UCF General Microbiology: Lab Practical
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
is in a broth
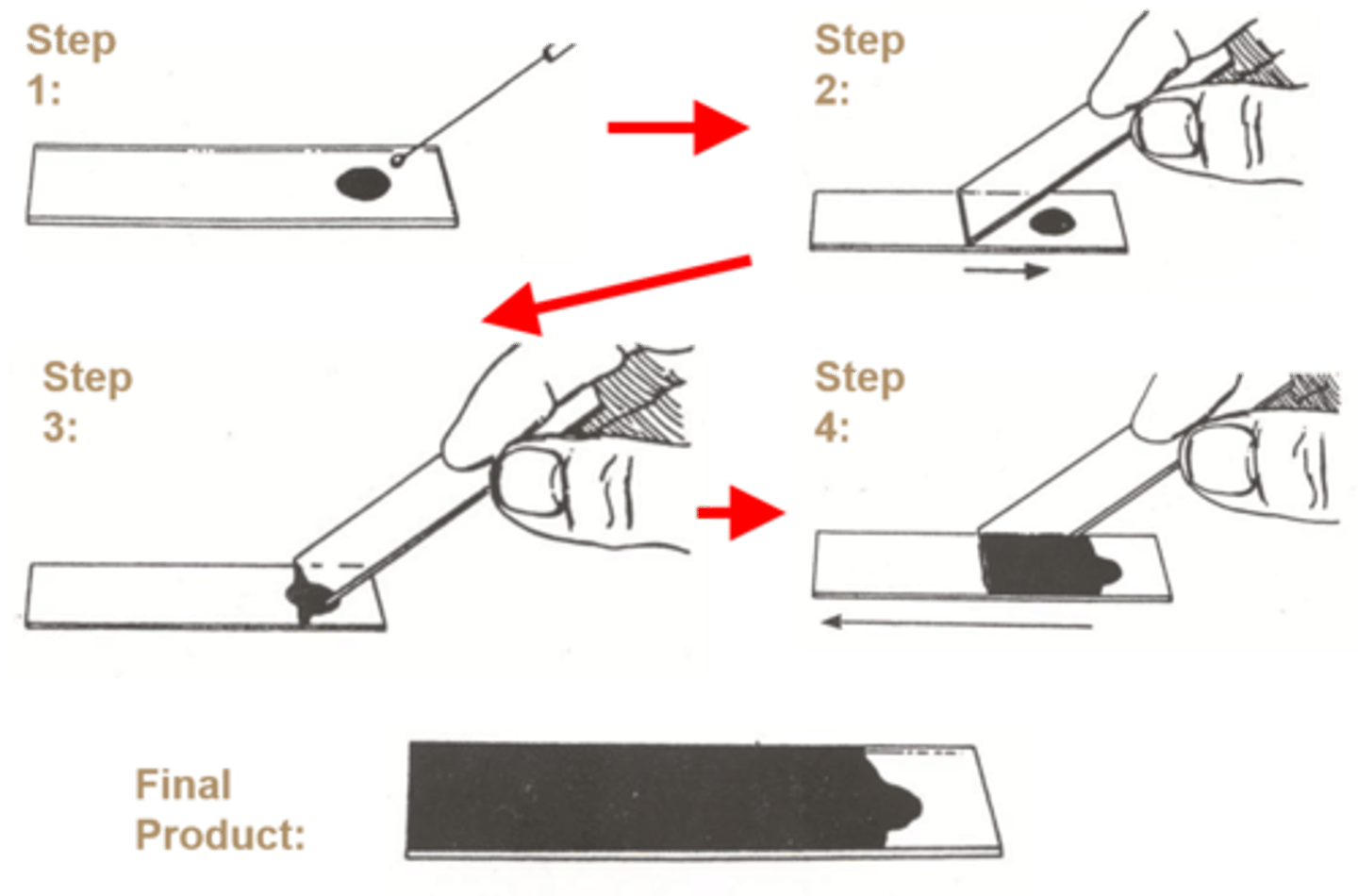
This technique is used in a culture that
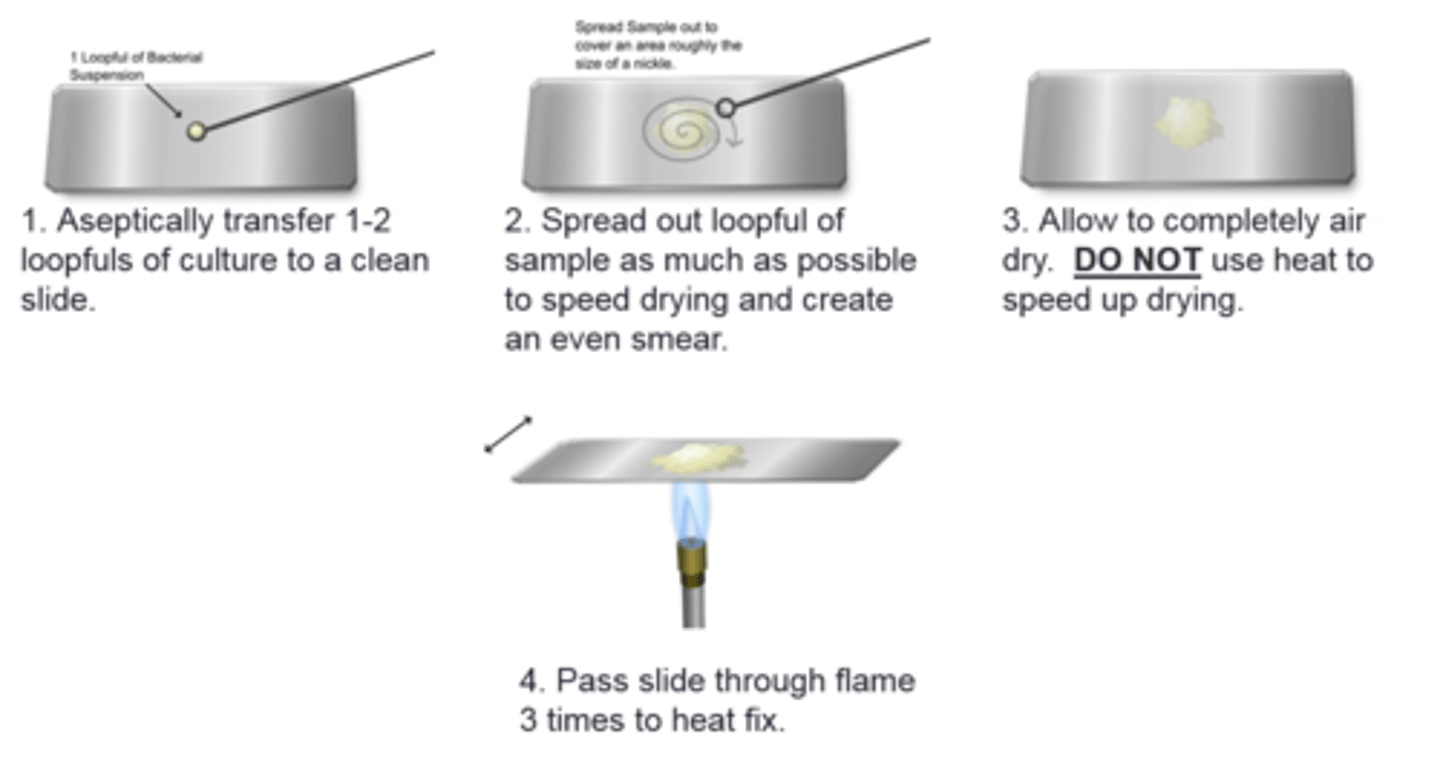
air drying
This is an example of
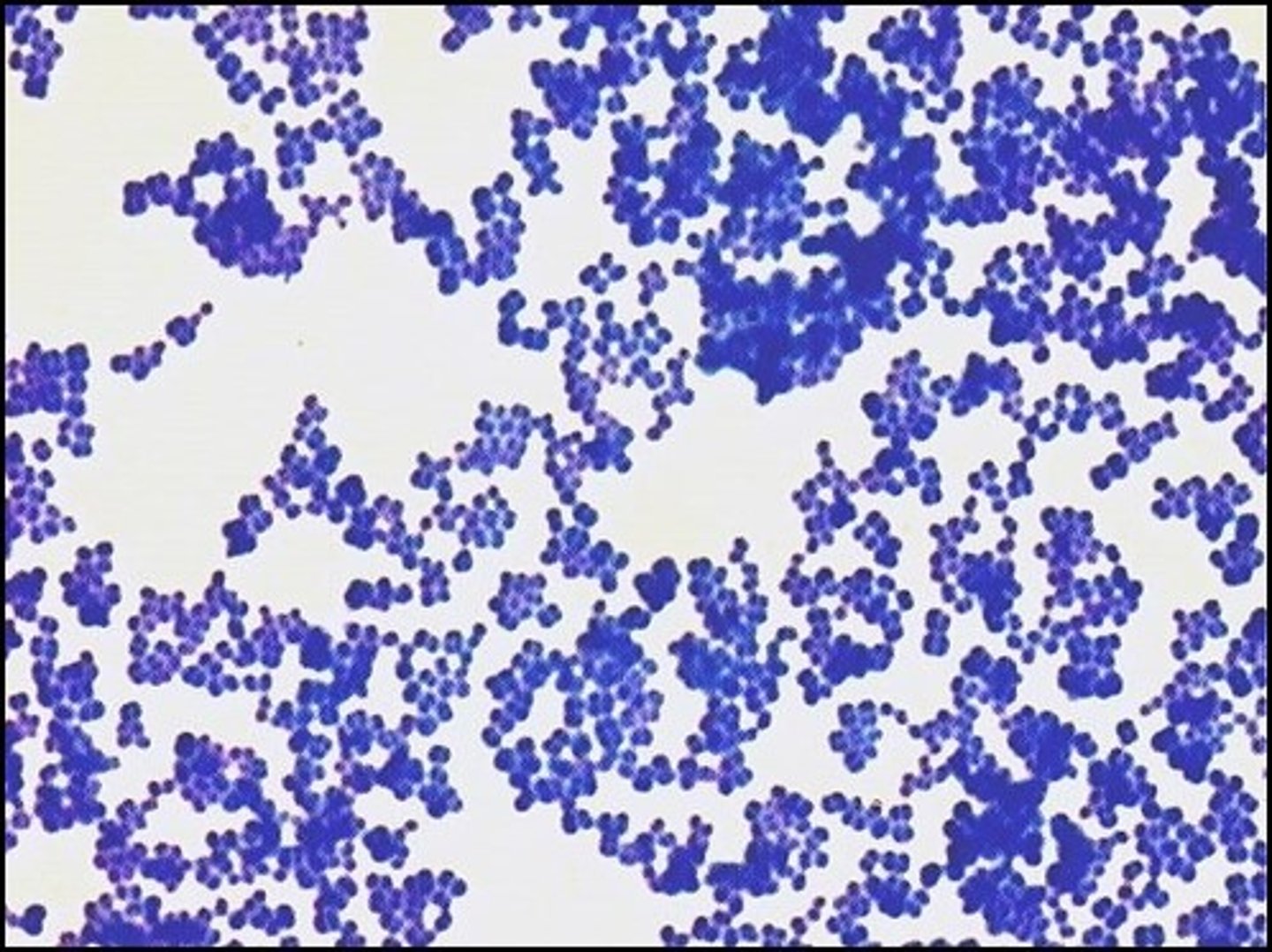
simple stain
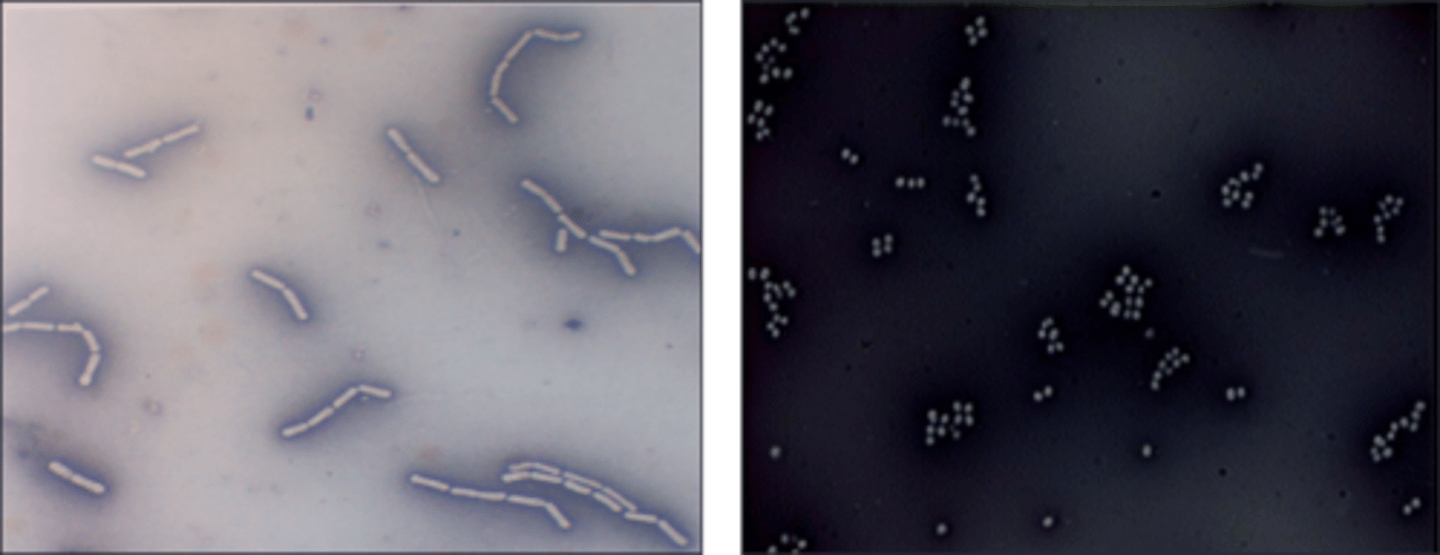
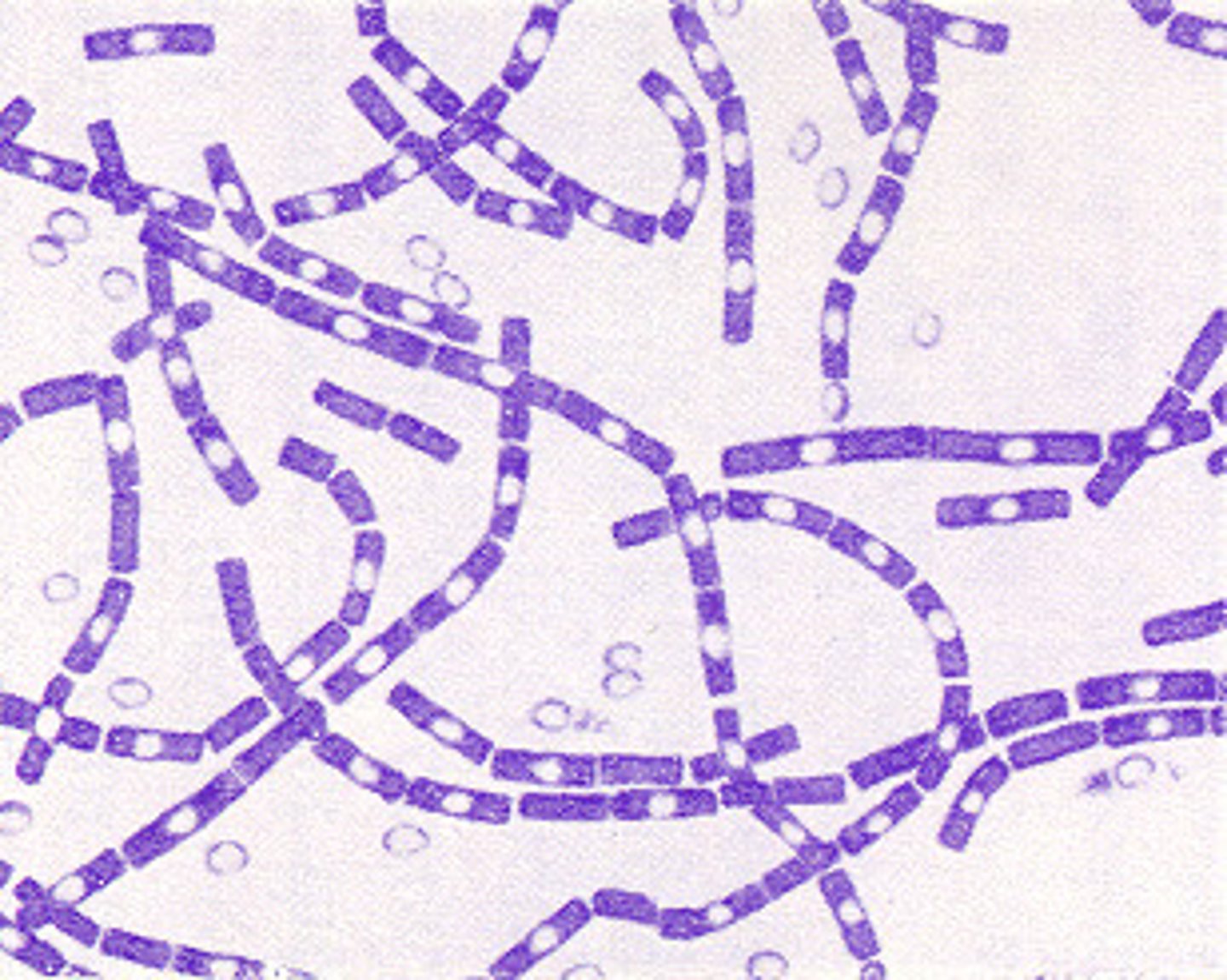
There are both gram negative and gram positive cocci on the picture. This stain is a
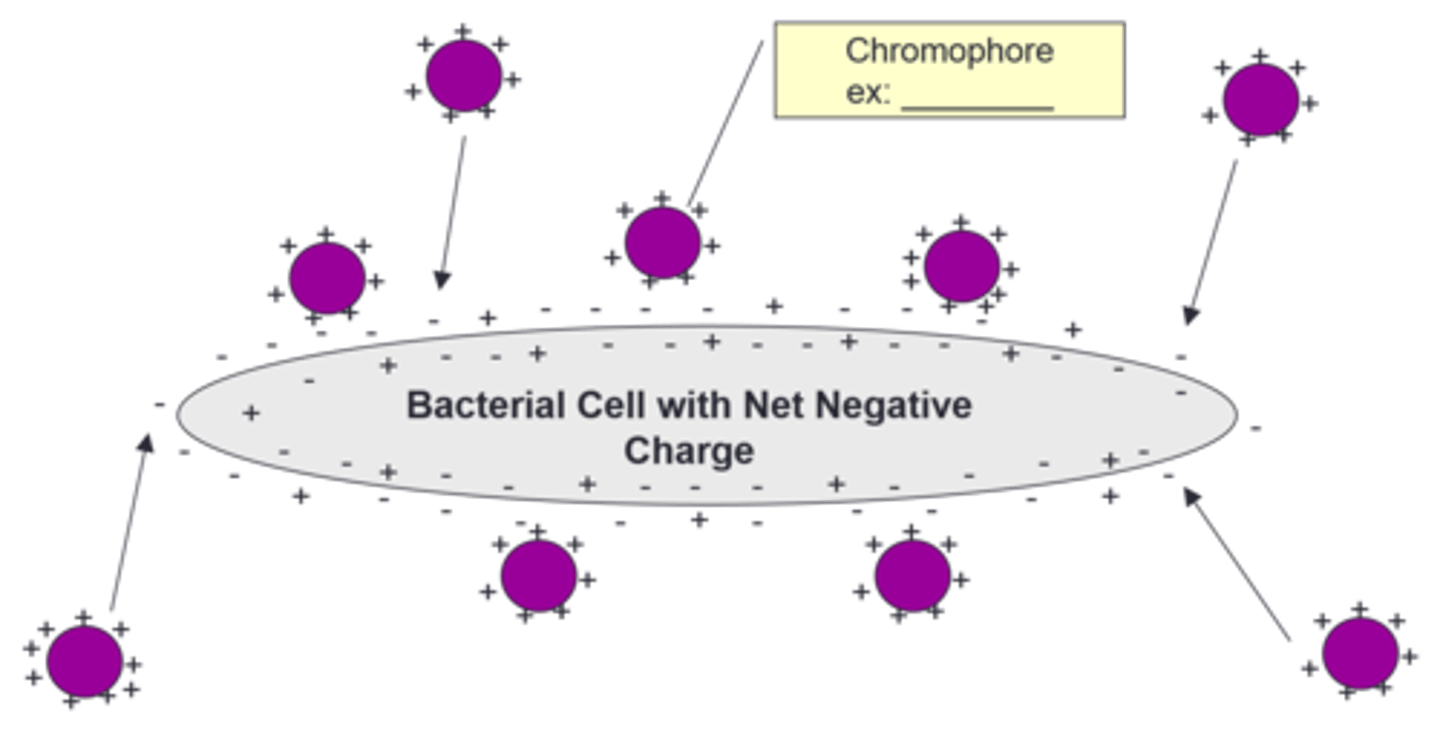
crystal violet, or any cationic dye
Fill in the blank:
negative stain
This procedure is for the
nigrosin
The second picture's dye is most likely
amount of peptidoglycan
What determines the gram stain result is the
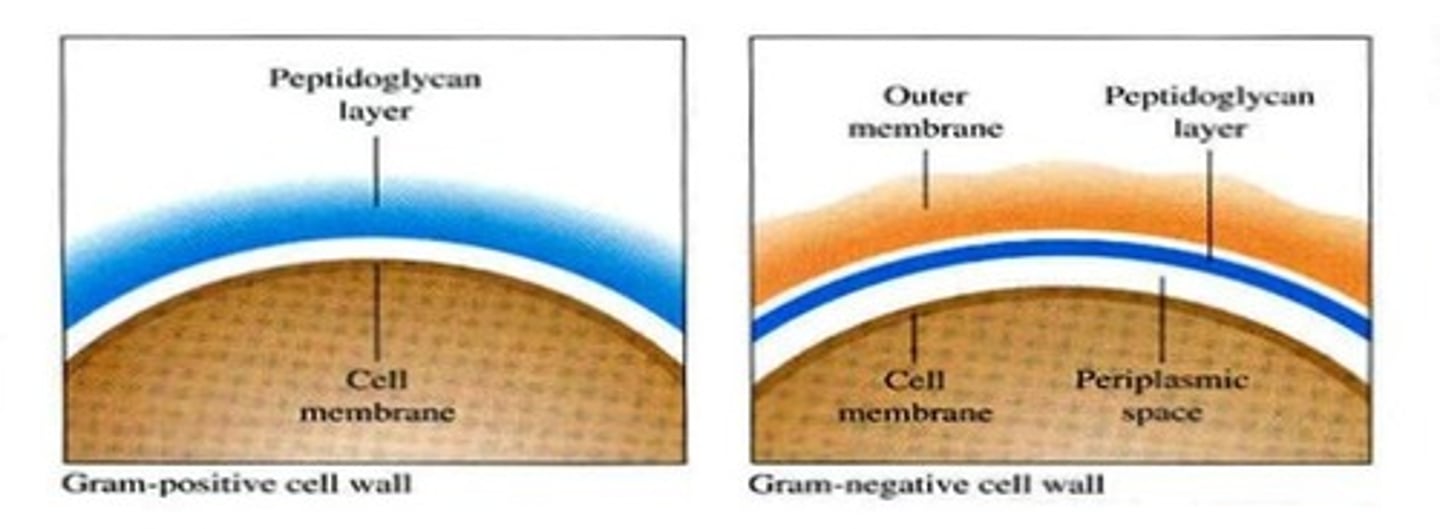
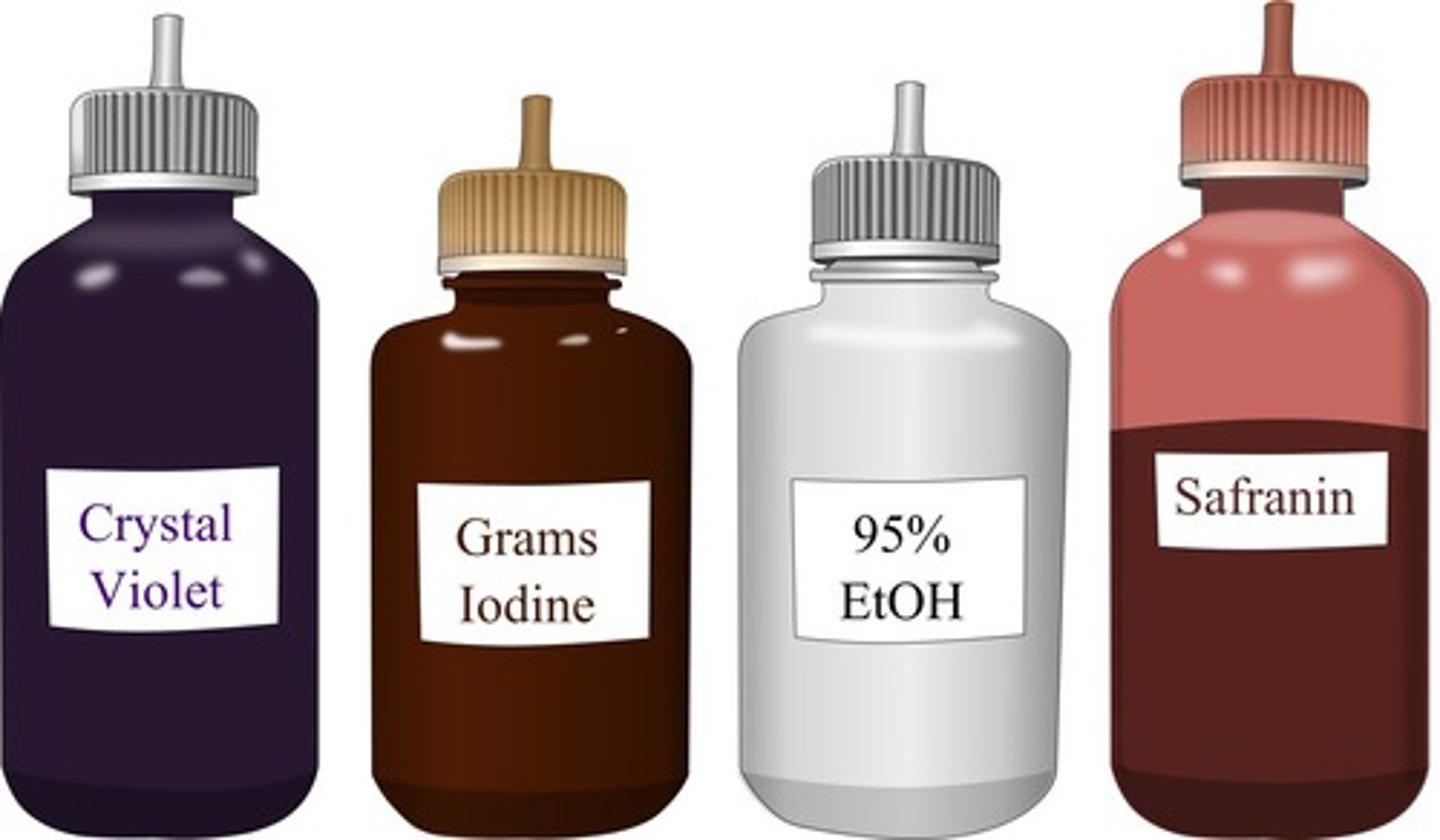
gram stain
These agents are used in the

gram negative
These are
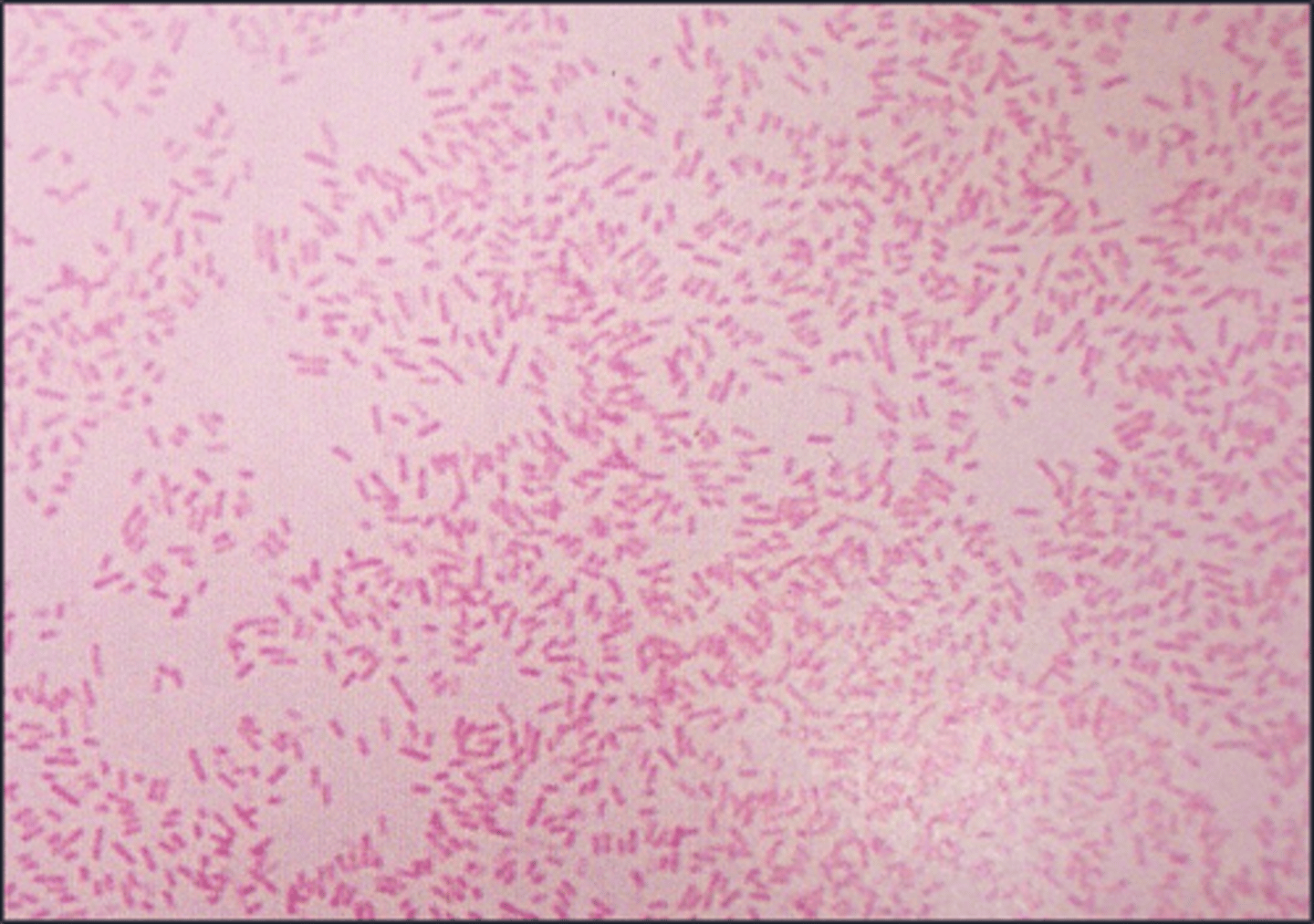
gram positive
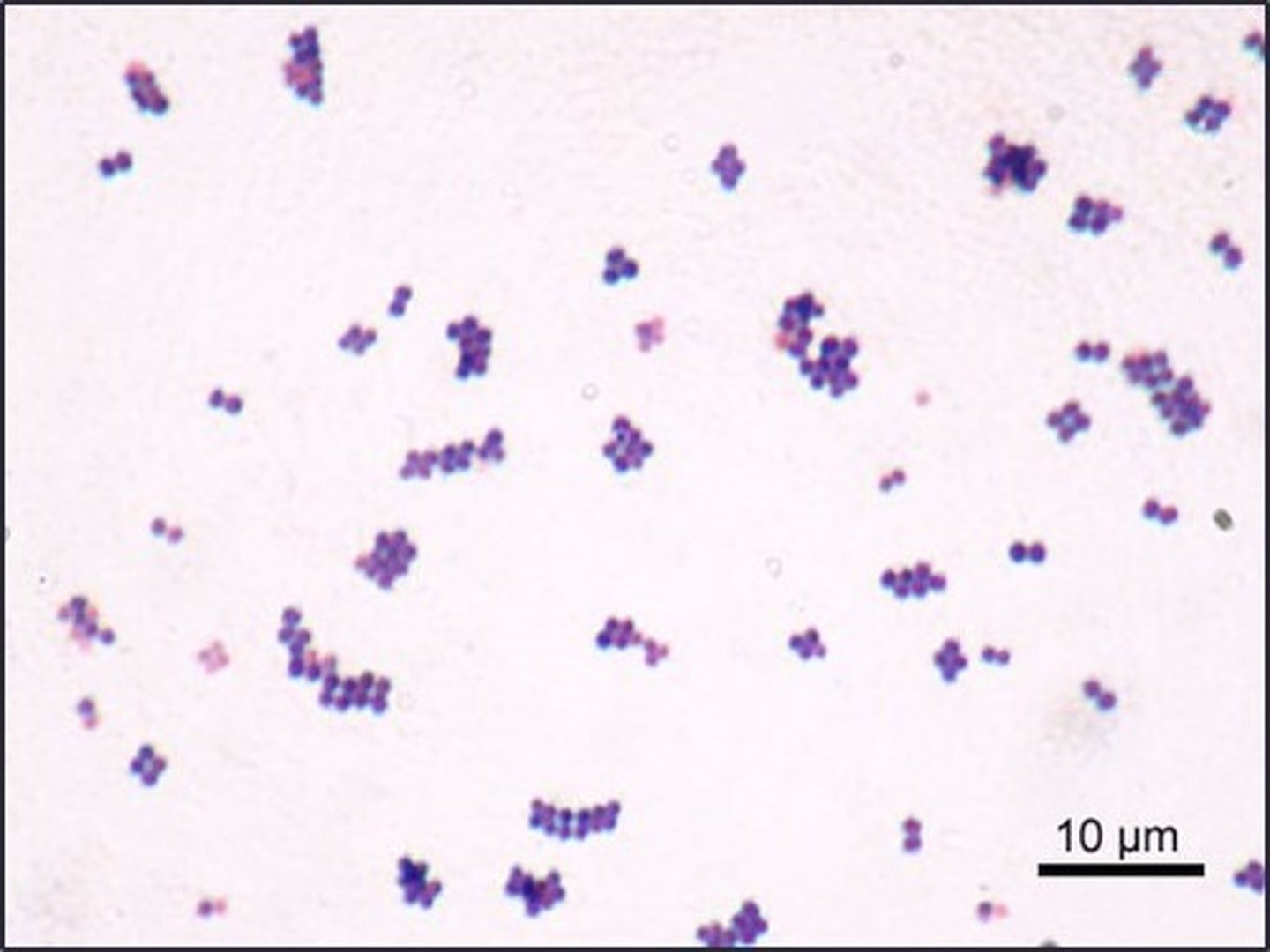
These are
staphylcoccus
This is
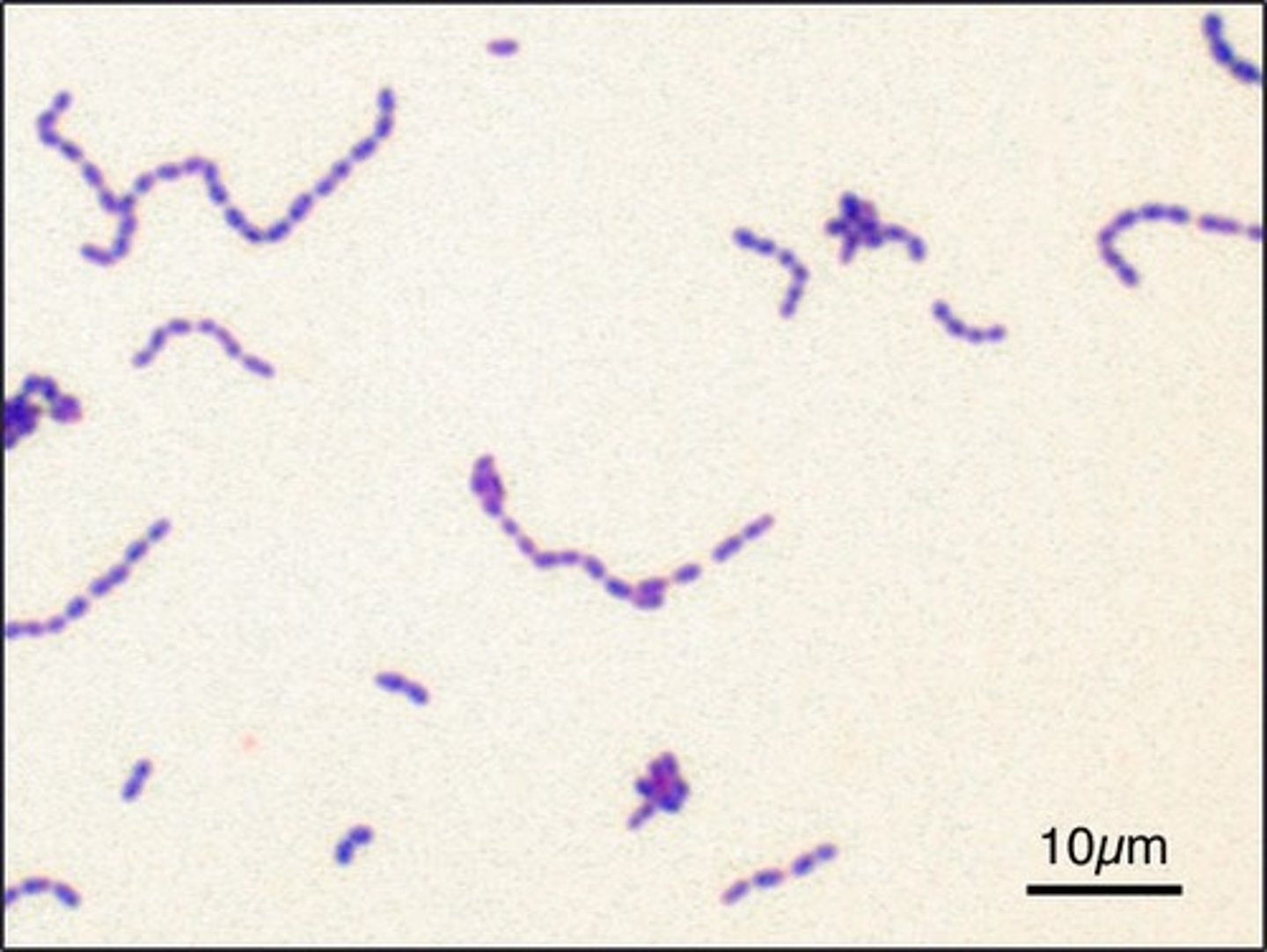
streptococcus
This is
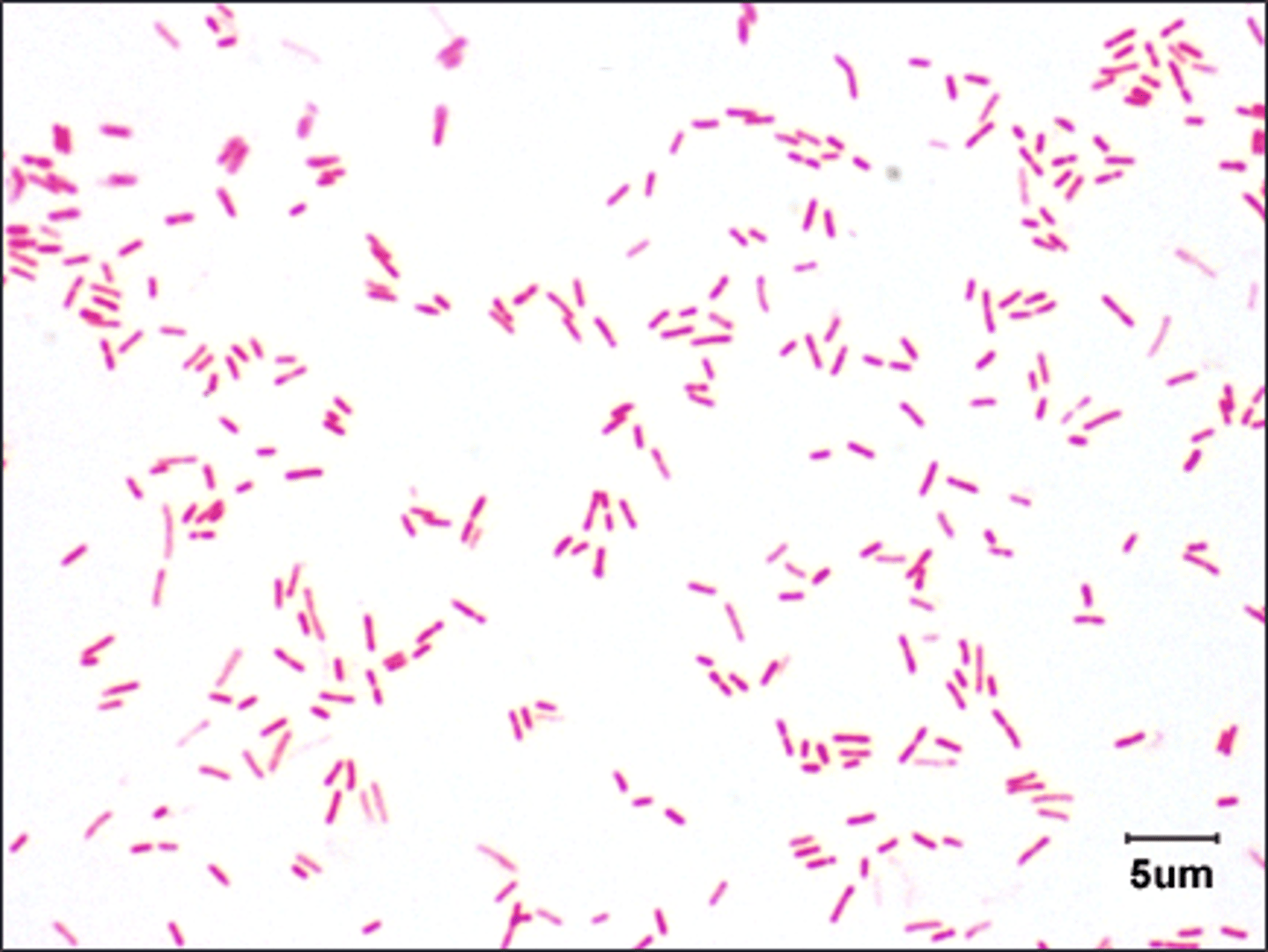
bacilli
This is gram negative
streptobacilli
This is gram negative
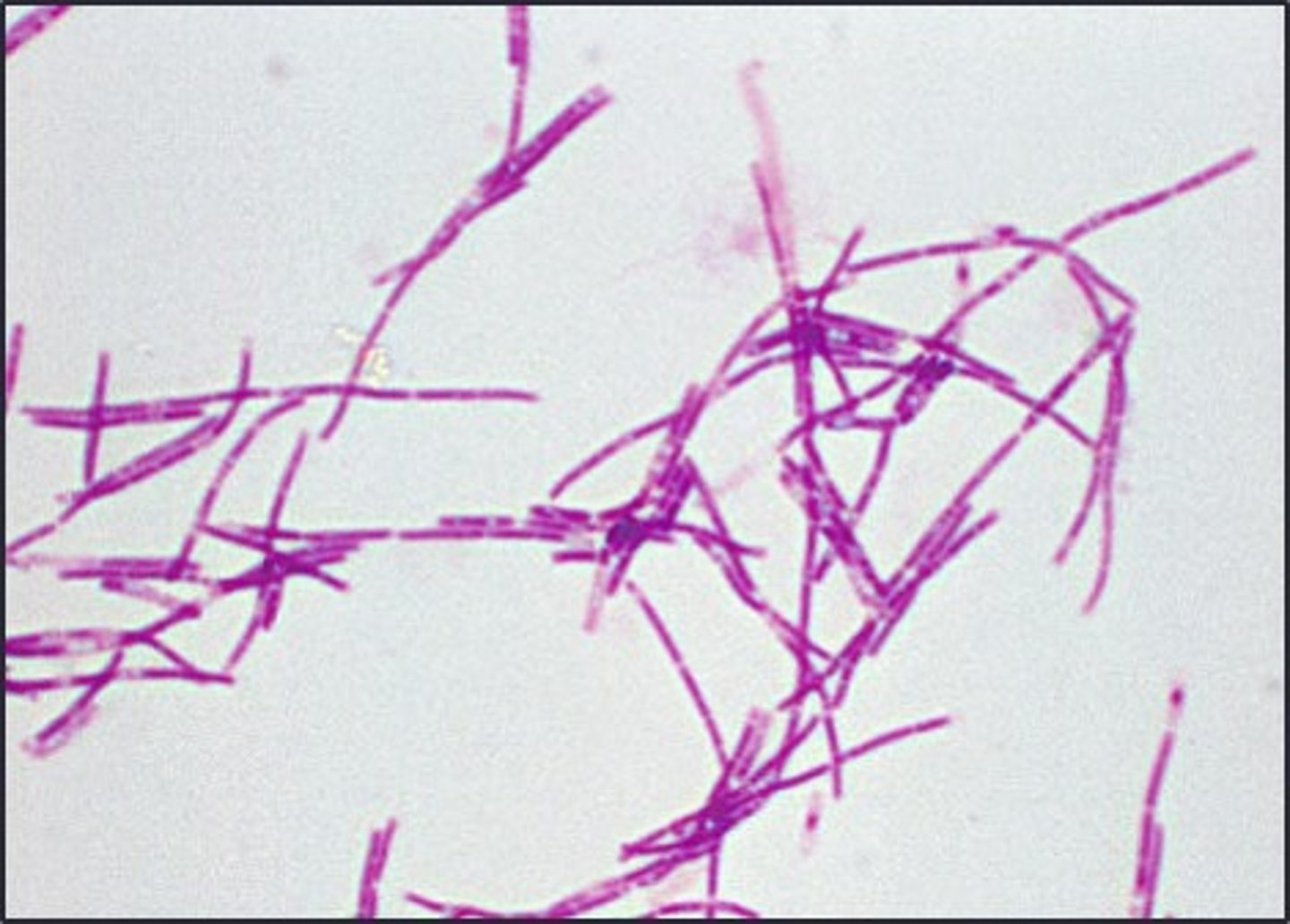
vibrio
This is an example of
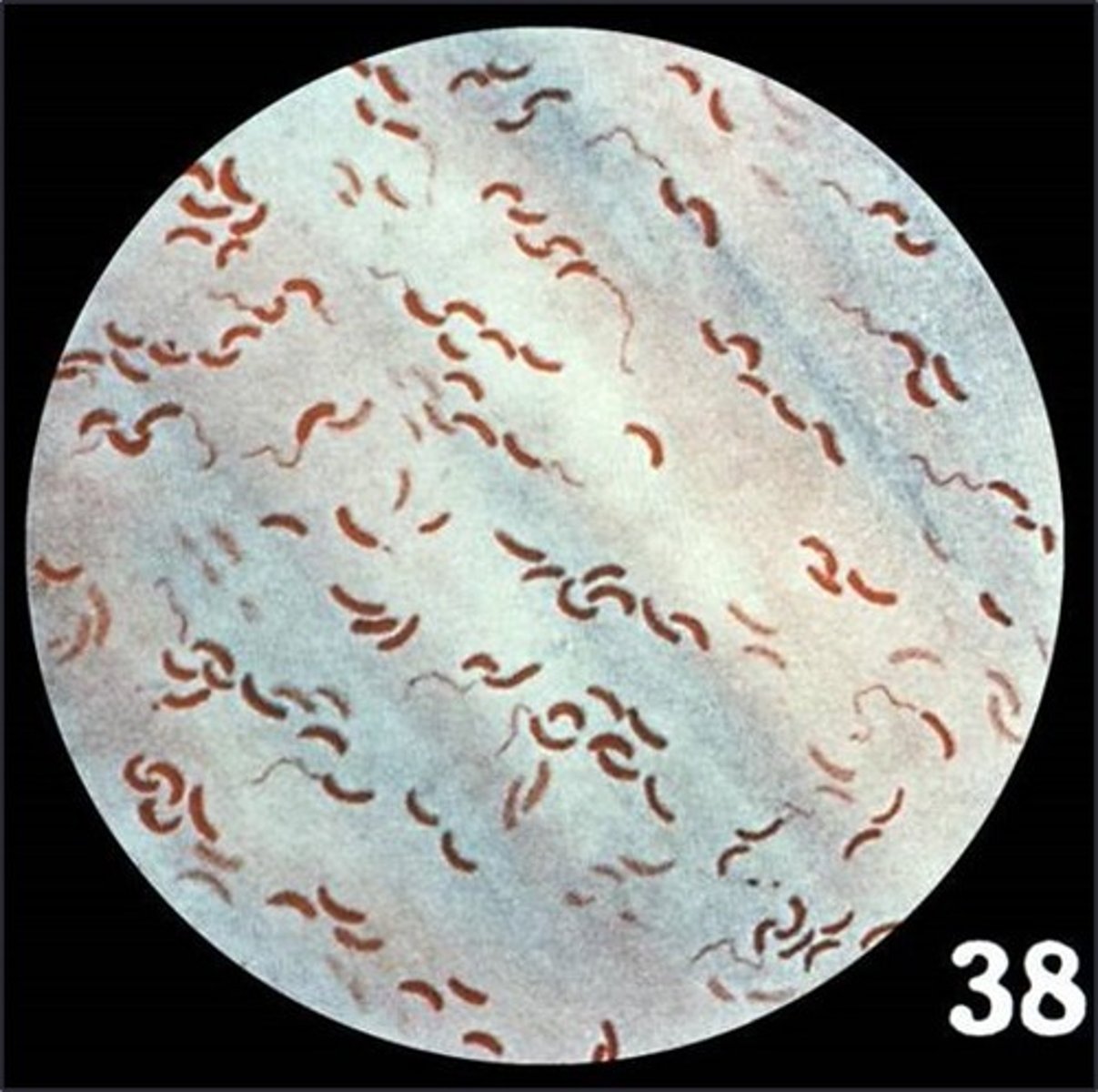
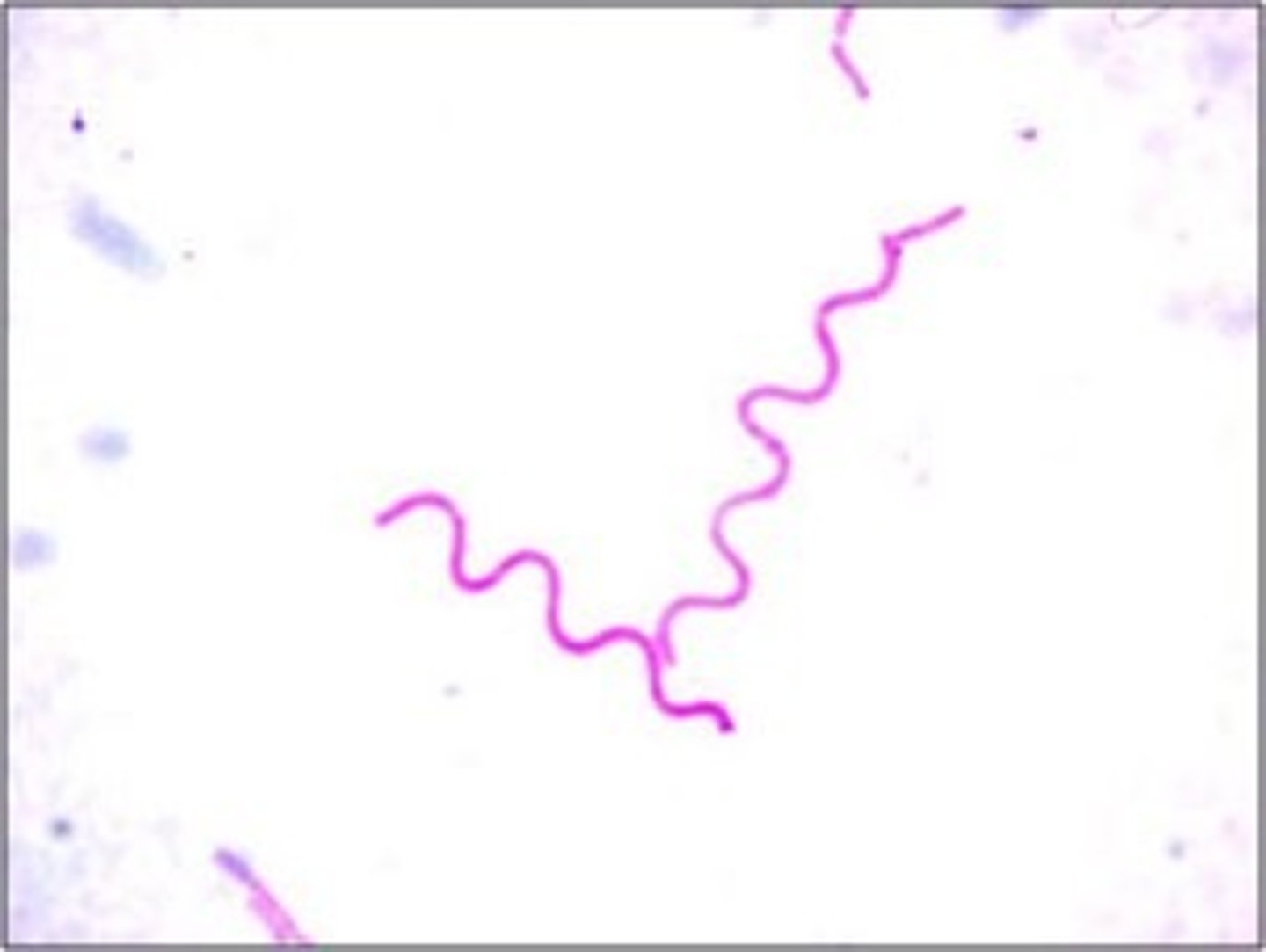
spirilium
This is an example of

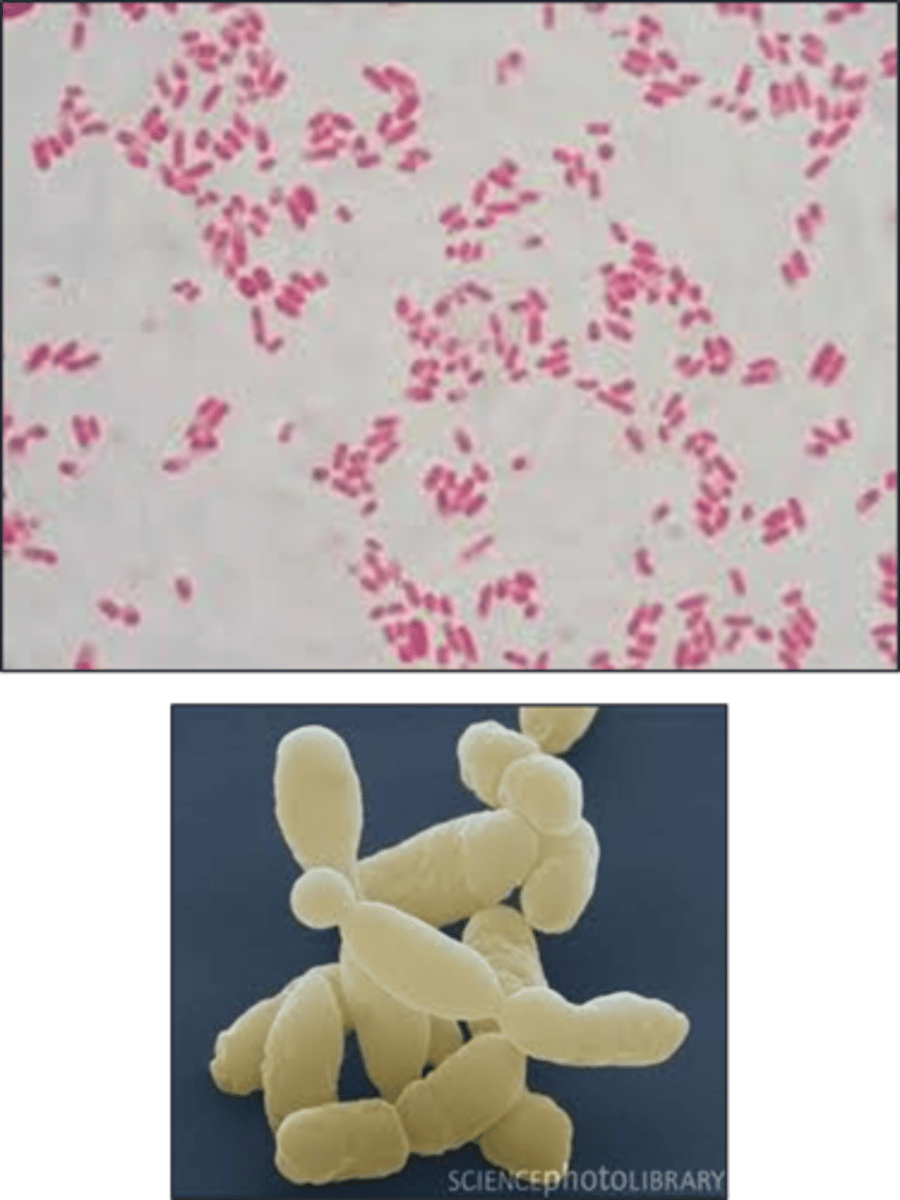
coccobacillus
Morphology:
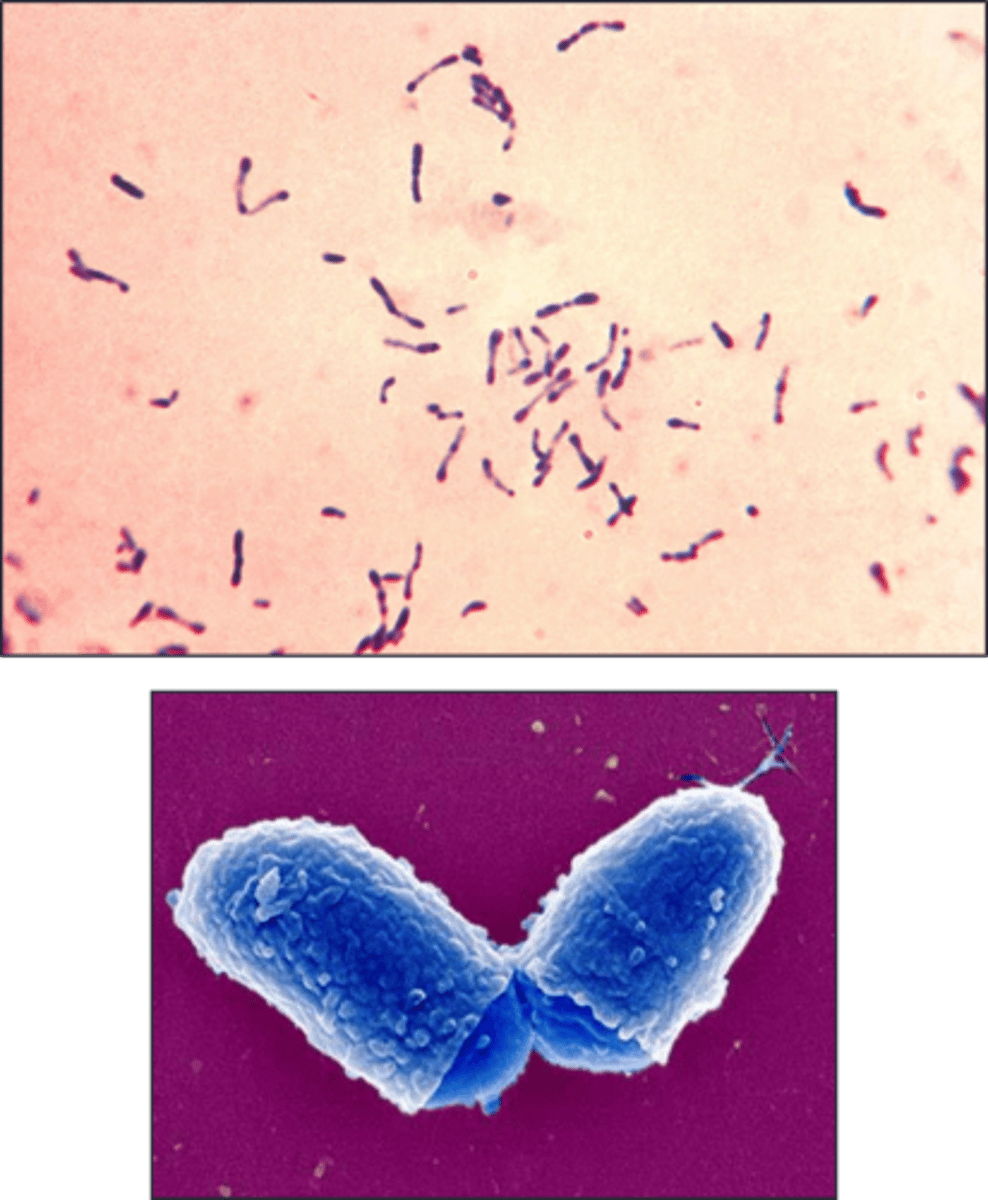
club-shaped
Morphology:
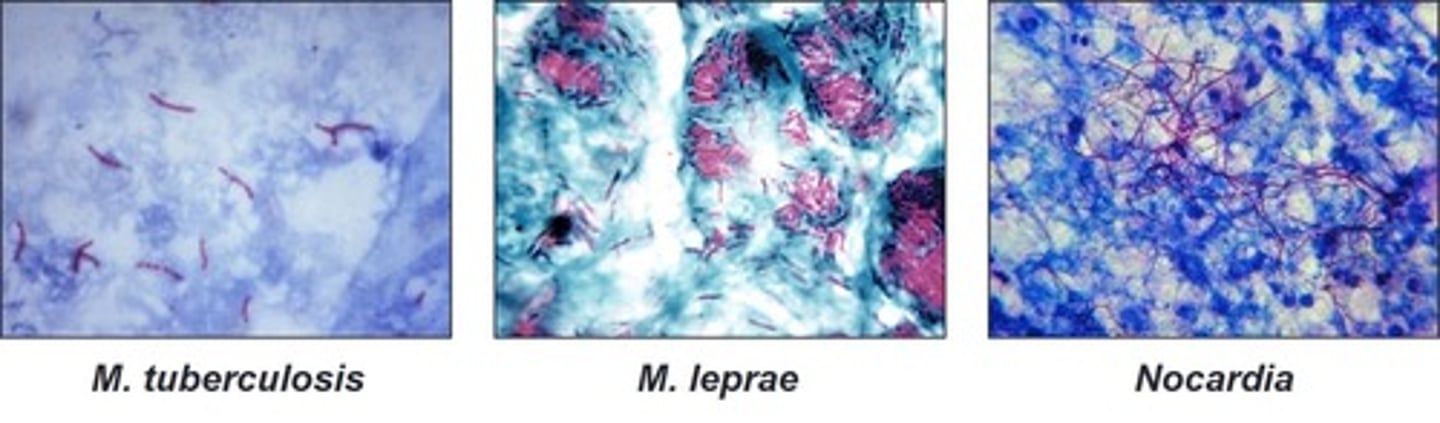
acid-fast-positive organisms
These are examples of
free spores and endospores
The green are
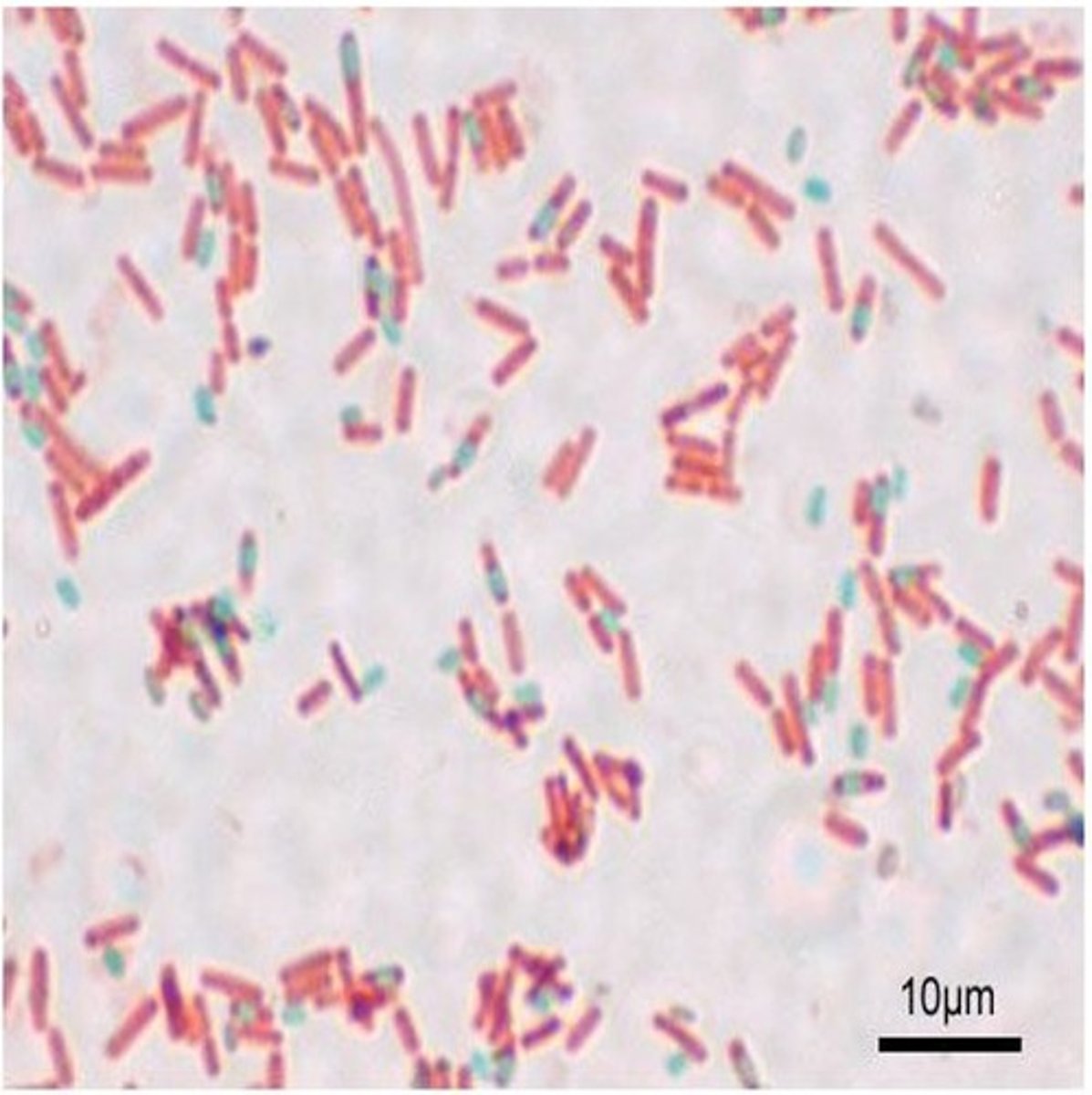
vegetative cells
The pink are
spore-forming organisms
These are
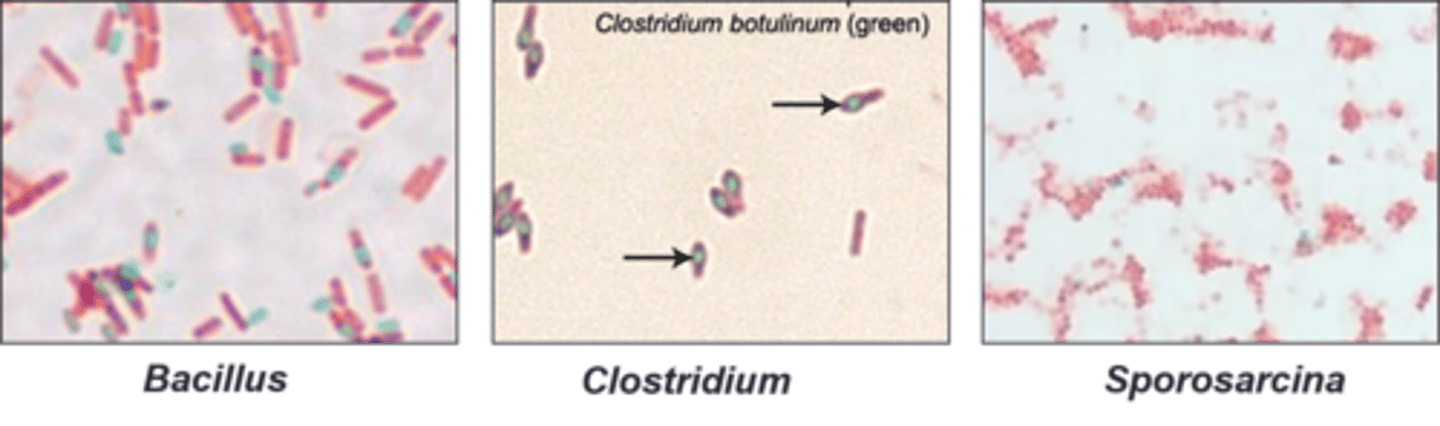
anaerobic
Clostridium is
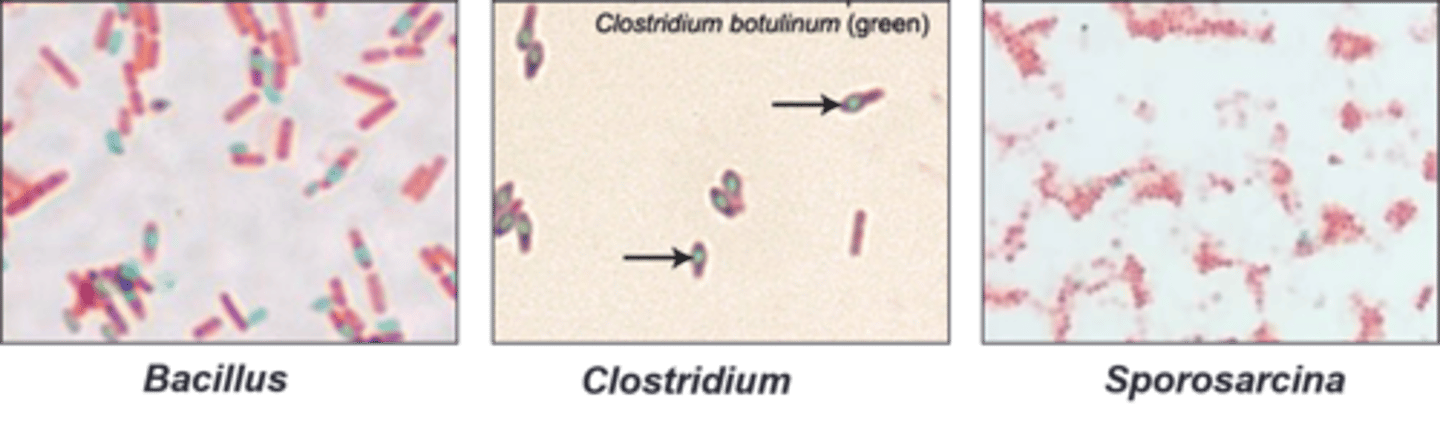
aerobic
Bacillus is
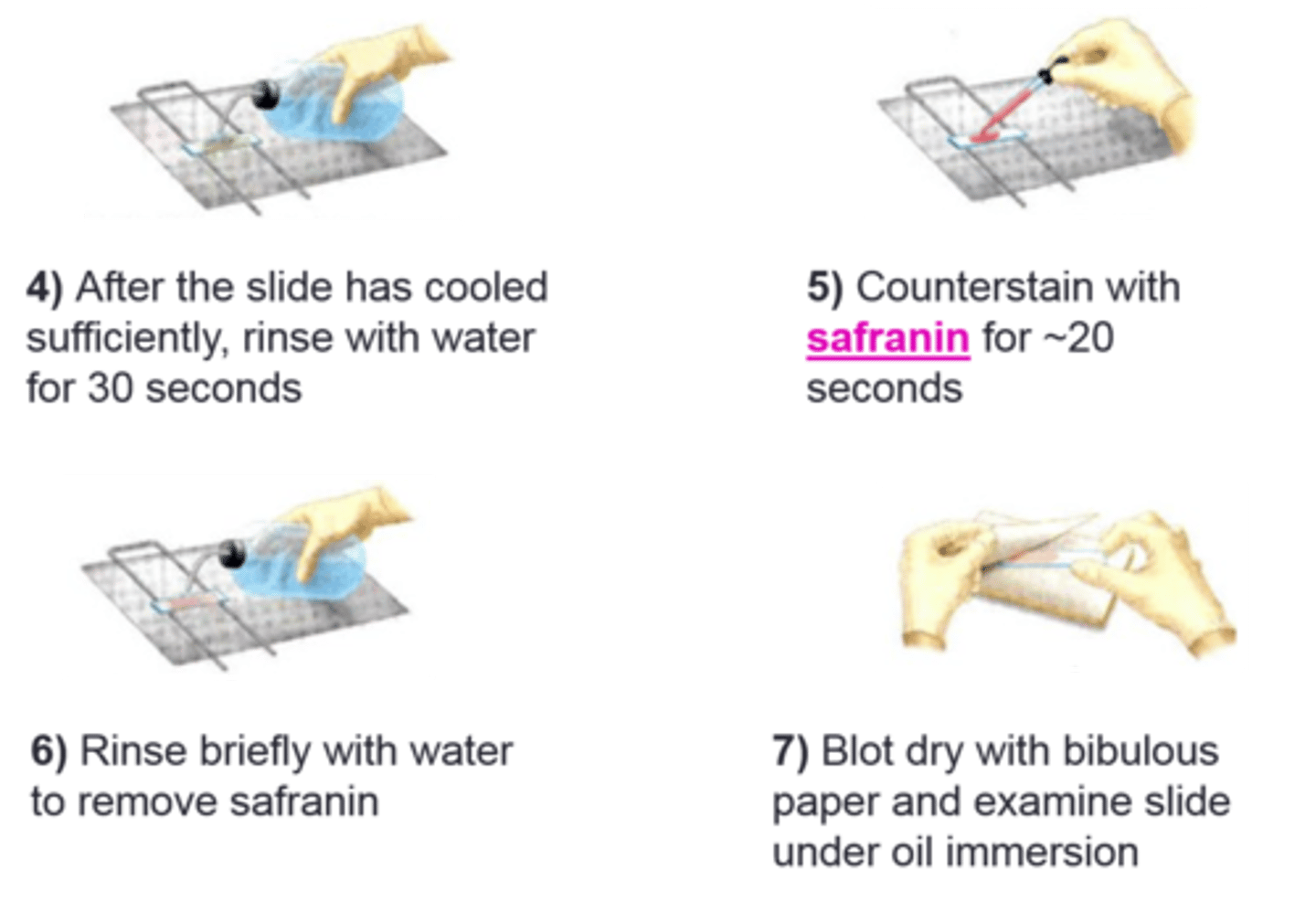
acid-fast and spore staining
This procedure is for
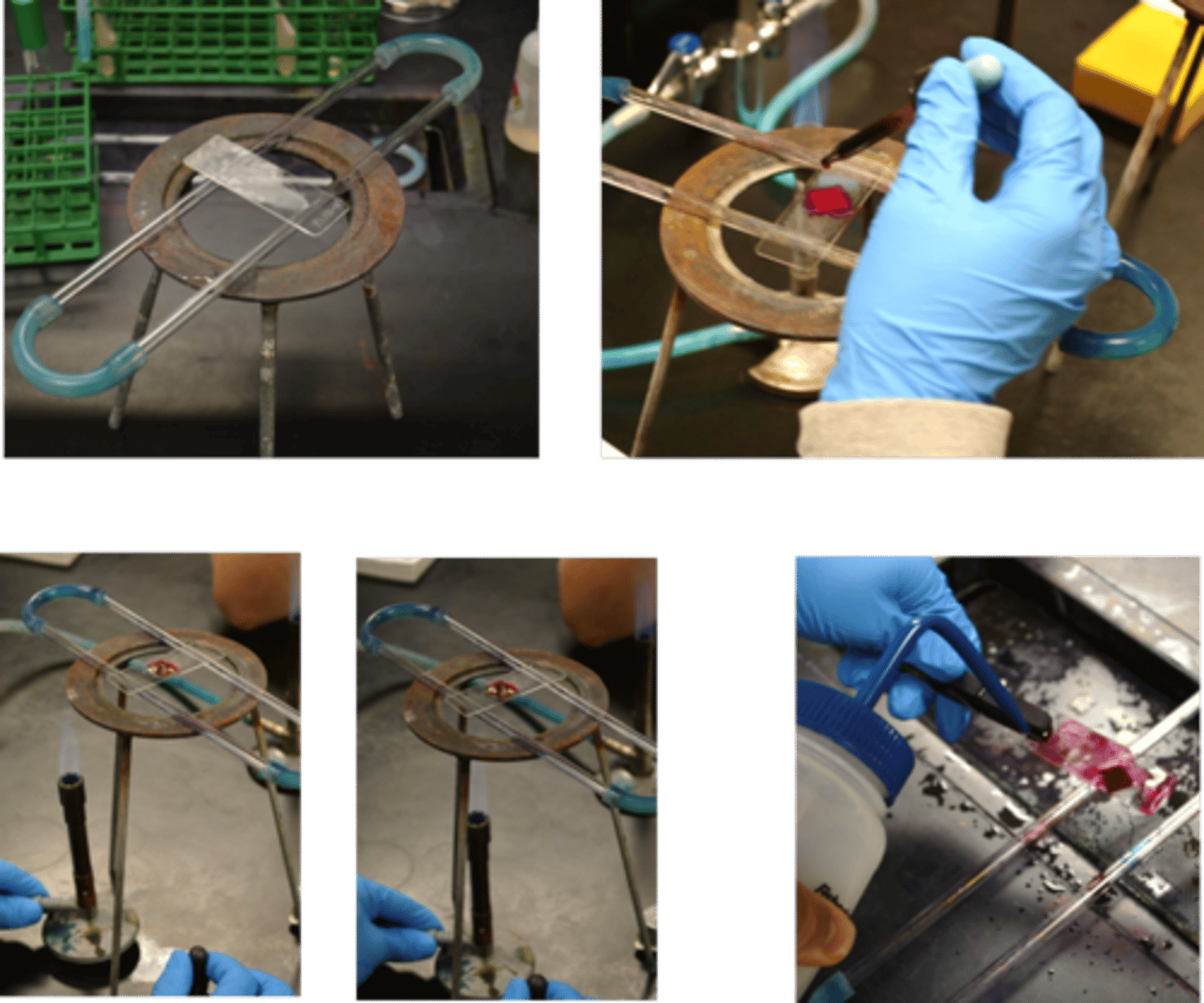
acid-fast stain
This procedure is for the

carbol fuschin
Primary dye for this procedure:

spore stain
This procedure is for the
malachite green
Primary dye for this procedure:
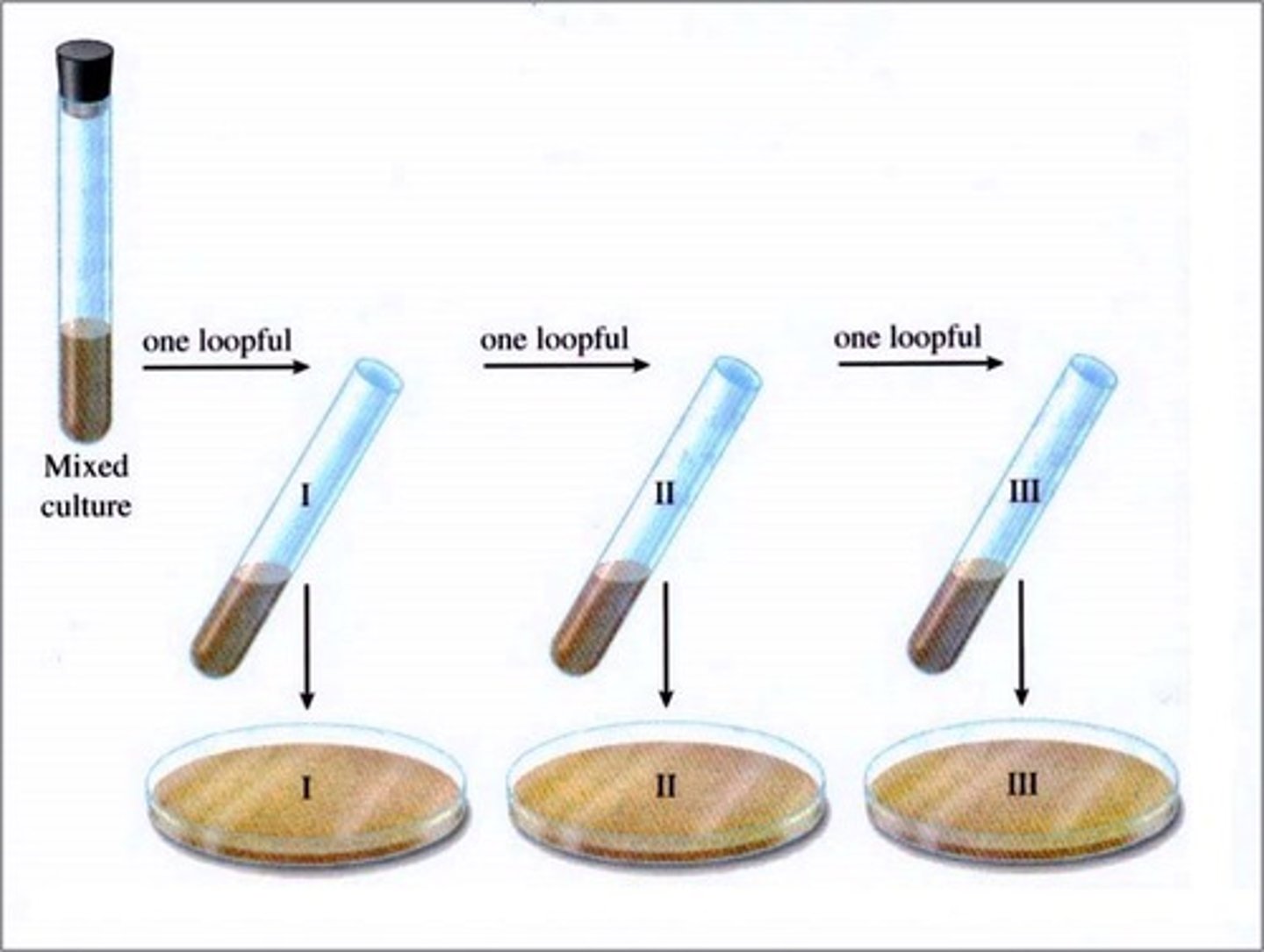
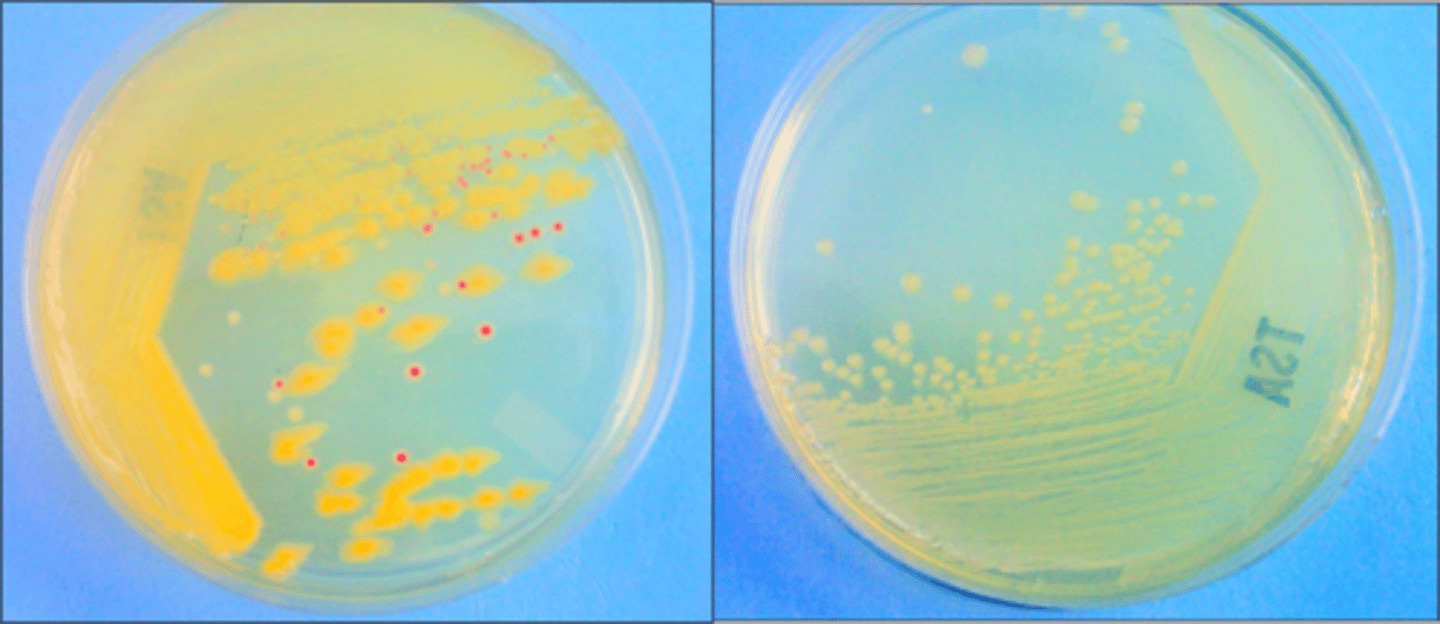
pour-plate method
This isolation method is the
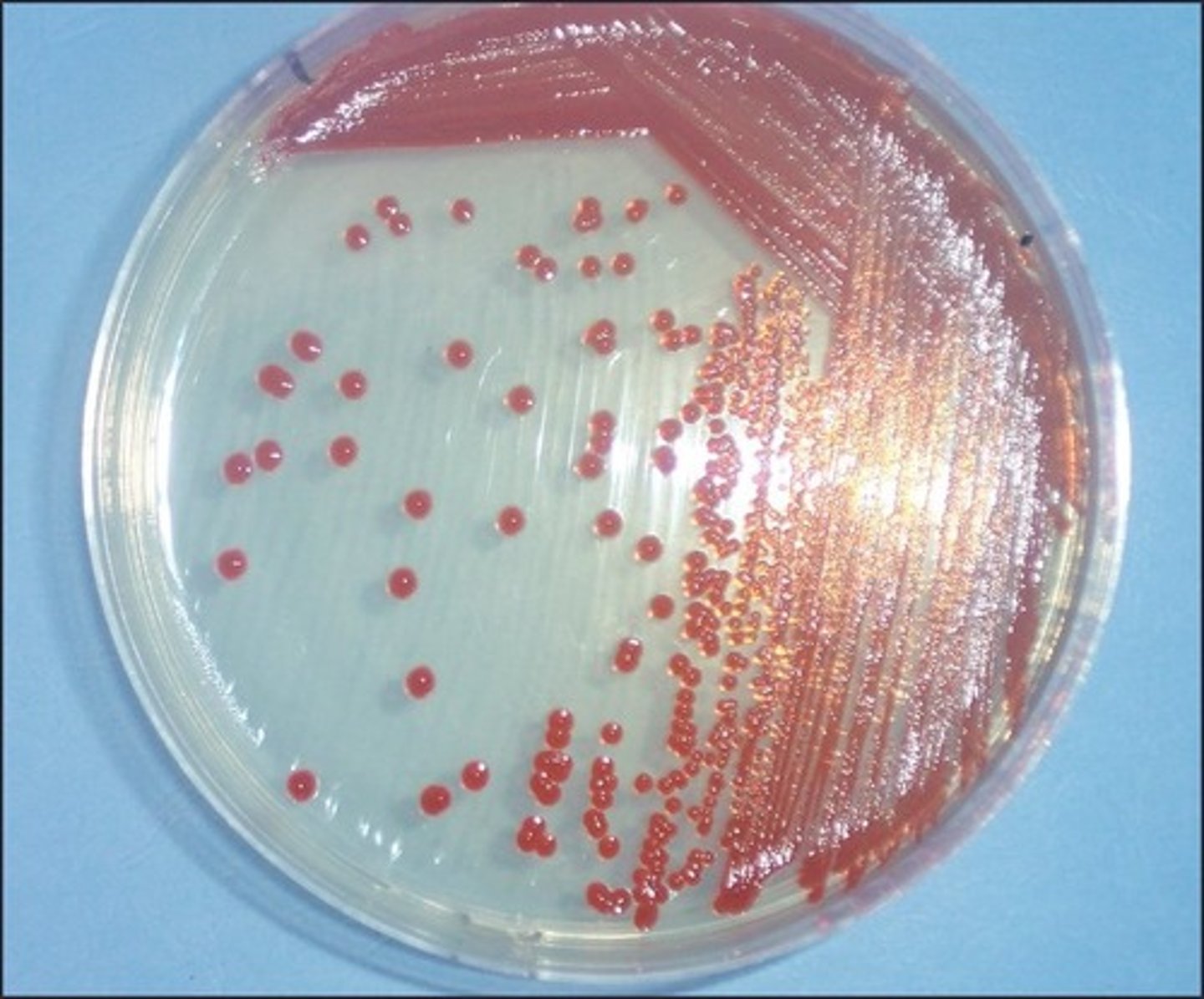
3-zone streak plate
This is a
primary streak
These both come from the same broth. The first plate is the
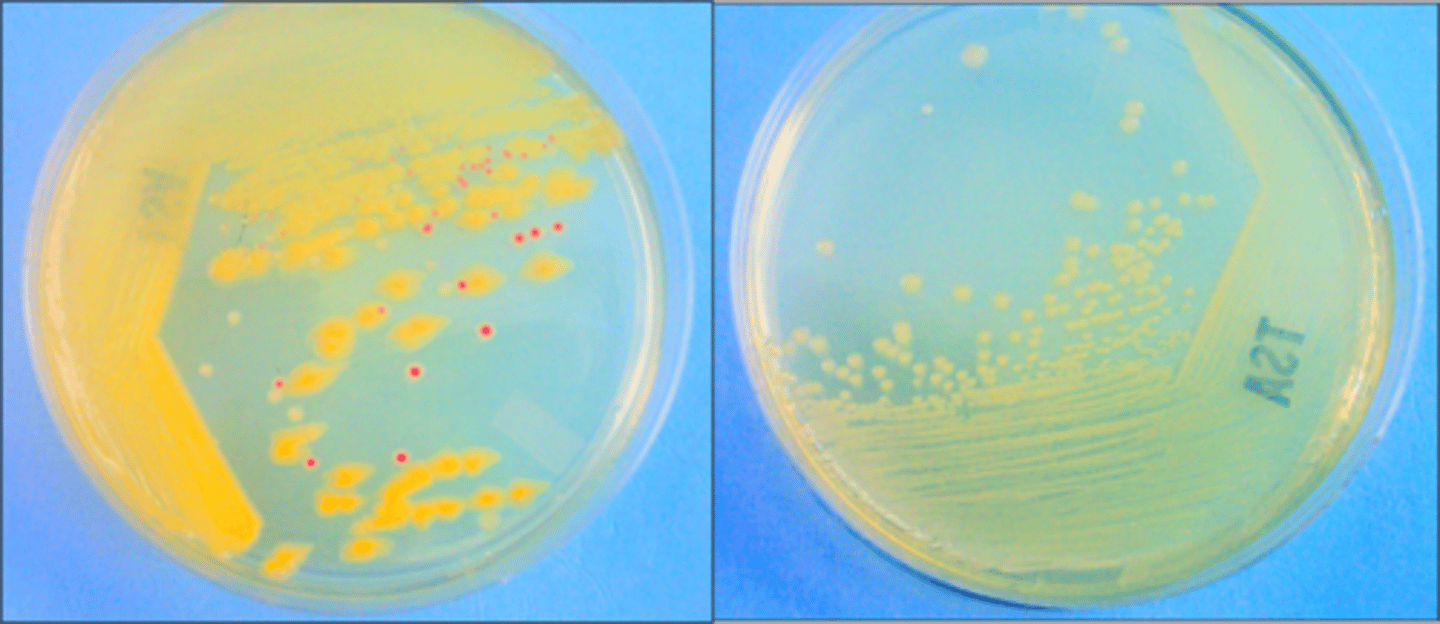
secondary streak, or subculture
These both come from the same broth. The second plate is the
surface colony
Looking from the top, the black arrow points to a(n)
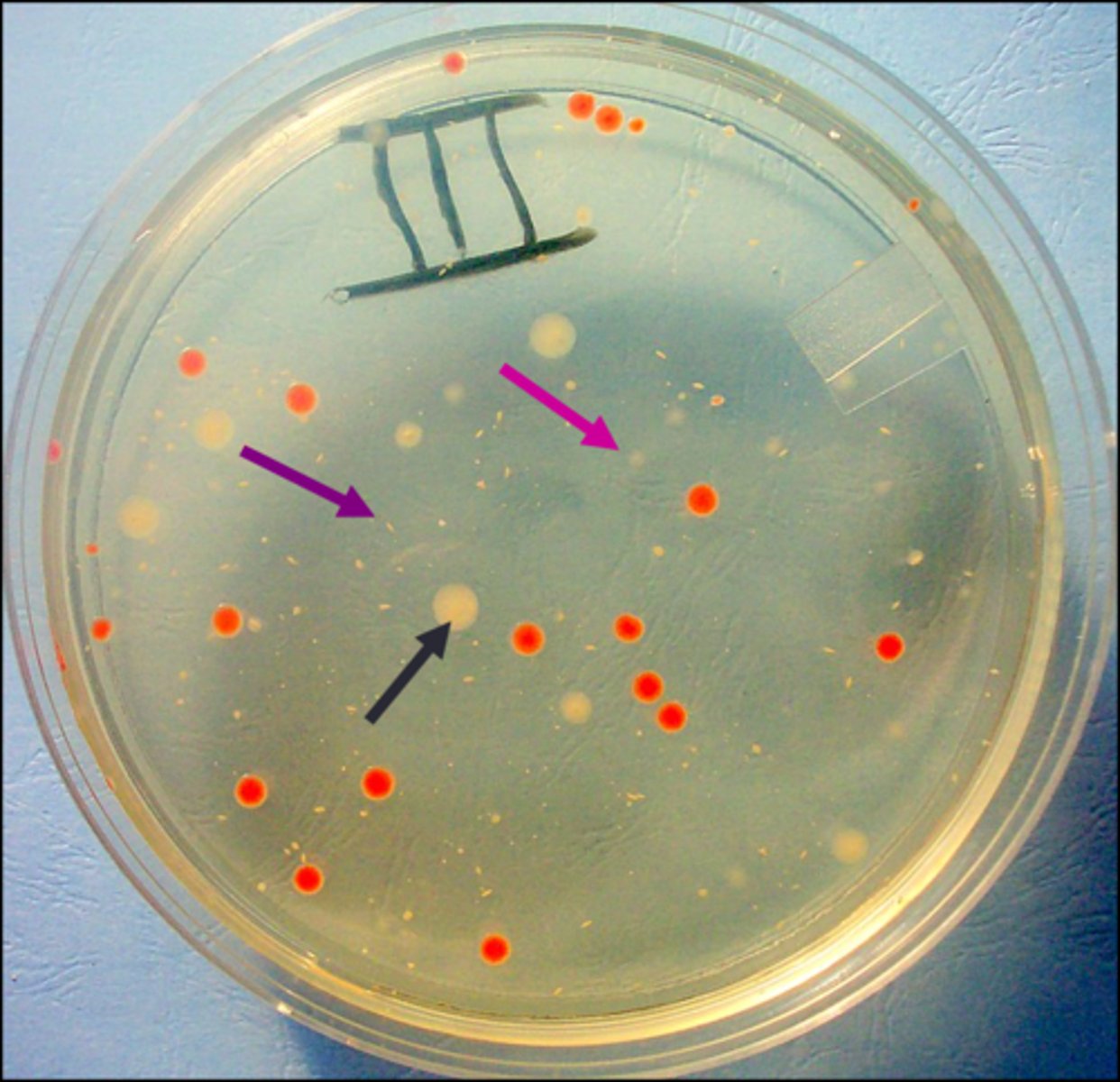
embedded colony
Looking from the top, the purple arrow points to a(n)
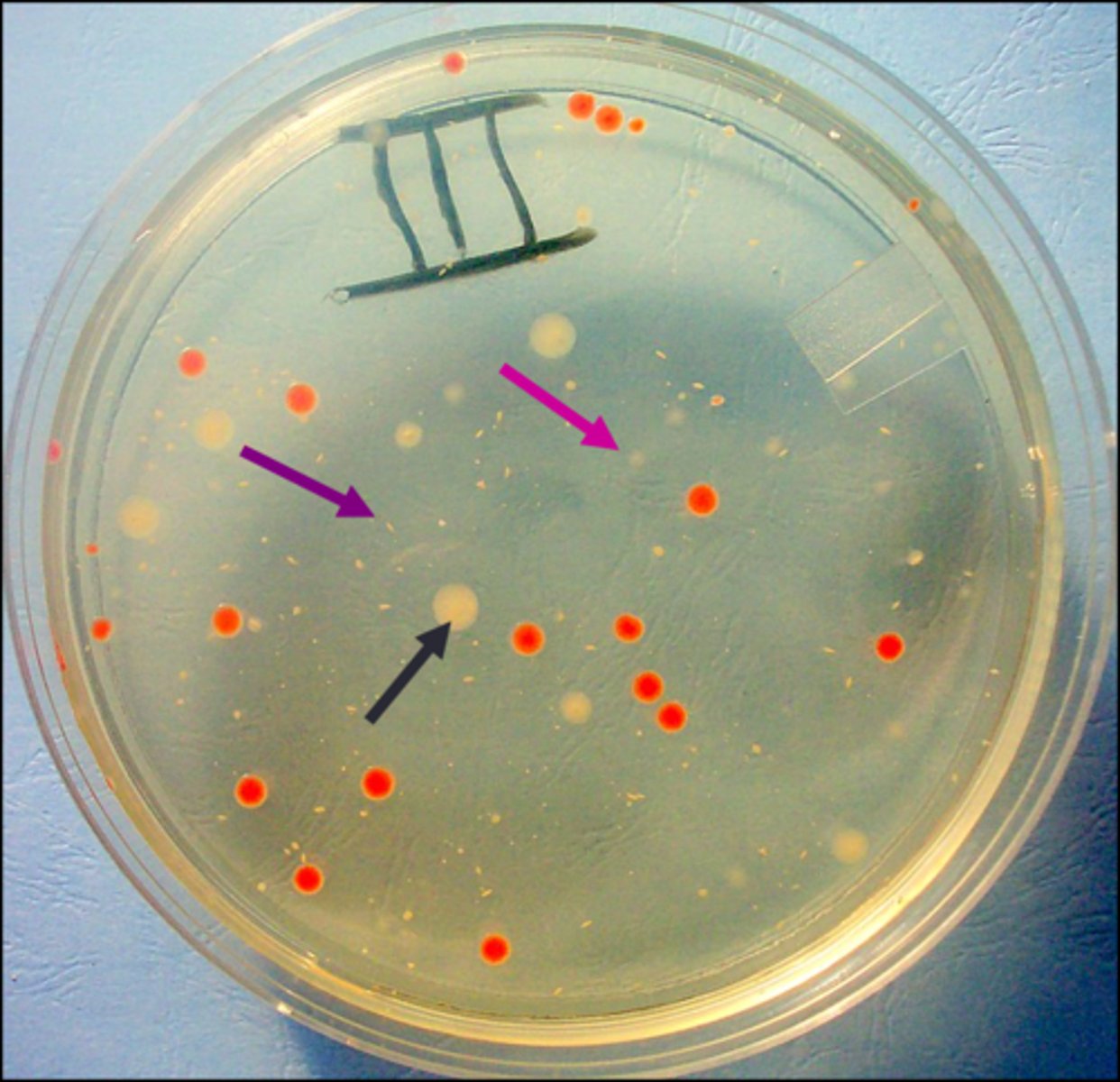
bottom colony
Looking from the top, the pink arrow points to a(n)
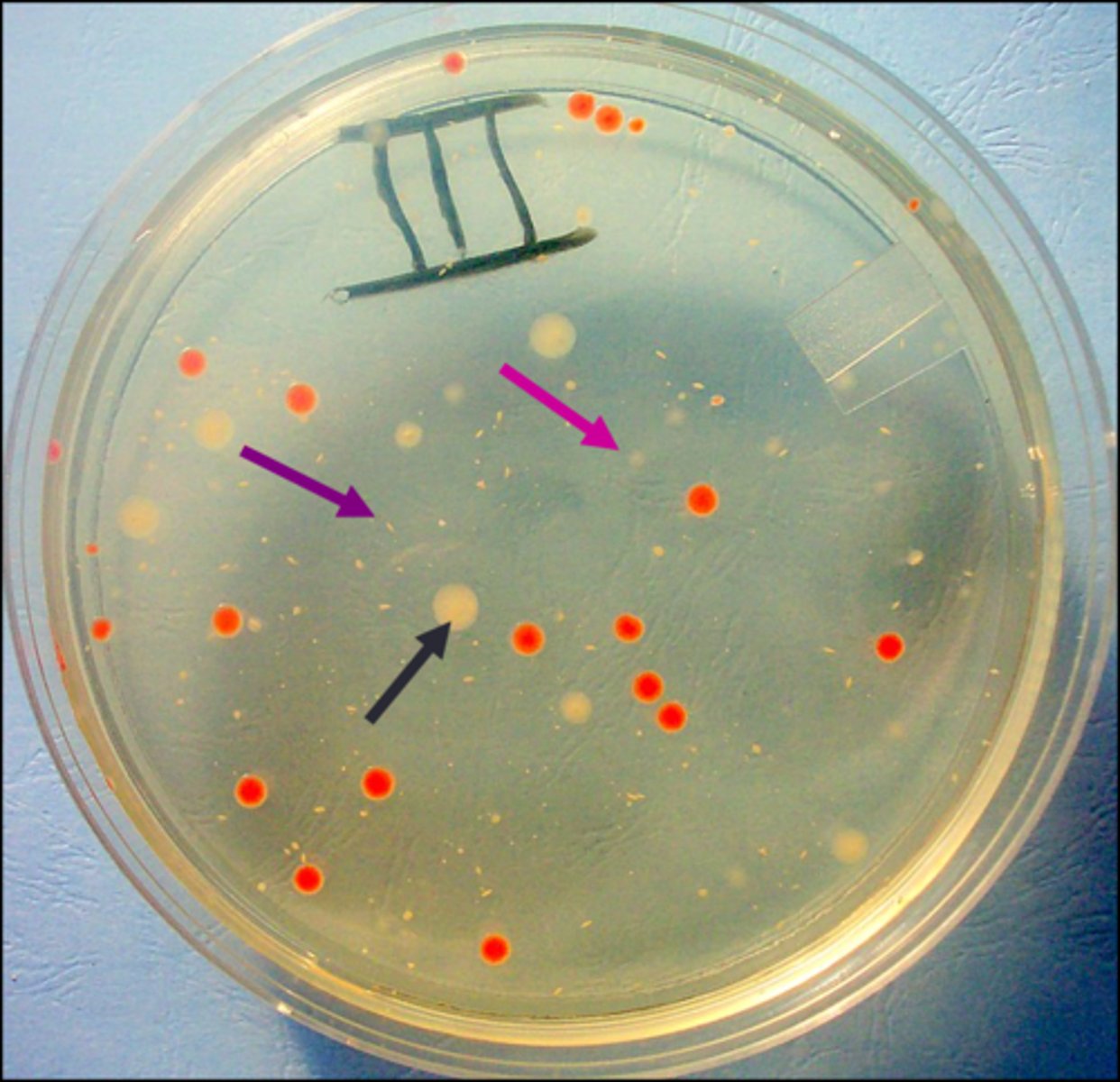
one cell
The assumption is that each isolated colony in zone 3B comes from
using a fourth zone
Error in streaking:
inadequate streaking
Error in streaking:
slashing the agar
Error in streaking:
making zones too large
Error in streaking:
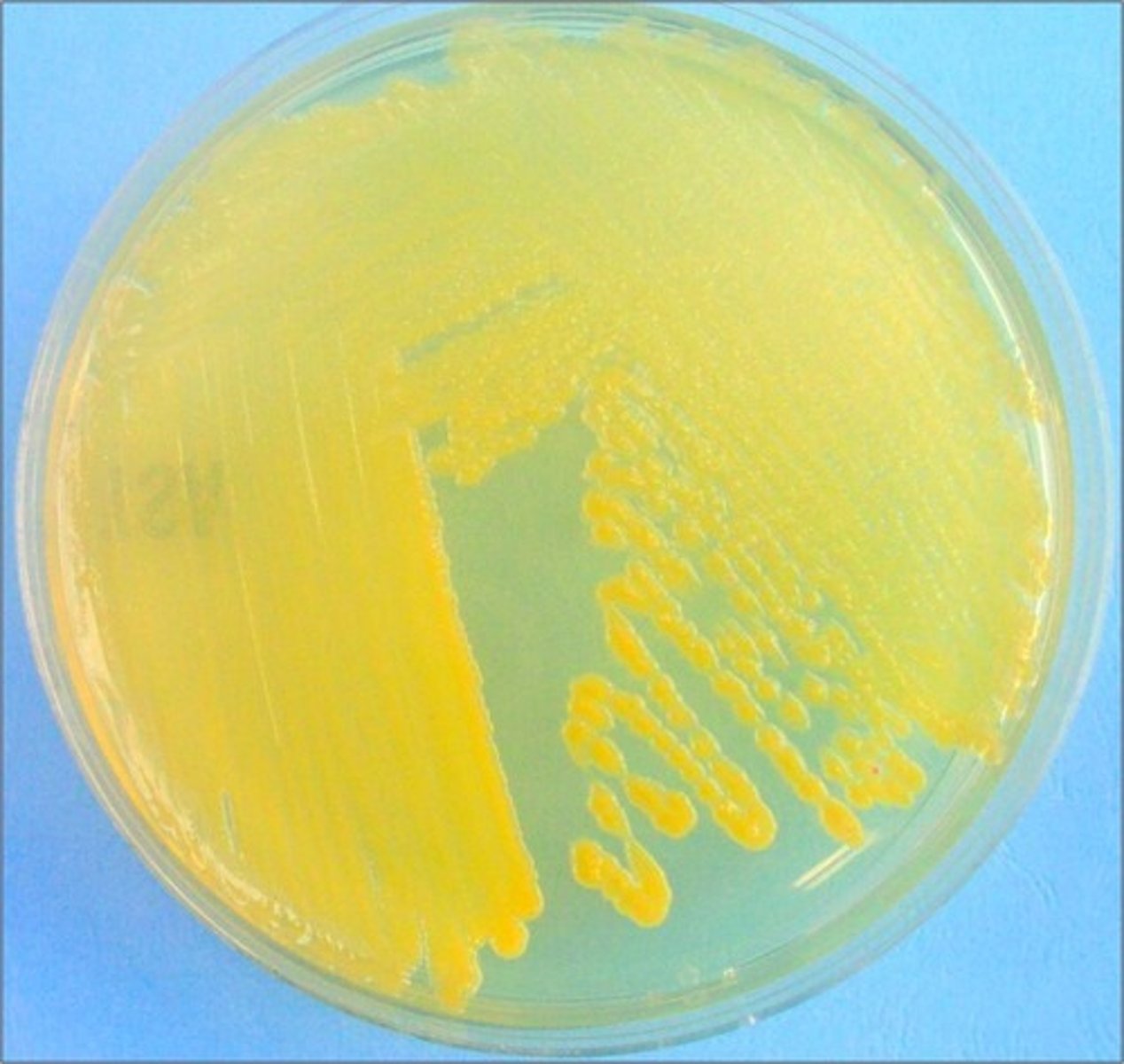
crossing over into other zones during final streak
Error in streaking:
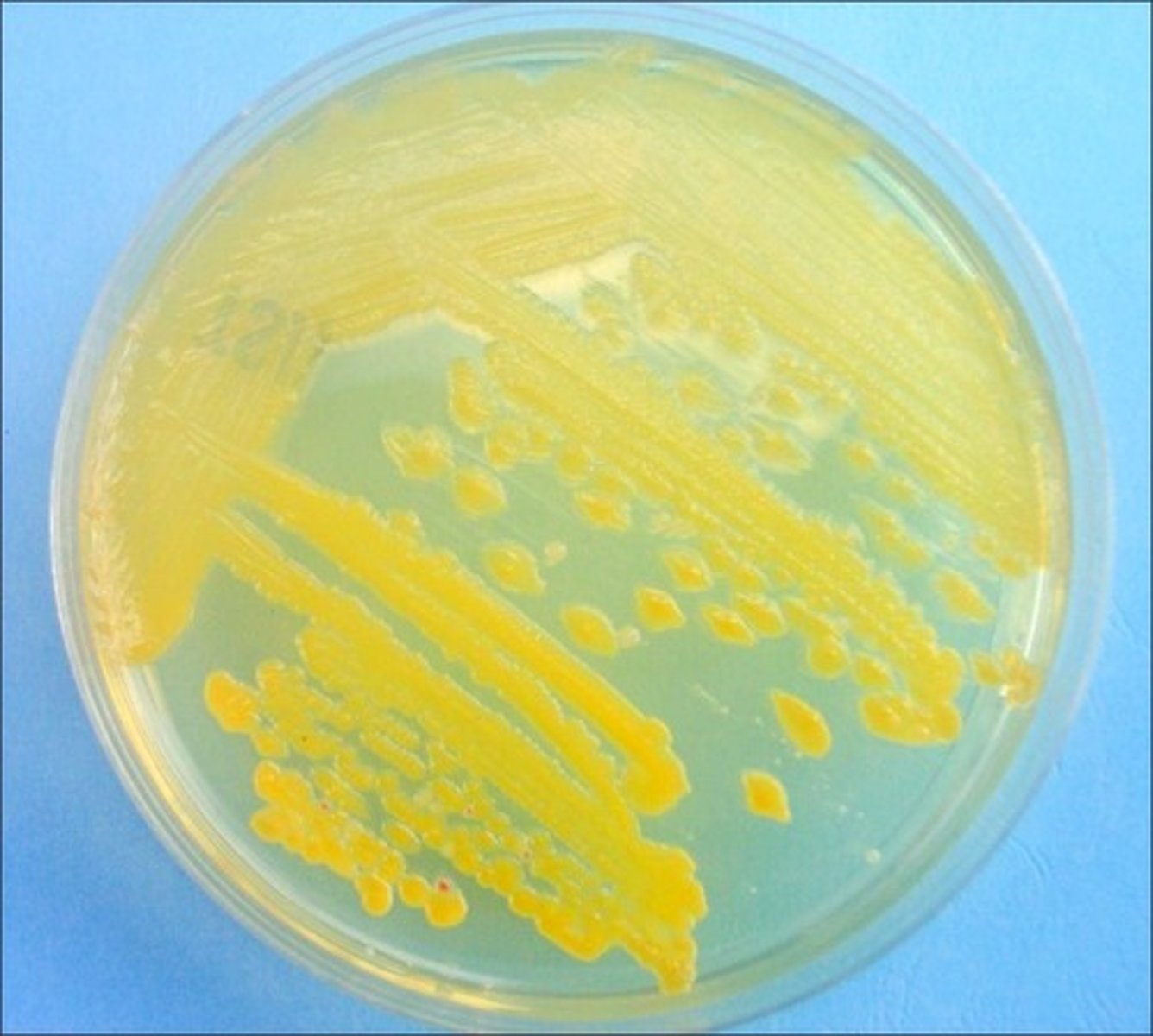
insufficient streaking in final zone
Error in streaking:
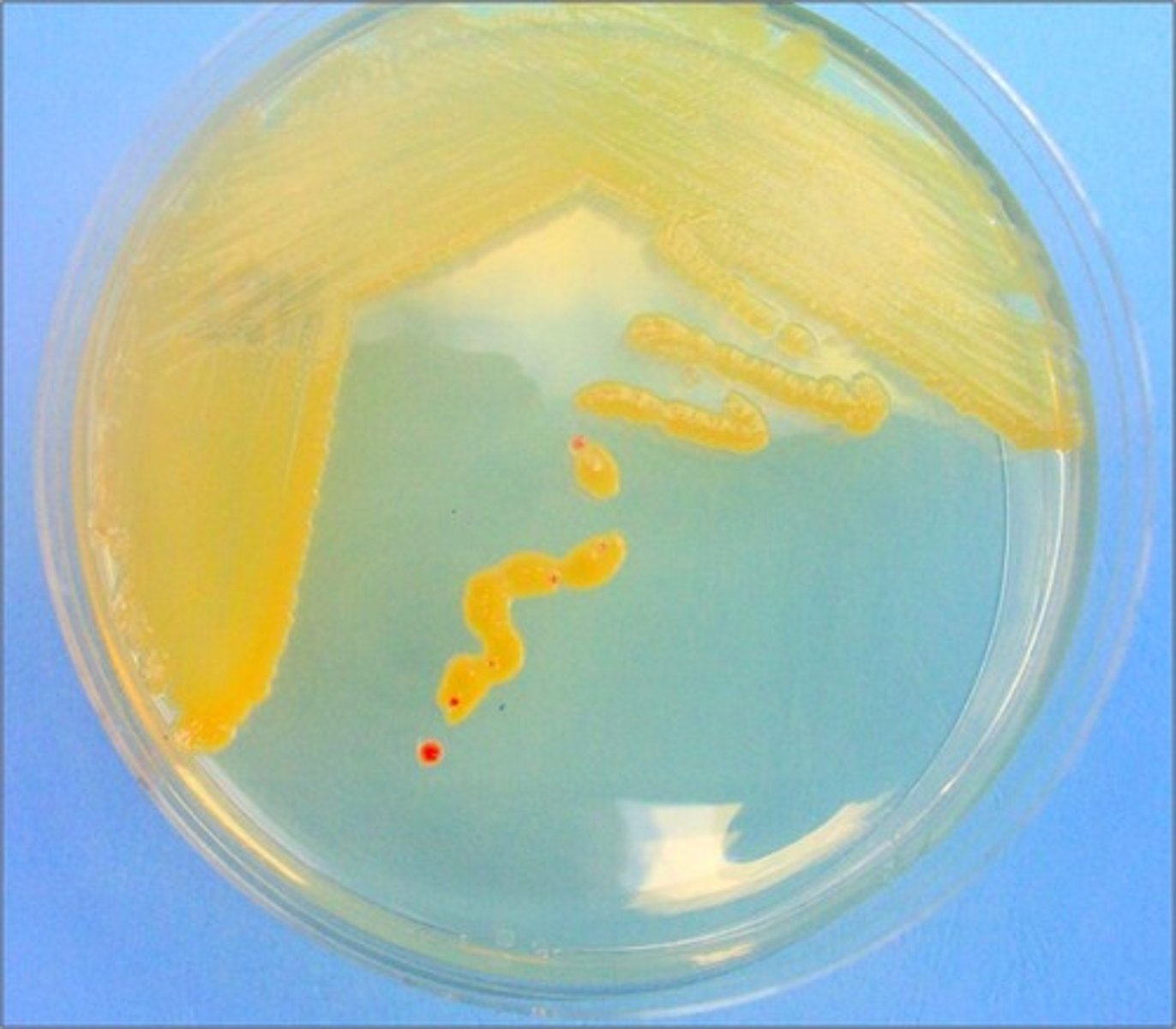
loop angle too flat on agar
Error in streaking:
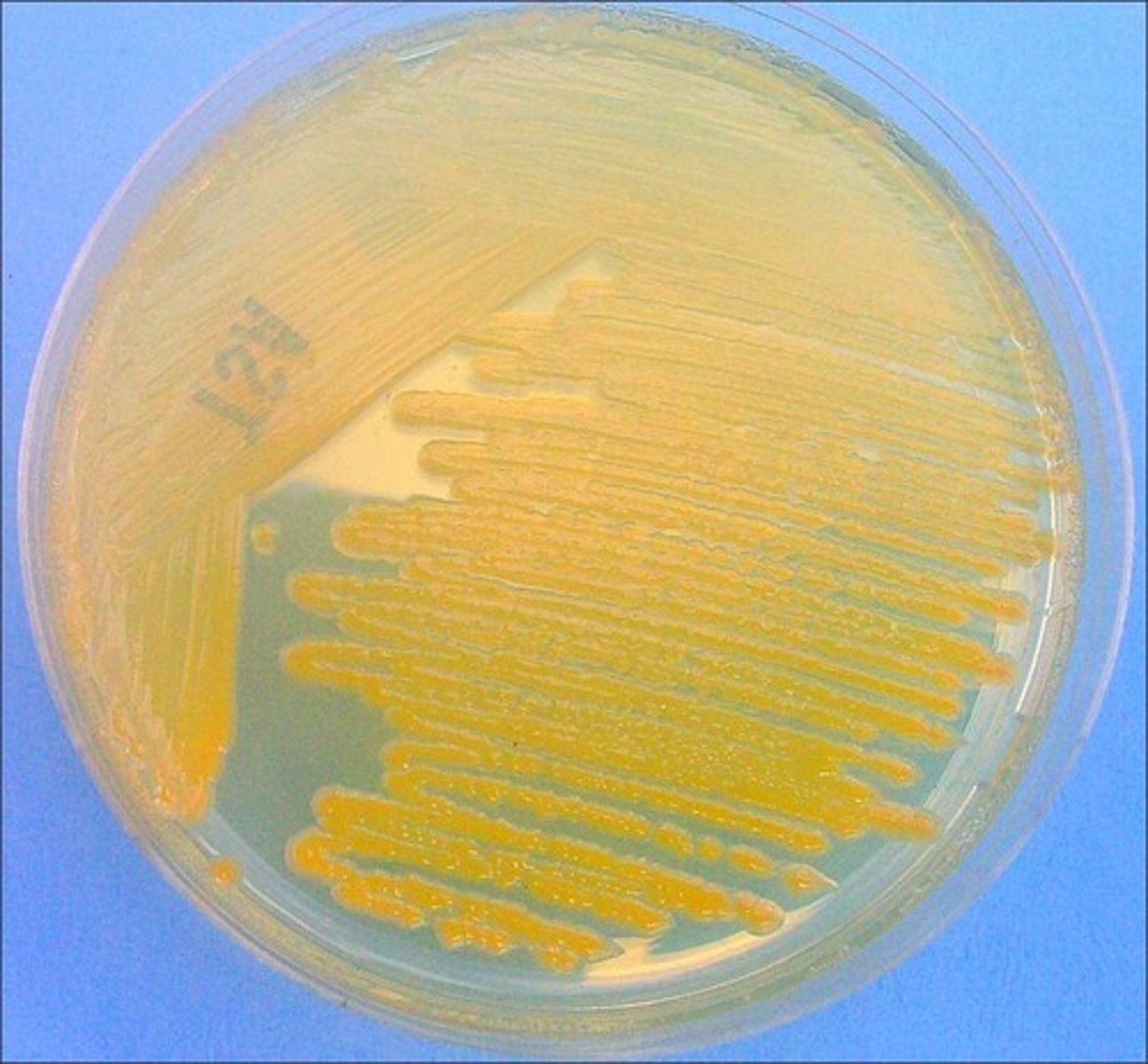
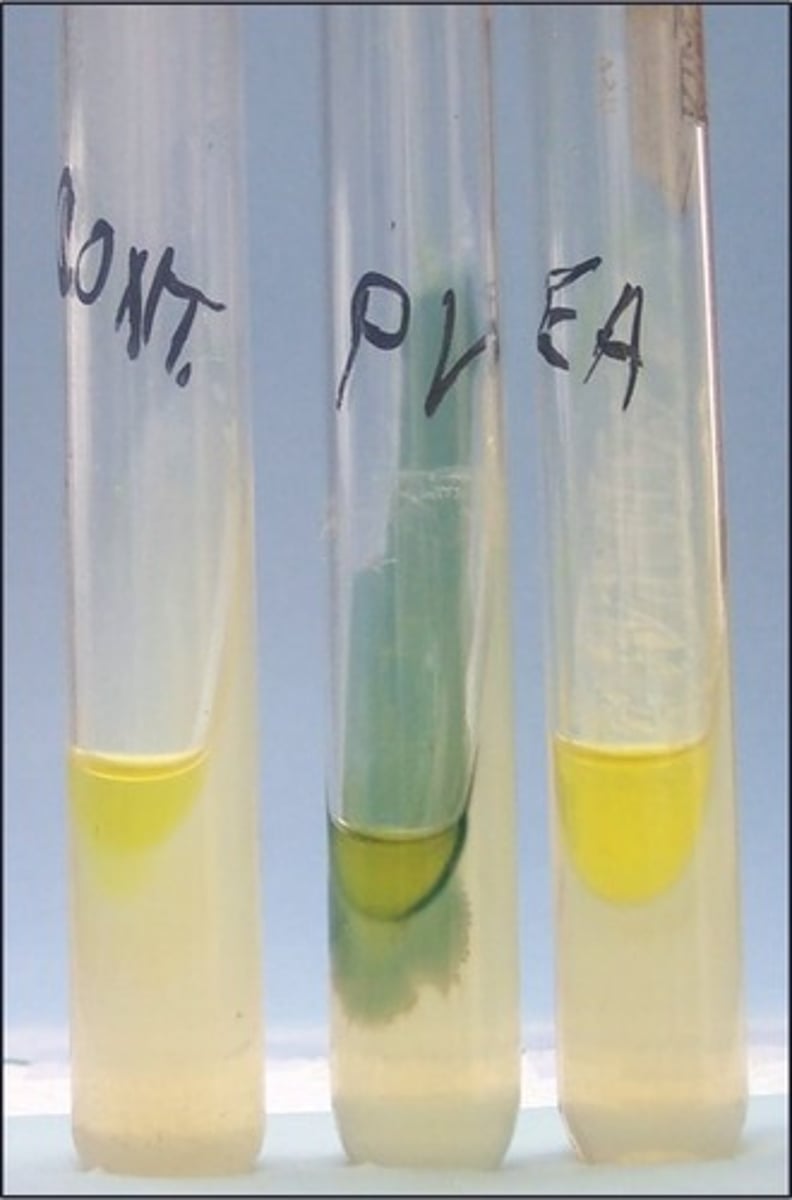
selective for gram positive
not differential
phenyl ethyl alcohol inhibits gram negatives
PEA
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
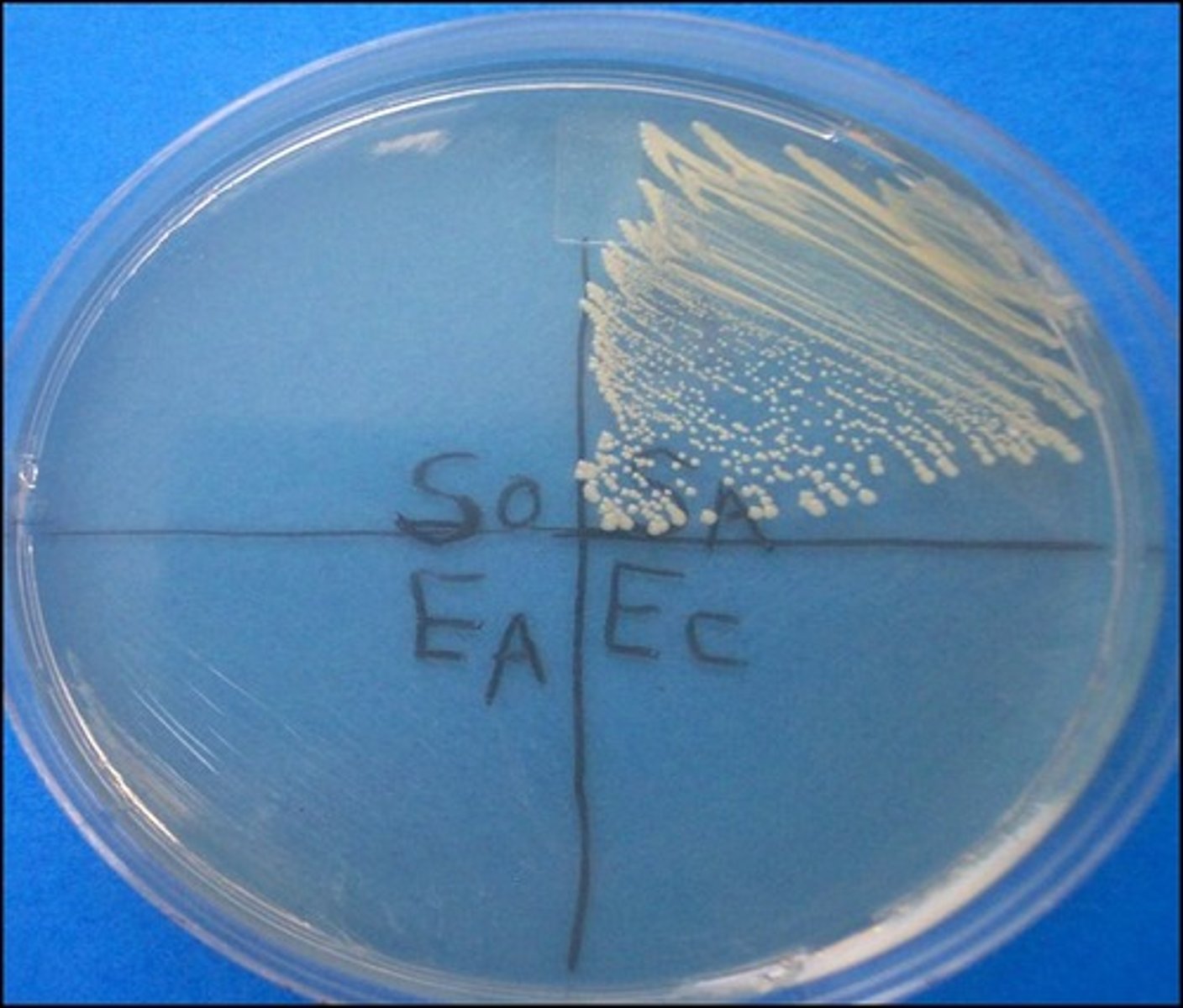
selects for gram negative
defferentiates lactose fermenters
eosin Y, methylene blue inhibit gram positives
EMB
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
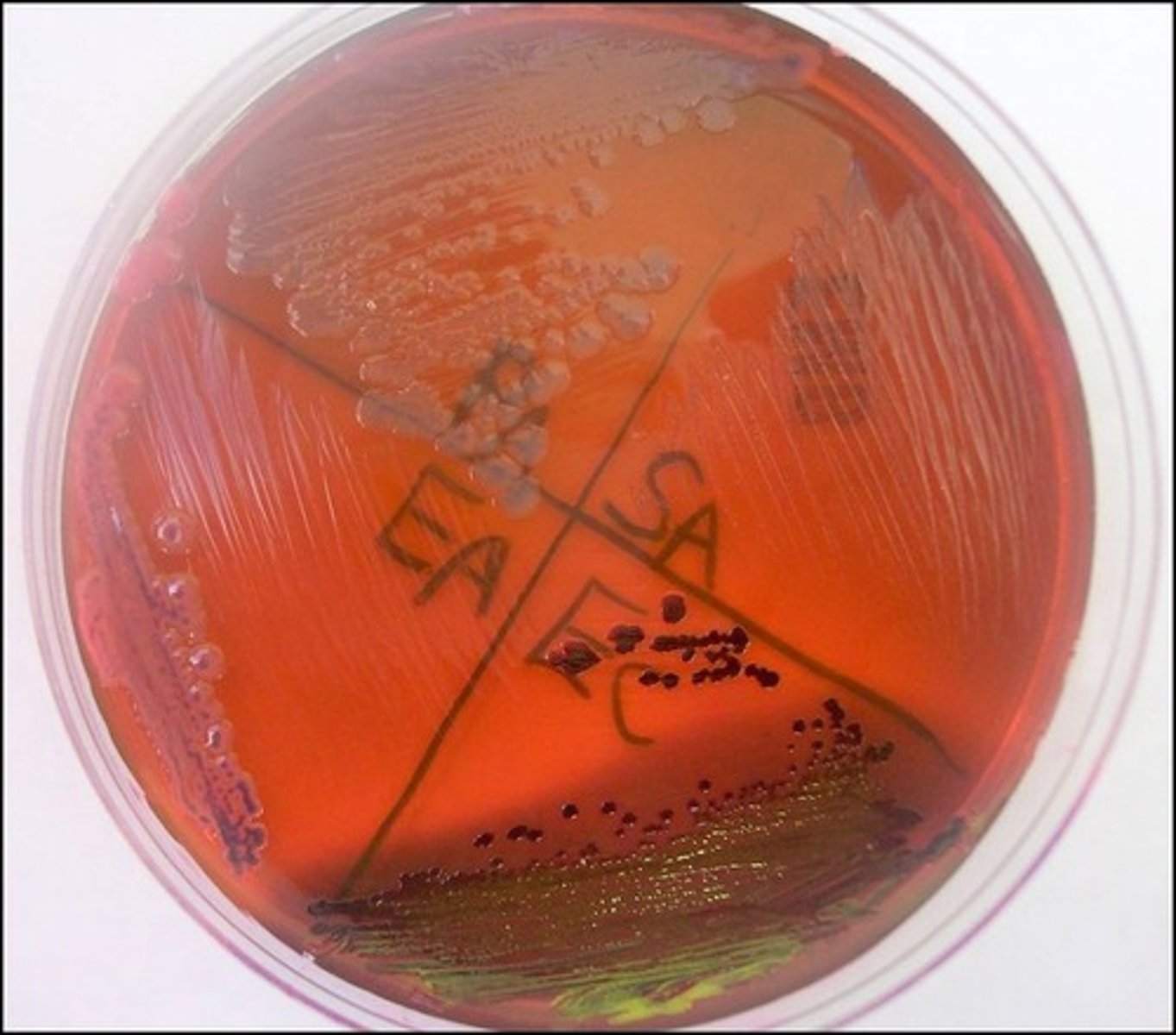
metallic green sheen
On EMB, E. coli produces a
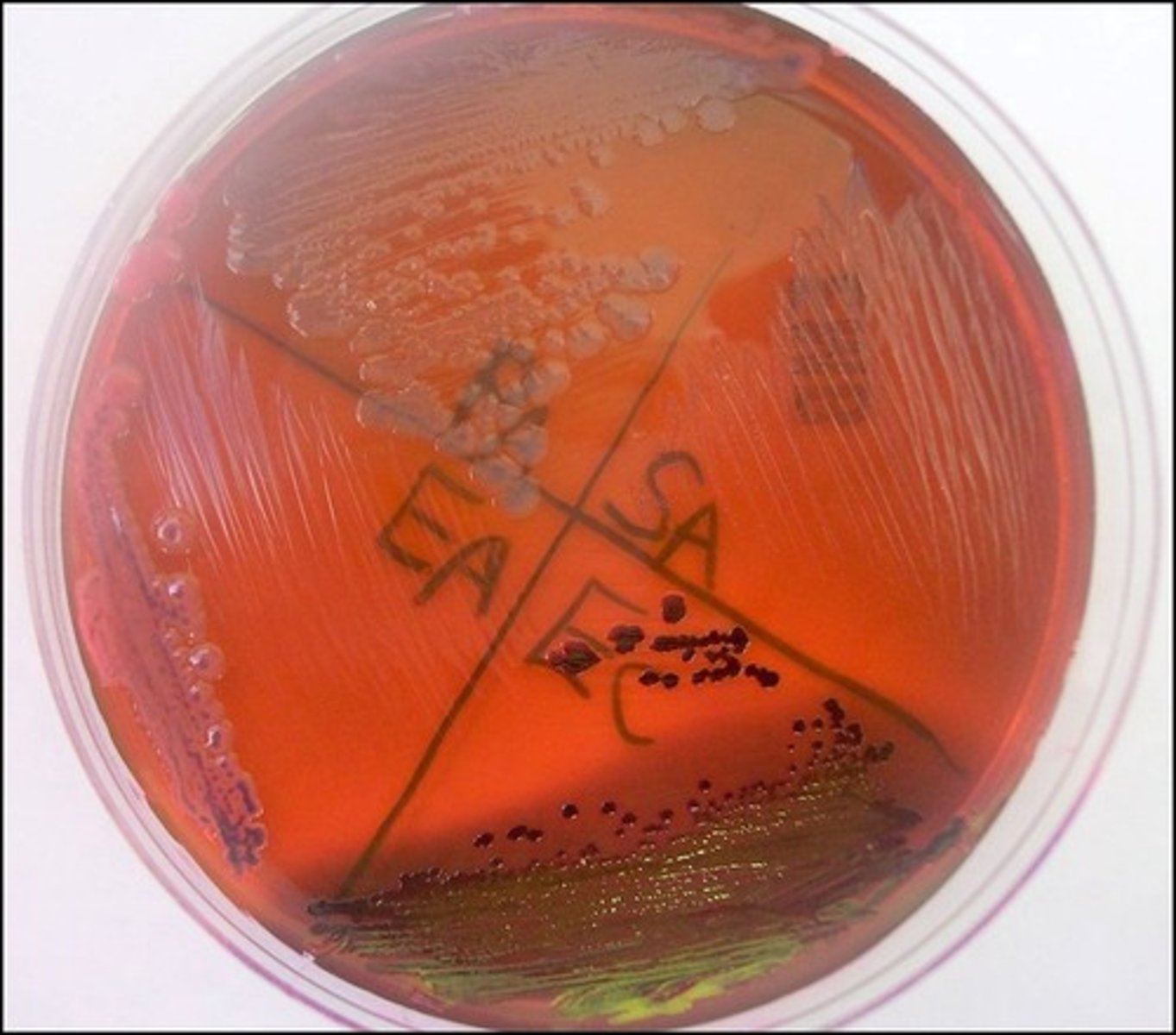
pale pink to lavender center
On EMB, E. aerogenes produces a
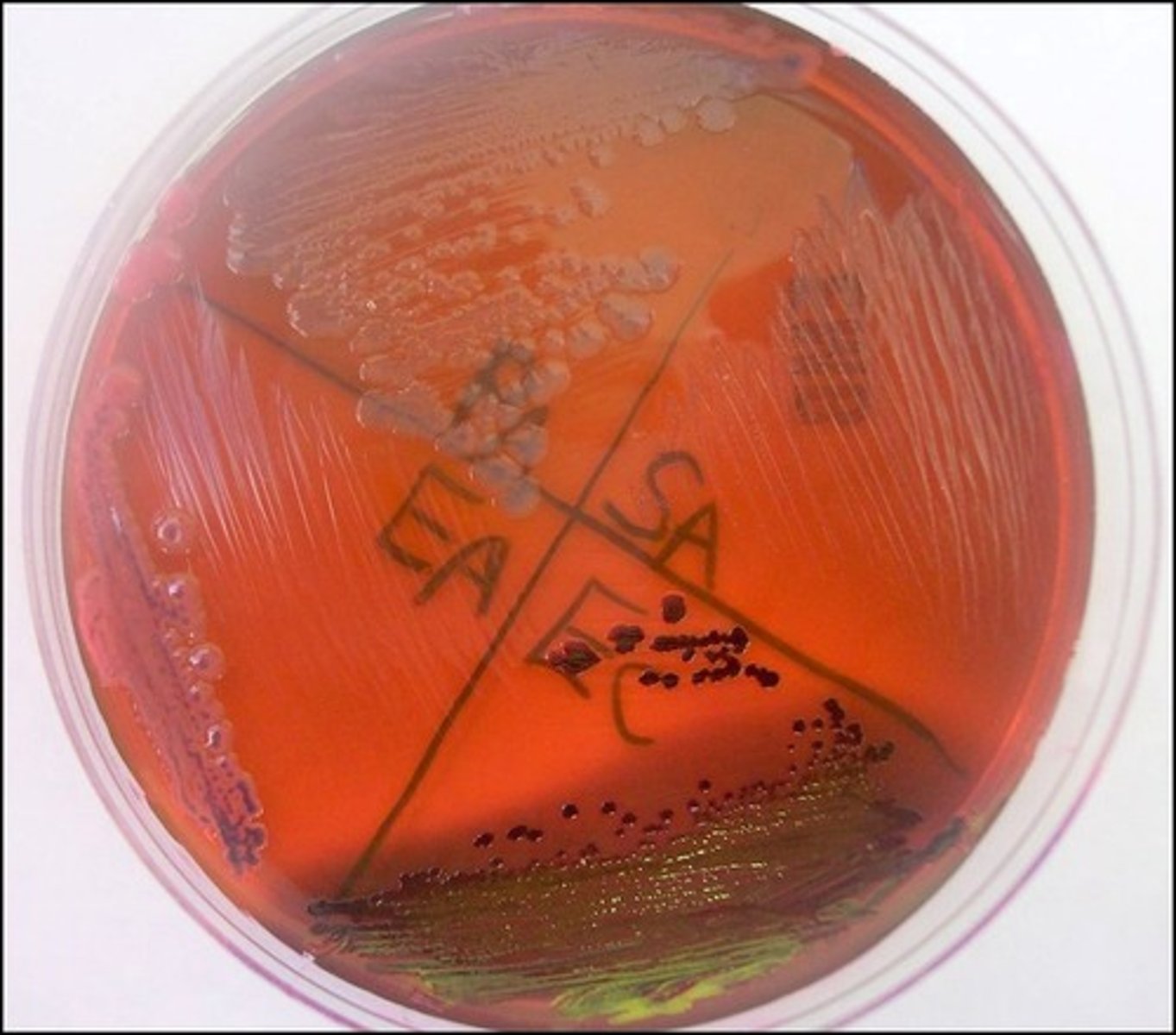
not a lactose fermenter
Based on the picture, P. aeruginosa is
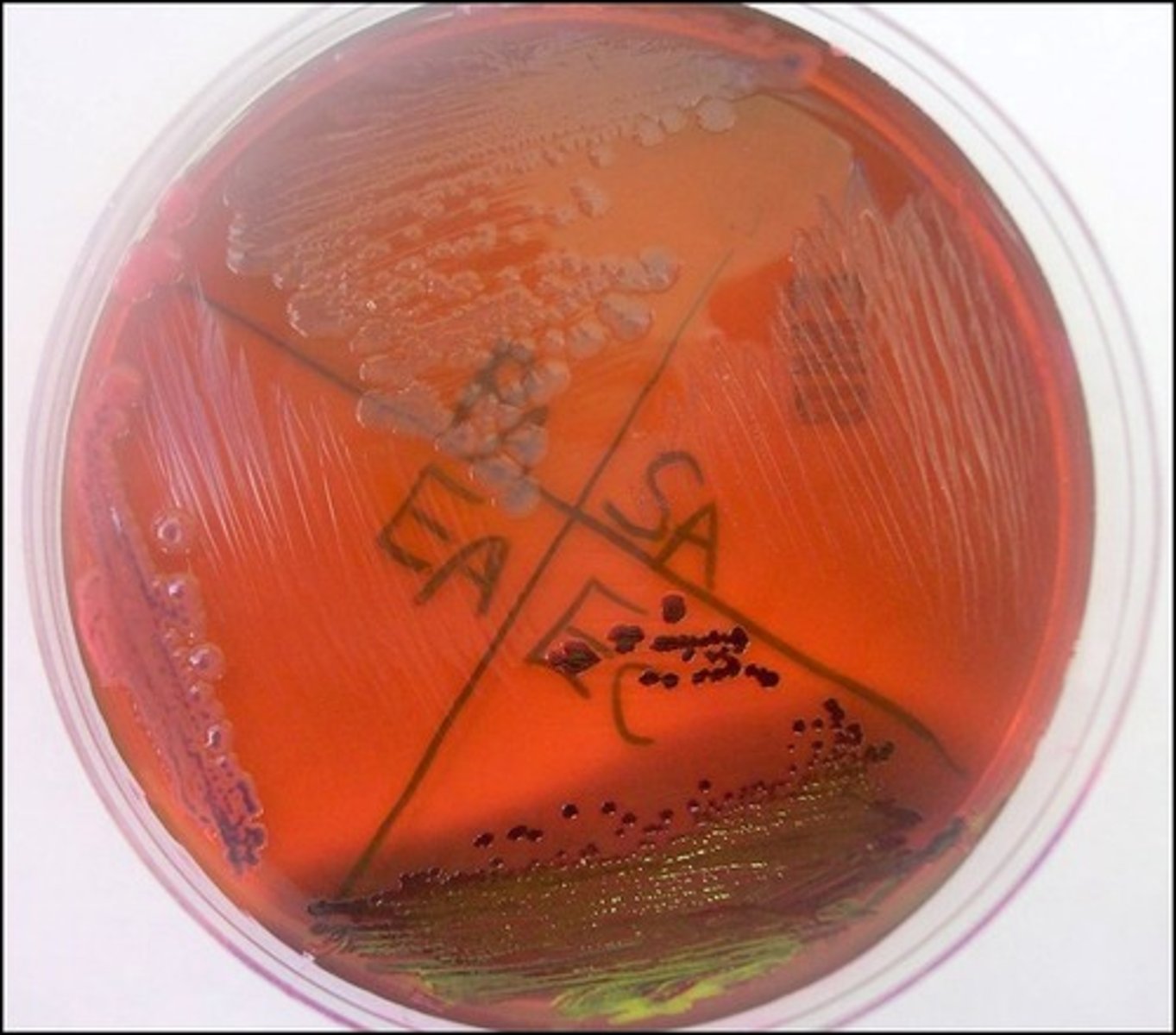
selects for gram negative
differentiates lactose fermenters
neutral red is absorbed by lactose fermenters
desoxycholate inhibits growth of gram positives
DES
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
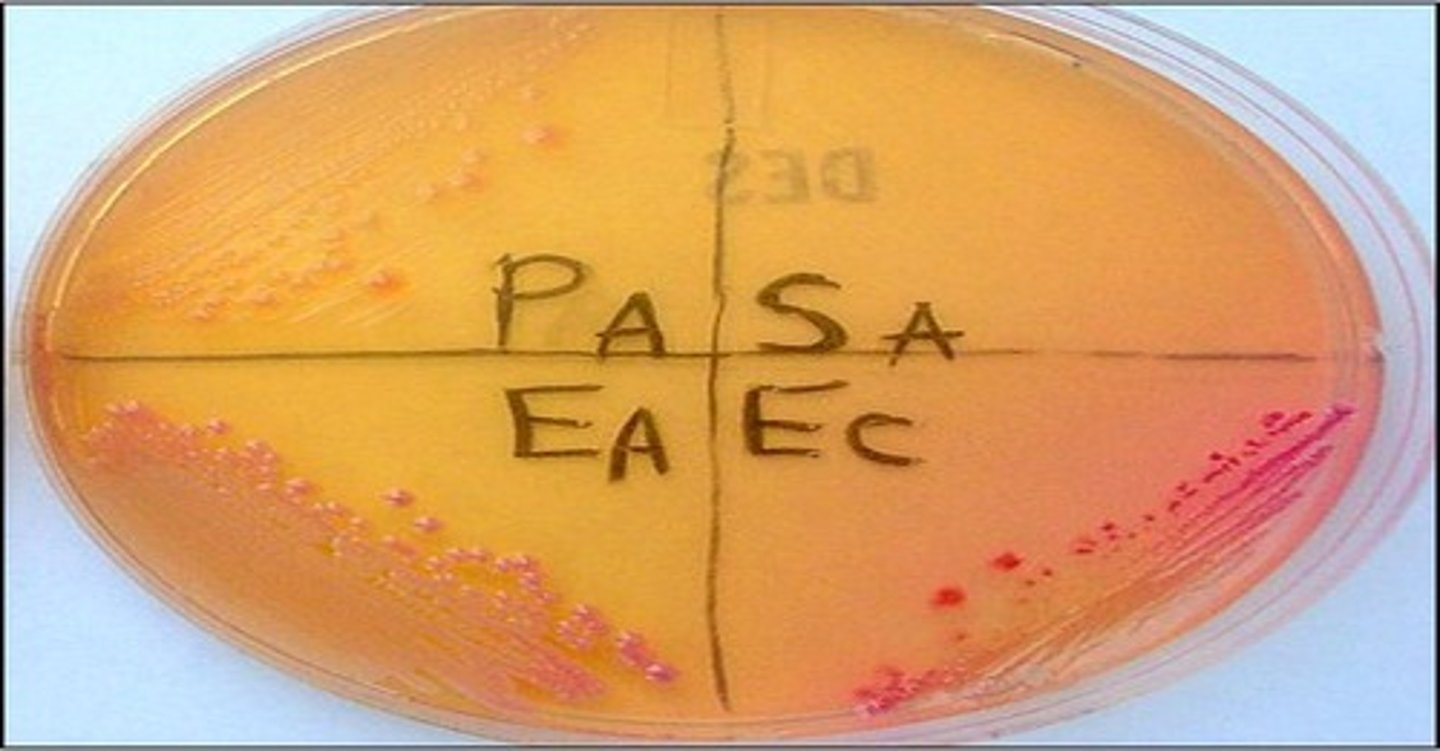
selects for gram negative
differentiates lactose fermenters
neutral red absorbed by lactose fermenters
bile salts, crystal violet inhibit gram positives
MAC
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
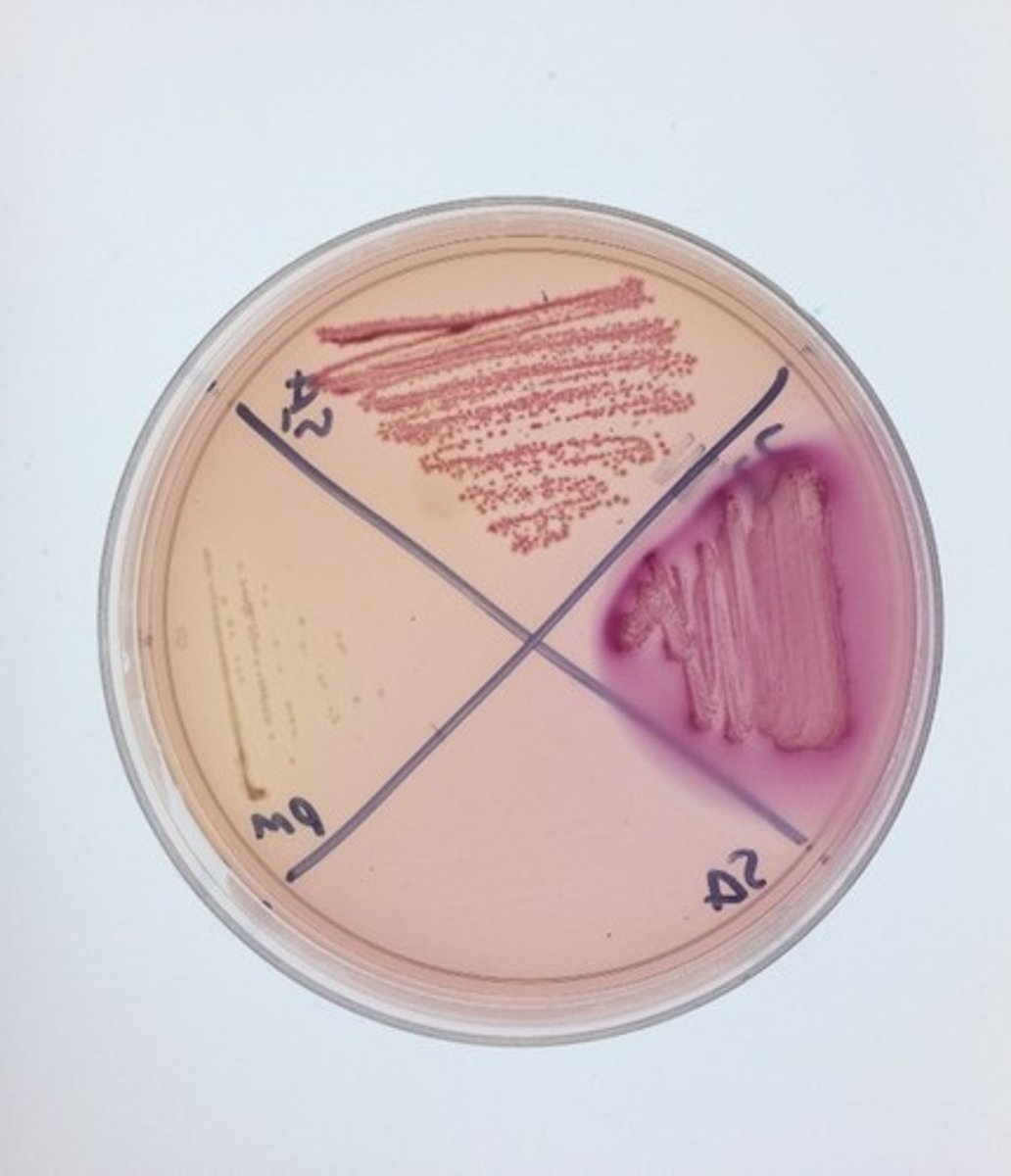
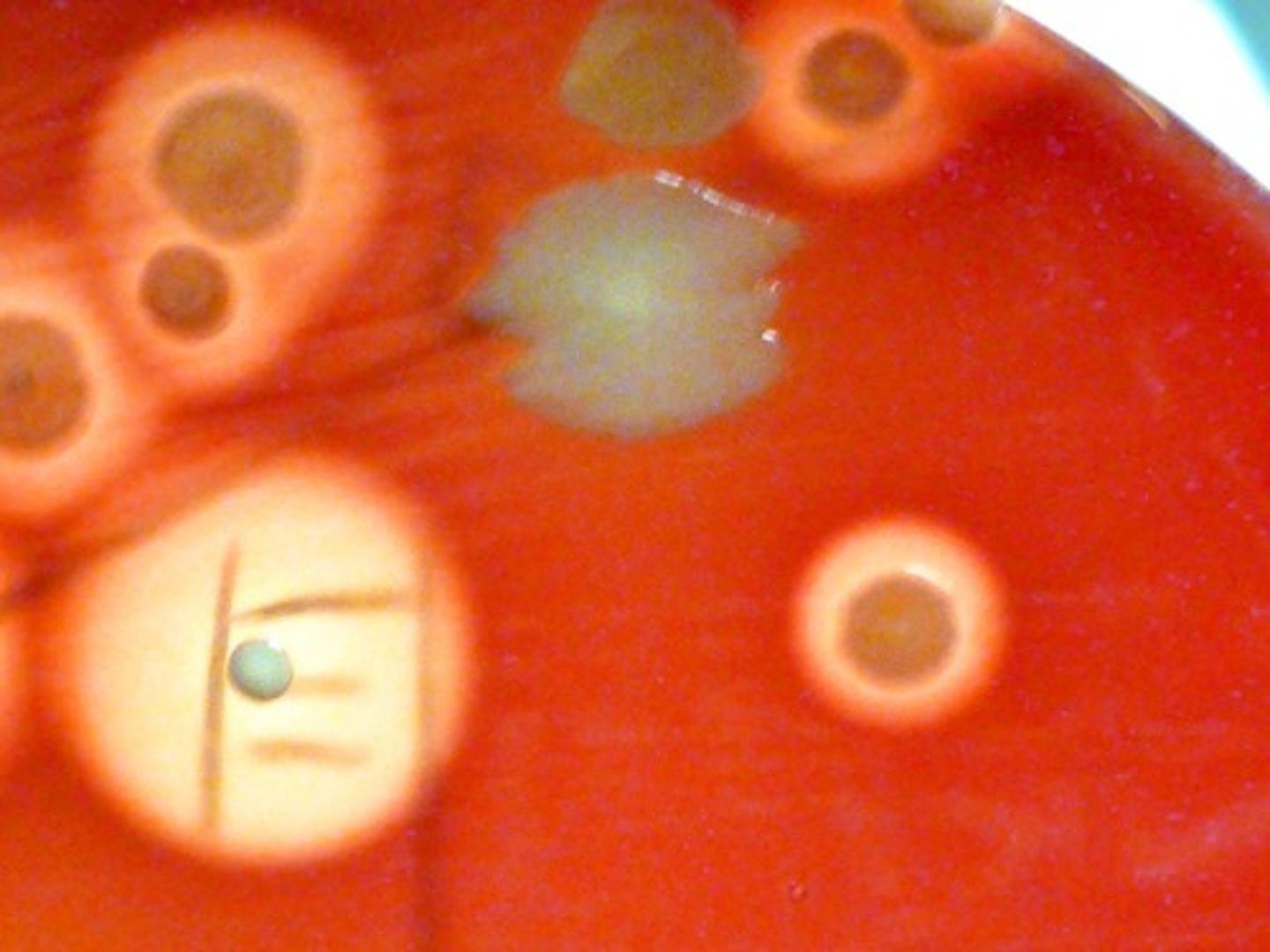
not selective
differentiates based on RBC hemolysis
5% sheep RBC used as hemolysis indicator
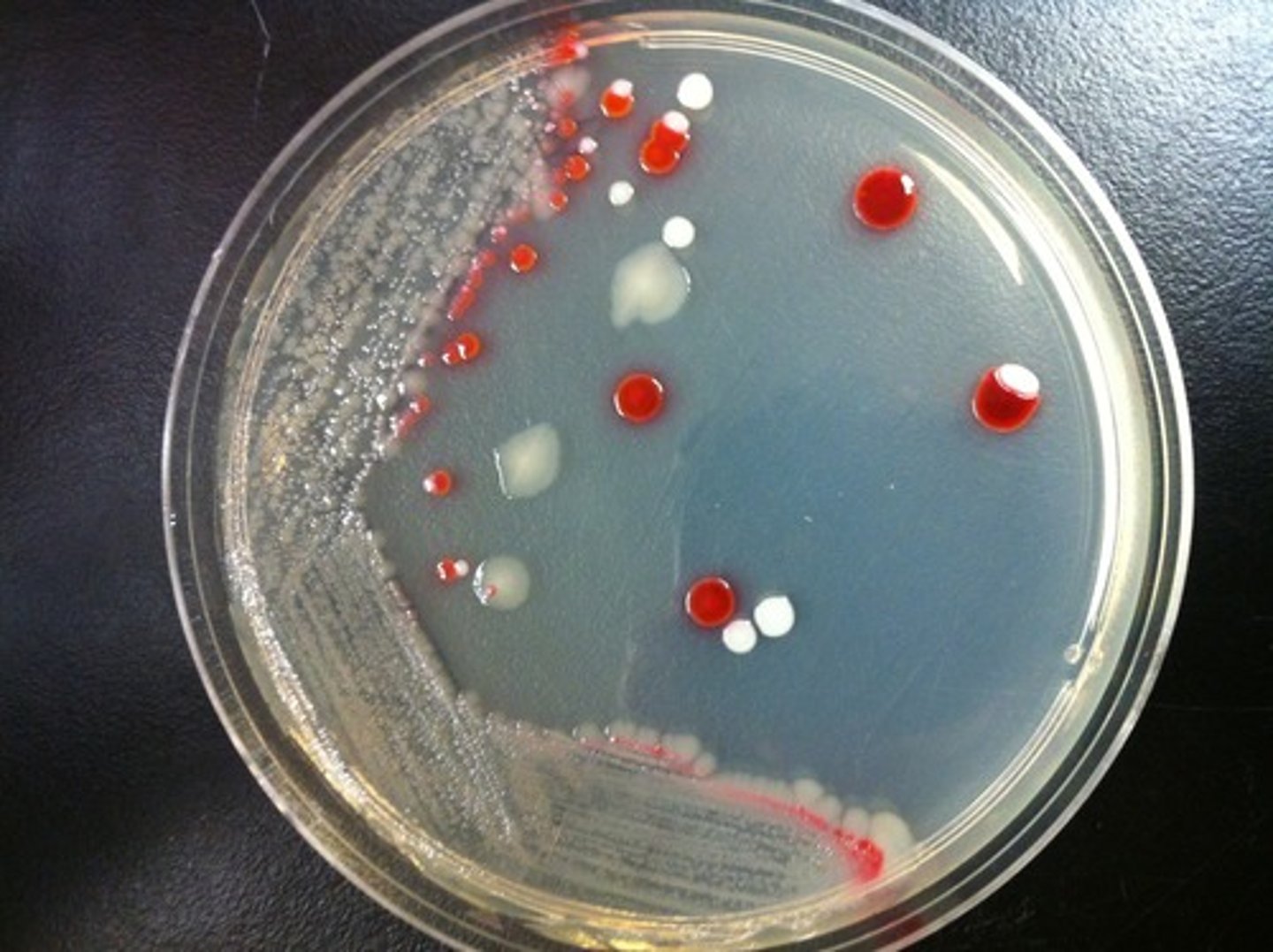
Blood Agar
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
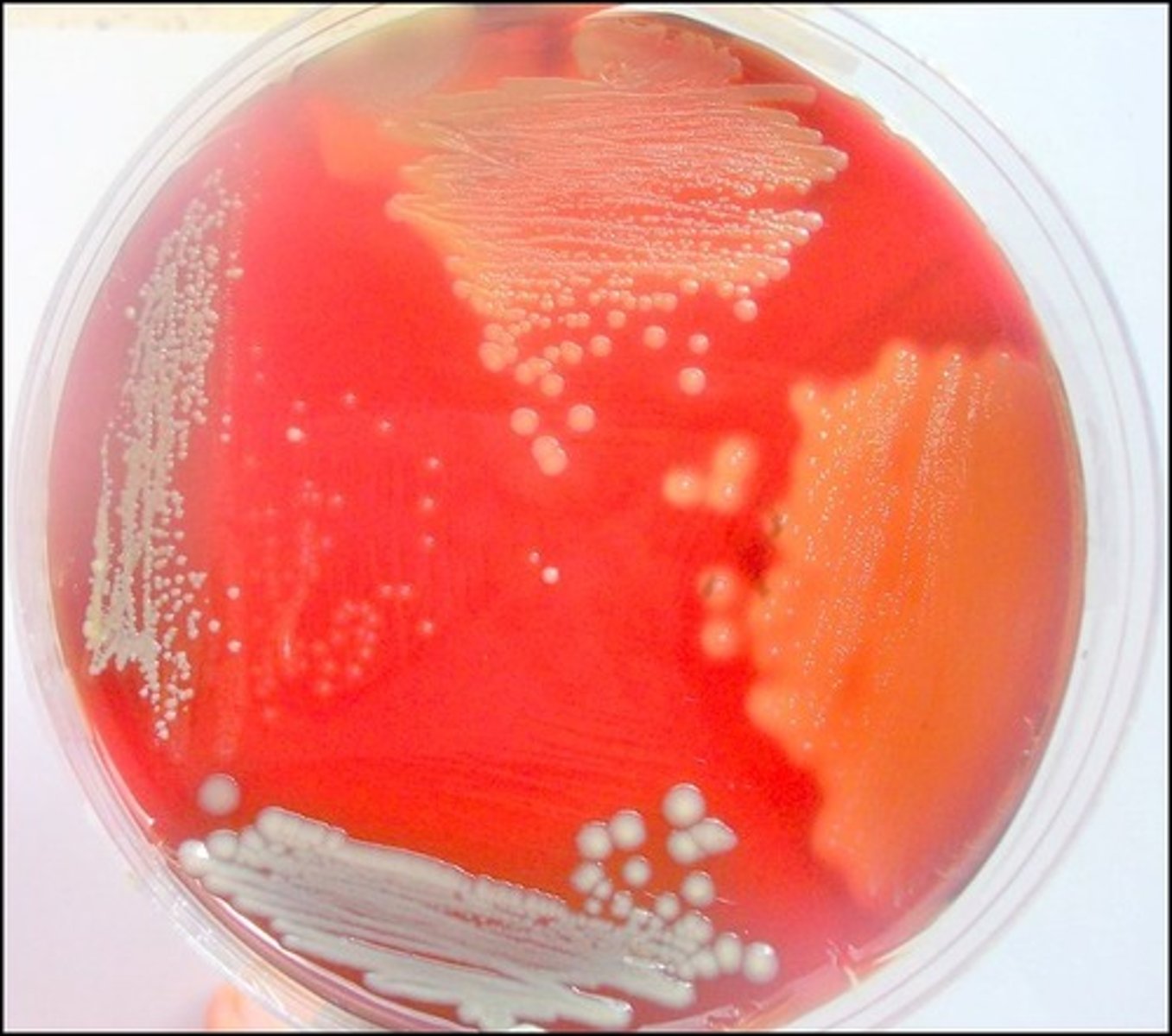
beta hemolysis
Organisms with the clear ring exhibit
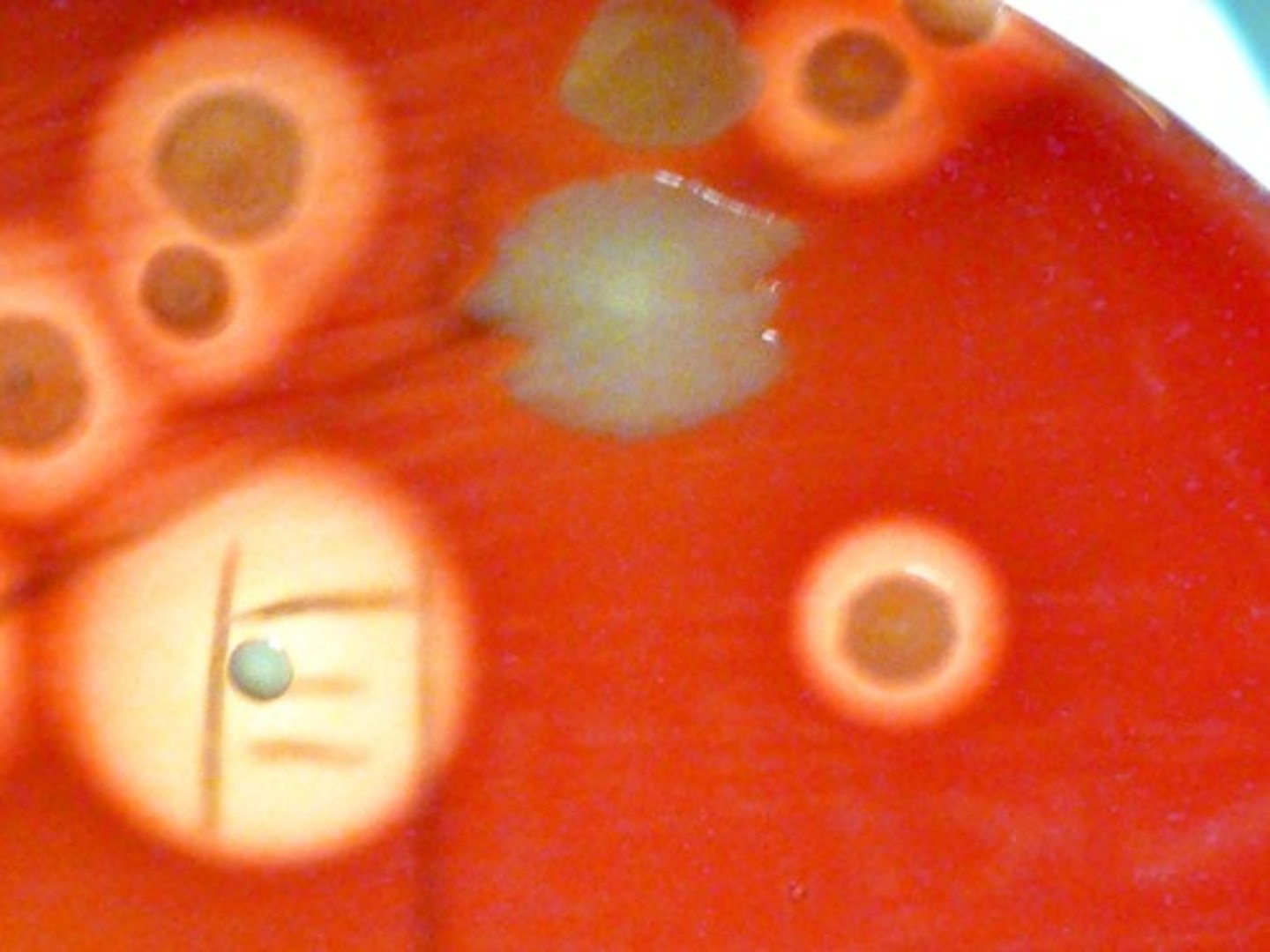
alpha hemolysis
Organisms with the cloudy ring exhibit
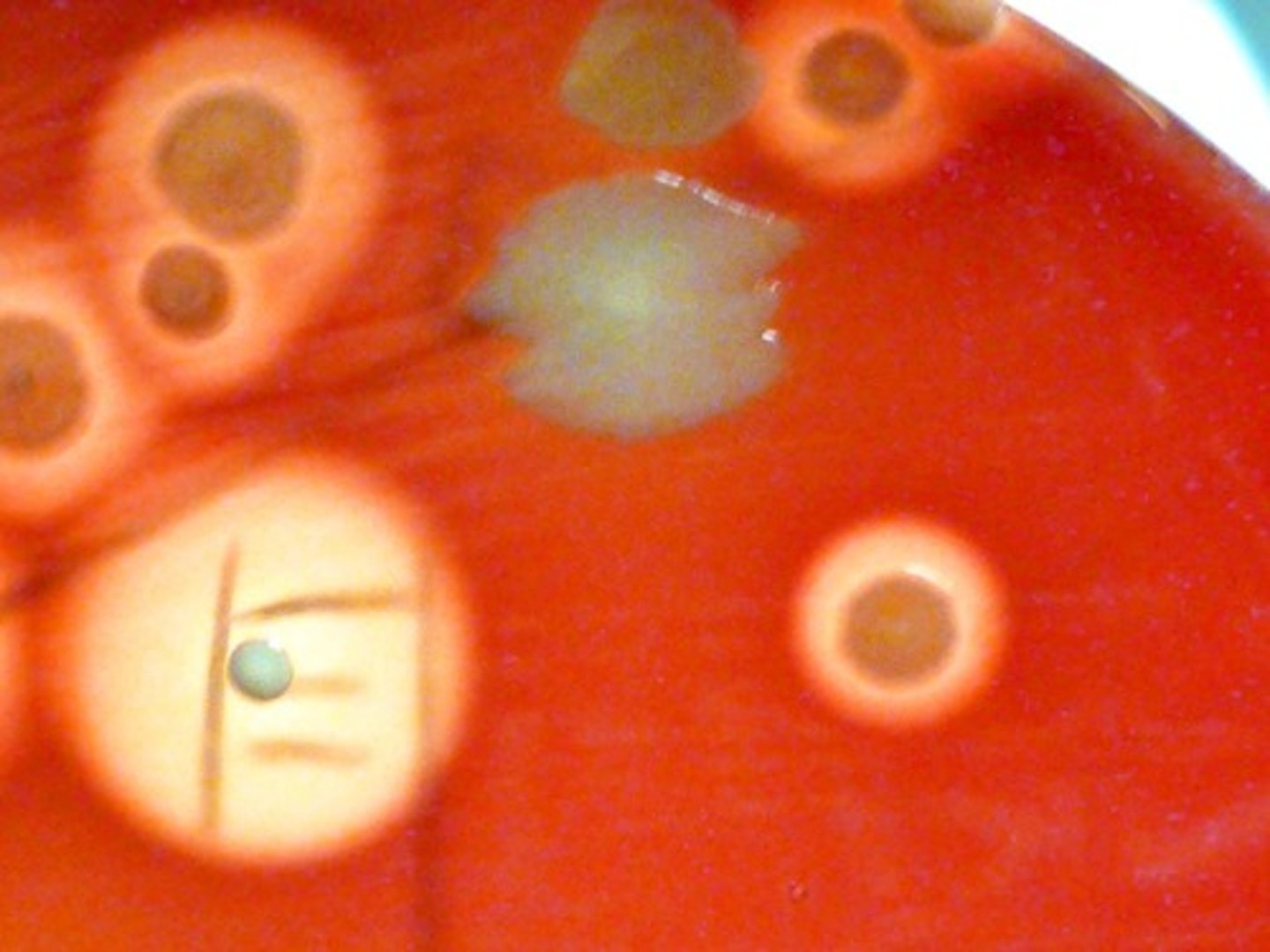
gamma hemolysis
Organisms with no ring exhibit
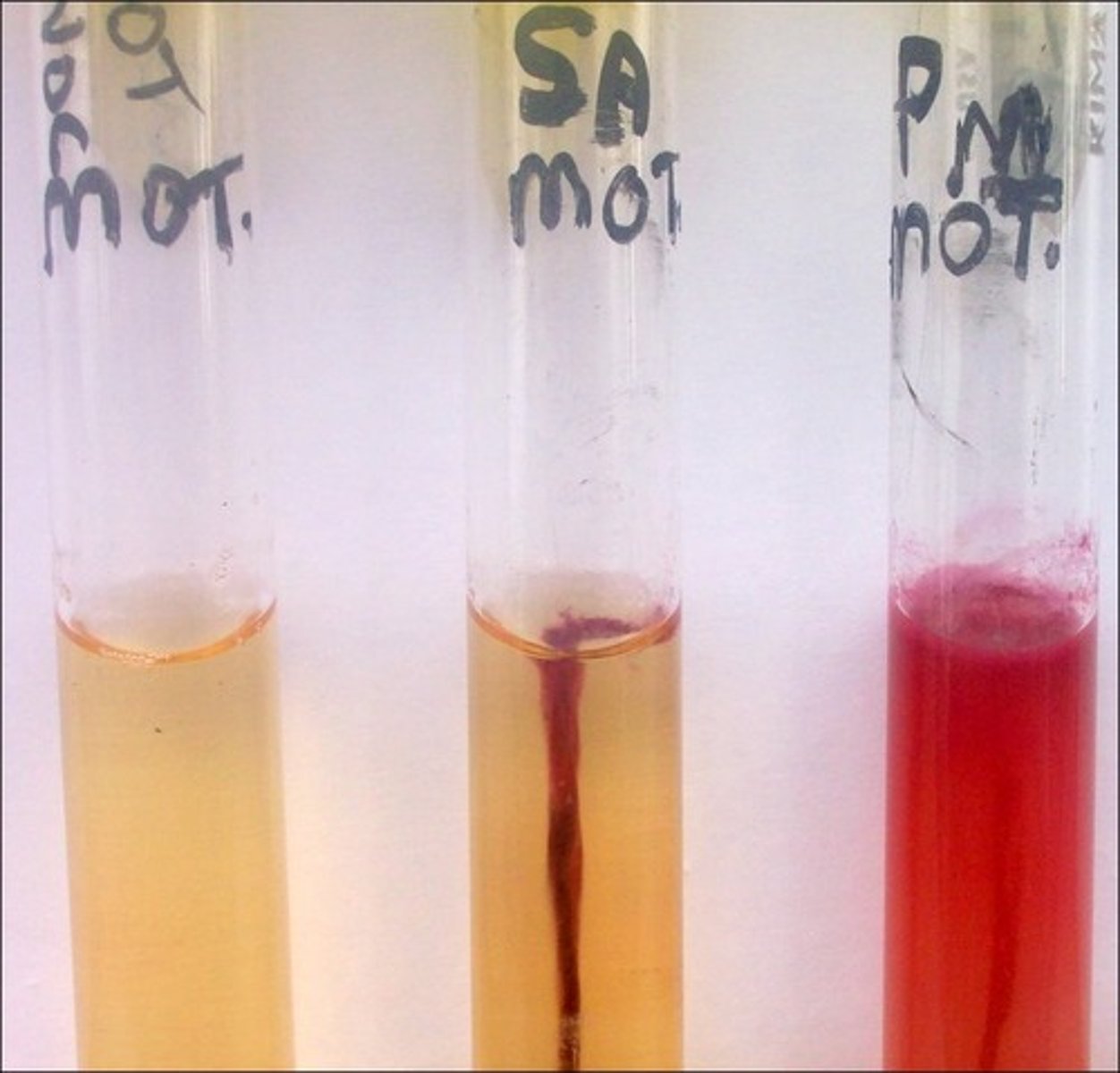
motility test
This is an example of a
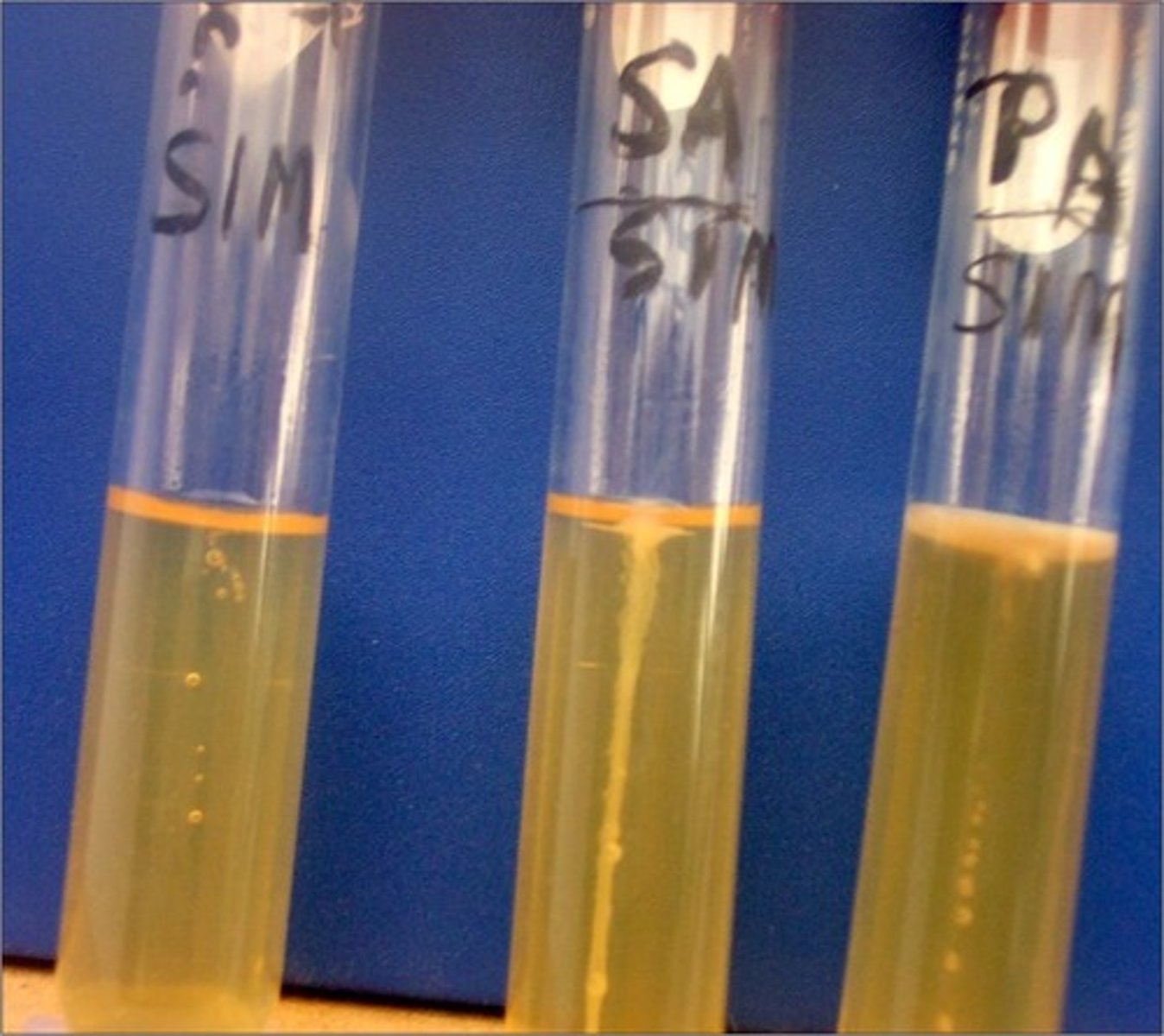

tetrazolium chloride
The dye in this procedure is

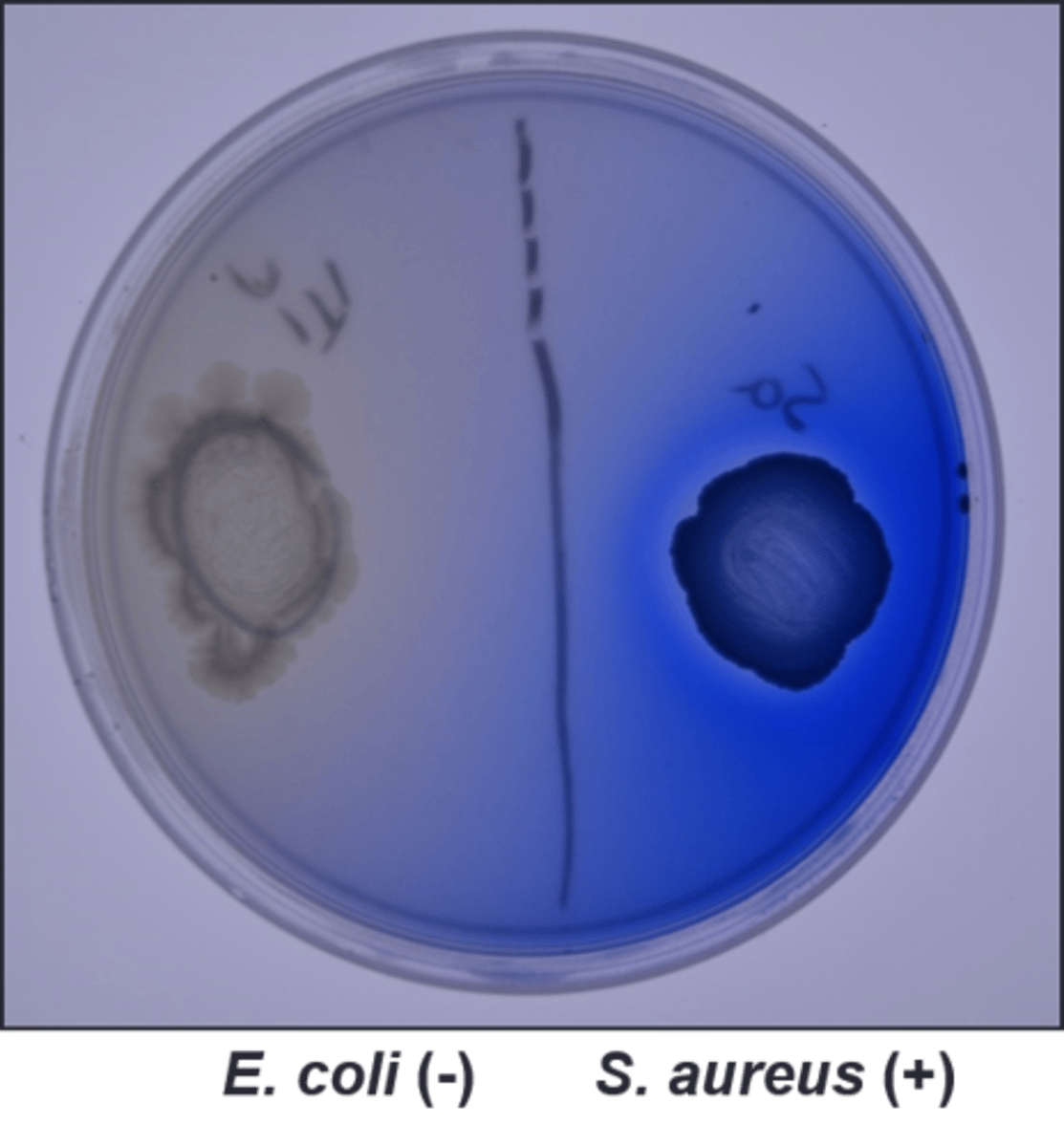
not selective
differentiates based on lipase production
spirit blue dye around the growth indicates lipase production
Lipase Plate
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
not selective
differentiates caseinase producers
casein in the milk is broken down, made clear in place of caseinase
Milk Agar
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
not selective
differentiates amylase producers
iodine added to edge of growth. if it has a clearing around organism, positive for amylase
Starch Agar
Selective:
Differential:
Dyes/Reagents:
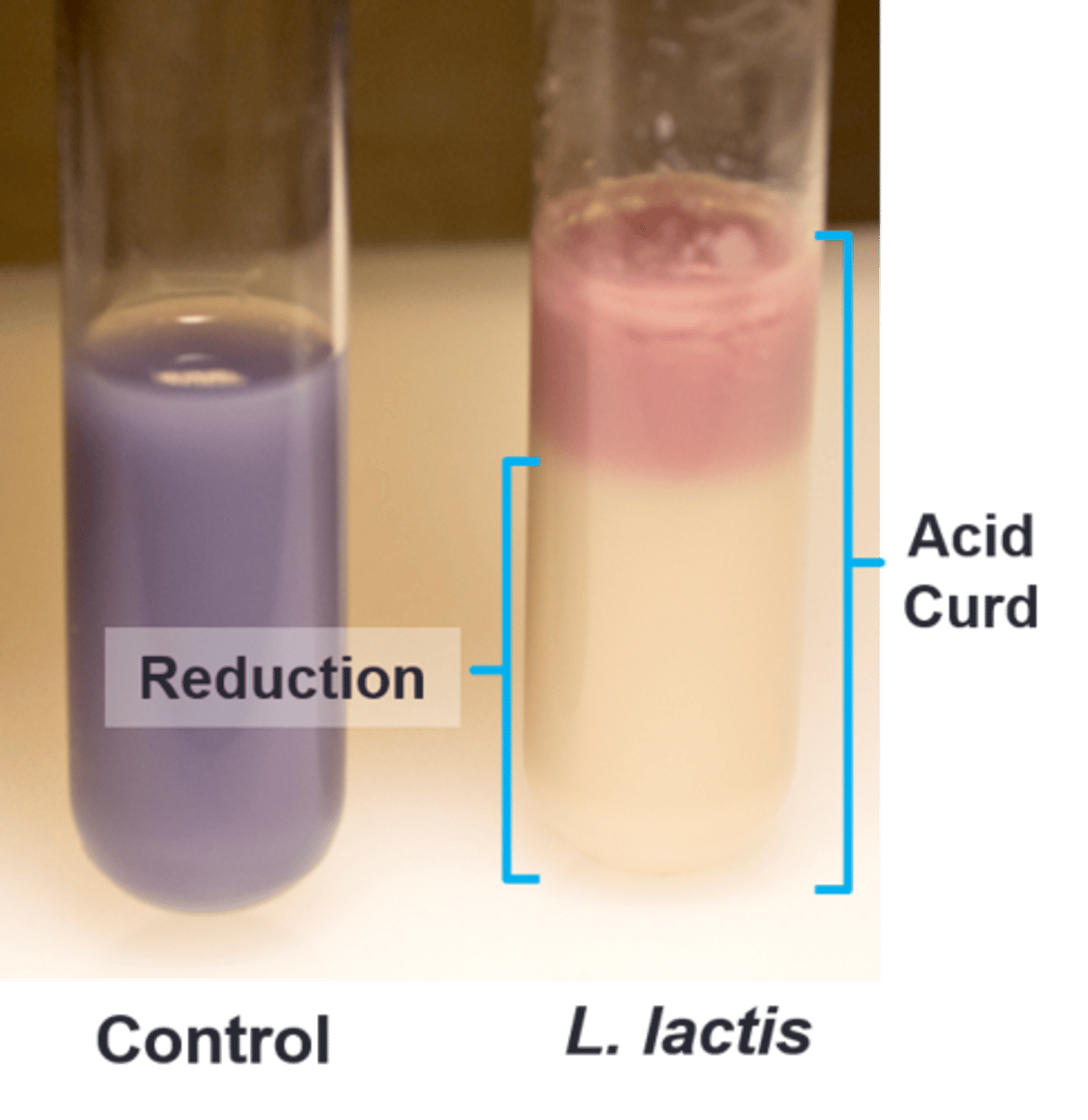
litmus milk
These tubes are filled with
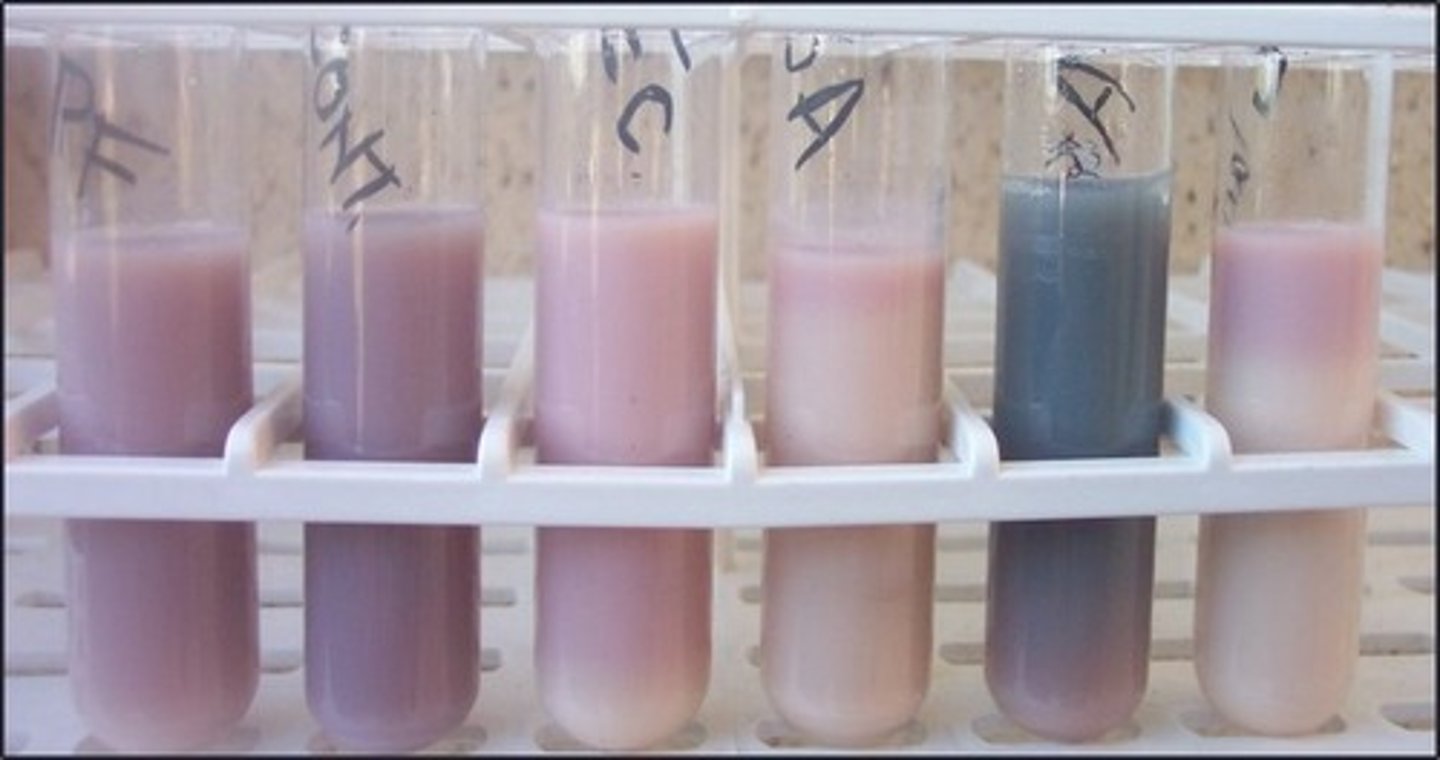

acid production in litmus milk
These are examples of a(n)

alkaline production in litmus milk
This indicates a(n)

reduced condition in litmus milk
The white indicates a(n)

oxidized condition in litmus milk
The color at the top indicates a(n)

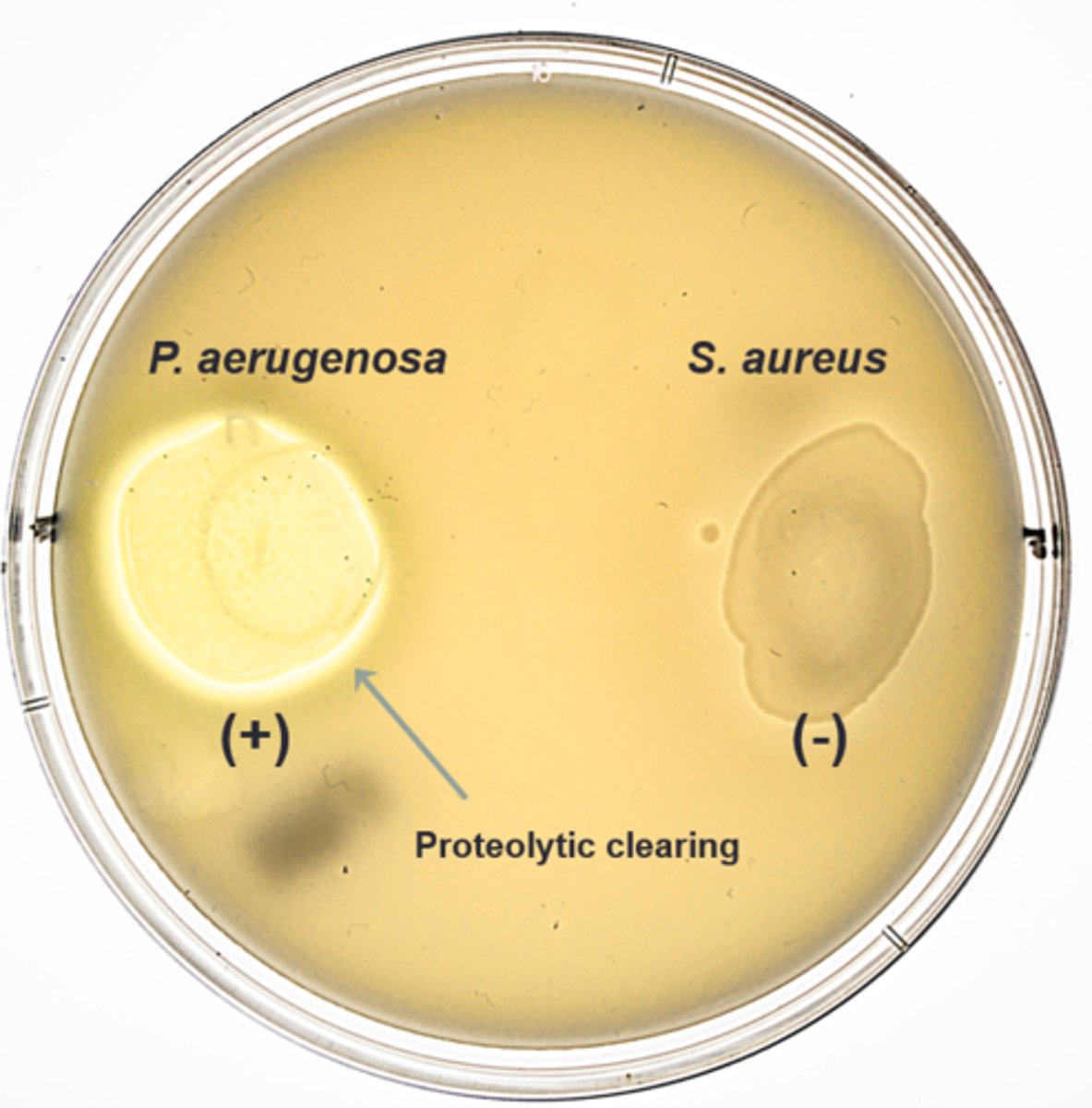
proteolysis from production of caseinase
What is happening to make the medium clear:
lactose fermentation that produces acids strong enough to denature the proteins
What causes the litmus milk to curd:
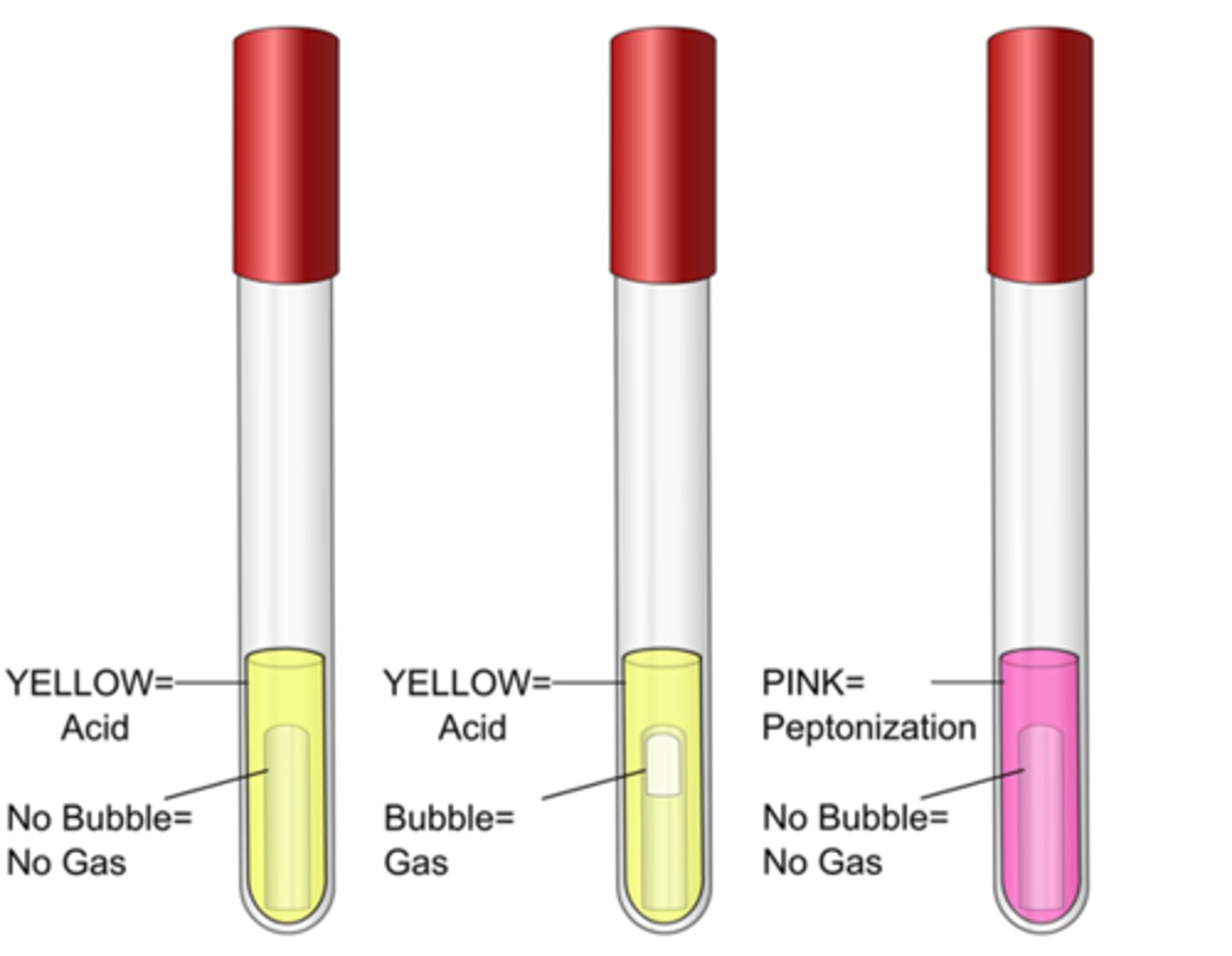
PR sugar broth
These are the results for the
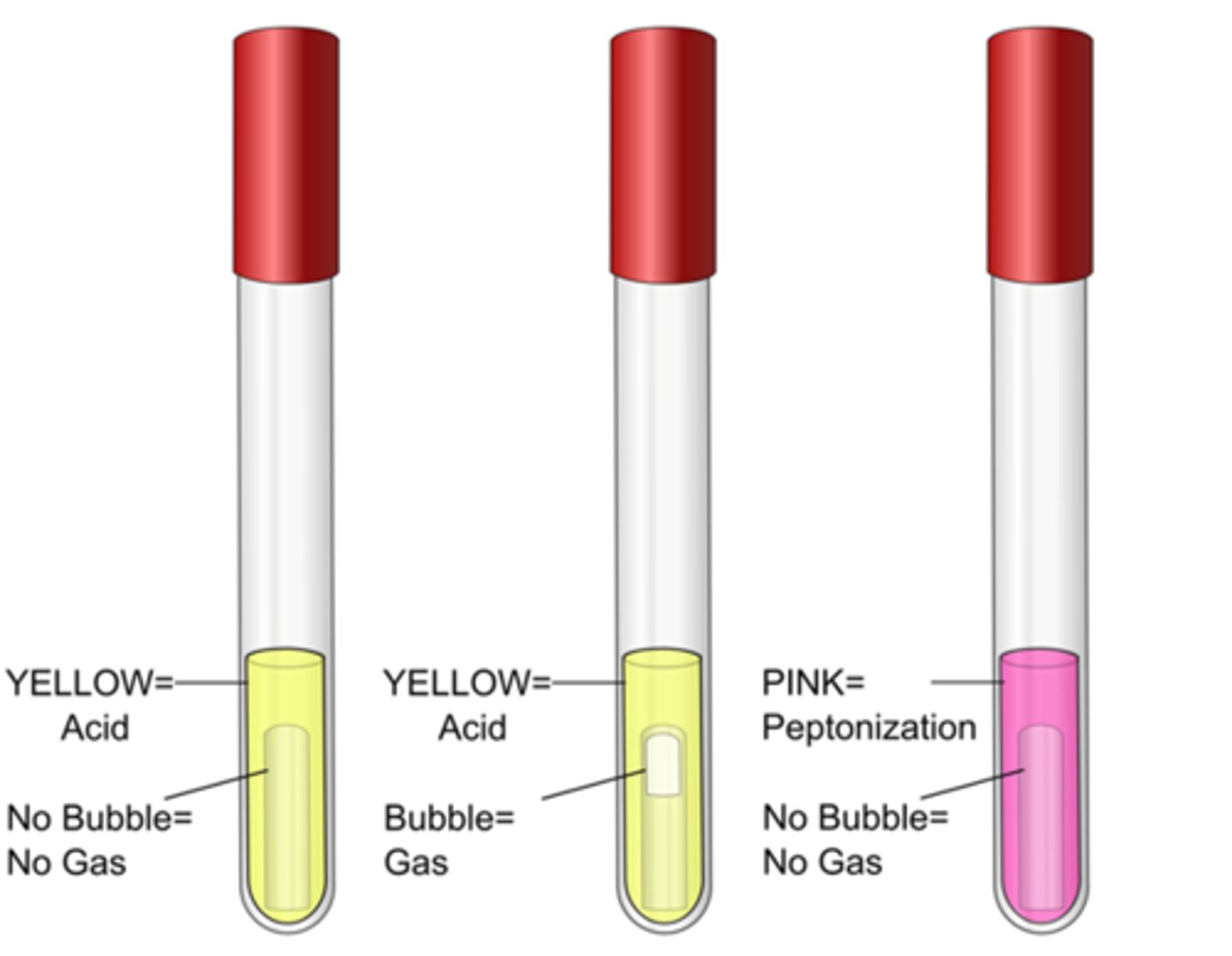
phenol red
Indicator in these tubes:
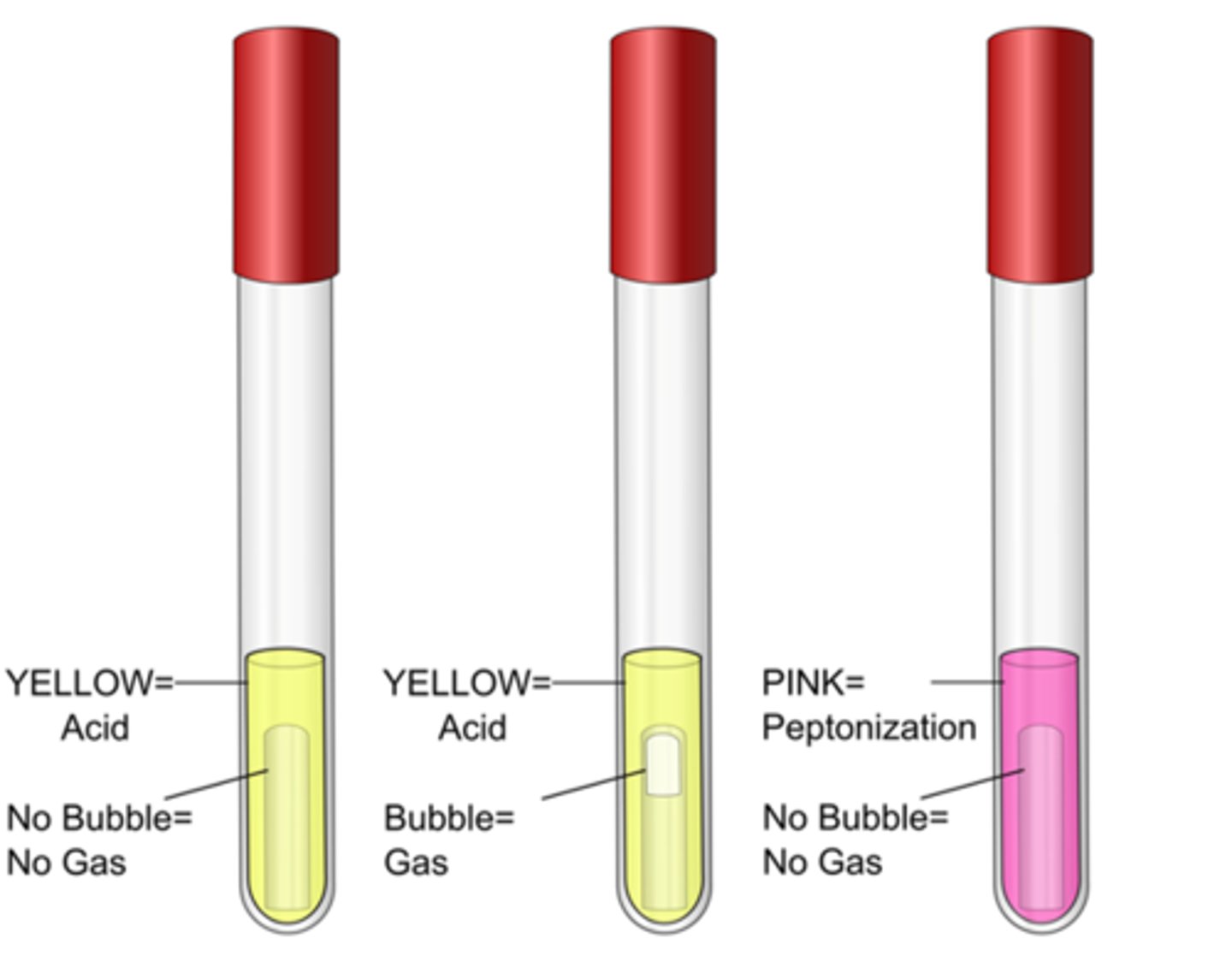
yellow, fermentation of sugar to acid (bubble present if gas formed)
Positive result color, interpretation:
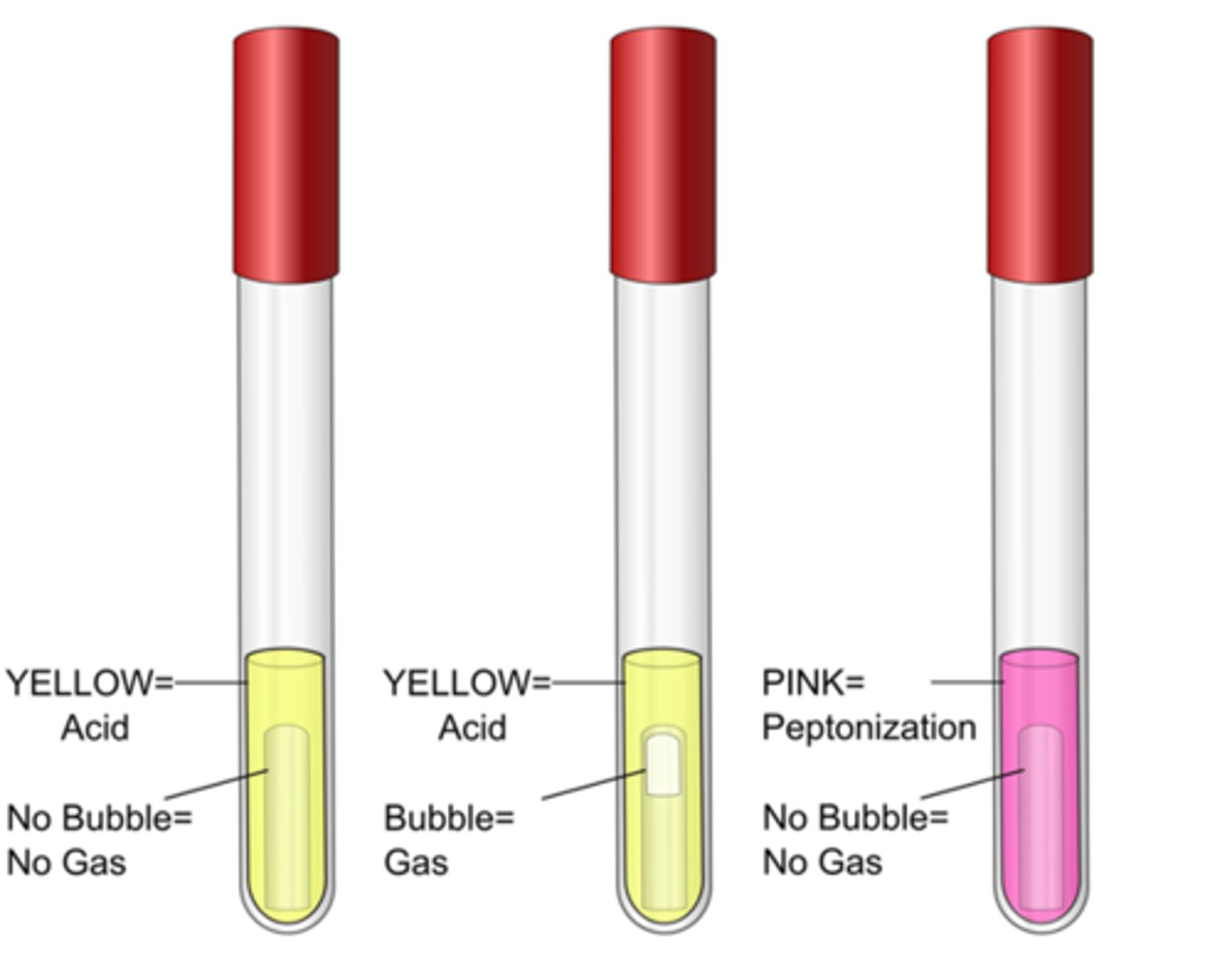
cerise (pink), peptone degredation increases pH by releasing ammonia
Negative result color, interpretation:
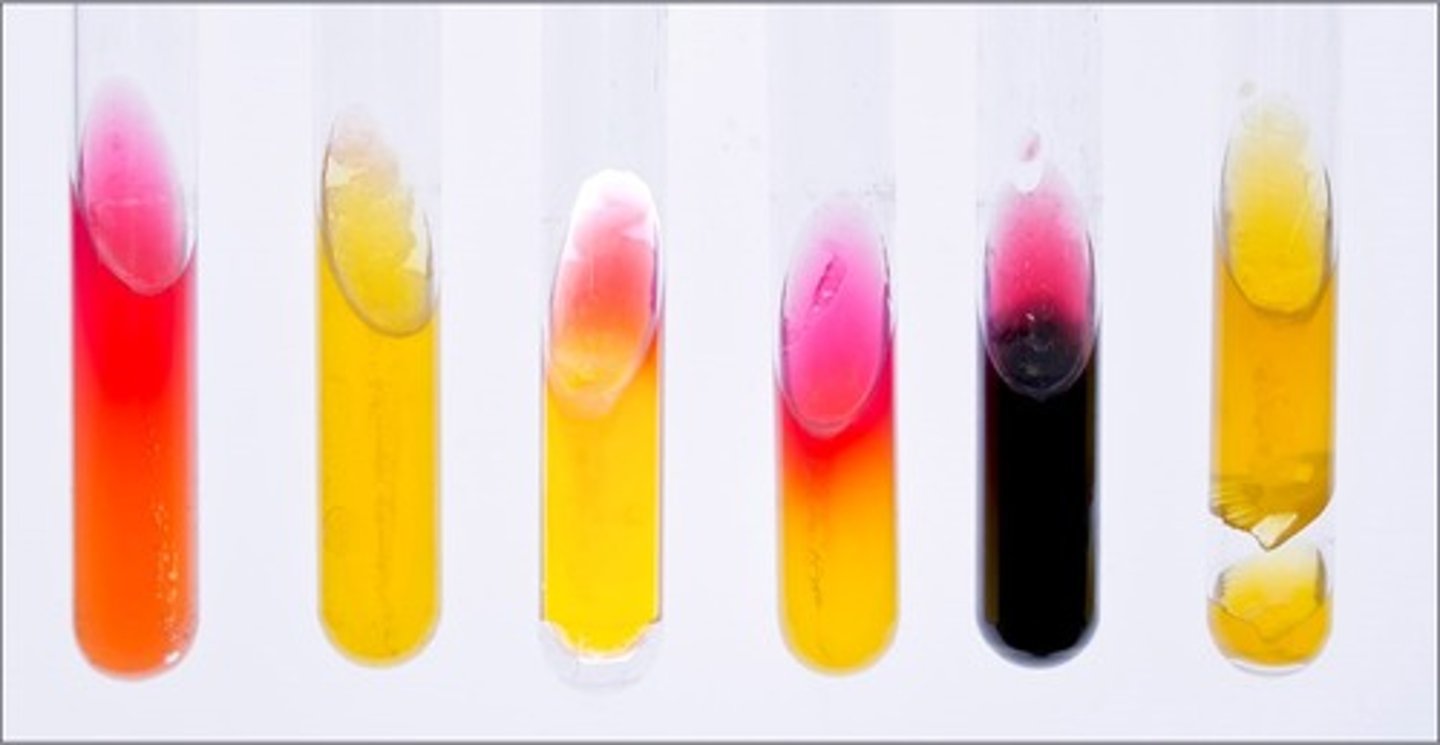
KIA/RDS media
These tubes are results from
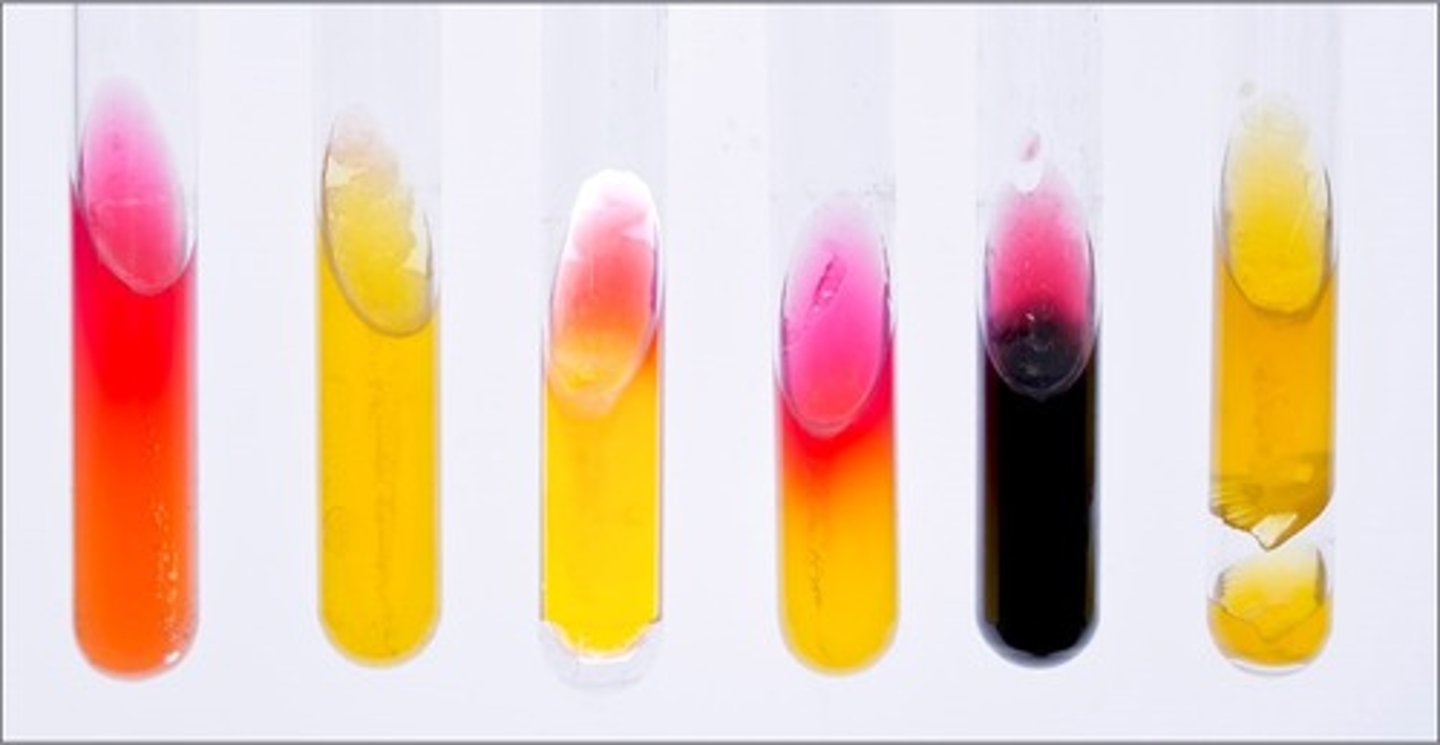

lactose and glucose fermentation
Interpretation of the 2nd tube:
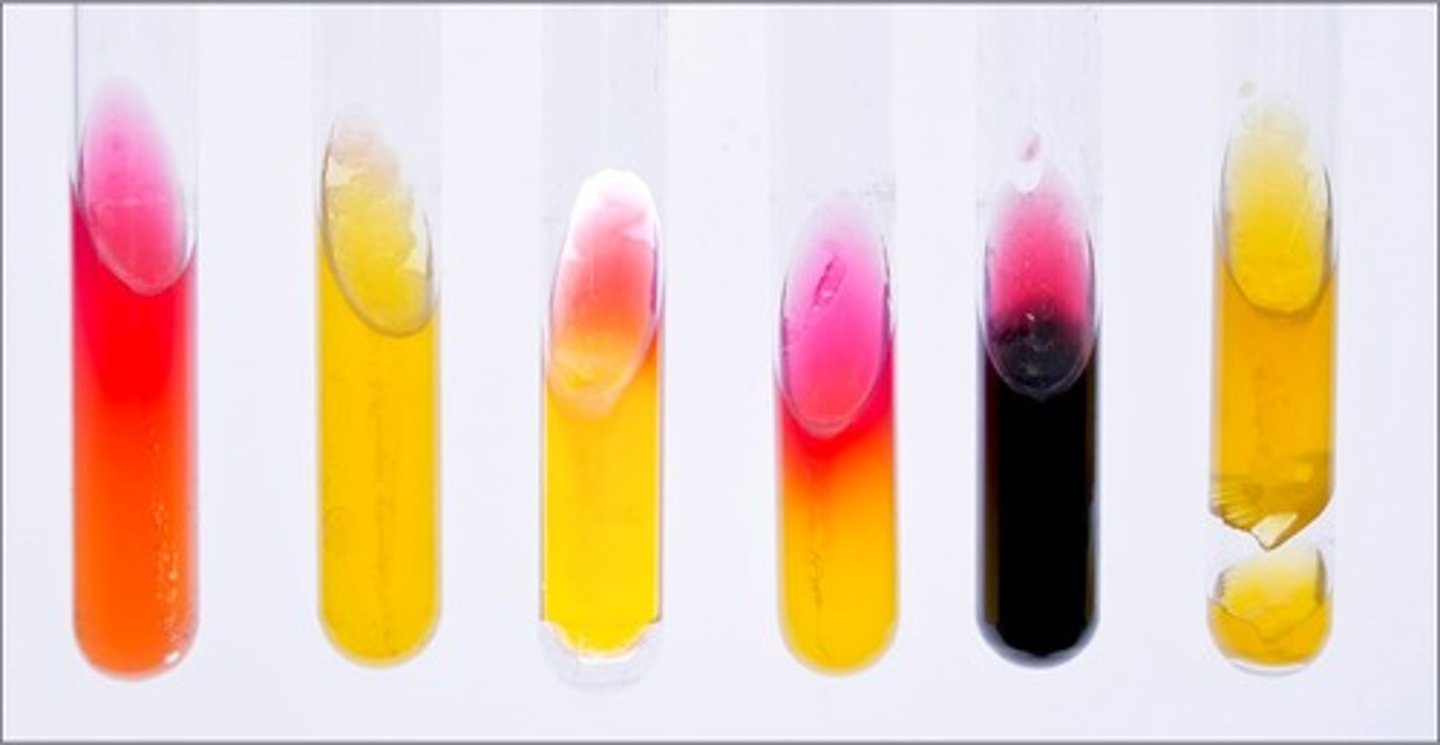

lactose fermentation by 2,3 butanediol fermenter, reversion from unstable acid products
Interpretation of the 3rd tube:
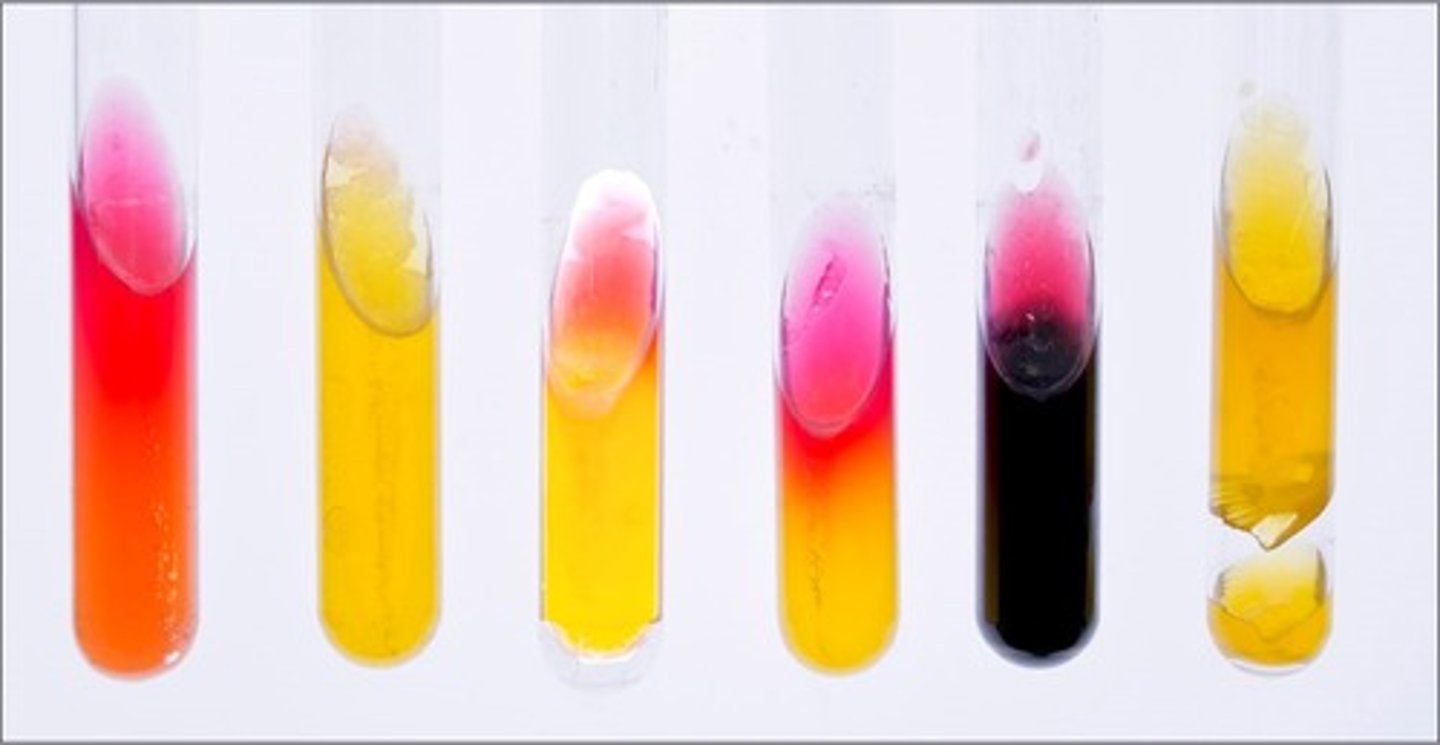

glucose fermentation and peptone degradation
Interpretation of the 4th tube:
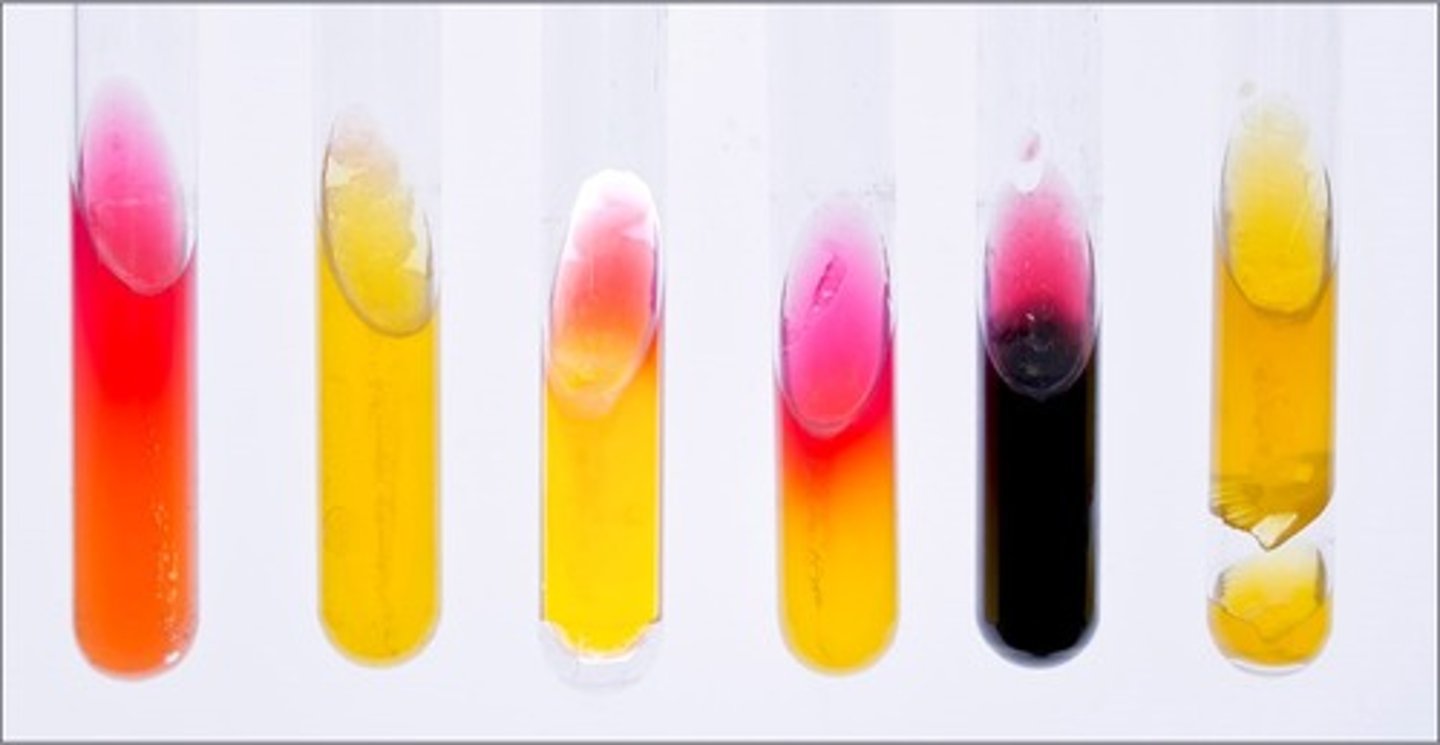

only KIA media
glucose fermentation only and sulfur reduction
Interpretation of the 5th tube:
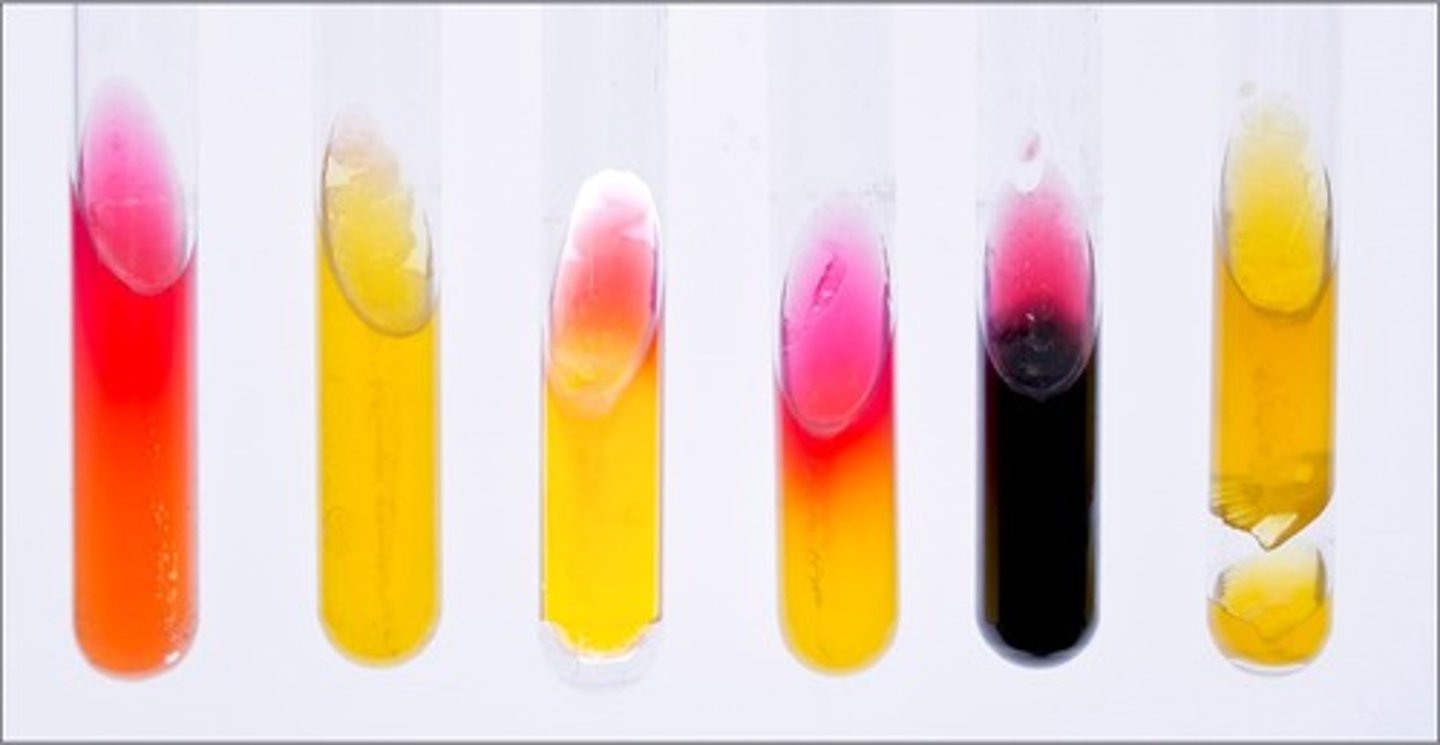

lactose and glucose fermentation
gas produced
Interpretation of the 6th tube:

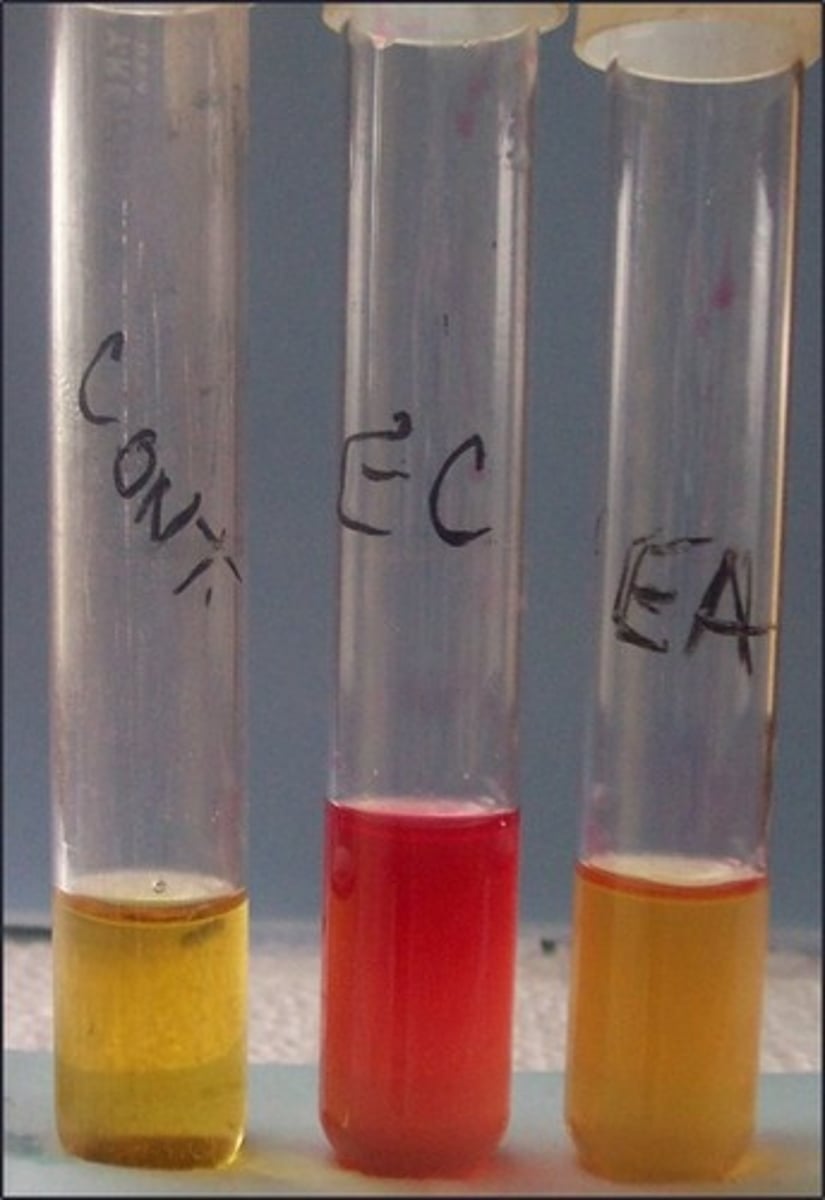
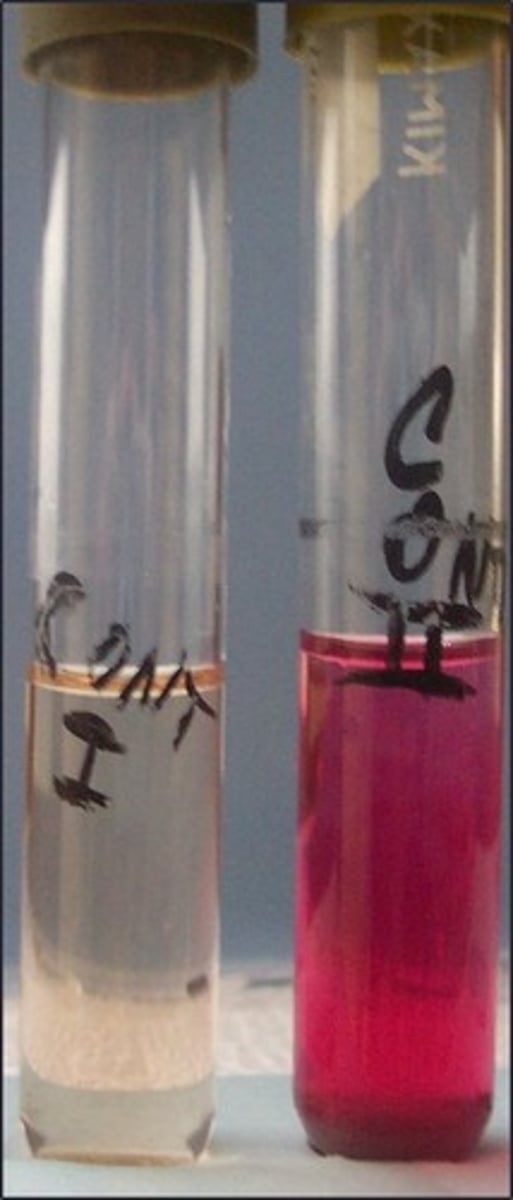
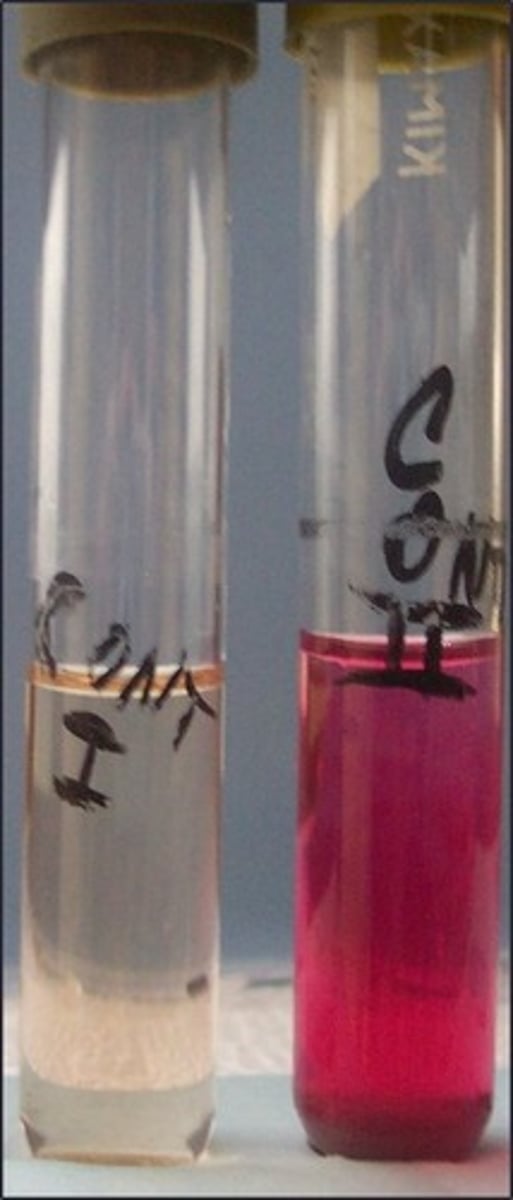
MR test
These are the results for
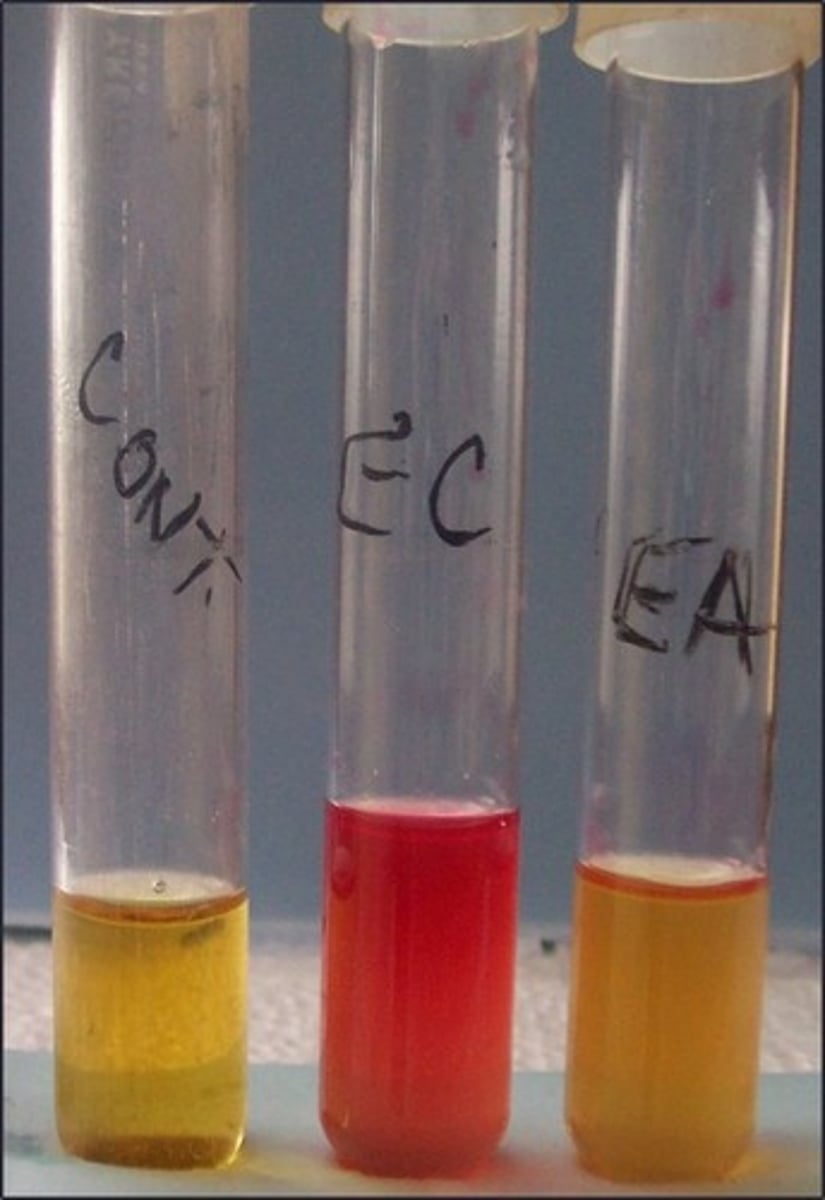

methyl red
Reagent for this test:
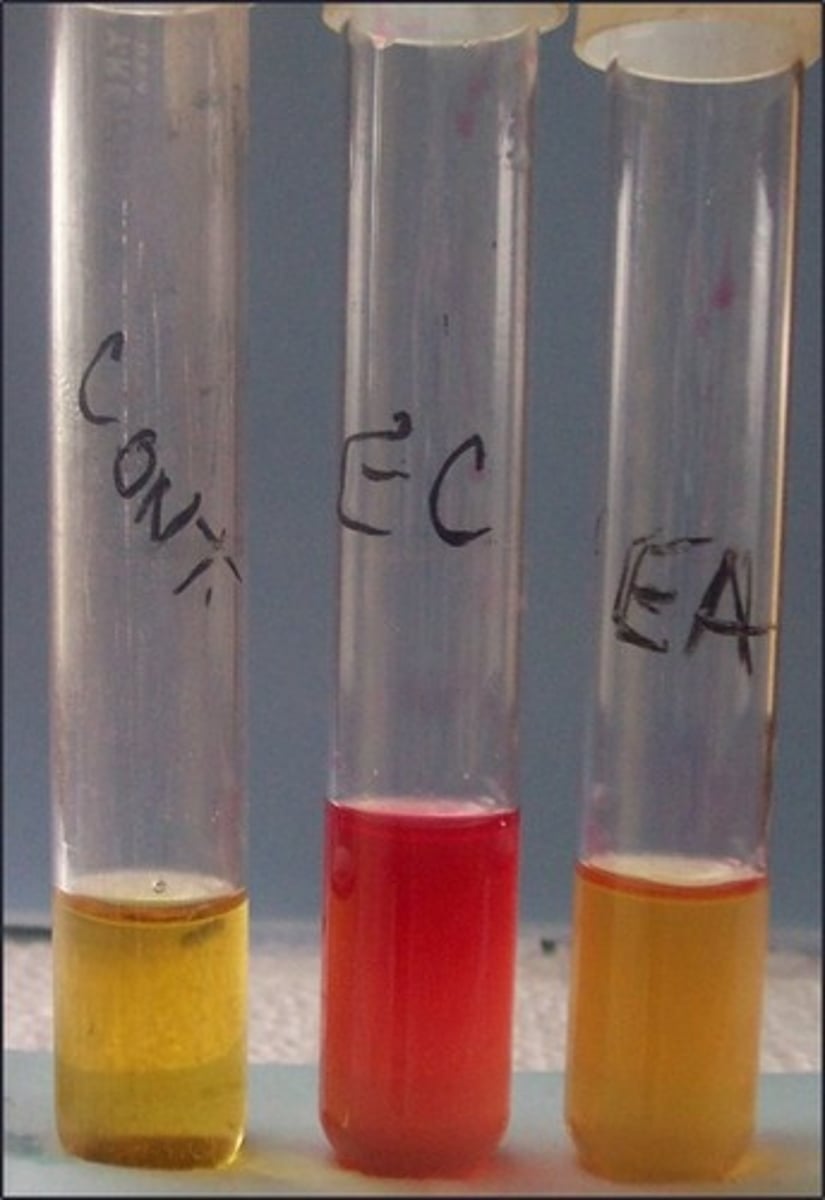

indicates mixed acid fermenters
Purpose of this test:

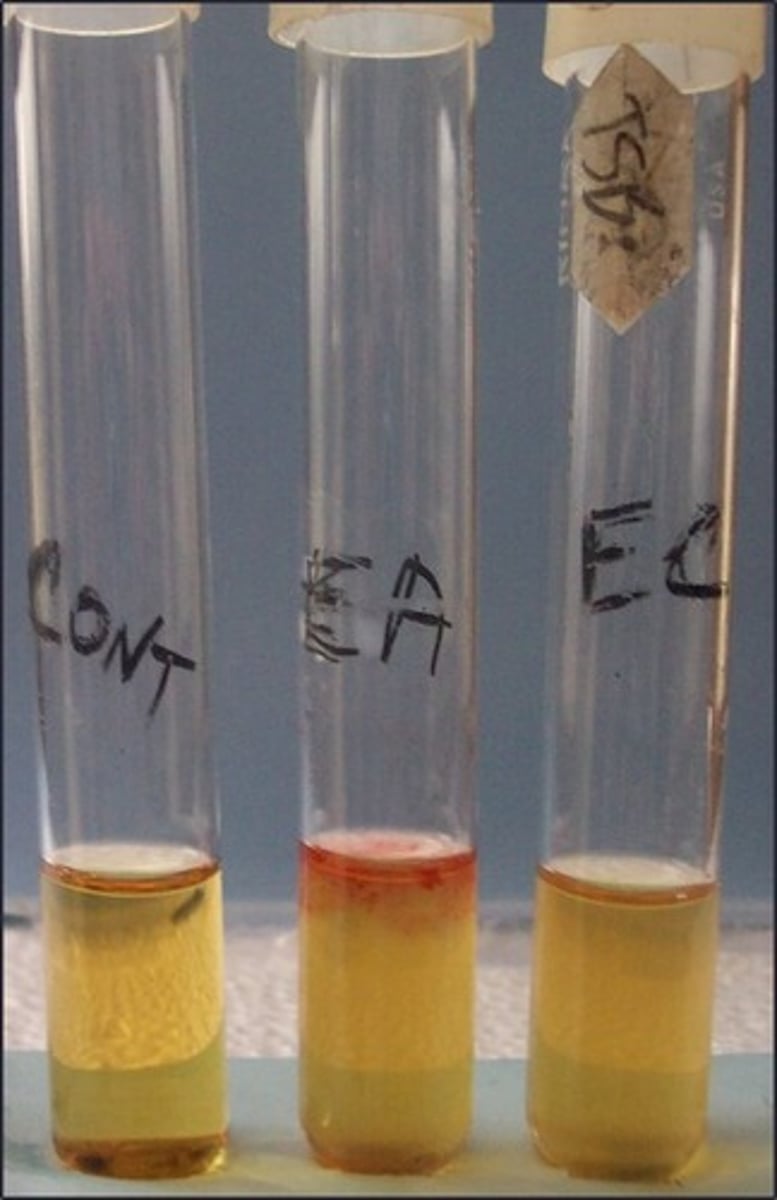
2,3 butanediol fermenters
This tests for:

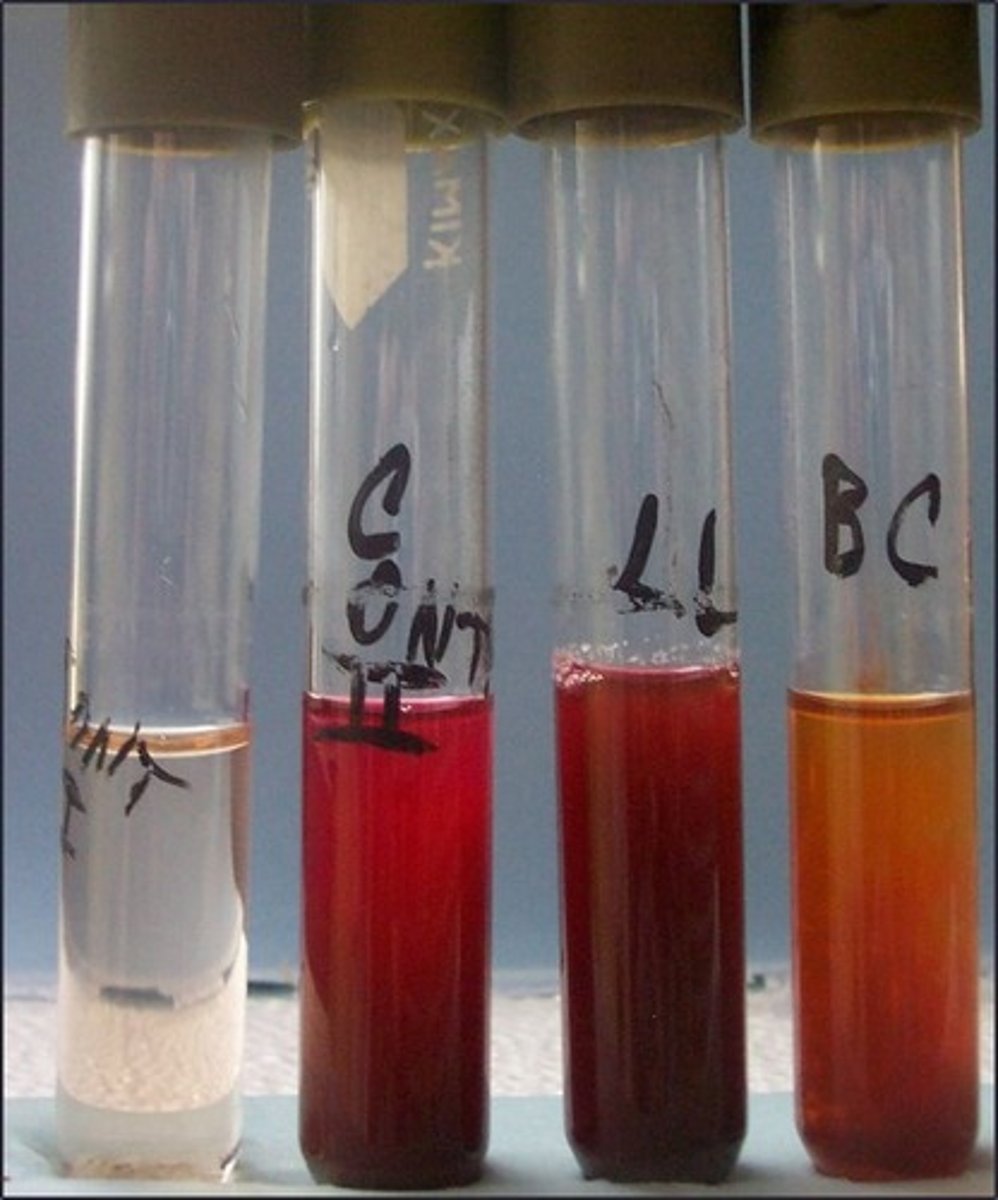
VP test
These are the results for
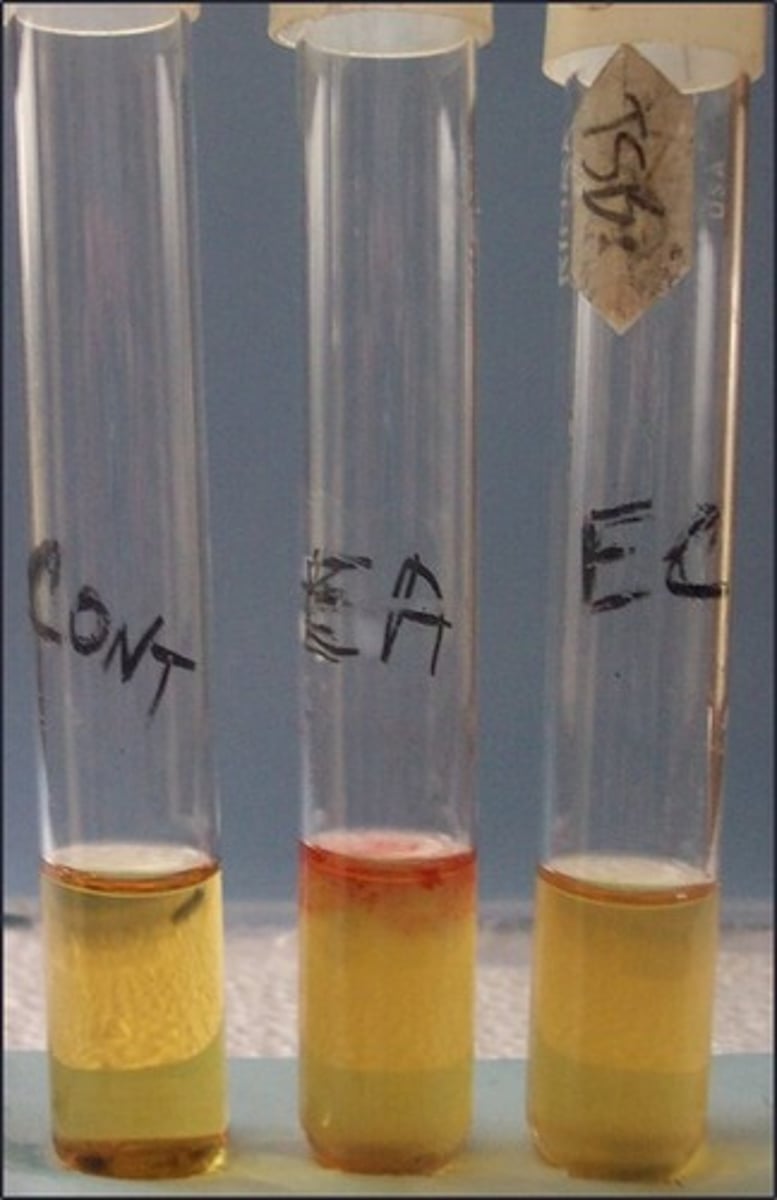

AMC produced by 2,3 butanediol fermenters
The reagents in this broth react with
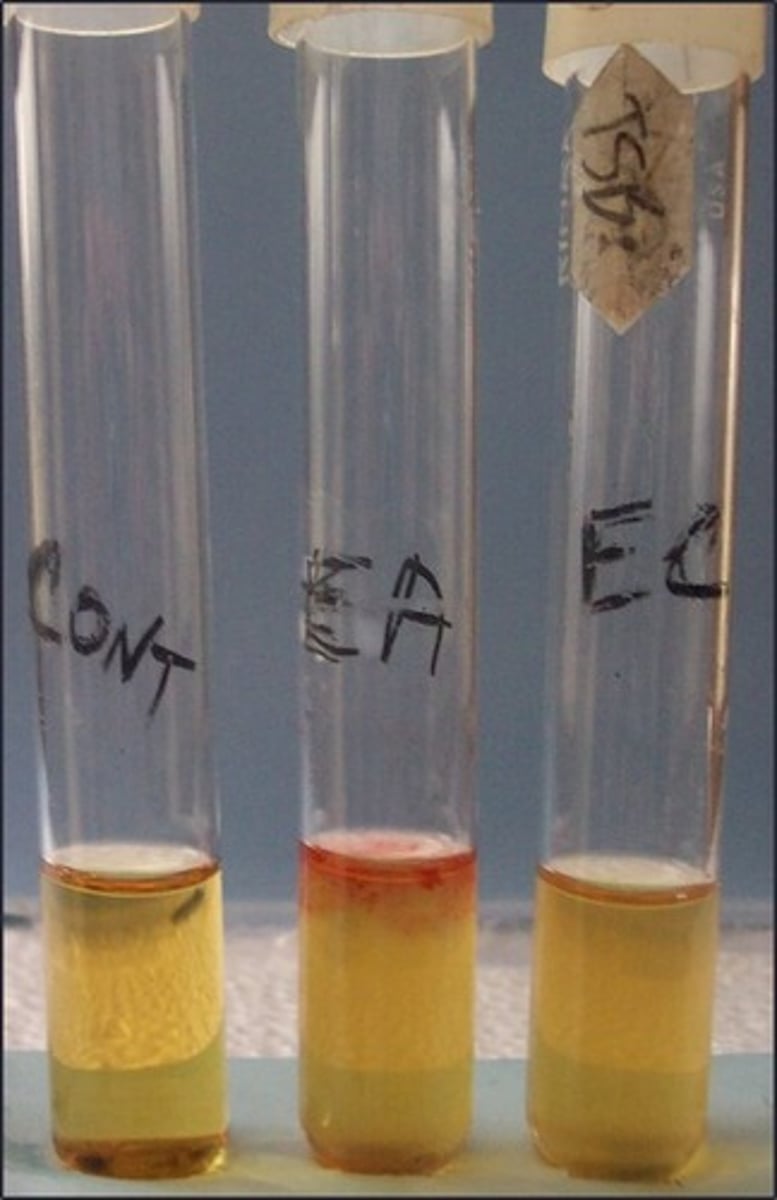

VP I (alpha napthol) and VP II (KOH)
Reagents with this test:
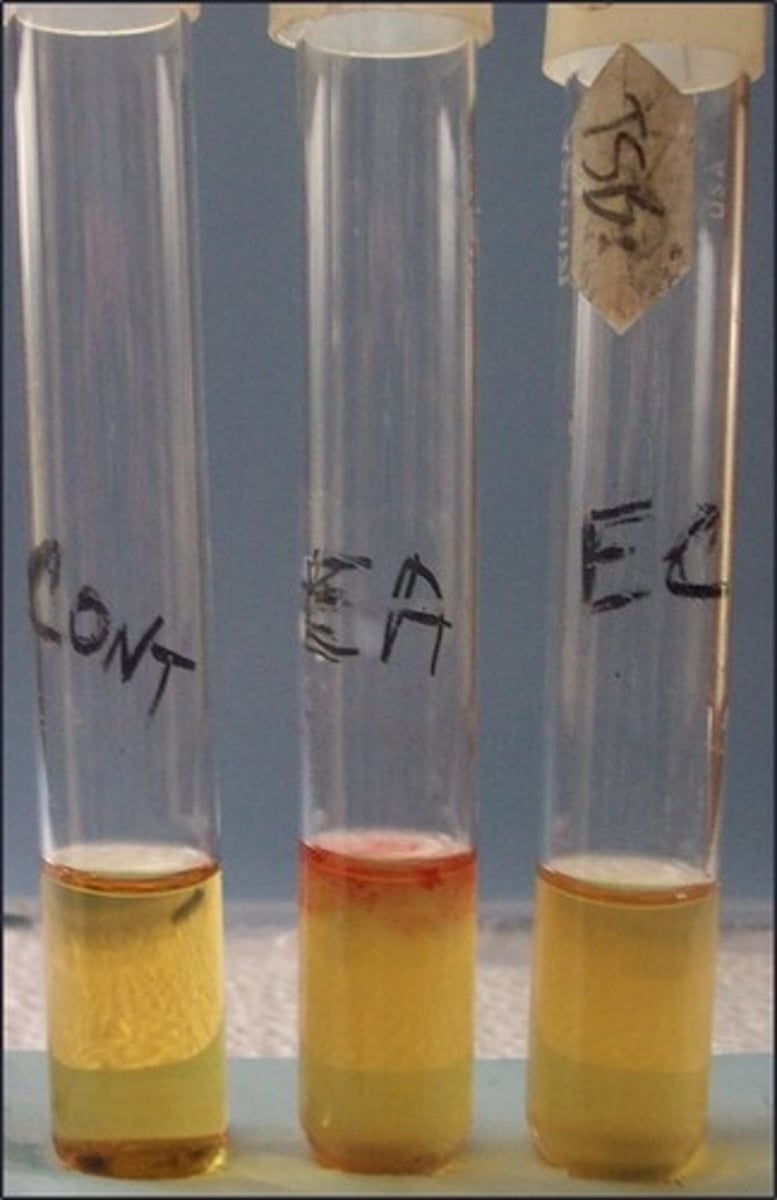

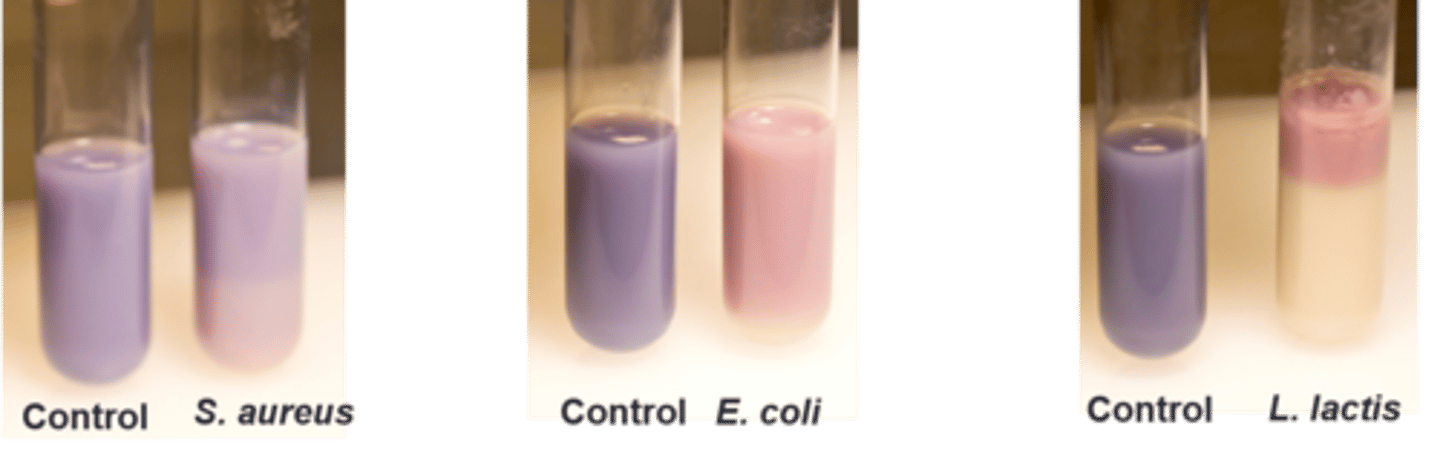
nitrate test
This is the

nitrate reductase
This tests for

Nitrate I (sulfanilic acid) and Nitrate II (dimethyl-alpha-napthylamine)
Zinc added as a catalyst
Reagents for this test, what it :

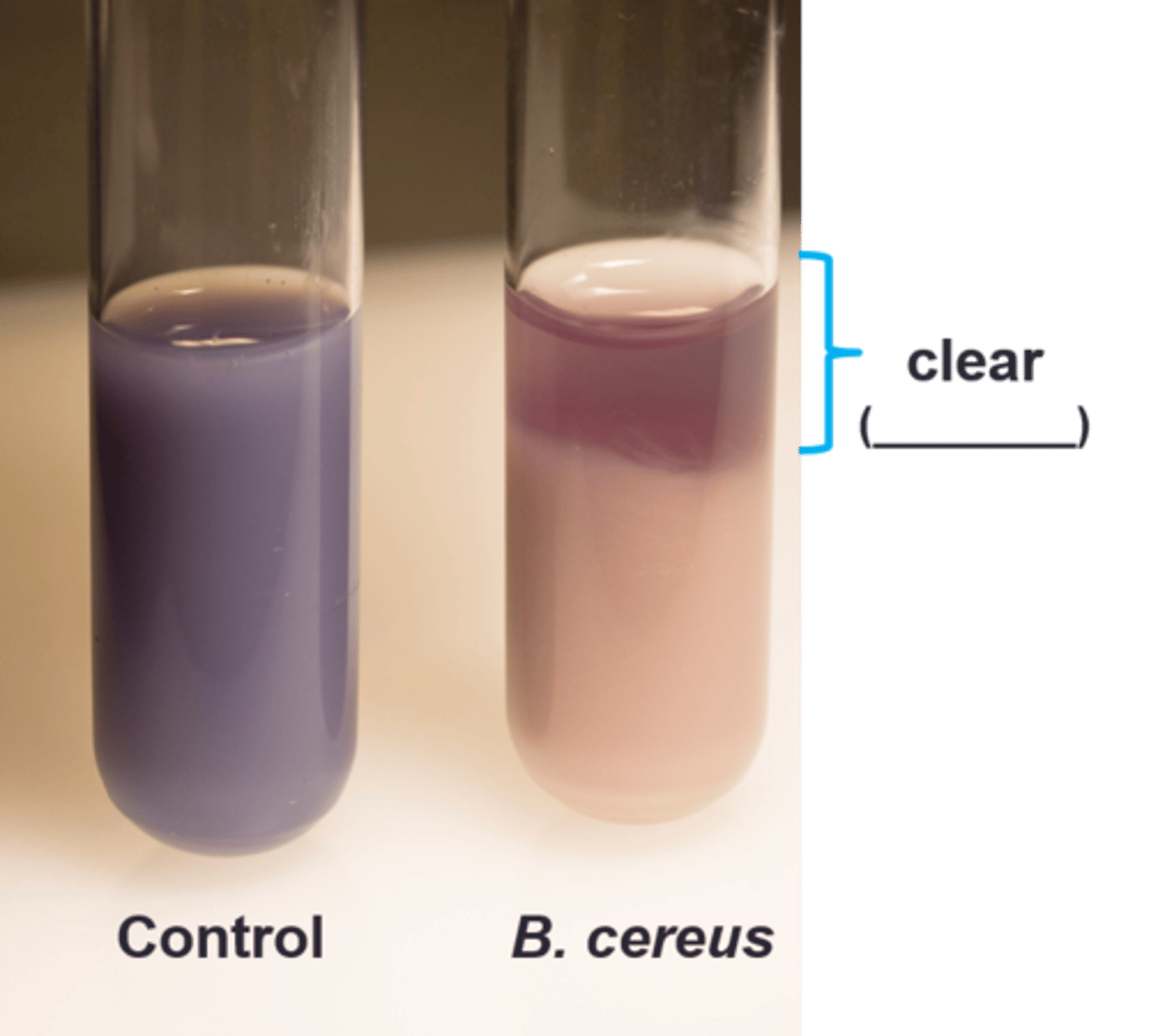
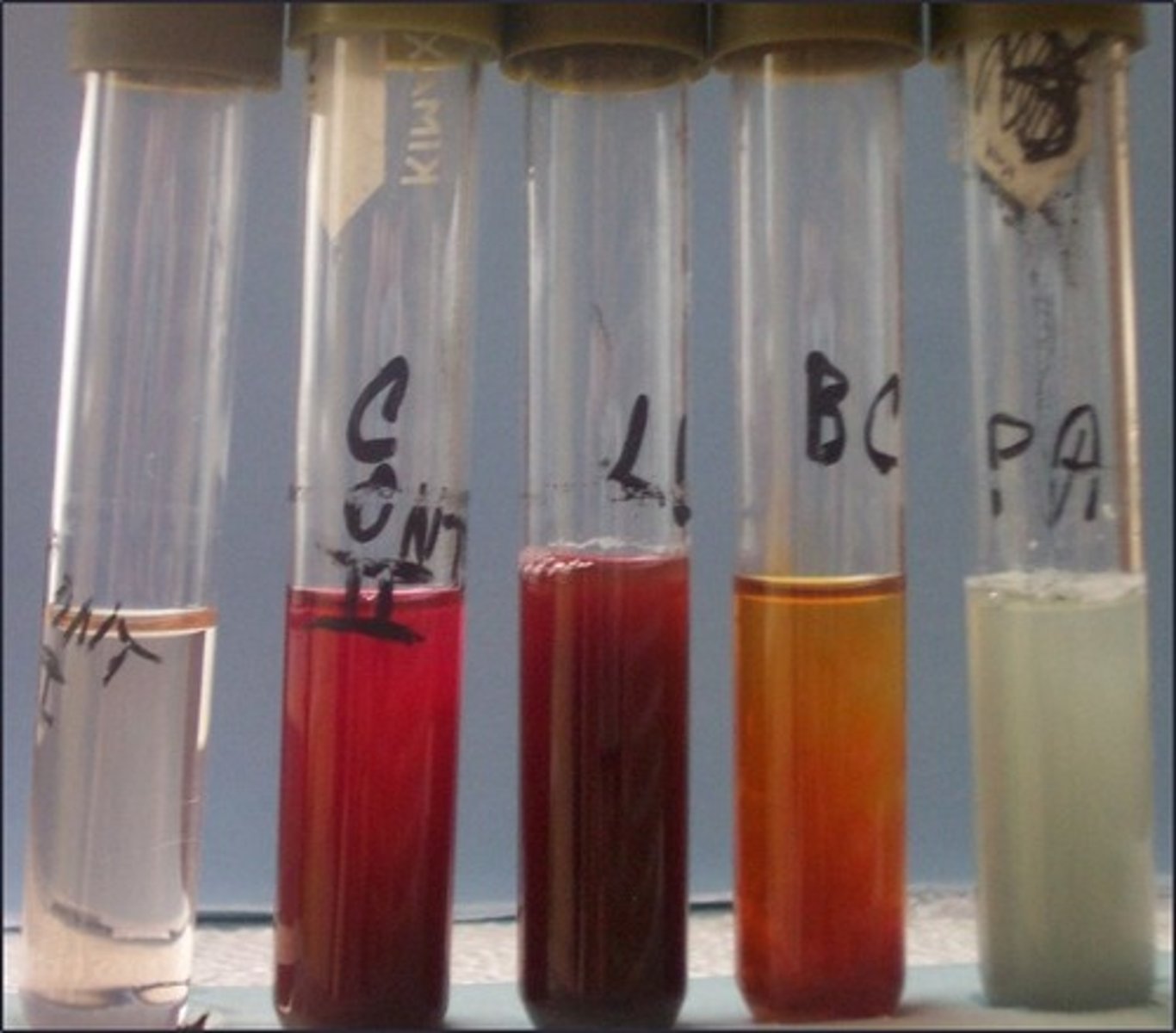
B. cereus, P. aeruginosa
Based on the picture, which organism(s) has nitrate reductase:
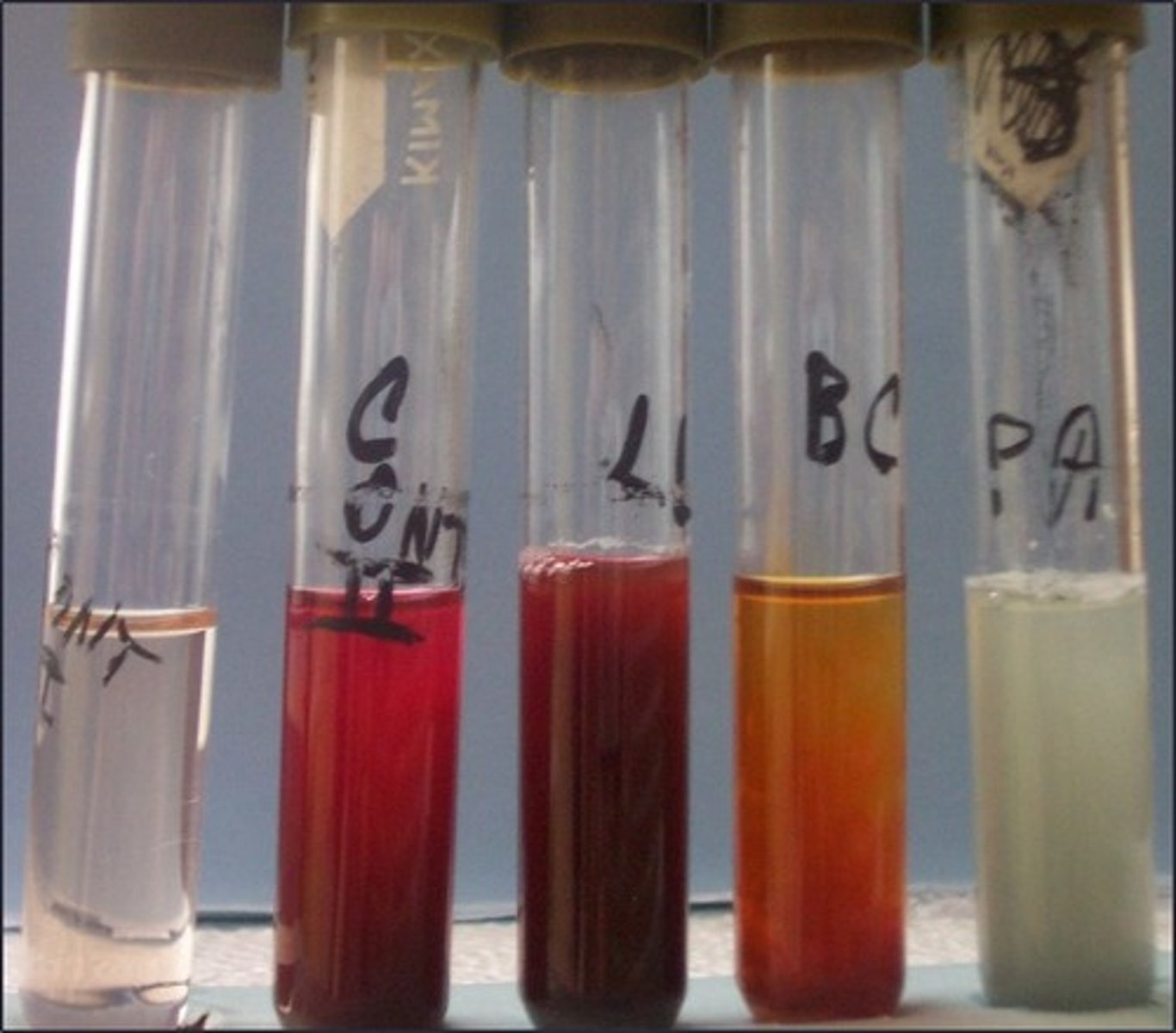

L. lactis
Based on the picture, which organism(s) does not have nitrate reductase:

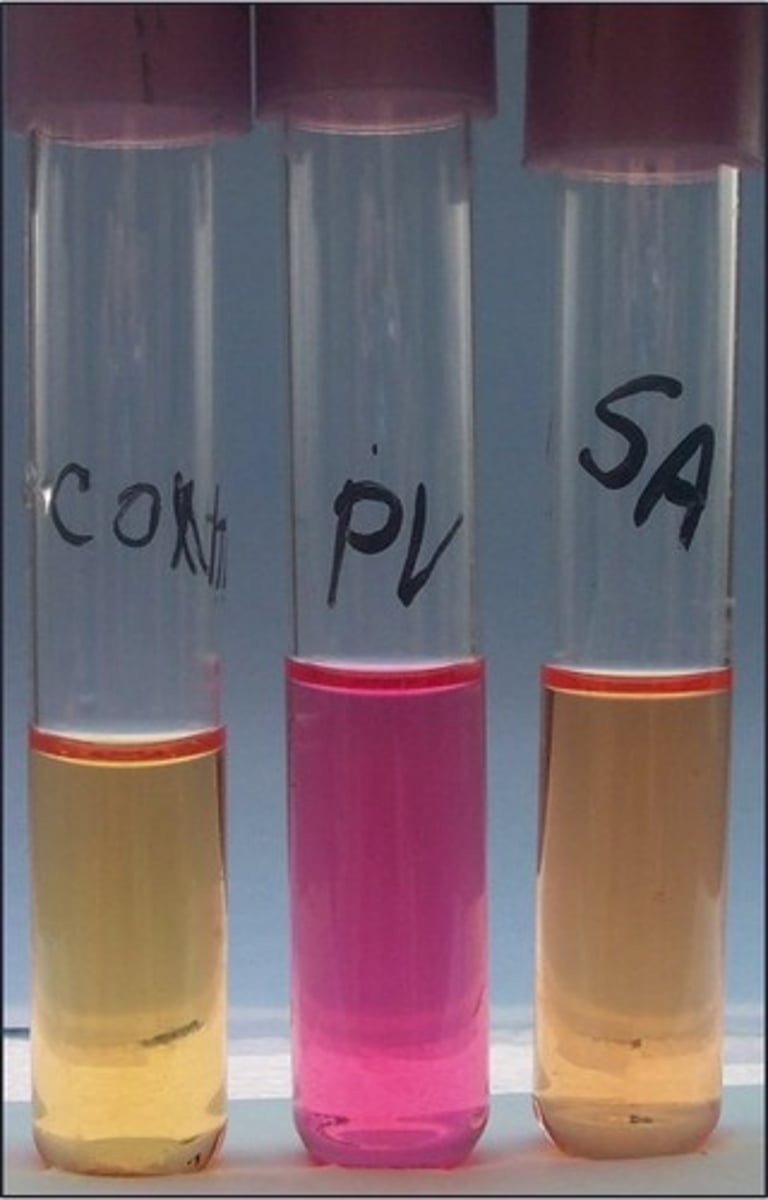
urea broth
This is the
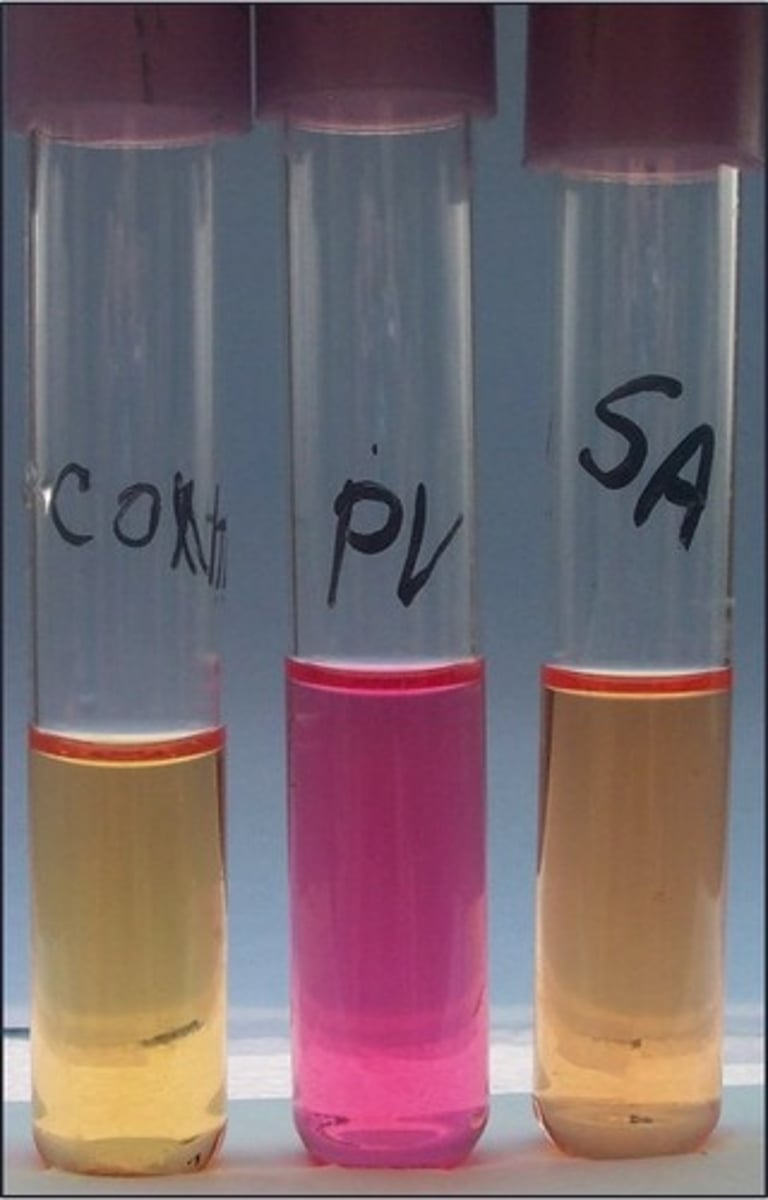
P. vulgaris
Organism with positive result:
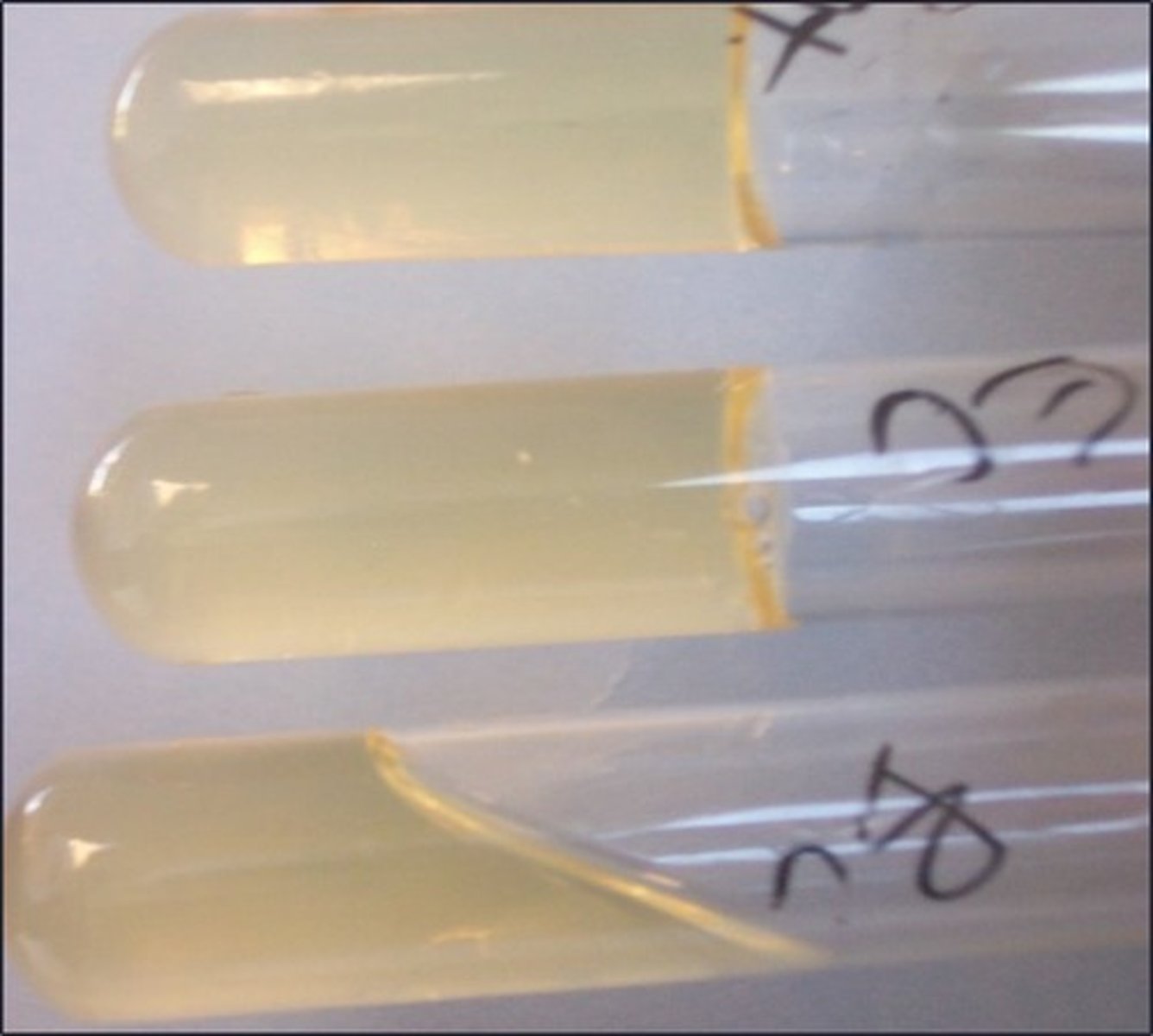
gelatinase
This test detects:
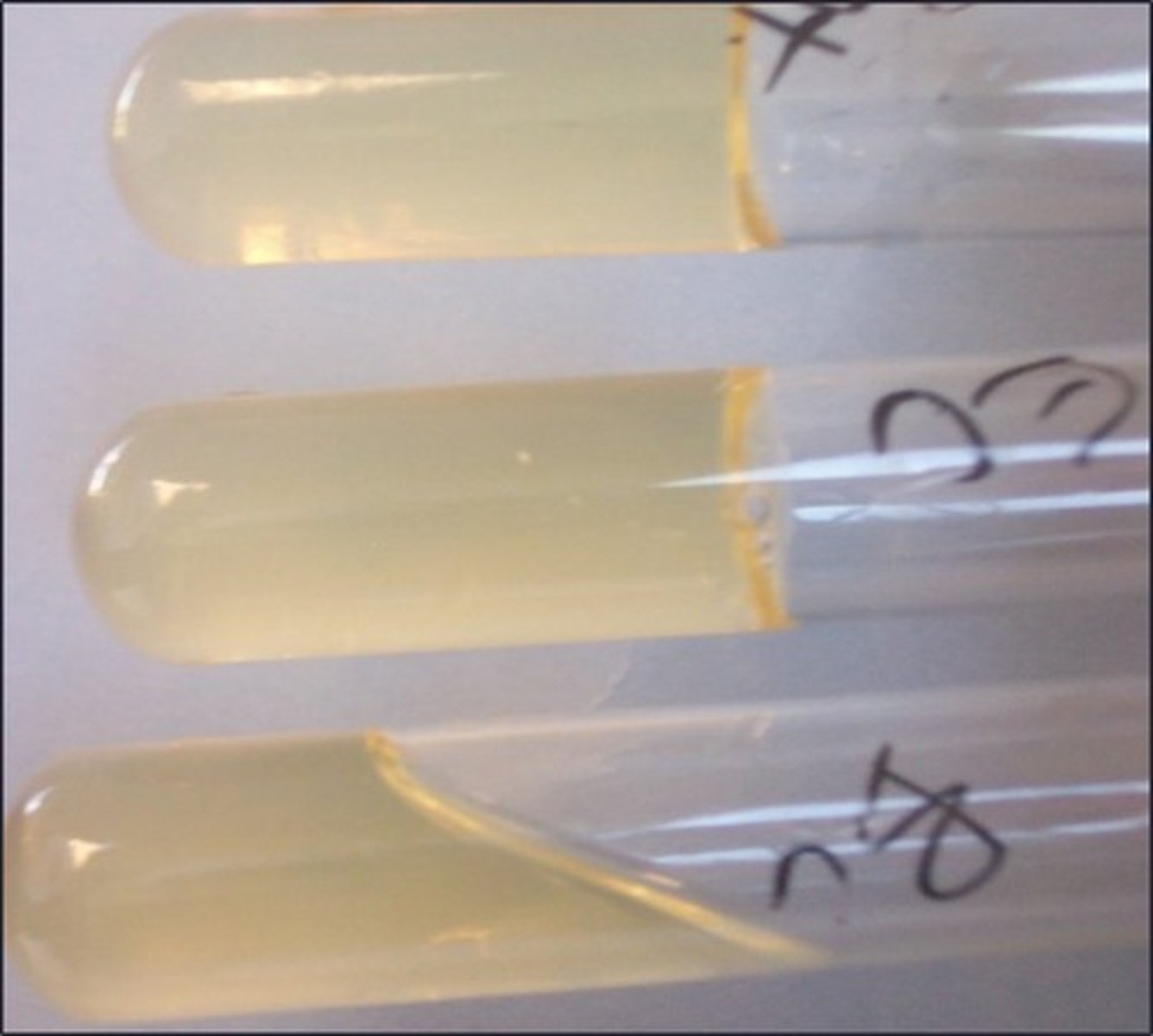
must put in ice bath
Special instructions with this test:
Simmons Citrate slant
This is the
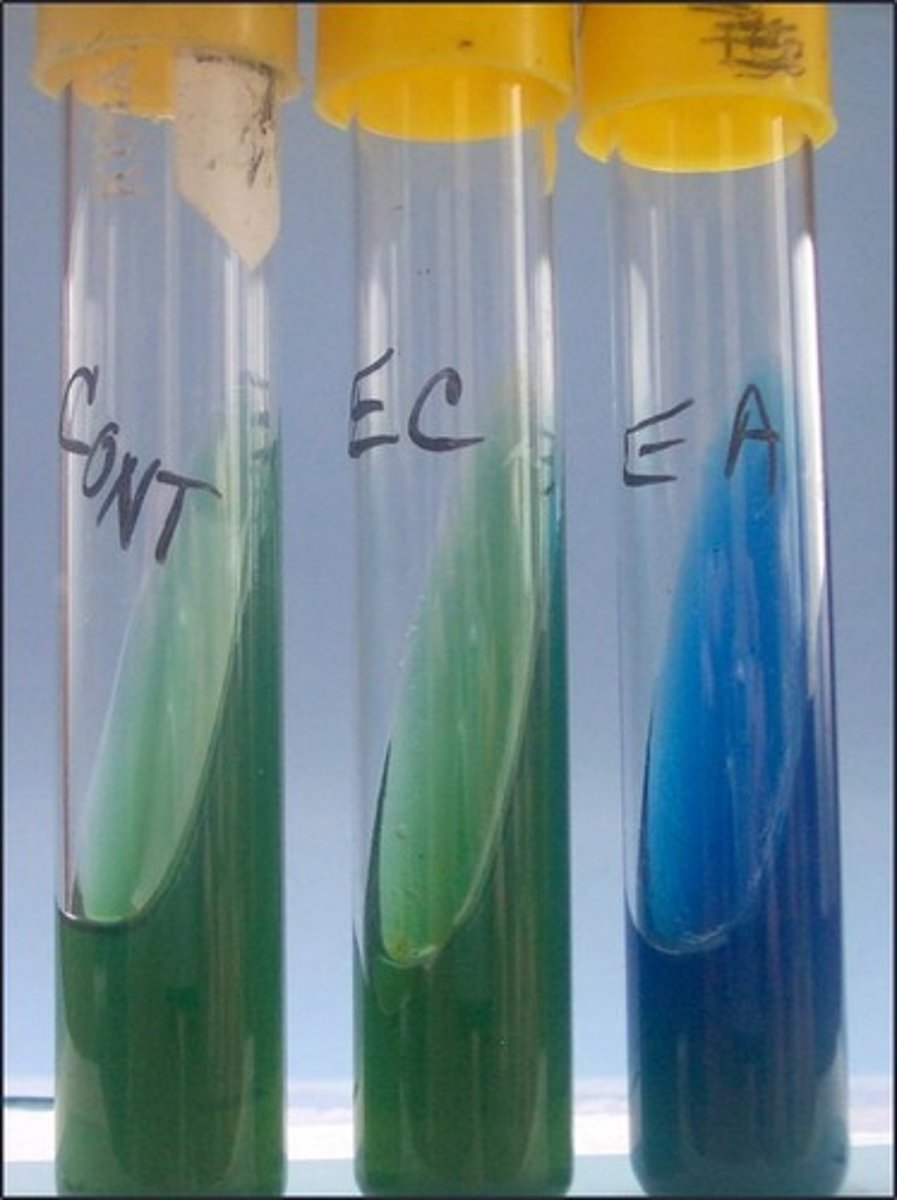

growth
Primary indicator in this test:
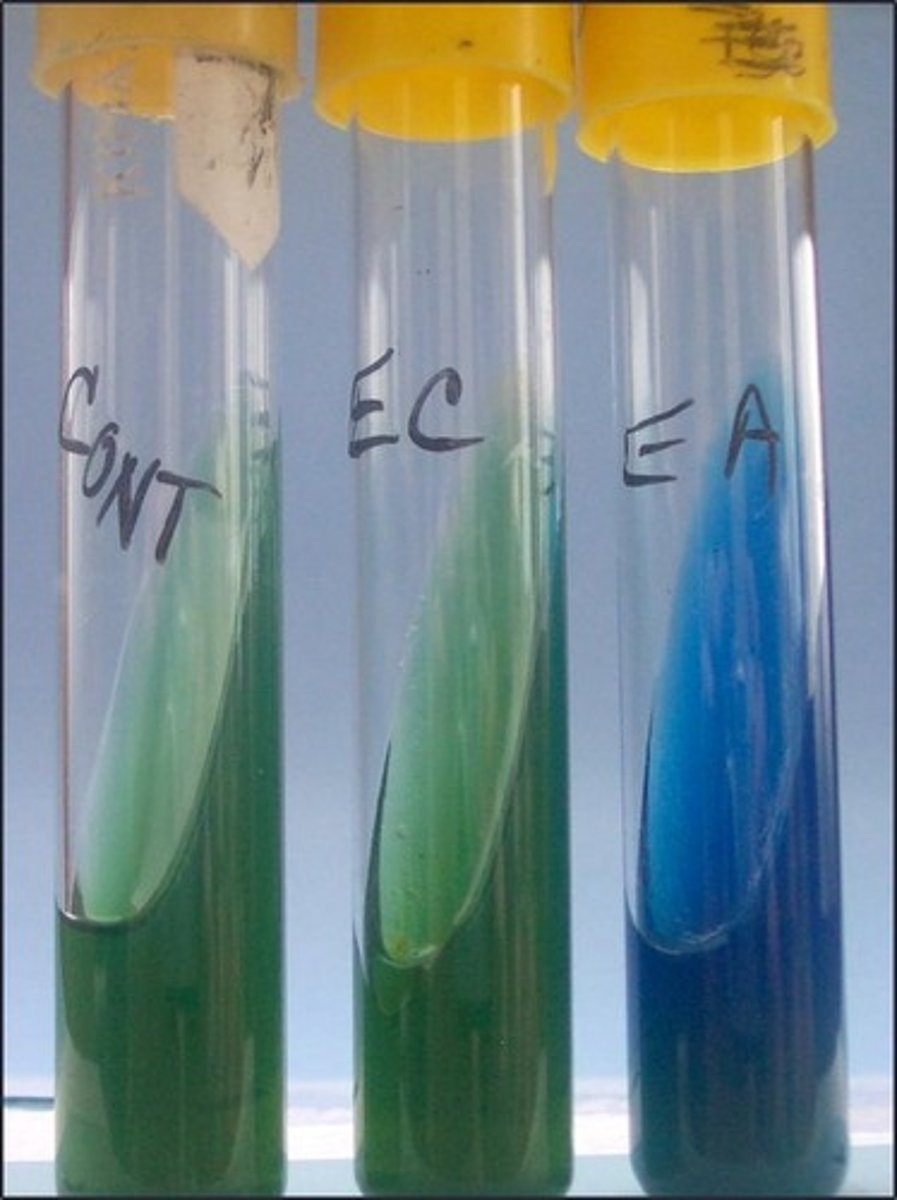

use of citrate as sole carbon source
This medium detects
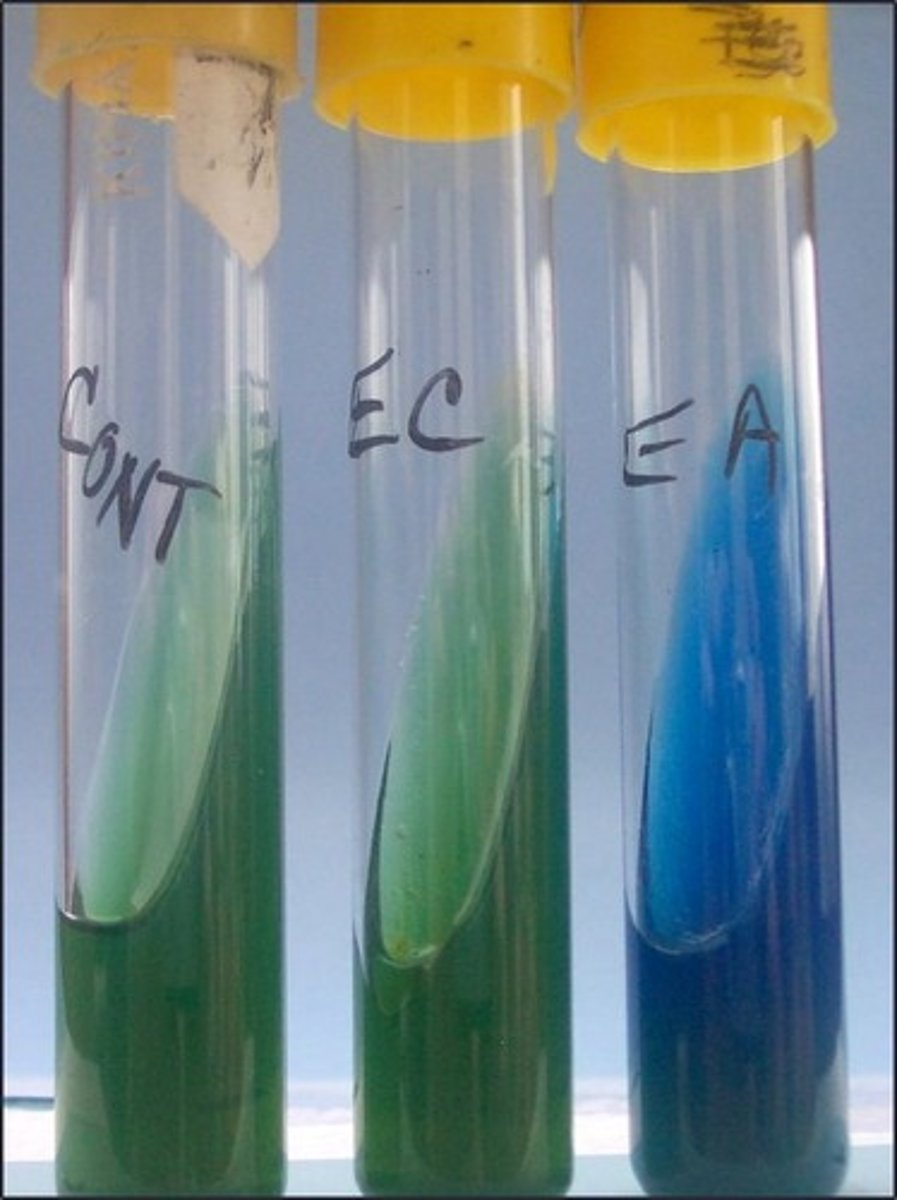

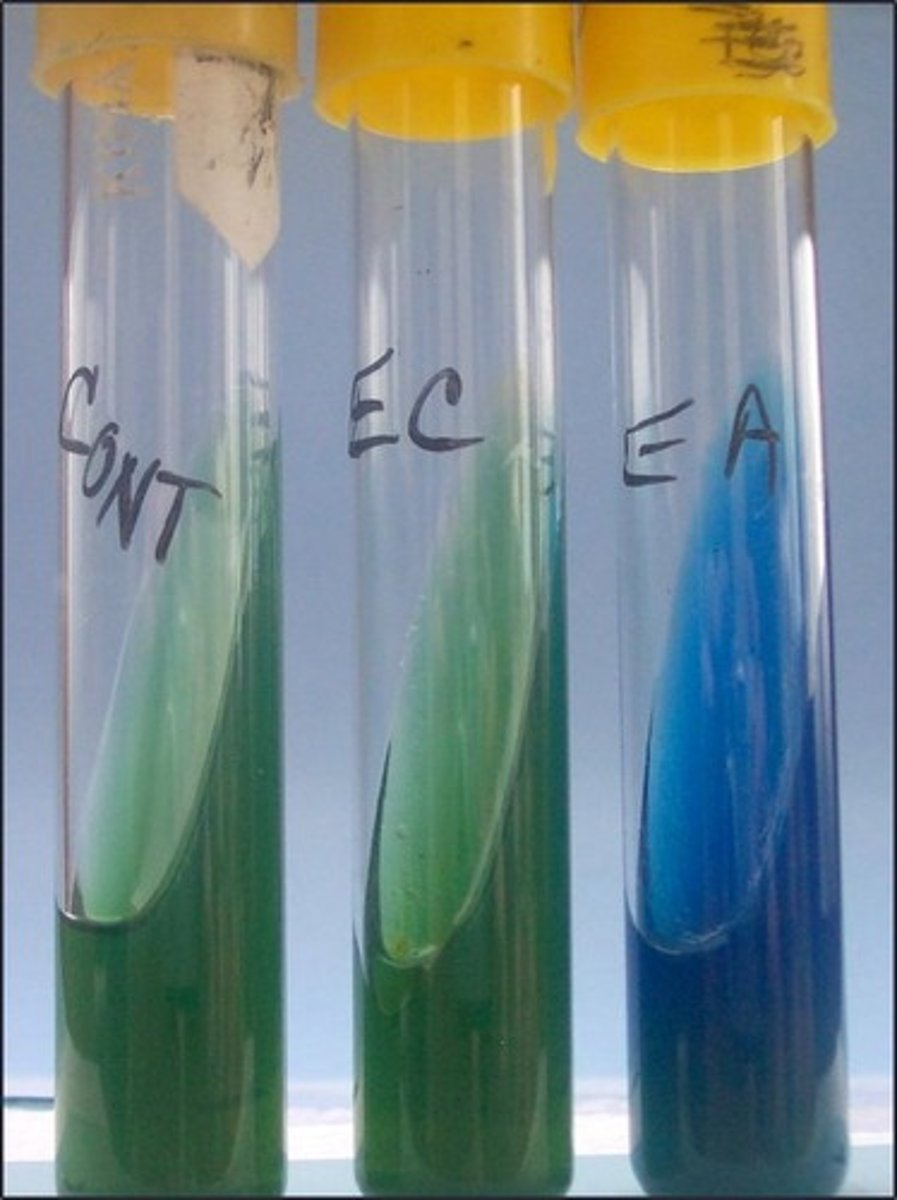
bromothymol blue
Indicator in this medium:

phenylalanine slant
This is the
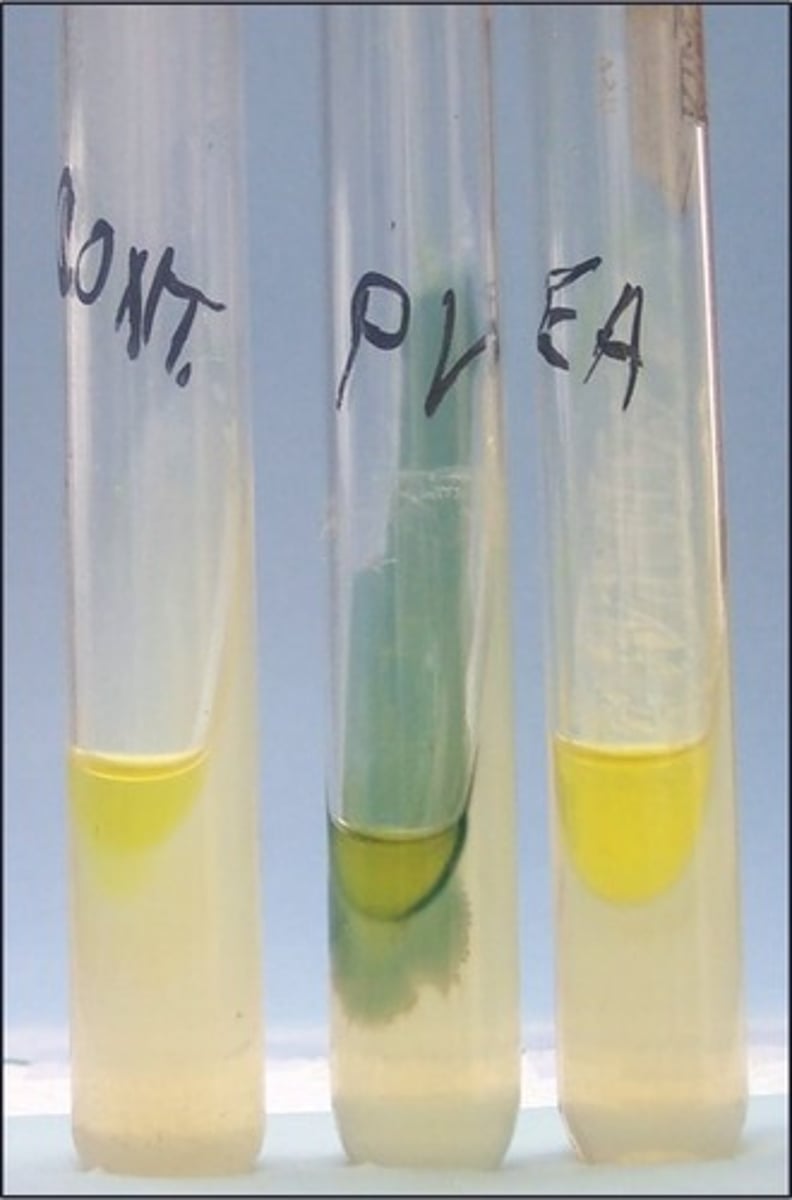

phenylpyruvic acid (PPA), which is a byproduct of the breakdown of phenylalanase
The reagent added to this test indicates presence of
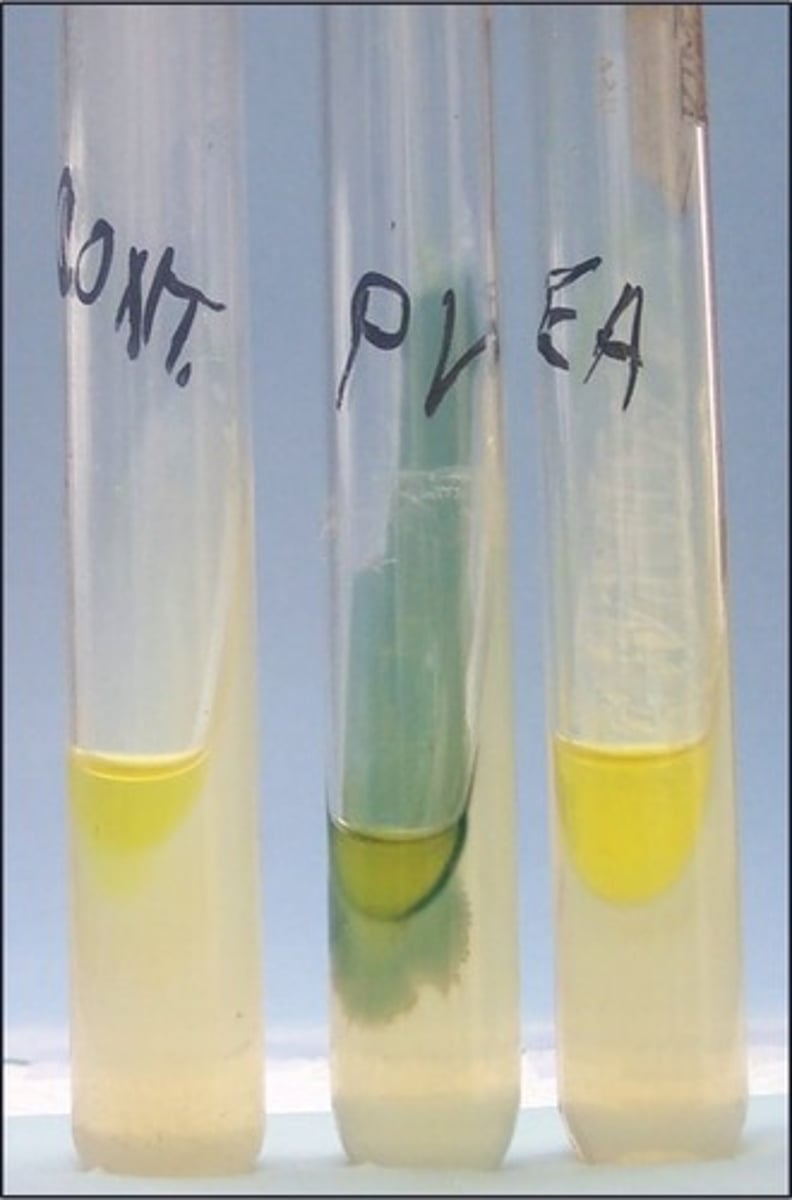

P. vulgaris
Organism positive for phenylananine deaminase:
