Cells, Division, and Specialization in Biology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Cell Theory
All living things consist of one or more cells.
Cytoplasm
The substance within a cell, excluding the nucleus.
Cell Structure
Design of cells for specific functions.
Cell Division
Process by which cells reproduce and create new cells.
Robert Hooke
Discovered cells in 1655 using a microscope.
Trillion Cells
Adult males have 36 trillion cells; females 28 trillion.
Cell Wall
Rigid outer covering found in plant cells.
Chloroplasts
Organelles in plant cells for photosynthesis.
Vacuole
Storage organelle in plant cells for materials.
Lysosomes
Organelles for waste disposal, absent in plant cells.
Membrane
Bilayer of phospholipids protecting organelles.
Nucleus
Control center directing cell activities.
Chromosomes
Structures containing DNA for genetic information.
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane separating nucleus from cytoplasm.
Nucleoplasm
Chemical mixture storing information for organelles.
Ribosomes
Organelles producing proteins via protein synthesis.
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance where organelles are suspended.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Folded membranes transporting materials within the cell.
Rough ER
ER with ribosomes, synthesizing proteins.
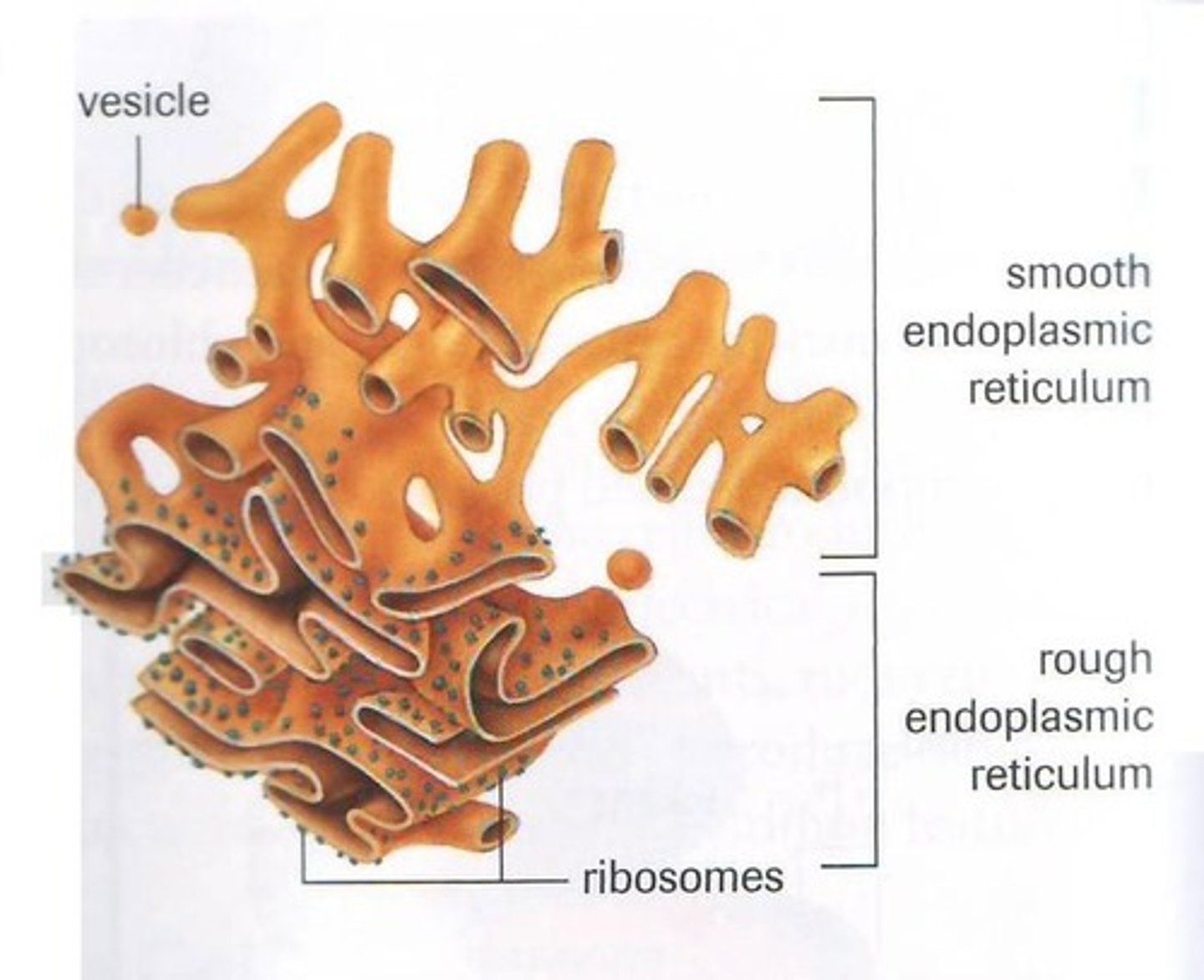
Smooth ER
ER without ribosomes, synthesizing lipids.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound structures transporting materials in cells.
Golgi Apparatus
Organelle packaging proteins and fats from ER.
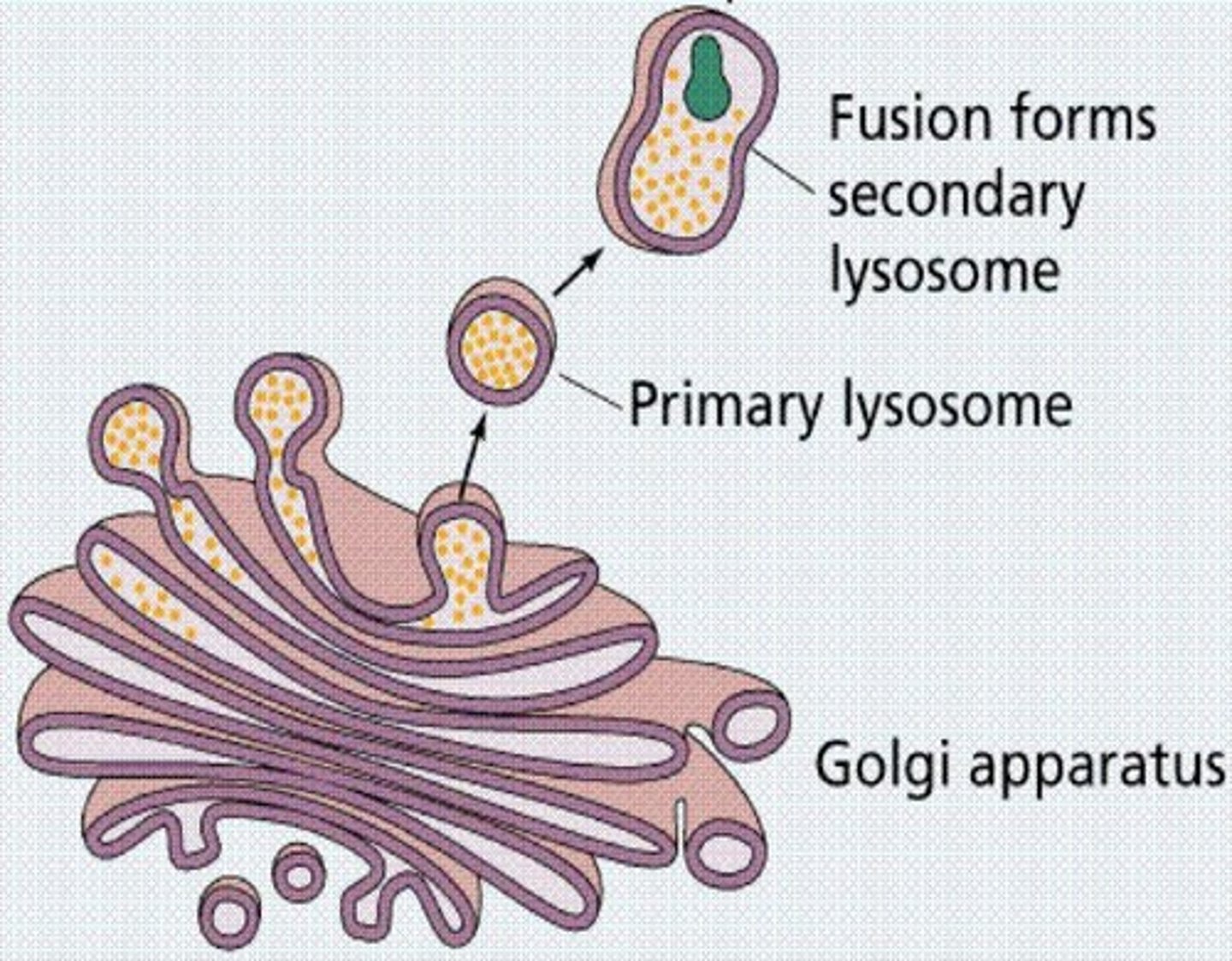
Lysosomes
Vesicles digesting food and destroying microorganisms.
Apoptosis
Process of programmed cell death.
Mitochondria
Organelle generating energy through cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
Process converting glucose into energy.
Chloroplasts
Organelles conducting photosynthesis in plant cells.
Photosynthesis
Process converting CO2 and water into glucose.
Thylakoids
Membrane compartments in chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
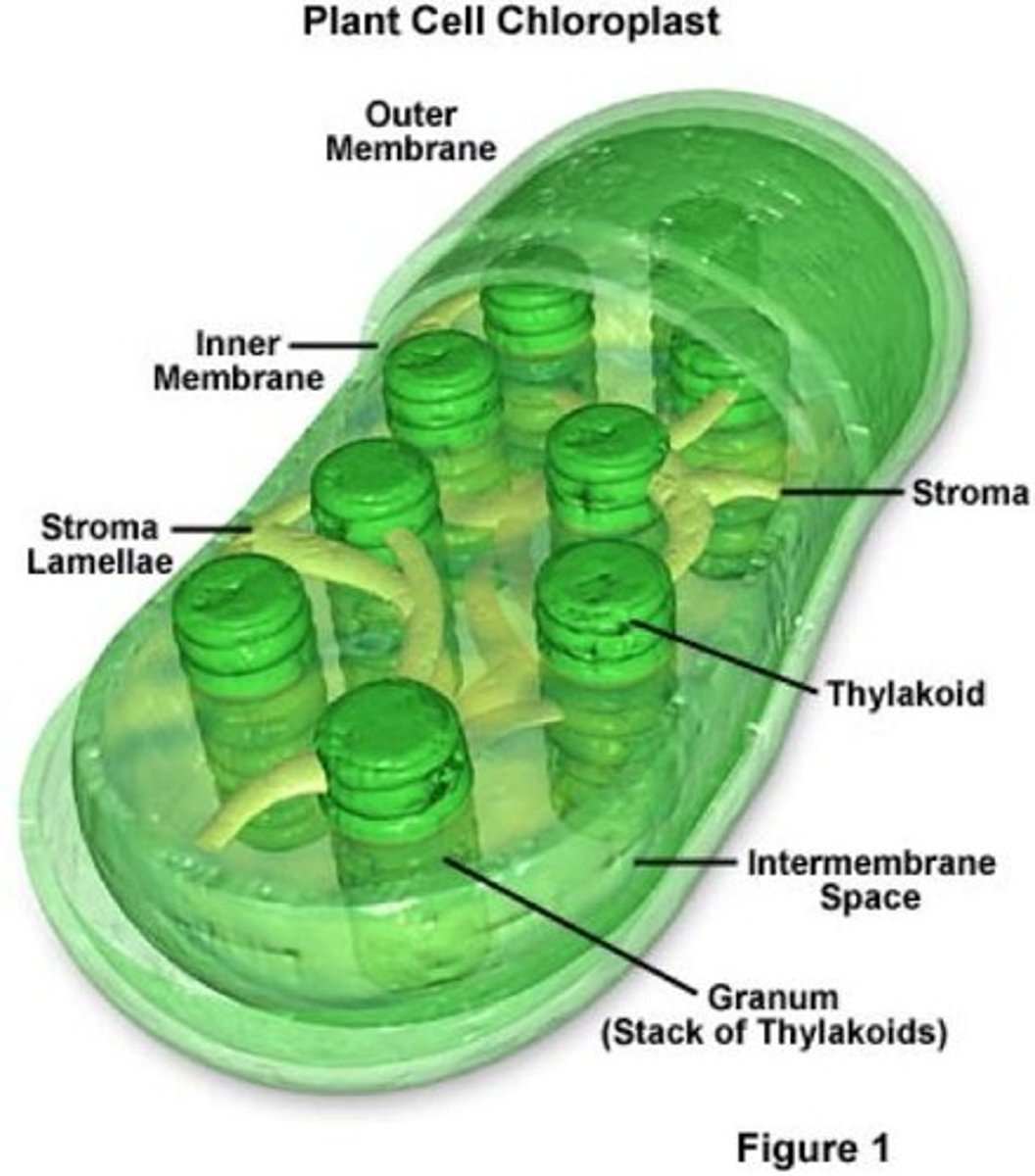
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in thylakoids, essential for photosynthesis.
Vacuoles
Large sacs maintaining turgor pressure in cells.
Cell Wall
Rigid structure providing support in plant cells.
Turgor Pressure
Pressure keeping plant cells firm and healthy.
Cell Division
Process for reproduction, growth, and repair.
Asexual Reproduction
Division involving one parent, producing identical offspring.
Sexual Reproduction
Involves two parents, offspring inherits traits from both.
Gametes
Sex cells containing half the DNA of body cells.
Passive Transport
Movement of substances across membranes without energy.
Simple Diffusion
Particles move from high to low concentration.
Equilibrium
State where particle concentration is equal on both sides.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Concentration remains constant, but particles still move.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration between two areas.
Rate of Diffusion
Speed of diffusion affected by temperature and solute concentration.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Double layer of phospholipids forming cell membranes.
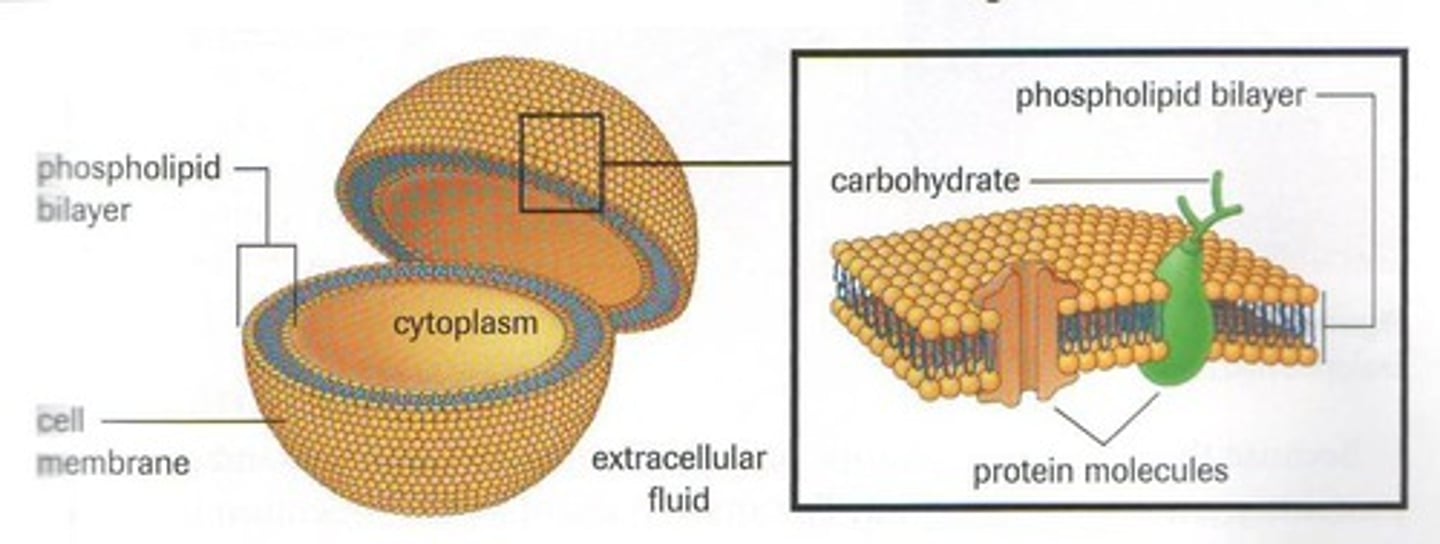
Channel Proteins
Proteins that facilitate movement across the cell membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion assisted by proteins for larger molecules.
Transmembrane Proteins
Proteins spanning the membrane, aiding substance transport.
Solute
Substance dissolved in a solvent, forming a solution.
Solvent
Liquid medium in which solutes are dissolved.
Selectively Permeable Membrane
Allows certain substances to pass, blocking others.
Chemical Reactions
Processes transforming substances in the cell.
Energy Source
Essential for cellular processes and growth.
Nutrients
Substances needed for cell growth and function.
Water
Vital solvent for chemical reactions in cells.
Gases
Essential for cellular respiration and metabolic processes.
Concentration of Solute Molecules
Higher concentration leads to faster dynamic equilibrium.
Facilitated Diffusion
Assisted transport through membrane by carrier proteins.
Simple Diffusion
Direct passage through phospholipid bilayer or channels.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes plasma membrane structure and function.
Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded in or spanning the membrane.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins located on the membrane surface.
Plasma Membrane Functions
Cell signaling, selective transport, waste excretion, support.
Osmosis
Net water movement across a selectively permeable membrane.
Hypotonic Solution
Solute concentration lower than water concentration.
Hypertonic Solution
Solute concentration higher than water concentration.
Isotonic Solution
Solute concentration equal to water concentration.
Active Transport
Movement of molecules against concentration gradient using ATP.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentration across a membrane.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Active transport mechanism for nerve and muscle cells.
Endocytosis
Bulk transport of materials into the cell.
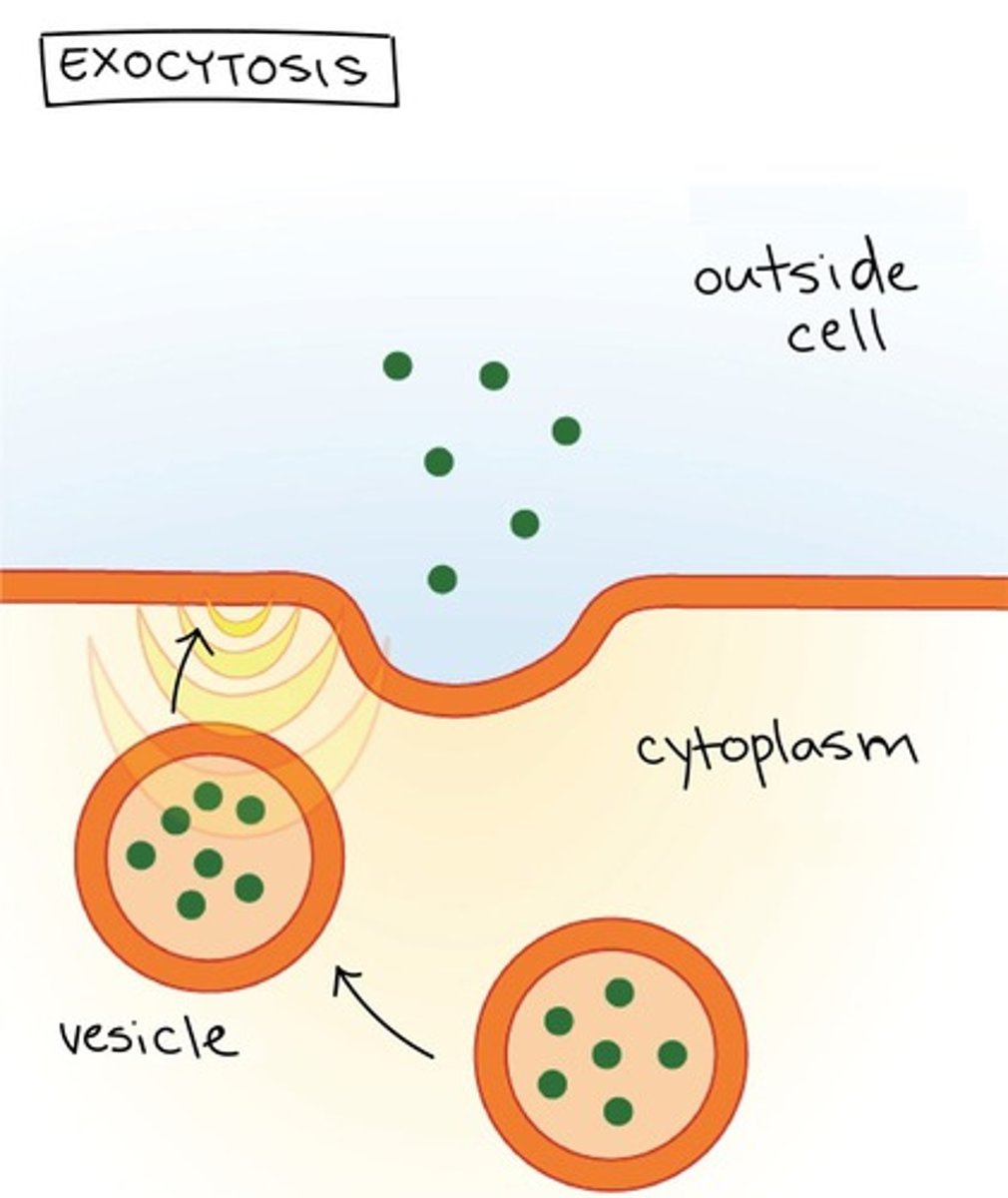
Exocytosis
Bulk transport of materials out of the cell.
Phagocytosis
Bulk transport of solids into the cell.
Pinocytosis
Bulk transport of liquids into the cell.
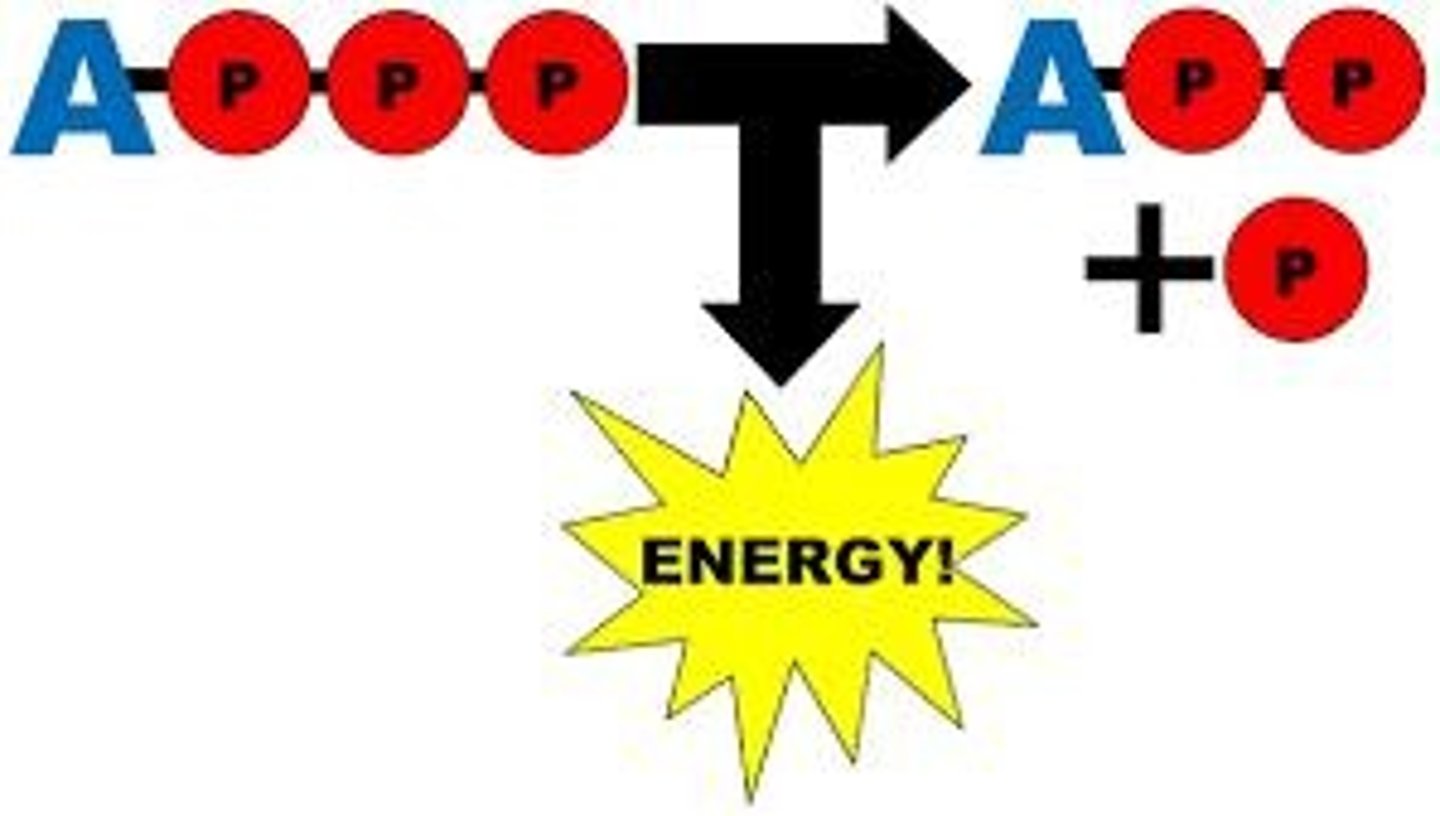
ATP
Energy currency used for active transport processes.
Carrier Proteins
Proteins that assist in transporting substances across membranes.
Selective Transport
Regulated movement of substances across the membrane.
Chemical Energy
Energy released from ATP for transport processes.
Cell Signaling
Communication between cells via membrane proteins.
Excretion of Wastes
Removal of cellular waste products through the membrane.
Exocytosis
Process of moving materials out of cells.
Secretory Vesicle
Membrane sac for transporting hormones or enzymes.
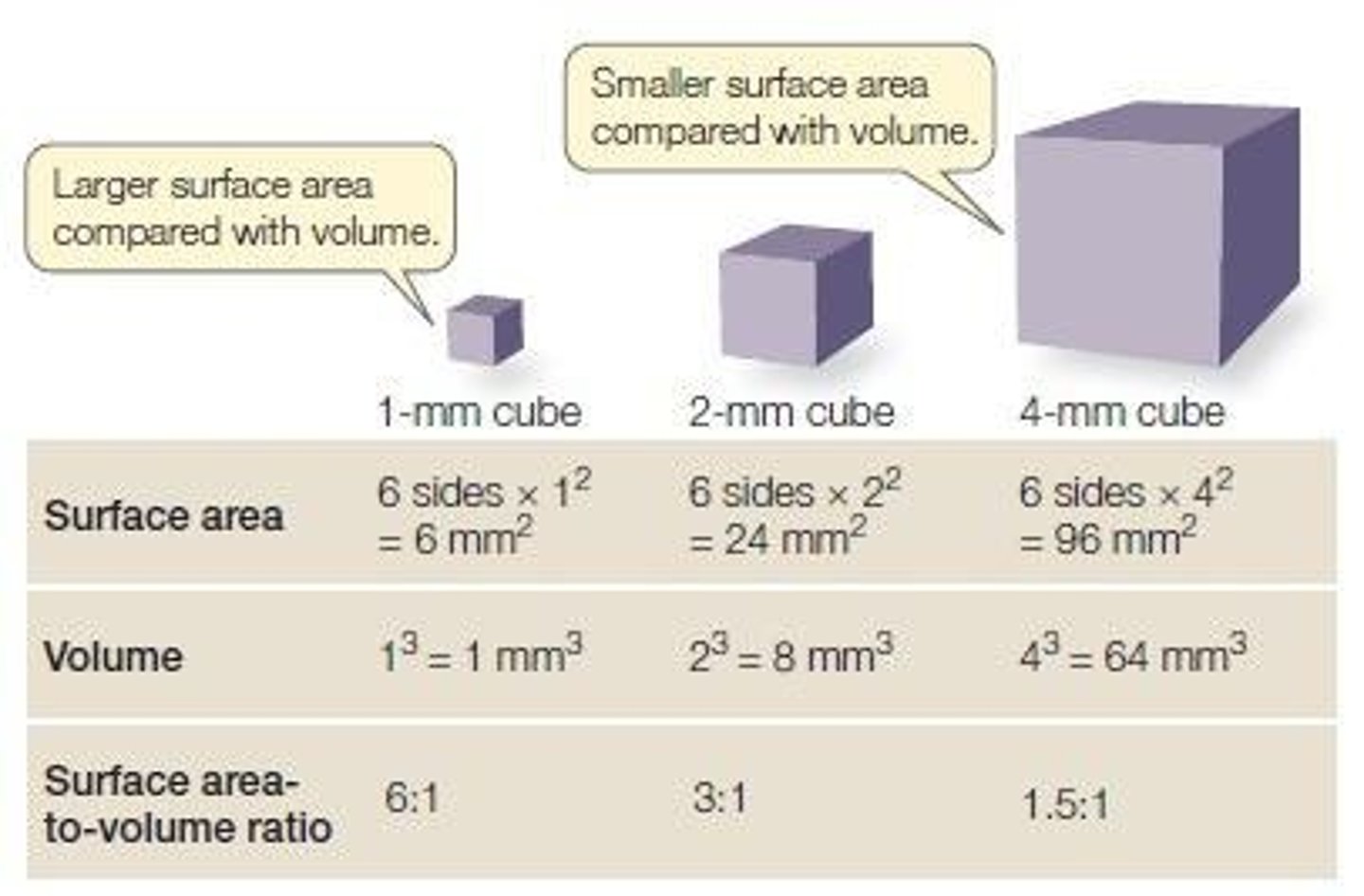
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Decreases as cell size increases, limiting growth.
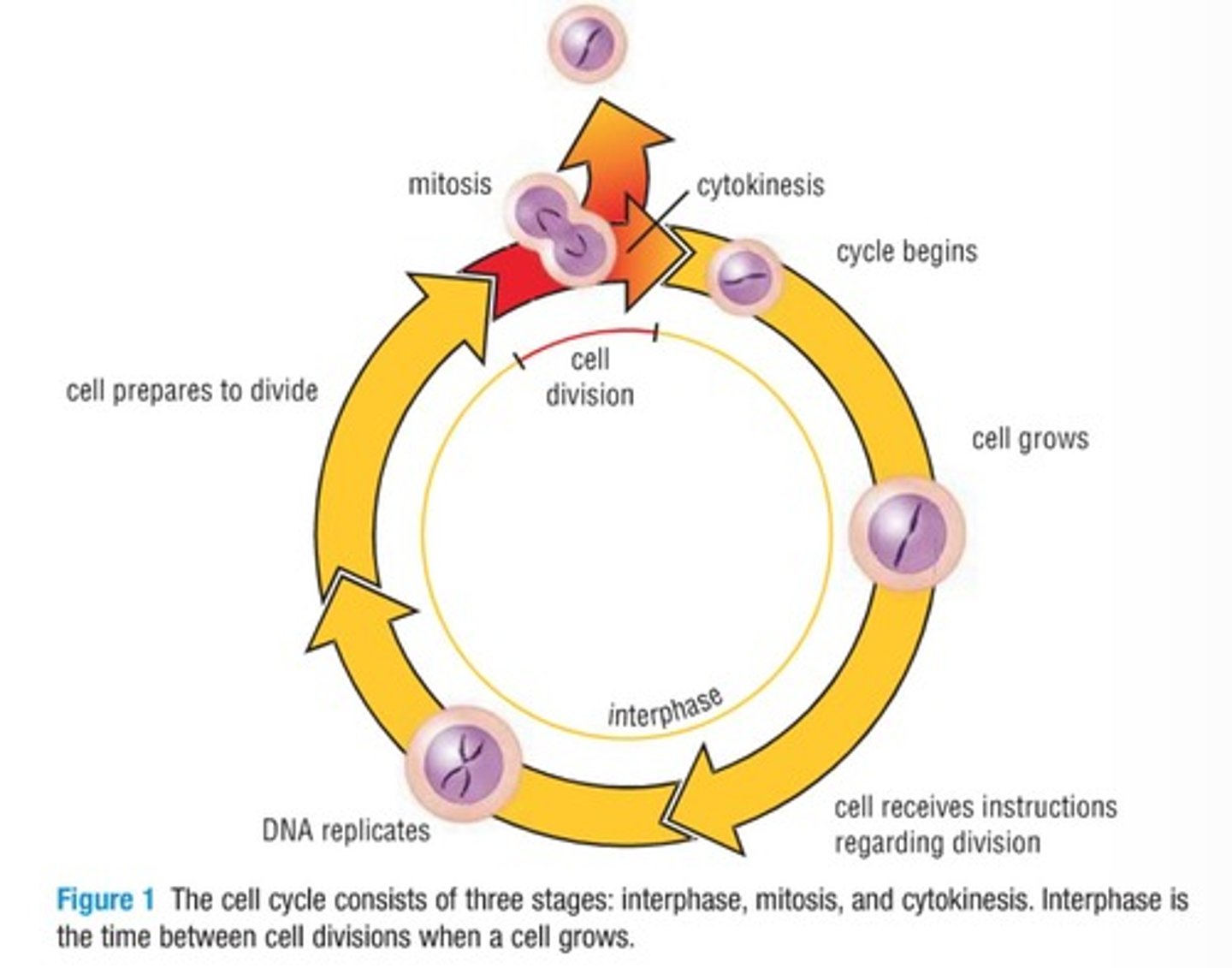
Cell Division
Process for growth, repair, and reproduction.
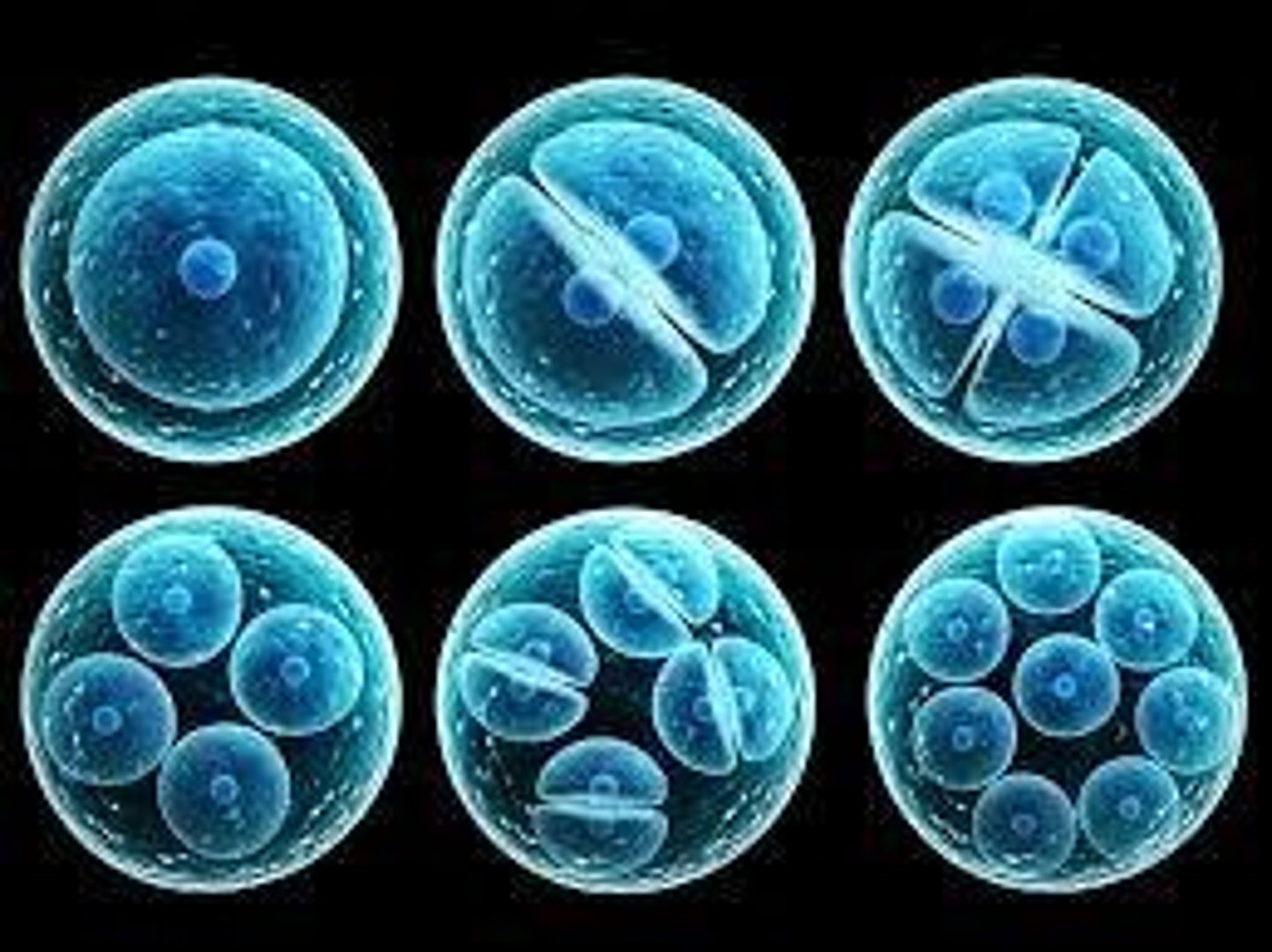
Mitosis
Division ensuring identical daughter cells with DNA.
Interphase
Phase where the cell performs life activities.
Cell Growth Limitations
Cells must stop growing if surface area insufficient.
Cellular Respiration
Process of converting nutrients into energy.
Chromatin Replication
Copying DNA before mitosis begins.
Red Blood Cell Lifespan
Average lifespan is 120 days.
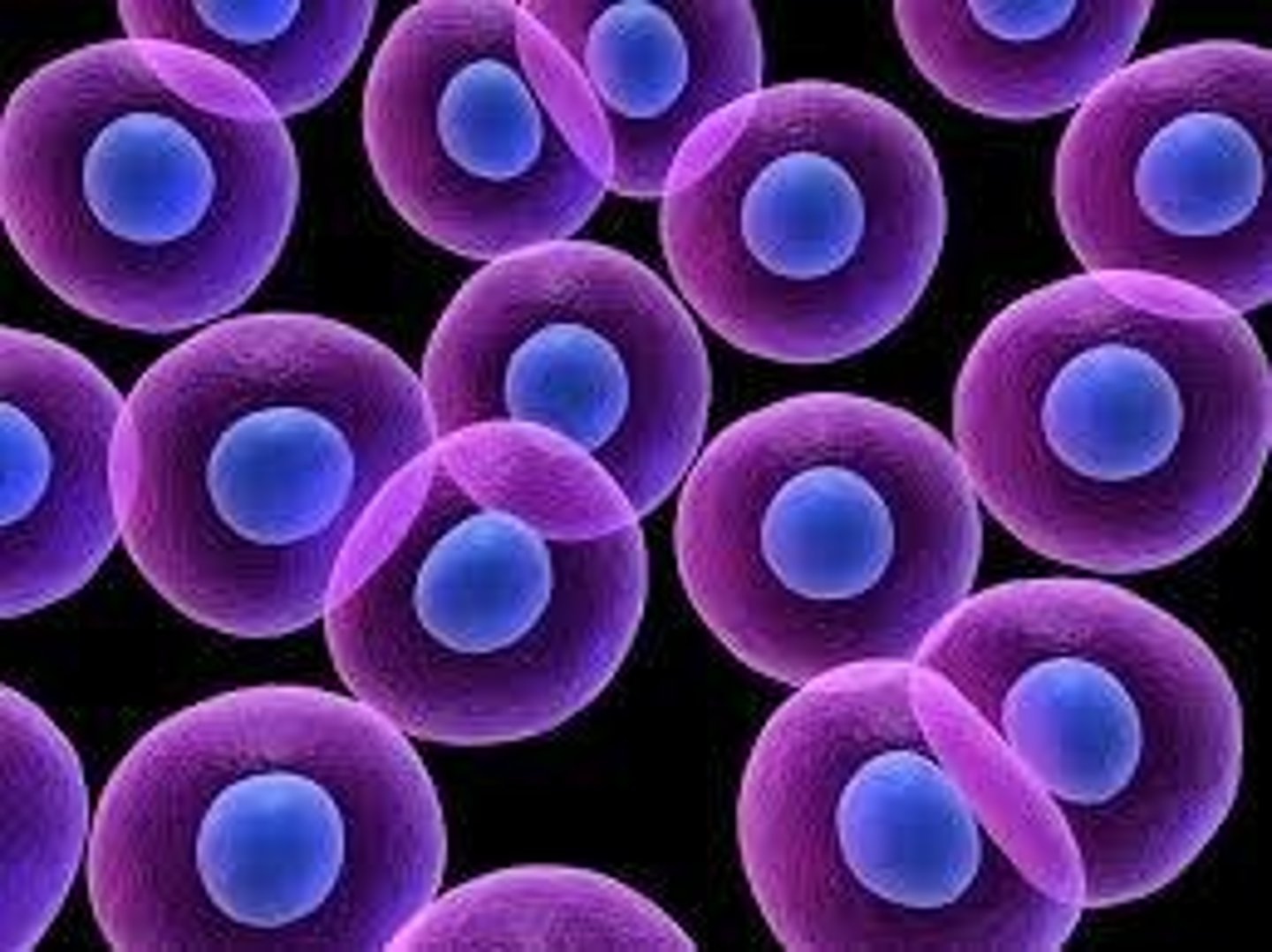
Cell Replacement
New cells replace dead or damaged ones.
Cell Size
Cells are microscopic, requiring a microscope to view.
Cellular Interaction
Cells must interact with their environment to survive.
Volume Increase
Cell volume grows faster than surface area.
Daughter Cells
Resulting cells from mitosis, identical to parent.
Growth Importance
Cell division is crucial for organism growth.
Healing Process
Cell division aids in tissue repair.
Fertilized Egg
Single cell that divides to form an organism.
DNA in Nucleus
Humans have over 6 feet of DNA.
Cellular Functions
Activities performed by cells during interphase.
Microscope Requirement
Cells are too small to be seen unaided.