Antibiotics/Antimicrobials
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Natural vs. Synthetic vs. Semisynthetic
Natural/antibiotic -
A substance naturally produced by a microorganism that can inhibit the growth of or kill another microorganism
Synthetic
Manufactured entirely in a lab w/ no natural origins
1st synthetic drug → sulfa drugs
Semisynthetic -
Chemically modified derivatives of natural antibiotics
Targets
Ultimate goal - target pathogen while minimizing host damage
Target pathogen-specific pathways
Cell wall
Protein synthesis/ribosomes
Cell membrane
Metabolism
Nucleic acid synthesis
Attachment and recognition
Mechanisms of Action
Interferes w/ Cell Wall Synthesis
Penicillin (β-lactams) work to prevent crosslinking of peptidoglycan in cell walls, weakening it and causing lysis
Interferes w/ Metabolism
Target unique pathways like folic acid synthesis
Inhibits Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Rifampicin → inhibits RNA synthesis in gram - and + bacteria
Binds to bacterial RNA polymerase and inhibits transcription
Gyrase & Topoisomerase IV only in prokaryotic cells
Damaging Cell Membrane
Interferes w/ fatty acid synthesis, distinct in prokaryotes
Inhibit protein + cell wall synthesis
Bactericidal vs. Bacteriostatic
Bactericidal:
Antimicrobial drugs that actively kill bacteria
Targets bacterial cell membranes and nucleic acid
Bacteriostatic:
Their mechanism of action stalls bacterial metabolism and growth without directly causing bacterial death
Targets bacterial protein synthesis + metabolic pathways
Gives the immune system time to clear the infection
Broad Spectrum vs. Narrow Spectrum
Broad Spectrum: A wide range of organisms affected
Gram + and gram - organisms
Narrow Spectrum: Few/specific organisms targeted
Gram + or mycobacterium only
How do Anti-fungals Work?
Affect the sterols in the plasma membrane of fungi
The principal target is ergosterol - an essential component of fungal cell membranes that determines the fluidity, permeability, and activity of membrane-associated proteins
Affect fungal cell wall
Unique
Echinocandins → inhibit the synthesis of glucan for cell wall
Affect nucleic acid synthesis
Flucytosine - Only in fungi, converted to 5-fluorouracil that interferes w/ RNA synthesis
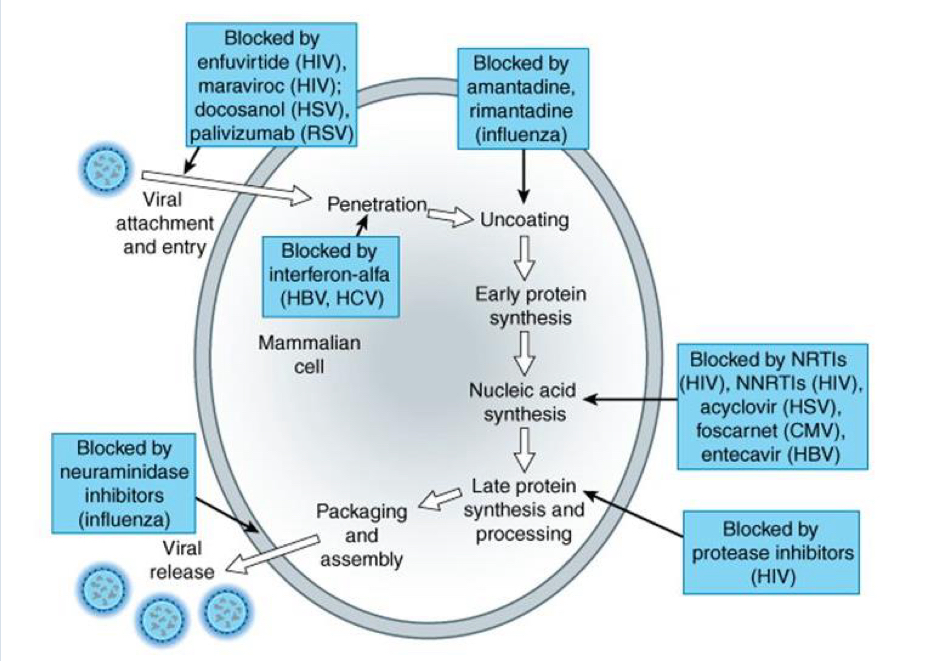
How do Antivirals Work?
Blocks entrance into host cells
Interferes w/ reproduction
Prevents virus protein synthesis
Stops the virus from assembling viral pieces and from leaving the infected cell
Drug Resistance
How does it develop?
Misuse
Overuse
Feeding animals antibiotics for growth
Antibiotics still prescribed for viral infections
Ineffective
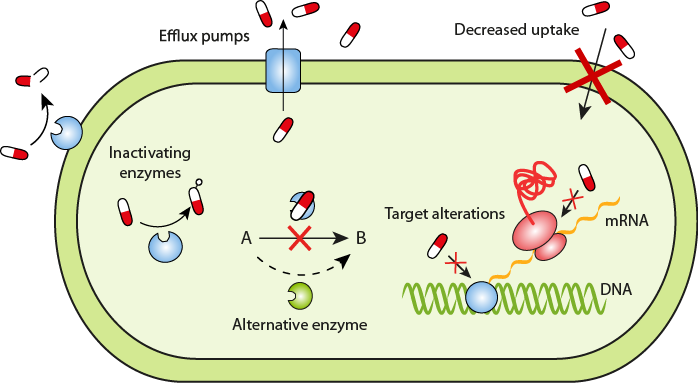
Bacterial Mechanisms:
Inactivating/destroying the drug
B-lactamases - enzymes that digest penicillin
Prevention of drug entry
Modify membrane proteins to stop antibiotics from entering
Efflux pump
Metabolic adaptation
Increases concentration of target protein to overcome drug effect
Target modification
Change target, like 50s subunit, so its no longer susceptible
How do we avoid drug resistance?
Maintenance of high-concentration
Proper time frame
Limitation of distribution
Avoid indiscriminate use and in everyday items (soap)
Use of multiple antimicrobials to inhibit growth without exception

Penicillin
Interferes with cell wall synthesis
Prevents crosslinking of peptidoglycan in cell wall, weakening it and causing lysis
Belongs to a group of 50 related antibiotics called β-lactams
Natural penicillin
Semi-synthetic penicillin
Narrow spectrum
Cephalosporin
Interferes w/ cell wall synthesis
Naturally occurring → fungi of the genus Acremonium
Bactericidal
Same mode of action as B-lactam but less susceptible to B-lactamases

Chloramphenicol
Protein synthesis inhibitor
Targets 50s subunit + inhibits the formation of peptide bonds
Synthetic, but originally isolated from Streptomyces
Bacteriostatic
Broad spectrum
Clindamycin
Protein synthesis inhibitor
Similar mode of action to Chloramphenicol
Broad spectrum
Useful in infections caused by MRSA, most strains of MRSA are still susceptible to Clindamycin
Rare cases: causes liver damage
Tetracycline
Protein synthesis inhibitor
Binds to the 30s subunit and interferes w/ tRNA attachment
Broad spectrum
Small amounts can enter mammalian cells - used for bacteria liked Rickettsia & Chlamydia
Erythromycin
Protein synthesis inhibitor
Binds to 50s and blocks mRNA movement
Bacteriostatic
Similar spectrum to penicillin G
A macrolide, contains a macrocyclic lactone ring

Rifampicin
Inhibits Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Inhibits RNA synthesis by binding to the bacterial RNA polymerase and inhibits transcription
Broad spectrum