Chemistry--Unit 4: Atomic Structures
Dalton’s Experiment
Atomic Theory:
1) Elements consist of invisible particles called atoms.
2) Atoms of the same element are identical.
3) Law of Conservation of Mass: Atoms cannot be created nor destoyed.
4) Law of Multiple Proportions: Atoms combine in whole number ratios: compounds.
Dalton’s model of the atom

1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Dalton’s Experiment
Atomic Theory:
1) Elements consist of invisible particles called atoms.
2) Atoms of the same element are identical.
3) Law of Conservation of Mass: Atoms cannot be created nor destoyed.
4) Law of Multiple Proportions: Atoms combine in whole number ratios: compounds.
Dalton’s model of the atom

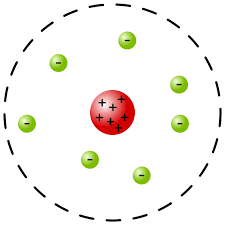
Thompson’s Experiment
Discovered electrons through his cathode ray tube test
1) Beam must contain negative charges since it’s repelled by the negative end of the magnent
2) If an atom has negative particles, it should also have positive particles
3) All matter is made up of positive and negative particles—he tested multiple samples and found similar results
Thompson’s model of the atom
Rutherford’s experiment
Discovered the nucleus through his gold foil test
1) Accurately predicted that most particles would pass through the foil, concluding that most of the atom is empty space
2) Small percentage bonced back, so the atom must have a small, positive center, since positive charges repelled one another
Rutherford’s model of the atom
Millikan’s experiment
Oil drop experiment
1) Found the charge and mass of a single electron
2) Charge is greater than mass
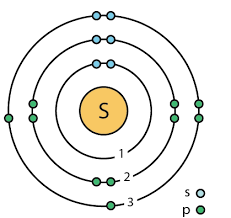
Bohr’s experiment
Discovered electron energy levels
1) Worked with hydrogen emission spectors, and modeled the atom
2) Found out that electrons would jump between energy levels based on whether it gains or loses energy
Bohr’s model of the atom
Schrödinger’s experiment
Discovered a quantum model
1) Found a mathematical equation for predicting an electron’s position
2) Created an orbital shape for electrons
Schrödinger’s model of the atom
What is a proton?
A positively charged particle in the nucleus
What is a neutron?
A neutral atom particle in the nucleus
What is an electron?
A negative particle found outside of the nucleus
What is the atomic number?
The number that represents the number of protons in an element and determines its identity
What is atomic mass?
The number at the bottom of the box that represents the average mass of all isotopes of that element
What is an element symbol?
A 1 or 2 letter symbol representing the element’s name
What is an ion?
A charged particle that has either gained or lost electrons
What is a cation?
A charged particle that has lost electrons. Positvely charged
What is an anion?
A charged particle that has gained electrons. Negatively charged
What is an isotope?
An atom that has more or less neutrons, which changes its mass
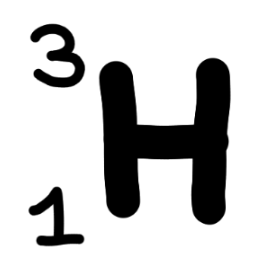
What notation is this represented in?
Isotope notation
What notation is ‘Hydrogen—3’ represented in?
Hyphen notation
What is the difference between mass number and atomic number?
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons.
The atomic number is the amount of protons.
What is the average atomic mass?
The weighted mass
The average mass of all isotopes of an element
What is the formula for average atomic mass (AAM?)
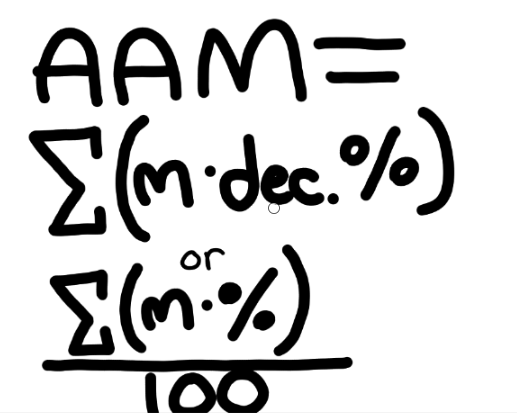
What is the equatio to find the percentage of abundance of an element?
