SPDI REFRESHER SET A by M.A.
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
7.48 gallons
One cubic foot is equal to ___.
WATER SERVICE PIPE
It is the pipe from the water main or other sources of water supply to the building served.
8.33 pounds
One gallon of water is equivalent to how many pounds?
2 fps
It is important to maintain a minimum of ___ velocity in public sewers.
INTERCEPTING SEWER
A sanitary sewer that conveys sanitary waste to a dispersal plant. It is commonly made of concrete pipe
2 cfh
2000 btuh is equal to ___.
SANITARY SEWER
It is a public sewer facility that carries regular sanitary wastes only. It terminated in a modern sewage dispersal plant.
323.14 gpm
0.72 cfs is equal to ___.
0.036
One inch water column is equal to ___ psi
62.4
One cubic foot of water is equal to ___ pounds.
avoid kinking
Bending a copper is easily done with pipe bending machine, another way of bending copper is by using a steel spring inserted inside the pipe to produce a smooth clean curve. Copper pipes are bent slowly on a wide radius to ____.
2.31 feet
One psi is equal to ____.
MOTOR OIL
During the process of threading, what is the best oil to apply to protect both the threader of the pipe?
1
3413 btuh = ____ kilowatt.
WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM
The water supply of the building or premises consists of the water service pipe, the water distributing pipes,, and the necessary connecting pipes, fitting, control valves, and all appurtenances in or adjacent to the building or premises.
SOLVENT WELDING
The simplest way of joining plastic pipe.
0.60 m
What is the maximum distance between trap weir and fixture outlet?
PRIVY
A concrete sealed vault with a wooden shelter constructed for the collection of raw sewage.
BRASS PIPE
One of the most expensive types of pipe. It is made of an alloy or zinc and copper mixed at 15% and 85% proportion respectively.
7
What is the neutral pH level of water?
WATER DISTRIBUTING PIPE
It is the pipe that conveys water from the water service pipe to the plumbing fixtures and other water outlets.
ASBESTOS PIPE
A kind if pipe which is superior for embedment in concrete structure having the same material properties.
14 TPI
For galvanized steel pipe, cutting is done by using a hacksaw blade applying forward strokes at the rate of about one stroke per second. What is the best TPI to use?
ROTARY TUBE CUTTER
In cutting copper pipes, what is the best tool to use?
VENT STACK
The vertical vent pipe installed primarily for providing circulation of air to and from any part of the soil, waste of the drainage pipe.
TRIBUTARY SEWER
It is classified as an intercepting sewer branch. Also known as the contributing sewer.
WASTE PIPE
A pipe which conveys only wastewater or liquid waste, free of fecal matter.
DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Includes all the pipings within public or private premises which convey sewage or other liquid wastes to a legal point of disposal but does not include the mains of a public sewer system or a public sewage treatment or disposal plant.
DRAINAGE PIPE
It refers to an installation that receives and conveys discharges from water closet with or without waste coming from other fixtures.
SEWAGE EJECTOR
It refers to the pump that will discharge waste in the sump and transfer it to the house drain installed overhead.
SOIL BRANCH
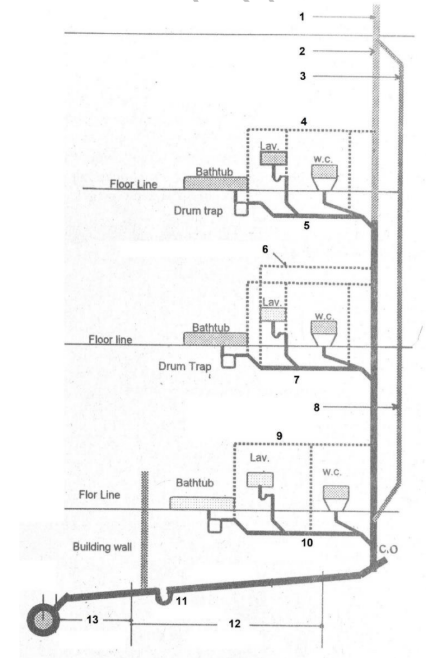
In Figure P-01, name the branch numbered 10.
42.42 cm
What is the travel distance of the pipe if the offset angle is 45° and the offset length is 30 cm?
ROTARY PIPE CUTTER
Which of the following shall not be used in cutting plastic pipes?
knife
hack saw
hand saw
rotary pipe cutter
CESSPOOL
A hole in the ground curbed with stones, bricks, concrete hollow blocks, or other materials laid in such manner to allow raw contaminated sewage to leach into the soil.
SCOURING
It means to flush or wash out, to remove dirt or grease by flowing through. A self-cleaning ability of the pipe.
SOIL STACK
A vertical soil pipe conveying fecal matter and wastewater.
WATER CLOSET
Which of the following is not a fixture?
slop sink
lavatory
urinal
water closet
VENT PIPE
A pipe or opening used for ensuring the circulation of air in a plumbing system and for relieving the negative pressure exerted on trap seals.
CIRCUIT VENT
In Figure P-02, identify the parts numbered 4.
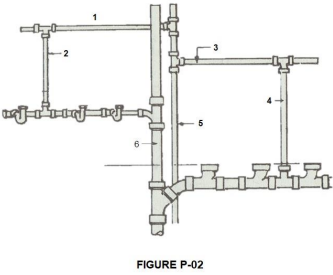
VENT STACK
In Figure P-02, identify the part numbered 5.
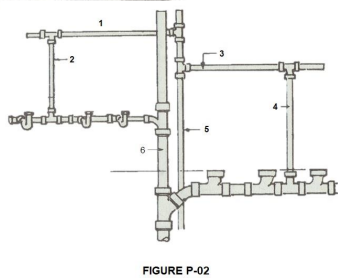
BRANCH VENT
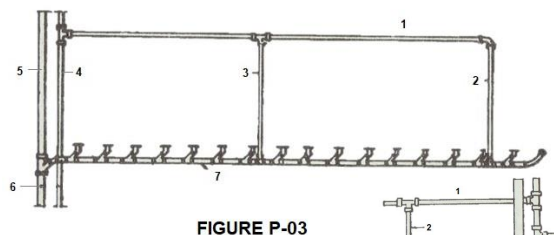
In Figure P-03, identify the parts numbered 1.
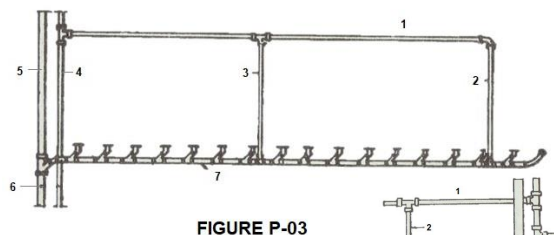
CIRCUIT VENT
In Figure P-03, identify the parts numbered 2.
VENT STACK
In Figure P-03, identify the parts numbered 4.
5.23 fps
Find the velocity of flow in a storm system of a 6” pipe sloped at 1/2” per foot.
0.48 cfs
Find flow flowing half full in a 6” storm pipe with a velocity of 4.90 ft/s.
0.185 cfs
Find flow in a 4” sanitary pipe at 1/8” slope flowing full flow.
5.71 fps
Terminal velocity is defined as the velocity in the stack that remains practically unchanged. Find terminal velocity of a stack when an 8” stack is flowing 40 gpm.
1.87 ft
Terminal length is defines as the distance that the terminal velocity is reached. Find terminal length of flow in a 6” stack with a terminal velocity of 6 fps.
2.47 ft
Find terminal length of flow in a 4” stack flowing 32 gpm.
423.9 gpm
What is the flow capacity in a 6” stack?
20.71 ft
Find terminal length for an 8” stack.
27.59 kW
How many KWs are required to heat a 119 gal. storage water heater with incoming water temperature of 45° and stored at 140°?
0.69 gallon of hot water
How many gallons of hot water will mix with cold water through a master mixing valve to provide 100 degrees to the building if stored water is 180 degrees and the cold water to the mixing valve is 45 degrees?
44%
What percentage of 180 degree hot water mixed with 45 degree cold incoming water to supply 105 degrees water?
105.33 gallons
How many gallon of water will 18kW heat up 70 degrees?
COMBINATION STANDPIPE
A pipeline system filled with water and connected to a constant water supply for the use of the BFP and the occupants of the buildings solely for fire suppression purposes.
DRY STANDPIPE
A type of standpipe in which the pipes are normally not filled with water. Water is introduced into the system through fire service connections when needed.
STANDPIPE SYSTEM
A system of vertical pipes in a building to which fire hoses can be attached on each floor, including a system by which water is made available to water outlets as needed.
CLASS I SYSTEM
This system is provided with 64 mm (2 ½ in.) hose connection for full-scale firefighting.
CLASS I SYSTEM
Dry standpipes shall be used for ____.
Class I System
Class II System
Class III System
Class IV System
40 m
All buildings with required enclosed stairway or smokeproof enclosure shall have at least one dry standpipe outlet connection located at every floor level landing above the first floor of every required enclosure.
What is the maximum travel distance from a dry standpoint outlet connection?
not less than 50 psi above the maximum working pressure
All dry standpipes shall be tested hydrostatically to withstand ____.
102 mm
What is the minimum required size of the standpipe in buildings in which the highest outlet is twenty-three (23) meters or less above the fire service connections?
153 mm
What is the minimum required size of the standpipe in buildings which the highest outlet is higher than twenty-three (23) meters above the fire service connections?
46 cm
All fire service connections shall be located on a street front, what is the minimum required distance above the grade and shall be equipped with an approved straight way check valve and substantial plugs or caps?
122 cm
Each standpipe shall be equipped with an approved sixty-four millimeters (64 mm) outlet, what is the maximum required distance above the floor of each storey?
25 mm
An approved durable sign with raised letters shall be permanently attached to all fire service street connections, cast on a plate or fitting that reads “DRY STANDPIPE.“ What is the minimum required height of the approved durable sign with raised letters?
22 m
Wet standpipes shall be located so that all portions of the buildings are within 6 m of a nozzle, what is the minimum length of the hose?
91 cm
All interior wet standpipe shall be equipped with thirty-eight millimeters (38 mm) valve in each storey, including the basement or cell roof of the building, what is the minimum required distance above the floor?
30 min
The wet standpipe shall deliver not less than one hundred thirty-two liters (132 L) of water per minute at not less than one and eight-tenths (1.8) kilos per square centimeters residual pressure from each of any two outlets flowing simultaneously, what is the required time?
150 mm
What is the minimum diameter required for a combination standpipe system?
2
All combination standpipe systems shall be equipped with a four-way fire service connection. What is the minimum number of four-way service inlet connection is required?
R.A. 9514
An act establishing a comprehensive fire code of the Philippines, repealing presidential decree no. 1185 and for other purposes.
PURIFIED WATER
Water that undergoes a process where the pollutants are removed or rendered harmless.
POLLUTED WATER
Water that contains one or more impurities that make the water unsuitable for desired use.
GRAY WATER
Water drained from lavatories, sink, laundry trays and showers; contains minor pollutants.
BLACK WATER
Water drained from water closets and urinals; carries body wastes and contains major pollutants.
STORM WATER
Rainwater drained from roof gutters and downspouts.
460 mm
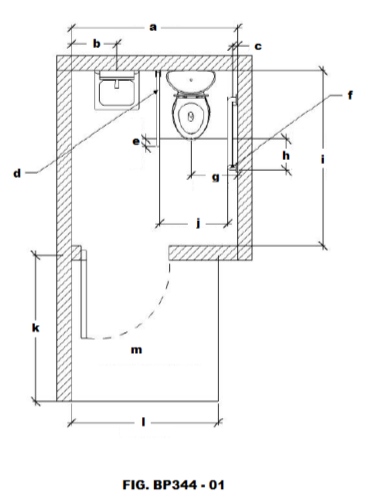
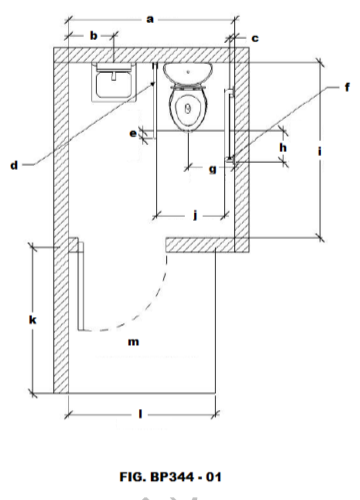
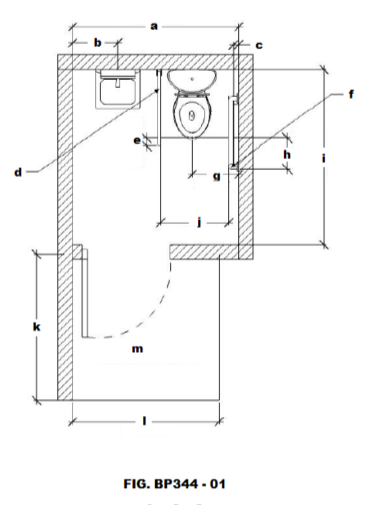
Identify letter “b” on FIG. BP344 - 01
AERATION
Water is sprayed into the air to release trapped gases and absorb additional oxygen for better taste.
COAGULATION
Is the chemical process in which the coagulant reacts with the sediment to make it capable of combining into larger particles. This is called destabilization.
FLOCCULATION
Is the physical process in which the sediment particles collide with each other and stick together.
3000 mm
Identify letter “a”
100 mm
Identify letter “e”
SEDIMENTATION
This is the process by which suspended solids are removed from the water by gravity setting and deposition. This process usually follows coagulation-flocculation. The objective of this process is to remove most of the suspended solids, reducing the loads on the filters.
FILTRATION
This is the passage of fluid through a porous medium suspended matter which did not settle by gravity. In water purification, matter to be removed includes suspended silt, clay, colloids, and microorganisms including algae, bacteria, and viruses. A filter bed consists of a granular non-porous material held one place by the force of gravity or by the direction of flow.
1700 mm
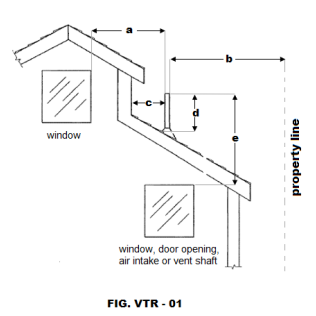
Letter “a”
DISINFECTION
This is the most important process used in the production of water of safe and sanitary quality. Chlorination is the method of introducing a controlled amount of chlorine to the water in order to attain a desired degree of disinfection.
300 mm
Identify letter “c”
SOIL DRAINAGE SYSTEM
The piping that conveys the discharge of water closets or fixtures having similar functions (containing fecal matter) with or without the discharges from other fixtures.
150 mm
Identify letter “d”
VENT SYSTEM
The piping system that receives a flow or air to or from a drainage system or to provide a circulation of air within such system to protect trap seals from siphonage or back pressure.
BUILDING DRAIN
Part of the lowest horizontal piping of a plumbing system, which receives the discharges from the soil, waste, and other drainage pipes inside of a building and conveys it to the house sewer outside of the building.
BUILDING SEWER
Extends from the house drain at a point 0.60 meters from the outside face of the foundation wall of a building to the junction with the street sewer or to any point of discharge, and conveying the drainage of one building site. No house/building sewer shall be smaller than 150 mm in diameter, nor less in size that the house/building drain.
FIRE PROTECTION
A sprinkler system that is installed for buildings is required for ___.
60
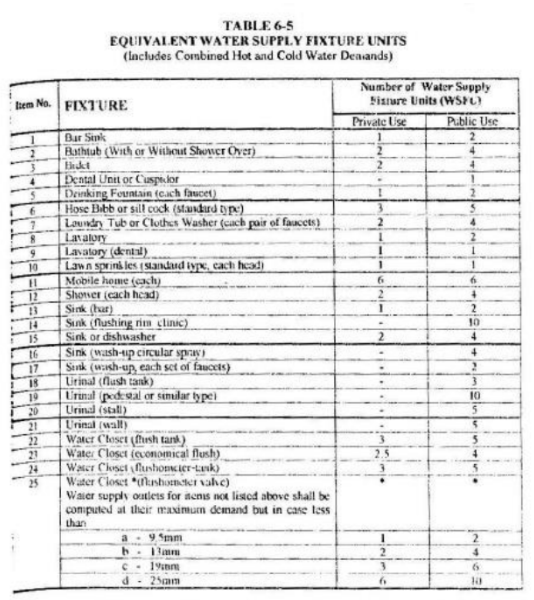
A house sewer system receiving sewage from a townhouse has 90 flush tank W.C., 90 shower heads, 30 kitchen sink, 90 lavatories, and 30 bidets. What is the total F.U. of the Kitchen Sinks? (Use Table 6-5)
PRIVATE SEWER
A sewer NOT directly controlled by public authority, is a ___.
POLYETHYLENE
What is a common pipe material used for services connection?
LAVATORY
What fixture is designed for washing hands or face, sometimes called washbasin?
FILTRATION
What is the process of water purification so as to remove the particles of vegetable matter, mud, and other particles present in the water? (Most commonly used materials are sand and gravel)