Work, Energy, and Power
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
The change in energy of a system by mechanical means:
Work
What mechanical means does work use to change the energy of a system?
Pushing or pulling
How to calculate work?
Force times displacement in the direction of force
Equation for calculating work:
Fd, where F is applied force in N, and d is distance moved by object in m
Unit for work:
Joules (J)
Is work a scalar or vector quantity?
Scalar
Can work have positive, negative, and neutral signs?
Yes
What does work with positive sign mean?
It is in the same direction as force
What does work with negative sign mean?
It is in the opposite direction of force
How to calculate work done by gravity?
W=mgh
If an object is moving downward, what is the sign of work done by gravity?
Positive
If an object is moving upward, what is the sign of work done by gravity?
Negative
What force is used to stretch a spring?
Applied force
What force tries to restore the spring after it is stretched?
Spring force
How to find work done by stretching a spring?
Applied force x change in length
Equation for finding work done by stretching force:
kx²
Why is the equation for finding work done by a stretching force kx²?
The work done by stretching a spring is applied force x change in length, and applied force = kx according to Hooke’s law

How to find the angle theta?
cos theta = FAx / FA
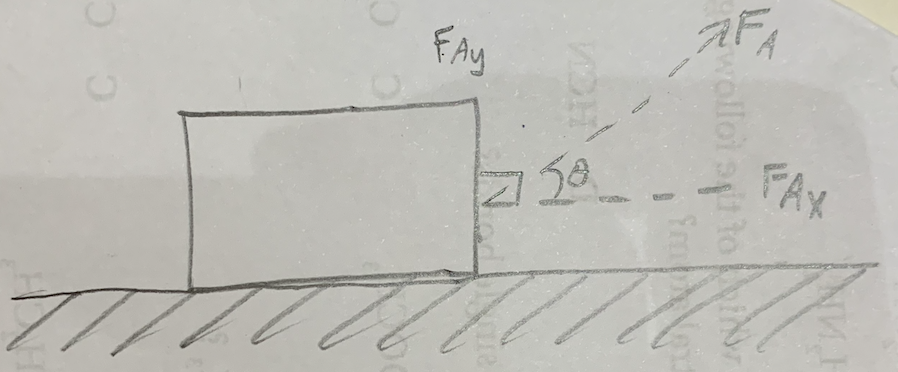
How to find FAx?
FA cos theta
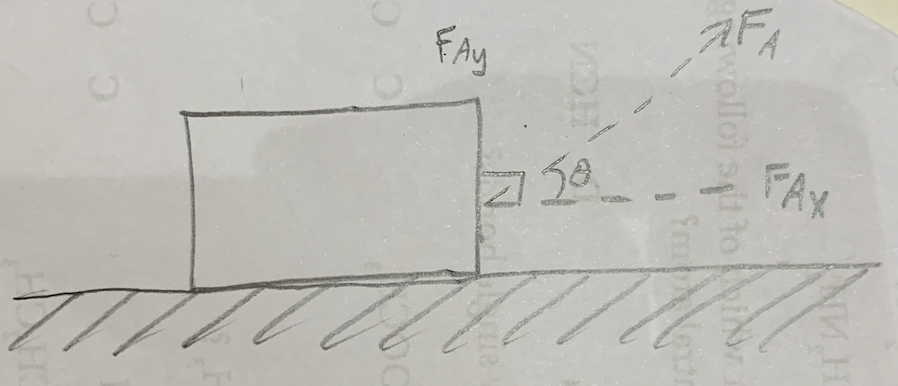
What is the work done by FAy?
0
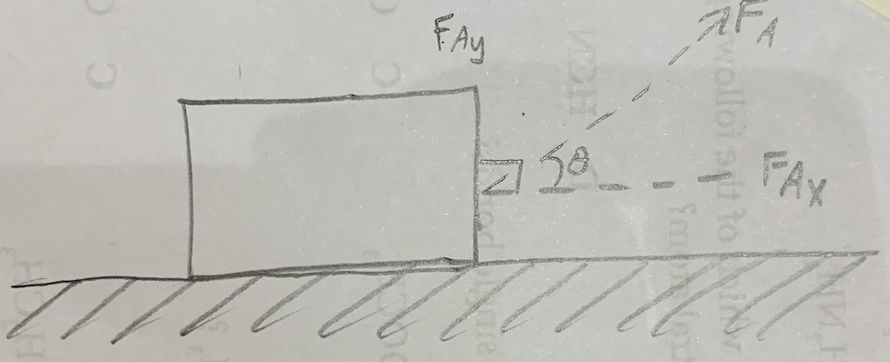
Why is the work done by FAy zero?
Because FA cos 90 d = 0
The sum of potential energy and kinetic energy:
Mechanical energy
Energy possessed by an object due to its position or shape?
Potential energy
Different types of potential energy:
Gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy
Energy that an object has relative to its position in the earth’s gravitational field:
Gravitational potential energy
How to calculate gravitational potential energy?
Mass x gravitational field strength x height
The energy possessed by elastic materials:
Elastic potential energy
Example of elastic materials:
Spring
Hooke’s law:
F=kx
What does the area of a load-extension graph represent?
Work done by stretching or compressing the spring
Equation for finding area of a load-extension graph:
1/2 (x)(F)
Equation for calculating work done by stretching or compressing a spring:
½ (k) (x²)
Why is work done by stretching or compressing a spring calculated using ½ (k)(x²)?
Because F=kx, and W=1/2(Fx), so W=1/2(kx(x)), or W=1/2kx²
Energy possessed by an object due to its motion:
Kinetic energy
Equation for calculating kinetic energy:
1/2mv², where m = mass and v = velocity
Rate of doing work:
Power
How to calculate average power?
Work done in J over time in seconds
What is the unit for power?
J/s or watt (W)
kW = ? W
1000
MW = ? W
10^6
How to further break down the equation average power = work done / time?
Average power = (force x distance)/time
How to calculate power of a moving object?
Fv, where F = force and v = velocity
What does the principle of conservation of energy state?
Energy can never be created or destroyed but the total energy always remains constant
What does the work-energy theorem state?
The amount of work done on a system is equal to the energy added to the system
Why is work = change in kinetic energy for a block changing from one velocity to another?
Vf² = Vi² + 2ad, so Vf² = Vi² + 2ad, or Vf²-Vi²=2ad, and F=ma, so a =F/m, so (Vf-Vi)²=2Fd/m, so m(delta v)²=2Fd, so 1/2m(delta v)²=Fd, so change in kinetic energy = work
How is work = potential energy?
Potential energy = mgh, and mg = F and h = d, so potential energy = Fd = work
What does the area of force-distance graph represent?
Work
What condition must be true for area of force-distance graph to equal work?
Force must be constant
If force must be constant for area of force-distance graph to equal amount of work done, what does this mean about the calculated work?
It represents average work
Which type of collision do theoretical models exhibit?
Elastic
Types of collisions:
Elastic and inelastic
What happens to the momentum of a system where no external force acts?
Constant
The collision of 2 objects that do not stick to each other after collision:
Elastic collision
What is collision called if kinetic energy is conserved?
Elastic
Why are collisions in real life inelastic?
Energy is loss to sound, friction, or deformation
Is energy conserved in most collisions in real life?
No
A collision in which the kinetic energy is not conserved:
Inelastic collision