seafloor spreading which helped move the continents apart
What happens at earthquakes?
Energy radiates out from the focus in all directions. It travels as vibrations called seismic waves
What is the correlation between distance of seismic wave and energy?
Directly Proportional - The further the distance, the weaker the energy
What is the epicentre?
The point on the surface DIRECTLY above the focus
What is the focus of an earthquake?
The exact point underground where the earthquake origins
What is a seismograph?
A special instrument that records ground motions and measures the size, location and time of the earthquake
What is the magnitude scale?
a measure of the power of the vibration and the amount of energy released, and is most commonly used in a Richter Scale
What is a tsunami?
A tsunami is a giant tidal wave caused by underwater seismic activity (earthquakes and coastal landslides)
What are the four spheres of the earth?
Geosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere, Biosphere
What is the GEOSPHERE?
The layers of Earth made up of solid rock and other rocky materials. (Entire solid earth, including the crust, mantle, and core)
What is the HYDROSPHERE?
The combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite
What is the ATMOSPHERE?
The envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet.
What is the BIOSPHERE?
The part of the planet occupied by living organisms
What is the difference between the Lithosphere and the Geosphere?
The lithosphere is Earth’s rigid outer layer (crust and upper mantle), while the geosphere includes all of Earth’s solid parts—the crust, mantle, and core.
What is an ecosystem?
A collection of living things that interact with each other and with their environment
What is a biotic factor?
Living organisms (Humans, Plants, Animals)
What is an abiotic factor?
Non Living Organisms (Rocks, Water, Oxygen)
What is the difference between consumers and producers?
Producers get their energy from sunlight
Consumers get their energy by consuming other living things
What is a Food WEB?
A complex model that shows energy flow through an ecosystem
What is a Food CHAIN?
A simple model that shows energy flow from one species to another
Something is considered living if it satisfies all elements of MRSGREN. What does MRSGREN stand for?
M - Movement
R - Respiration
S - Sensitivity
G - Growth
R - Reproduction
E - Excretion
N - Nutrition
What is ecology?
The study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment
Food is needed by organisms for 2 reasons. What are they?
Matter to grow and repair our bodies
Energy to power our bodily functions and activities
What is the process of photosynthesis?
A chemical reaction that converts carbon dioxide and water into sugar (stored energy) and oxygen
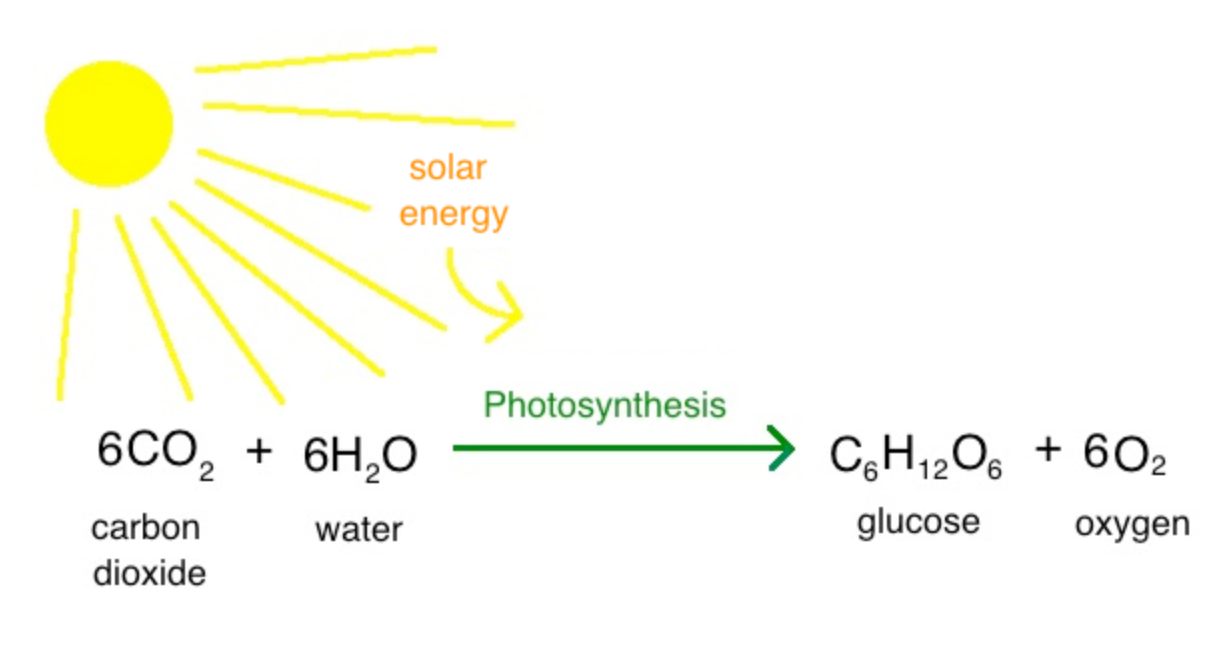
What is the process of cellular respiration?
A chemical reaction that converts glucose (stored energy) and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water and energy (the opposite of photosynthesis)
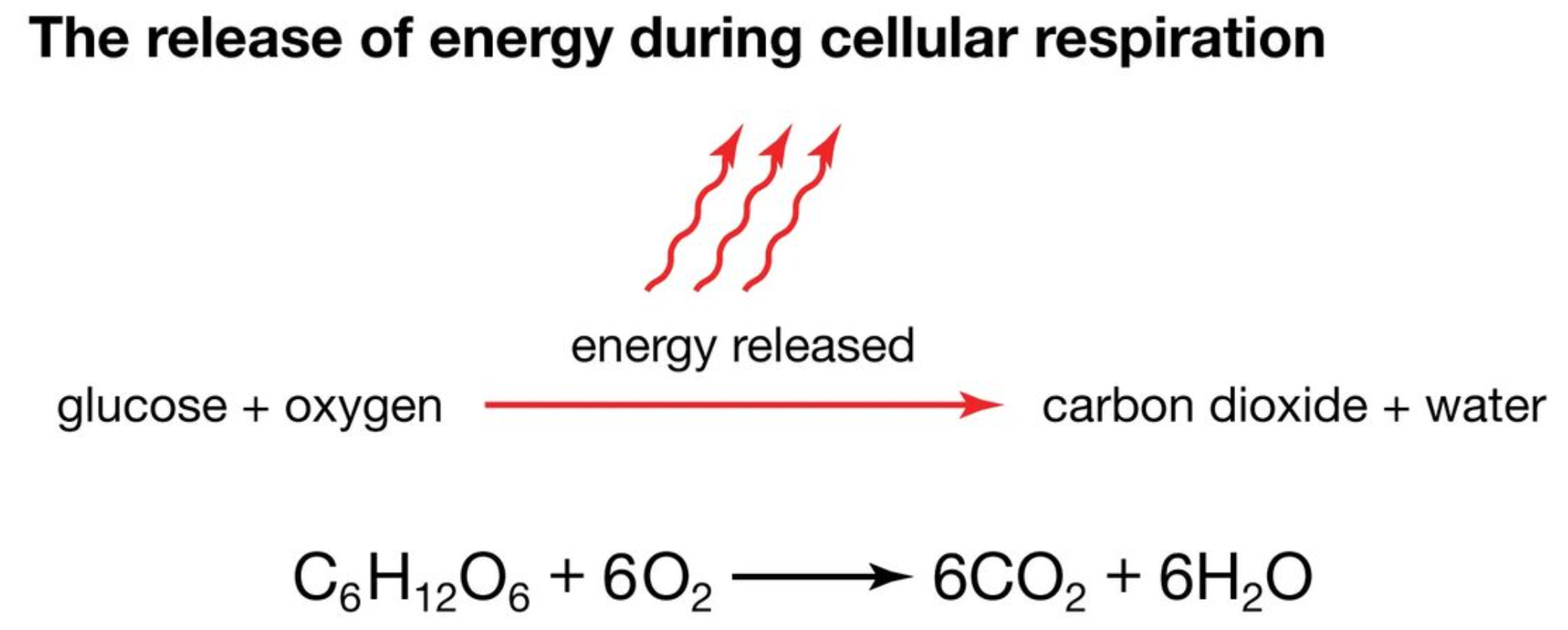
What is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis explains how energy enters food chains in the first place. Cellular respiration explains how organisms make use of this energy to stay alive.
What is the main difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to short-term changes in the atmosphere
Climate refers to long-term weather patterns over a long period of time in a specific area
What is an ice core?
A cylindrical chunk of ice drilled out from glaciers and ice sheets, and act as time capsules that reveal past climate conditions
What is the purpose of extracting ice cores?
Ice cores provide direct information about how greenhouse gas concentration has changed in the past. They can provide climate information up to a million years ago.
What is global warming?
The long-term warming of the atmosphere due to the build up of greenhouse gases (notably carbon dioxide) due to human activity
What are some negative impacts of global warming?
A warmer earth may lead to changes in rainfall patterns, increase in extreme weather events, a rise in sea level, and a wide range of impacts on plants, wildlife, and humans.