endocrine system
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pt A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Endocrine system acts with nervous system to
coordinate and integrate activity of body
cells. So it is the second great control system of the body
nervous system regulates the activity of muscles and glands using
electrochemical impulses
Endocrine system Influences metabolic activities
via hormones
The response of cells to hormones in endocrine system is
slower, but lasts longer compared to nervous system
in the nervous sytem, they initiate responses rapidly while the endocrine system initates responses
slowly
in nervous system, it has short duration responses(miliseconds) while the endocrine system has
long duration responses
in nervous system, neurotransmitters act over very short distances while the endocrine systems hormones
act over long distances
major processes that hormones control are
– Reproduction
– Growth and development
– Maintenance of electrolyte, water, and nutrient balance of blood
– Mobilization of body defenses
how are the endocrine organs in the body?
widely scattered throughout the body
Endocrine glands release _______ into the surrounding tissue fluid and typically have a
rich vascular and lymphatic drainage that receives the hormones
Hormones,
Endocrine glands organ names:
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal glands, pancrease, and gonads (testes and ovaries)
Hypothalamus is ________ organ
neuroendocrine
Though hormones circulate systemically, only cells with receptors…
for the specific hormone are affected
Target cells
tissues with receptors for a specific hormone
Hormones alter target cell activity
means that increasing or decreasing the rates of normal cellular processes
The response depends of the target cell type: for example
when epinephrine(fight or flight response receptor) binds to smooth muscle in bv walls, they contract. epinephrine binding to cells other than muscle cells will have a different affect(muscles will instead contract)
hormone action on target cells produces one of the following changes
-alter plasma membrane permeability
-stimulate synthesis of enzymes and proteins
-activate or deactivate enzymes
- Induce secretory activity
- Stimulate mitosis
Hormones act at receptors in one of two ways, depending on their chemical nature and
receptor location
– Water-soluble hormones – can’t enter the cell
OR
Lipid-soluble hormones – can enter cell
– Water-soluble hormones – can’t enter the cell
▪ Act on plasma membrane receptors
▪ Act via G protein second messengers
▪ Triggers response of target cell
Lipid-soluble hormones – can enter cell
▪ Act on intracellular receptors that directly activate genes
▪ Makes a protein
▪ These new proteins (often enzymes, receptors, or structural proteins) alter the cell
activity.
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling mechanism – This is a second messenger
1. Hormone (first messenger) binds to receptor
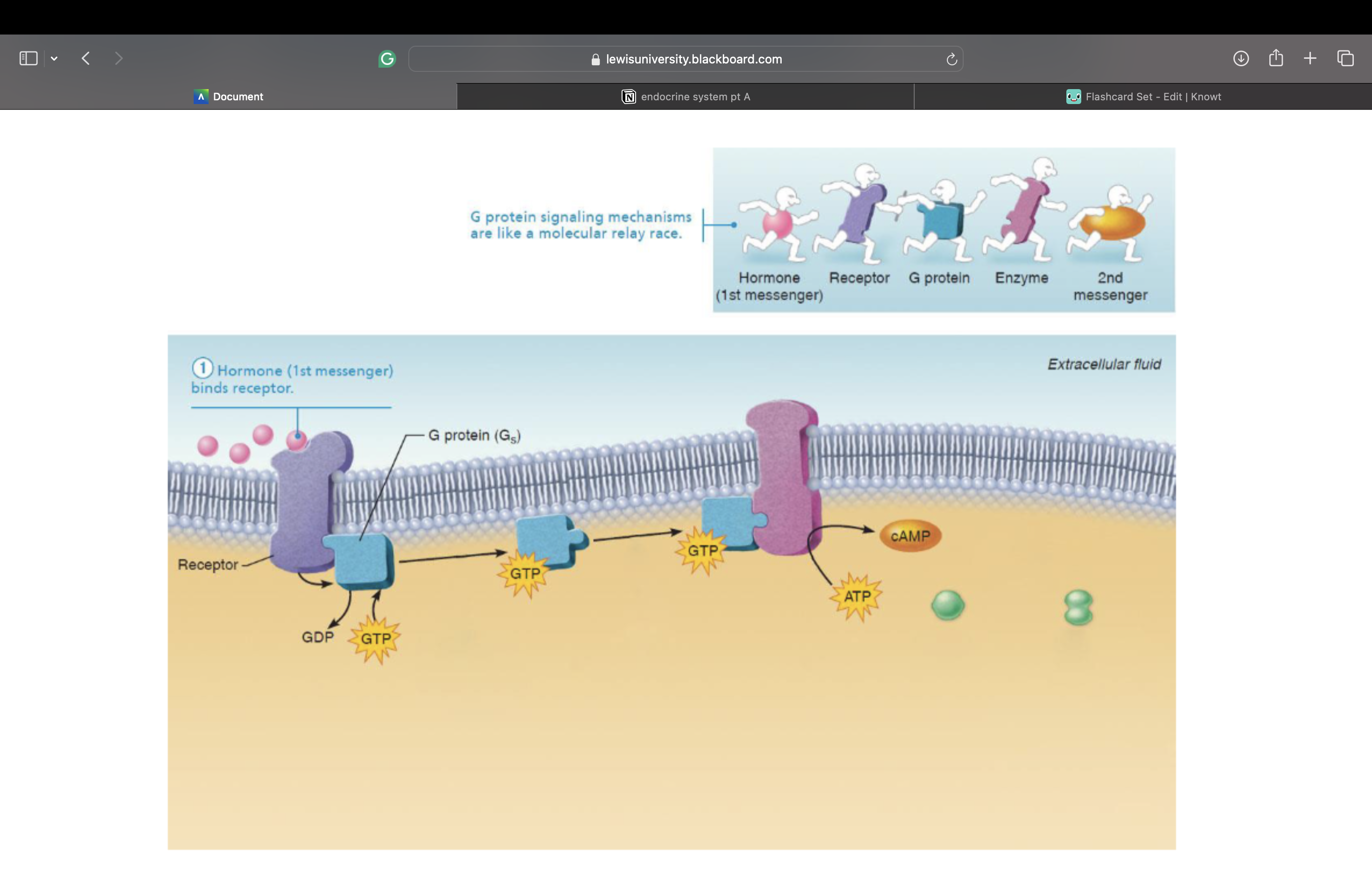
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling mechanism – This is a second messenger
2. Receptor activates a G protein
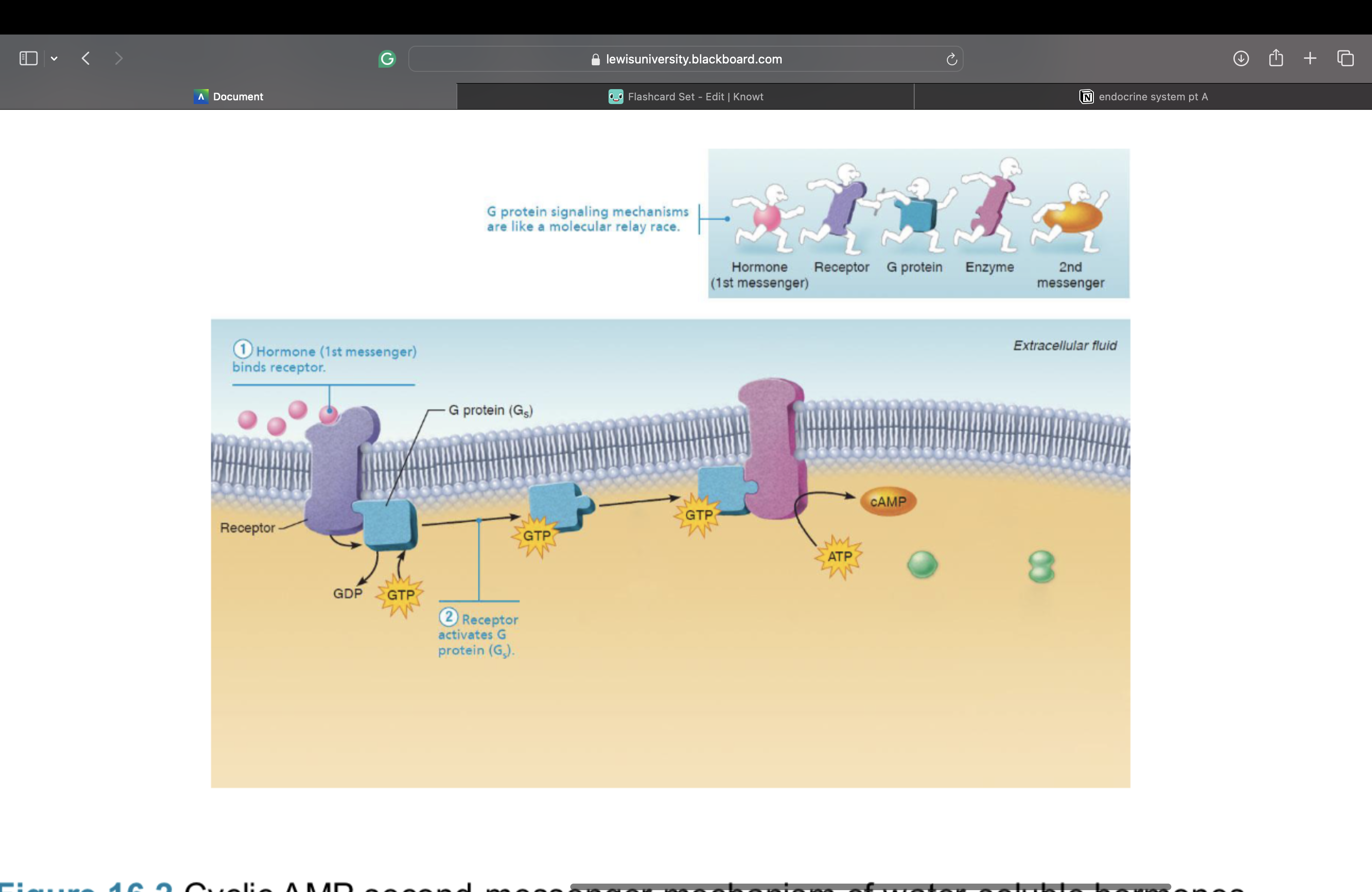
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling mechanism – This is a second messenger
3. G protein activates or inhibits effector enzyme adenylate cyclase
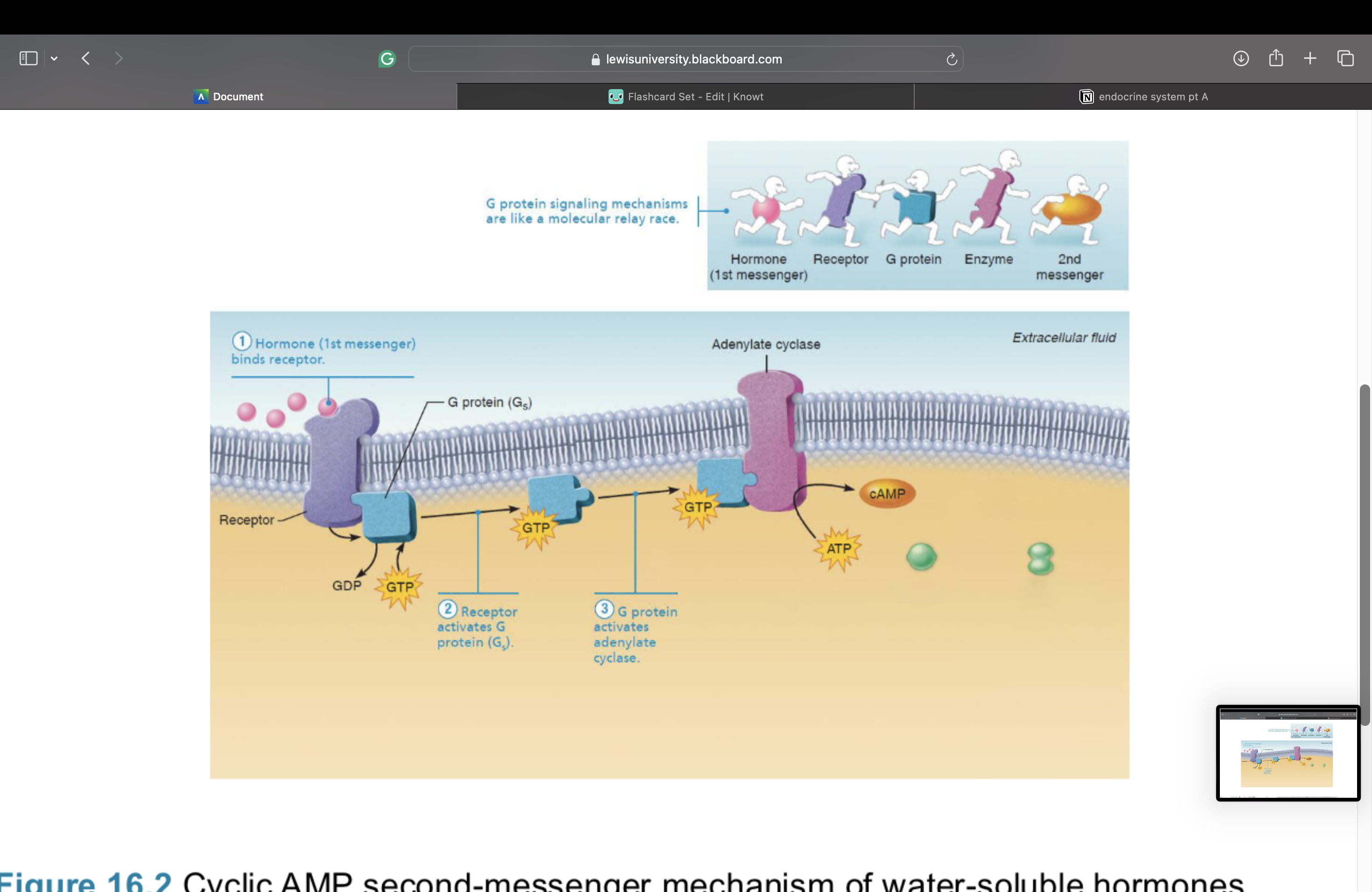
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling mechanism – This is a second messenger
4. Adenylate cyclase then converts ATP to cAMP (second messenger)
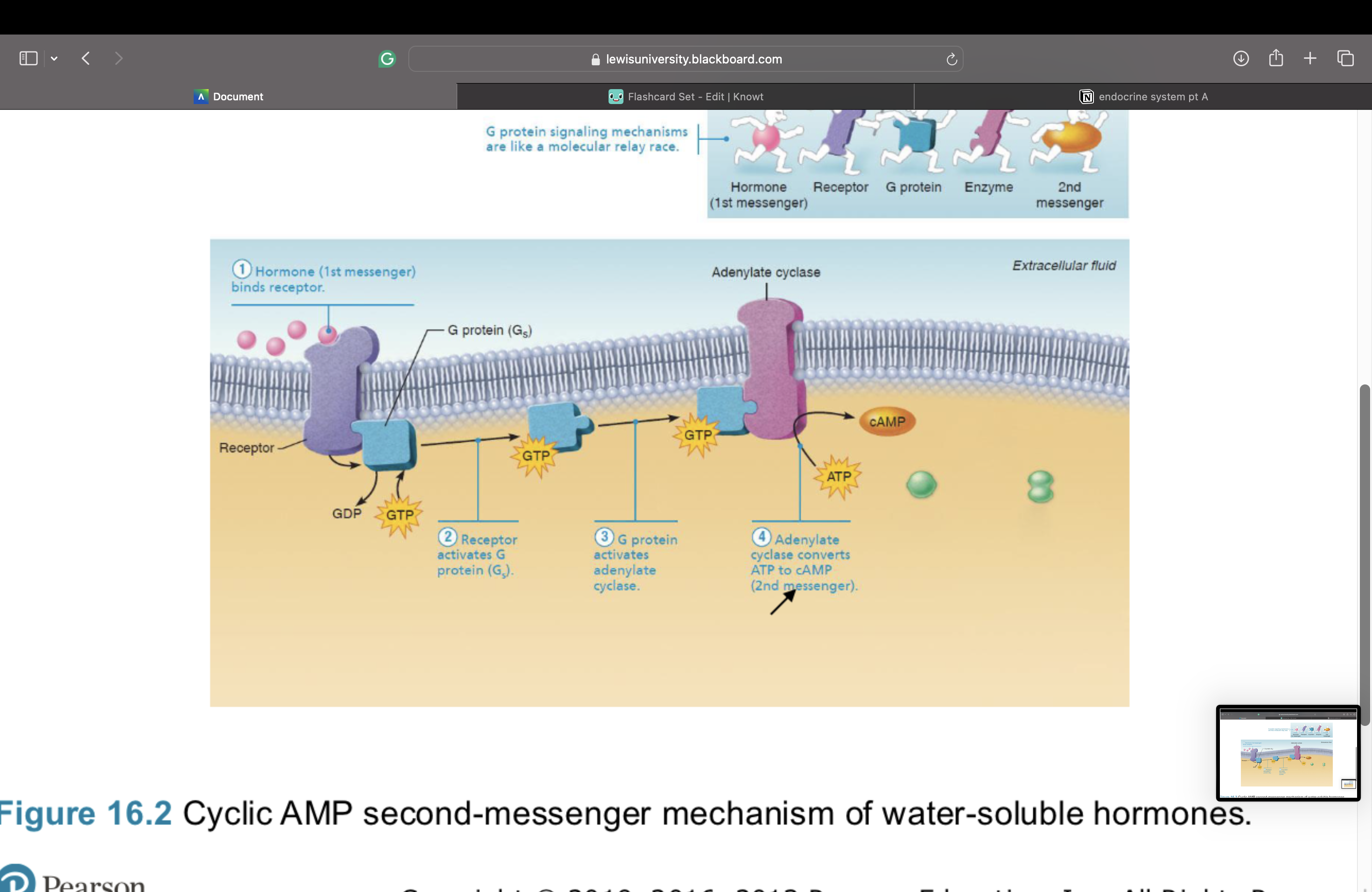
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling mechanism – This is a second messenger
5. cAMP activates protein kinases that phosphorylate (add a phosphate) to other
proteins
this triggers a cell response
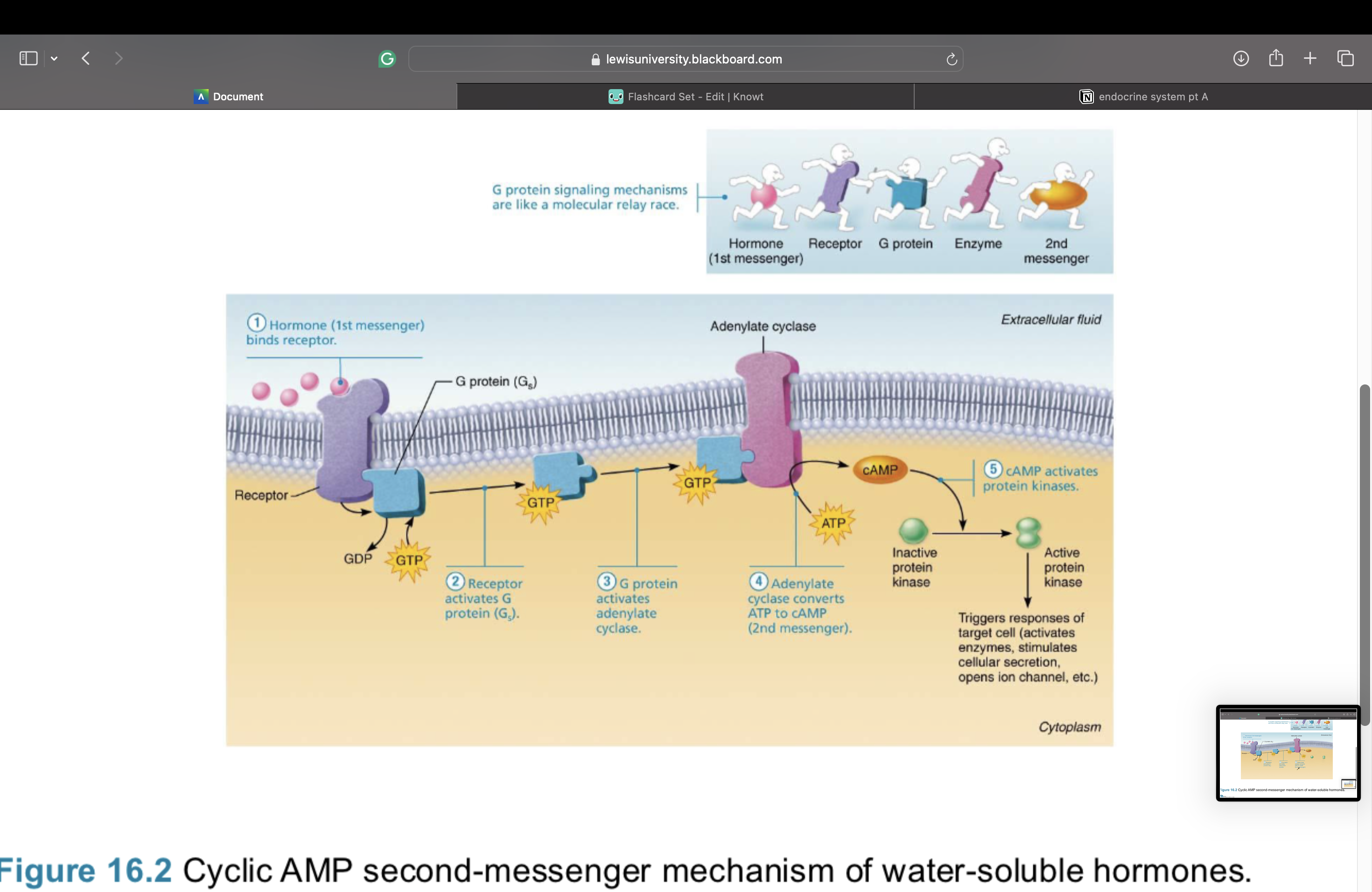
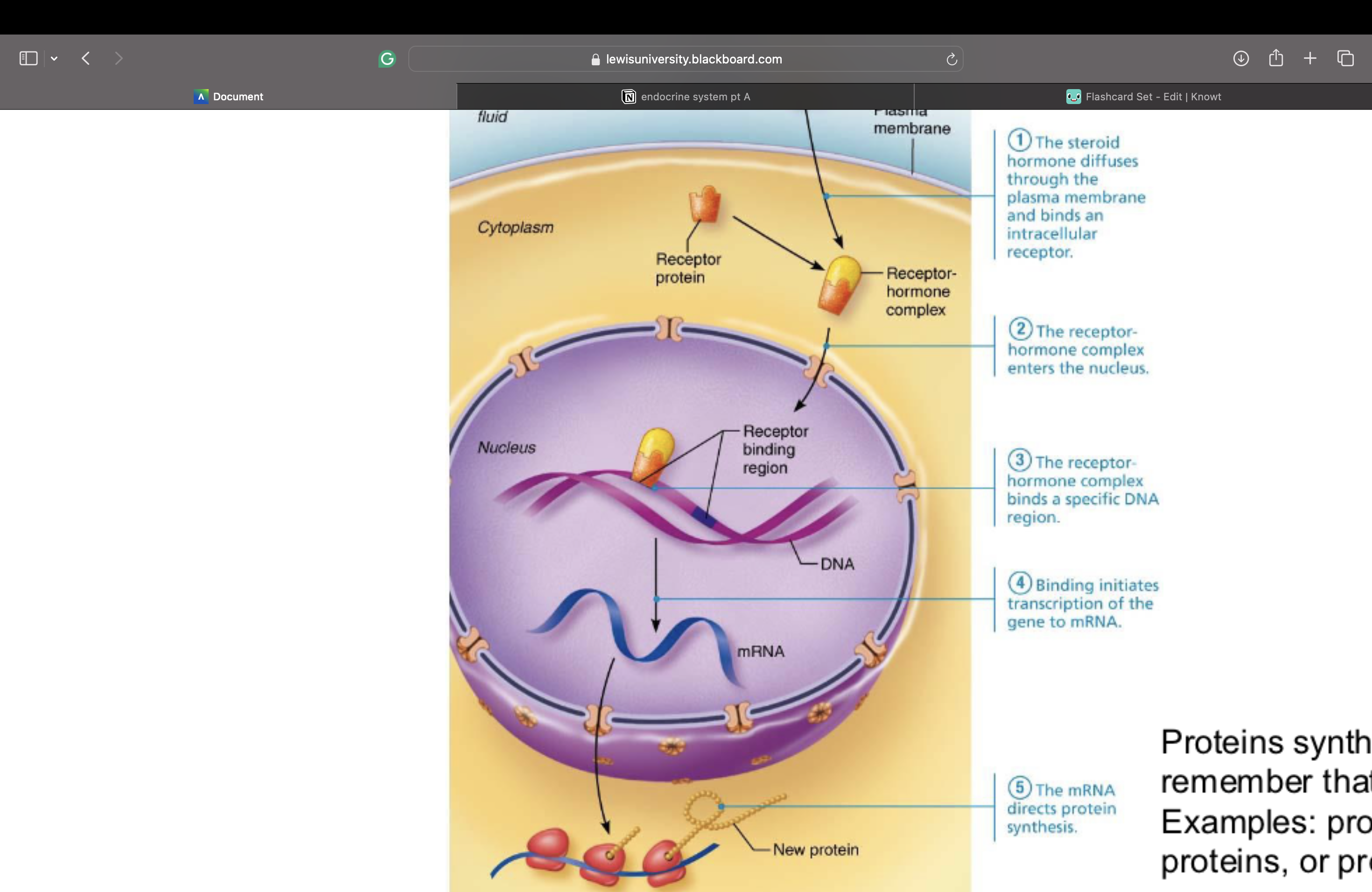
Intracellular Receptors and Direct Gene
Activation
1.Lipid-soluble steroid hormones and thyroid hormone diffuses thru plasma membrane and
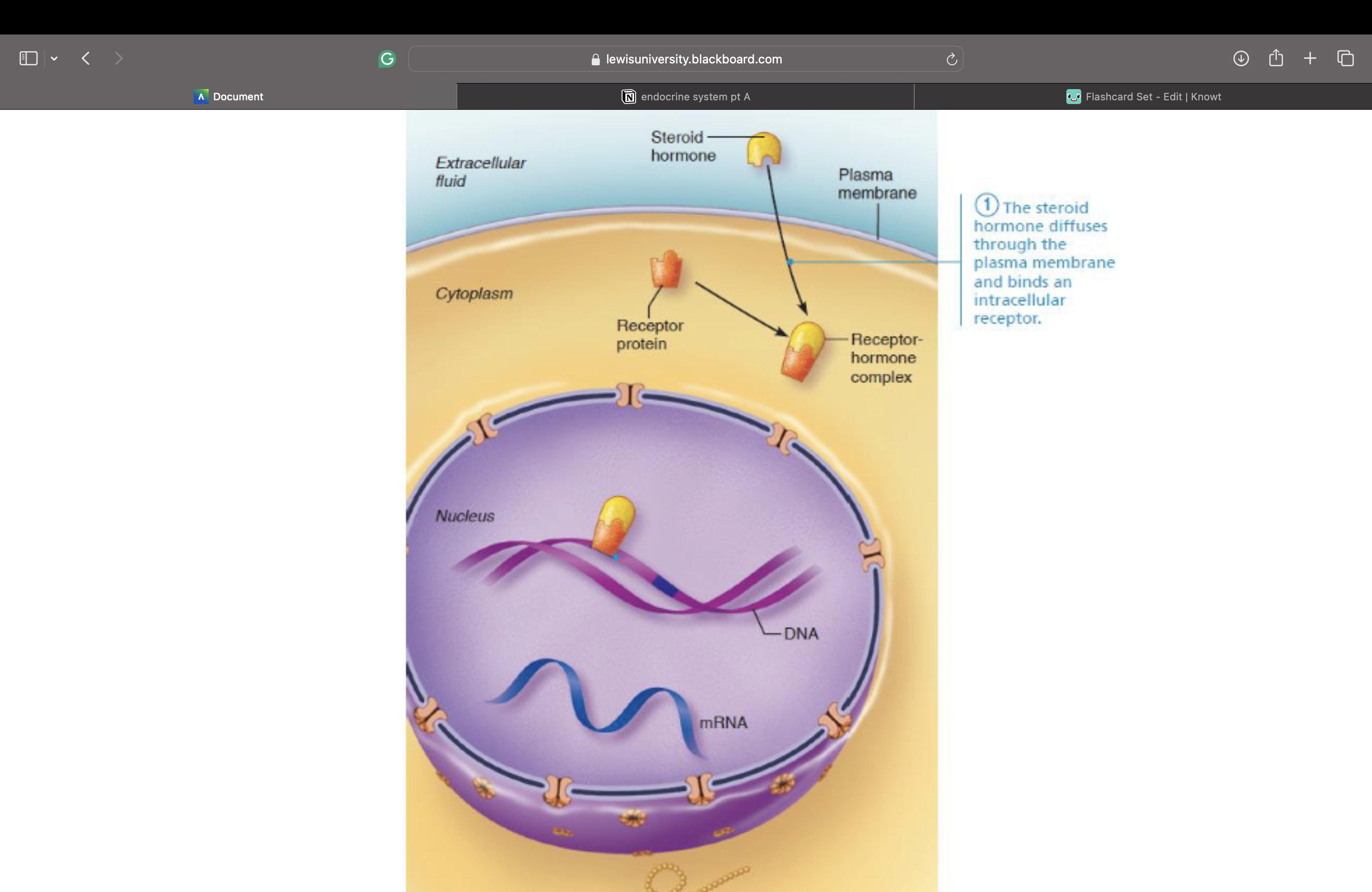
Intracellular Receptors and Direct Gene
Activation
3. Receptor-hormone complex enters nucleus and binds to specific region of DNA
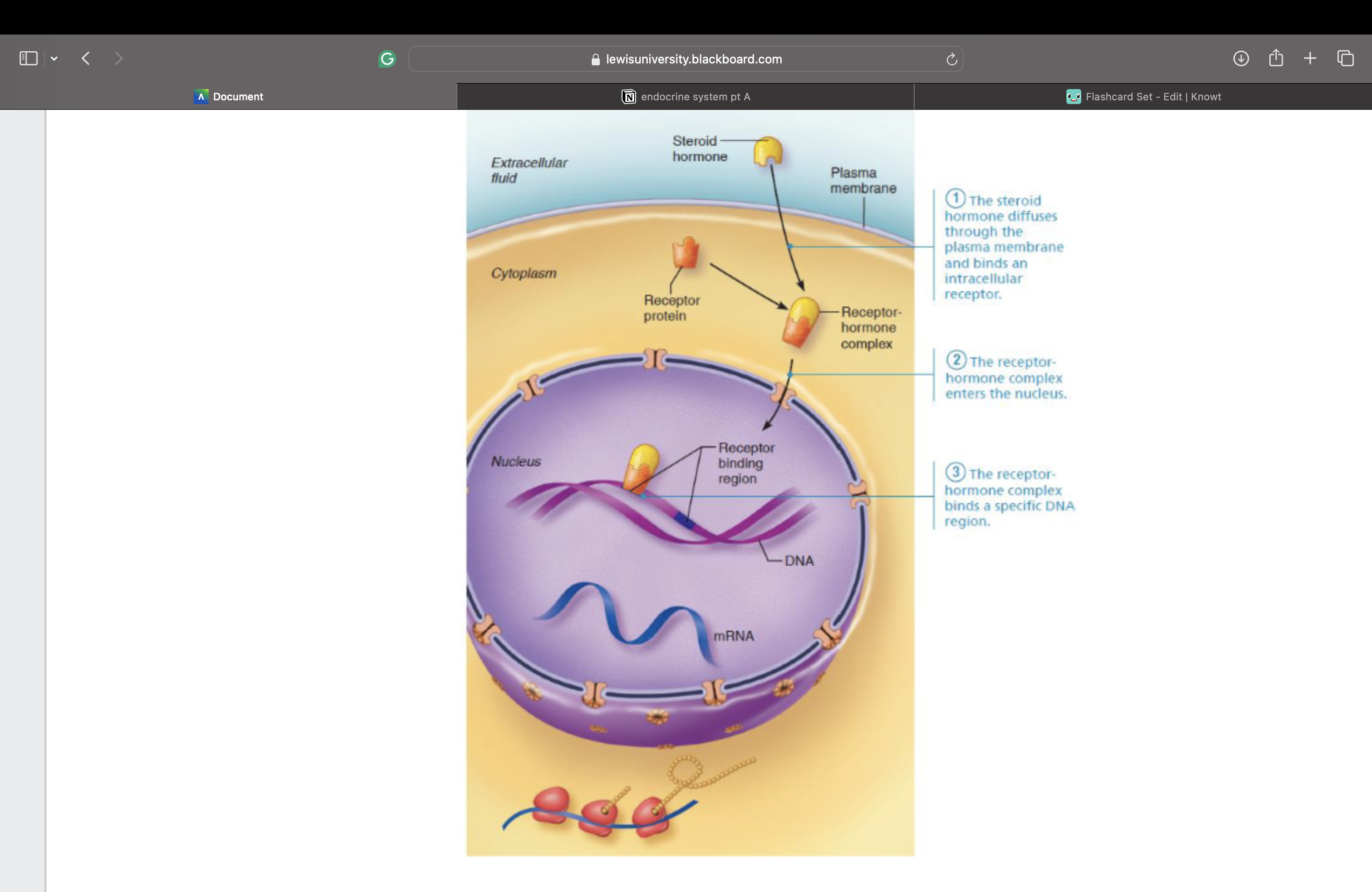
Intracellular Receptors and Direct Gene
Activation
Helps initiate DNA transcription to produce mRNA
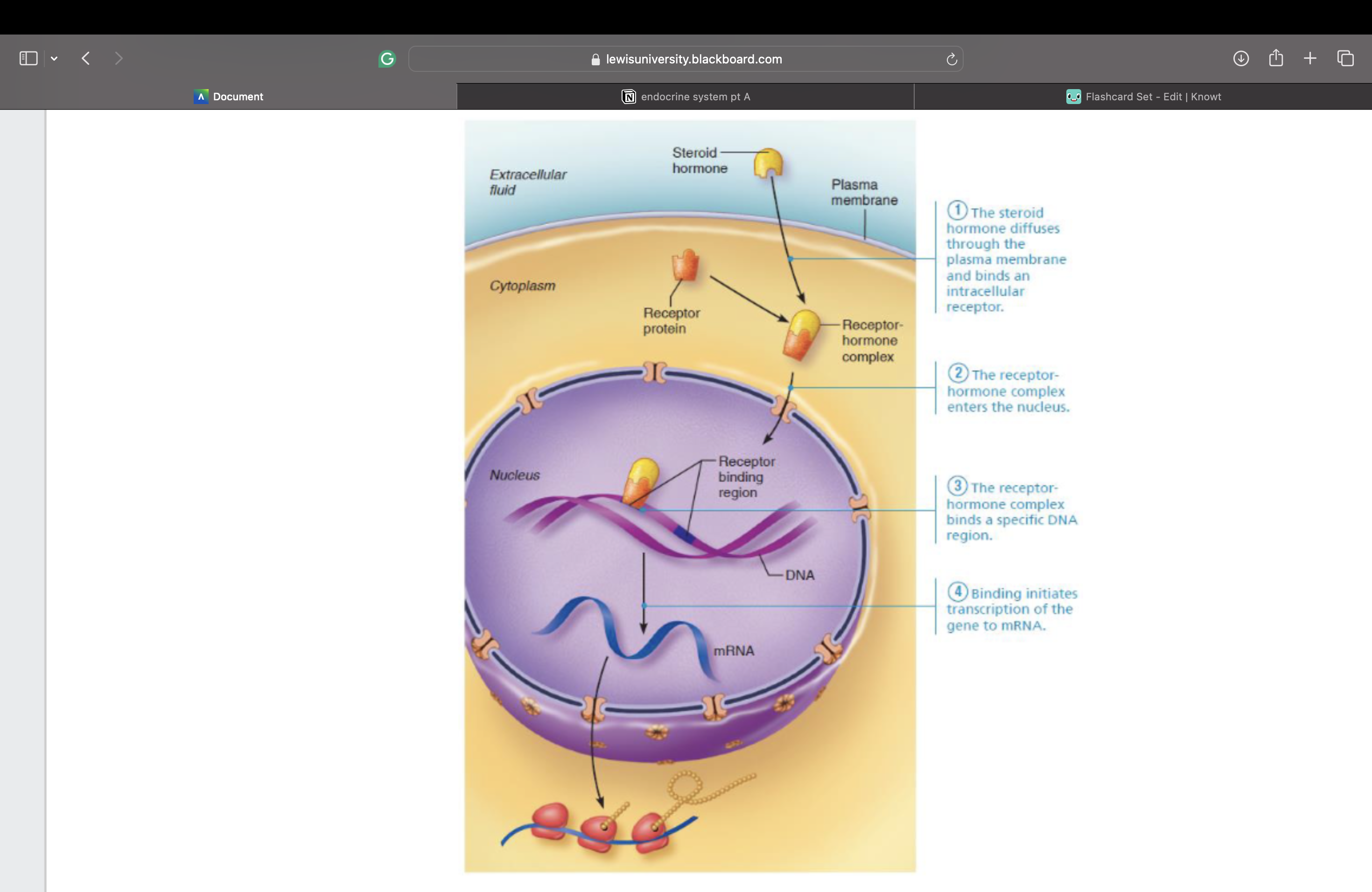
Intracellular Receptors and Direct Gene
Activation
mRNA is then translated into specific protein
– Proteins synthesized have various functions – remember that proteins include
enzymes
– Examples: promote metabolic activities, structural proteins, or proteins to be
exported from cell
blood levels of hormones, Controlled by negative feedback systems
— stimulus triggers hormone secretion
— when a hormones effect reaches a certain level, sensors detect this and reduce further secretion (often in the hypothalamus, pituitary, or target organ)
— As a result of negative feedback systems, blood levels of many hormones vary
only within a narrow range
▪ Too high → could damage tissues
▪ Too low → vital processes would slow or fail
Endocrine glands are stimulated to synthesize and release hormones in response to one
of three stimuli:
– Humoral stimuli
– Neural stimuli
– Hormonal stimuli
Humoral stimuli
Changing blood levels of ions and nutrients directly stimulate secretion of
hormones
example of humoral stimuli: calcium in blood
▪ Declining blood Ca2+ concentration stimulates parathyroid glands to secrete
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
▪ Parathyroid gland monitors the body's crucial blood calcium levels
▪ PTH causes Ca2+ concentrations to rise, and stimulus is removed
Neural stimuli
– Nerve fibers stimulate hormone release
▪ Sympathetic nervous system fibers stimulate adrenal medulla to secrete norepinephrine and epinephrine
▪ emergency hormones, preparing you for rapid action under stress
Humoral stimuli
Changing blood levels of ions and nutrients directly stimulate secretion of hormones
example of humoral stimuli
calcium in blood: Declining blood Ca2+ concentration stimulates parathyroid glands to secrete
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
▪ Parathyroid gland monitors the body's crucial blood calcium levels
▪ PTH causes Ca2+ concentrations to rise, and stimulus is removed
Endocrine glands are stimulated to synthesize and release hormones in response to one of three stimuli:
Hormonal stimuli
Hypothalamic hormones stimulate release of most
anterior pituitary hormones
Anterior pituitary hormones stimulate targets to secrete
still more hormones
Hypothalamic–pituitary
target endocrine organ feedback loop
-Hormones from final target organs inhibit release of anterior pituitary hormones
Hypothalamus is connected to
pituitary gland via stalk called infundibulum
Pituitary gland is seated in the
sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
pituitary gland secretes at least
8 major hormones
pituitary gland has 2 major lobes
posterior pituitary
anterior pituitary
posterior pituitary
composed of neural tissue that secretes neurohormones
anterior pituitary
consists of glandular tissue
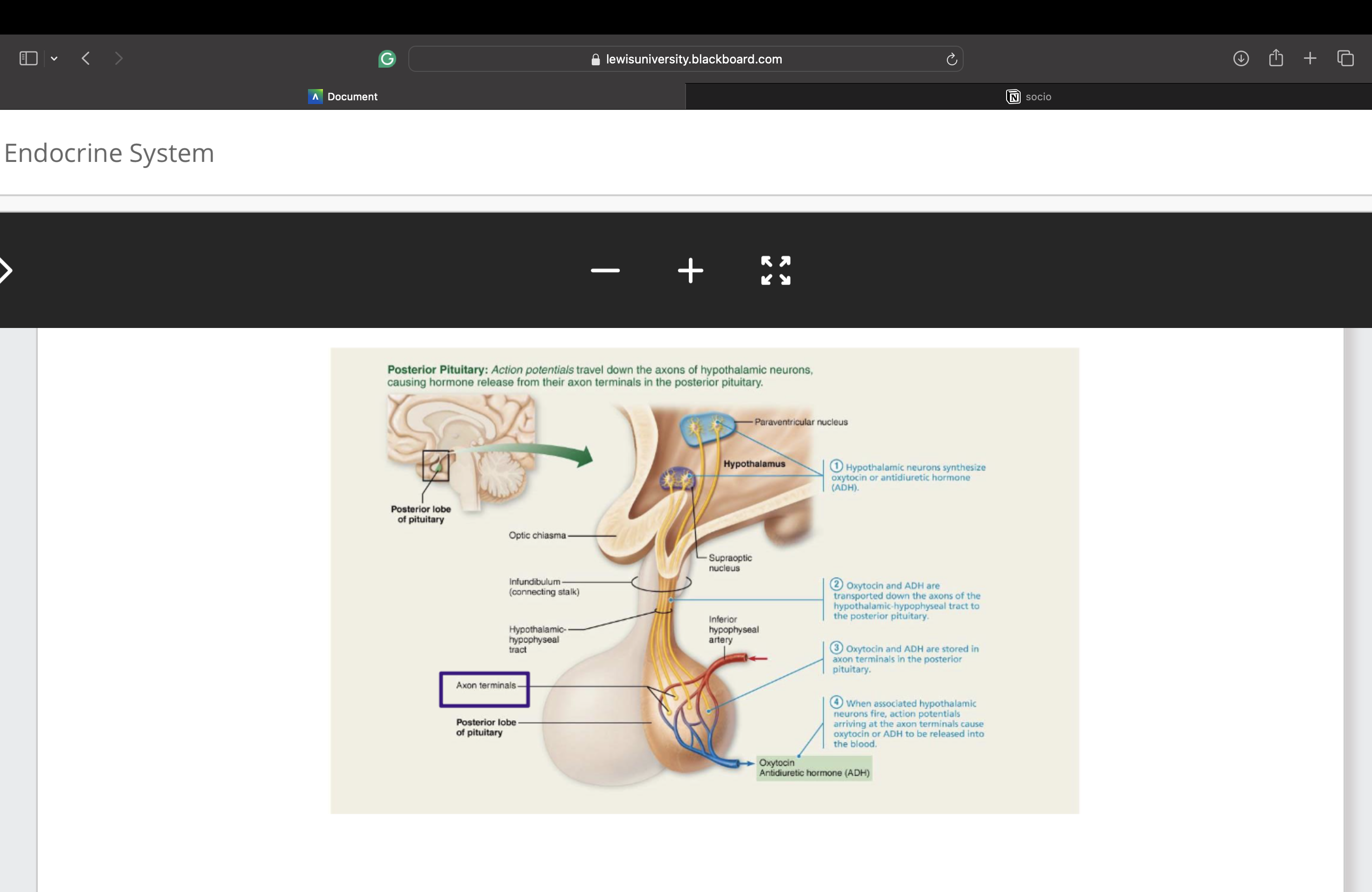
Posterior lobe is neural tissue derived from
a downgrowth of brain
posterior lobe Maintains neural connection to hypothalamus
hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract
hypothalamic-hypophyseal Tract arises from neurons in
paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in hypothalamus
Runs through infundibulum
posterior lobe Secretes two neurohormones
(oxytocin and ADH)
▪ Action potentials travel down the axons of hypothalamic neurons causing
hormone release from their axon terminals
▪ Are released into blood
steps of release of hormones from posterior pituitary glands
Anterior lobe is glandular tissue derived from an outpocketing of..
oral mucosa
The anterior pituitary is not connected to the _________ by neurons
Hypothalamus
The anterior pituitary is connected by a vascular system called the…
hypophyseal portal system(a special blood vessel network)
The hypothalamus releases regulatory hormones (releasing or inhibiting hormones)
into the HYPOPHYSEAL PORTAL SYSTEM. where do these hormones travel to?
directly to the anterior pituitary and control the secretion of pituitary hormones (like ACTH, TSH, GH, LH, FSH, prolactin).
Posterior Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones (OXYTOCIN)
Strong stimulant of uterine contractions released during childbirth
targets surrounding milk producing glands and they contract to force milk out during suckling
Synthetic oxytocin is used to
induce labor
milk is produced in response to
prolactin
Posterior Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones (Antidiuretic hormone (ADH))
prevents wide swings in water balance, helping to avoid dehydration and water overload
If concentration of solutes too high, posterior pituitary triggered to secrete ADH
Targets kidney tubules to reabsorb more water to inhibit or prevent urine formation
As solute levels fall, ends ADH release
antidiuretic is a substance that
inhibits or prevents urine formation
Hypothalamus contains osmoreceptors that monitor
solute concentrations of the blood.
he osmoreceptors transmit excitatory impulses to the hypothalamic
neurons which release ADH
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
6 hormones
Most activate target cells via cAMP second-messenger system
6 hormones in anterior pituitary glands
– Growth hormone (GH)
– Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
– Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
– Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
– Luteinizing hormone (LH)
– Prolactin (PRL)
Anterior pituitary hormones: GH Effects on Glucose During Growth
1. Stimulates Protein Synthesis (for growth)
2. Glucose Sparing
3. Promotes Fat Use as Fuel – adipose tissue
4. Supports Liver Glucose Output
1. Stimulates Protein Synthesis (for growth)
1. GH promotes amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
2. Protein building requires lots of energy → the body must spare glucose for growth and brain function.
2. Glucose Sparing
1. GH reduces glucose uptake by muscle and fat
2. This prevents peripheral tissues from “hogging” glucose, ensuring plenty remains in the blood for the brain.
3. Promotes Fat Use as Fuel – adipose tissue
1. GH increases lipolysis → fatty acids are released from fat stores.
2. Growing tissues (like muscle and bone) can use these fatty acids for energy, conserving glucose.
4. Supports Liver Glucose Output
1. GH(growth hormone) stimulates gluconeogenesis in the liver → more glucose enters the blood.
2. Keeps blood glucose stable during times of high demand (e.g., growth spurts).
growth hormone:GH Effects on Glucose During Growth
main idea
•Glucose is conserved and prioritized for the brain.
•Fat becomes the main fuel for muscles and other tissues.
•This ensures energy is available both for growth processes (protein synthesis, cell
(proliferation) and for vital brain function.
indirect actions on growth
GH (growth hormone)triggers liver, skeletal muscle, and bone to produce insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
IGFs stimulate actions required for growth
– uptake of nutrients from the blood used to synthesize DNA and
proteins needed for cell division
– Formation of collagen and laying down of new bone
– Stimulates the epiphyseal plate which leads to long bone growth
– Promotes protein synthesis and this increases muscle cell growth and
thus muscle mass
Anterior Pituitary Hormones– Regulation of secretion
-GH release or inhibition chiefly regulated by…
hypothalamic hormones
– Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH)
stimulates GH release
• Triggered by low blood GH or glucose, or high amino acid levels
Growth hormone–inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
iinhibits release
• Triggered by increase in GH and IGF levels
Anterior Pituitary Hormones : Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
– Stimulates normal secretory activity of thyroid
– Release triggered by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from hypothalamus
– Inhibited by rising blood levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) that act on both
pituitary and hypothalamus
Anterior Pituitary Hormones :Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids, mainly glucocorticoids
glucocorticoid: a stress hormone that increases blood sugar, suppresses
immunity, and helps the body adapt to stress.
– Regulation of ACTH release
▪ Triggered by hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
▪ Rising levels of glucocorticoids feed back and block secretion of CRH and
ACTH release