Immune System - Anatomy & Physiology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the immune system
Our primary line of defense
The enemies: bacteria, fungi, protists, viruses, and parasites
Parts of lymphatic system
Lymphatic vessels
Lymph nodes
Lymphatic organs
Lymphatic vessels
Blind ended, one-way vessels that pick up excess fluid in the tissues and return it to the blood stream
Lymph nodes
We have 500-600 lymph nodes
Job: filter lymph
Lymphatic organs
Spleen: filters blood (instead of lymph) removing bacteria, viruses, etc. and destroys worn out blood
Thymus: site where T cells mature
2 types of body defenses
Non-specific defenses (also called Natural/Innate immunity)
Specific defenses (also called Adaptive/Acquired immunity)
4 parts of Non-specific defenses
Physical Barriers
Cells
Antimicrobial Chemicals
Other defenses
Physical barriers (nonspecific defense)
Keratinized skin + acidic secretions
Mucous membranes
Cells (nonspecific defense)
Phagocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils
Natural killer cells: kill virus-infected and malignant cells (cancerous)
Antimicrobial cells (nonspecific defense)
Interferons: Secreted by virus-protected cells to protect neighbors
Lysozyme: enzyme that kills bacteria (in tears, saliva, mucus, human milk)
Other defenses (non-specific)
Fever
Inflammatory response
Calor, dolor, rubor, tumor (heat, pain, redness, swelling)
Tries to keep pathogen in one place
Cleans damage/sets stage for repair
Complement: plasma proteins that bind foreign cells and either punch holes in them (lyse) or make them more “tasty” to phagocytes (opsonization)
4 characteristics of specific defenses
Specificity
Diversity
Self/Non-Self Recognition
Memory
Specificity
Antigen (Ag): any substance capable of causing an immune response. (Antibody Generating)
Antibodies (Ab) are produced in response to specific antigens.
Diversity
The immune system can recognize and respond to millions of different invaders
Self/Non-self recognition
Cells of the immune system are “trained” to recognize and not attack “self” proteins
Self proteins are generally non-antigenic
Memory
immune system can “remember” antigens it has encountered and react more quickly on subsequent exposures (acquired immunity).
A large population of memory cells are produced.
Names for cytotoxic t-cells
TC cells
CD8 cells
MHC I dependent cells
Names for helper cells
TH cells
CD4 cells
MHC II dependent cells
Specific defenses
Specific identification of antigen/pathogen generates a response
Humoral (antibody mediated)
Cellular (cell-mediated) response
Cellular (cell-mediated) Immune Response
Cytotoxic T-cells (aka CD8, MHC I dependent)
Recognize + kill self-altered cells (virally infected cells and cancerous cells)
Can only see antigens presented in MHC I proteins
Helper T cells (aka CD4, MHC II dependent)
Help activate cytotoxic t-cells
Help activate B-cells
Help make the macrophages better phagocytes
Can only see antigens presented in MHC II proteins
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Proteins expressed on outside of cells
MHC I and MHC II
MHC I
Expressed on almost all body cells
Express self proteins when cell is healthy
Express viral proteins when cell is infected and altered self-proteins when cell is cancerous
MHC II
Expressed on Antigen presenting cells (APC): macrophages, B-cells, and dendritic cells
Present Ag (antigen) to TH cells (helper cells)
Antibodies
A class of proteins called immunoglobins (Ig) made by B cells
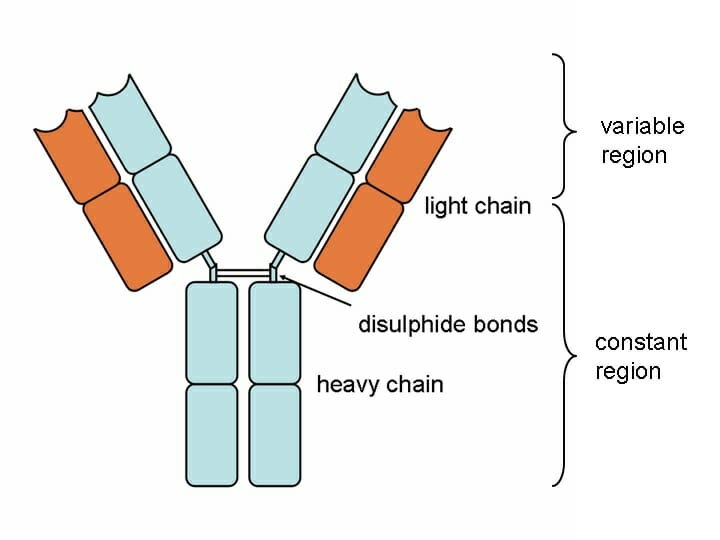
Basic antibody structure: 2 heavy protein chains and 2 light chains with constant and variable regions
5 types of antibodies
IgM: free in plasma, attached to B cells, activate complement, released during primary response
IgA: in saliva, tears, milk, gastric juices
IgD: attached to B cells
IgG: free in plasma, activate complement, cross placenta from mom to fetus, released during secondary response
IgE: in GI and respiratory tract secretions, involved in allergic response
4 functions of antibodies
Opsonization: coat the pathogen and make it more tasty to macrophages
Neutralization: bind to the pathogen to block its entry into your cells
Agglutination: Ab crosslink pathogens together into clumps that are easier for the phagocytes to eat
Complement fixation (activation): protein cascade activates opsonization
2 types of Humoral (antibody mediated) immunity
Active immunity (long term)
Passive immunity (short term)
Active humoral immunity
Is direct exposure to an antigen so you acquire immunity to it
Get sick with disease and then get better
Get vaccinated against the disease
B cells bind antigen, B cells become active plasma B cells that secrete antibodies specific to the antigen
Some B cells become memory B cells that produce a secondary response if pathogen is encountered in the future
Has memory (long-term immunity)
Passive humoral immunity
When you are given the antibodies rather than making them yourself
Lasts only a few weeks/months (temporary immunity)
No memory is established because it wasn’t your B cells that made the antibodies → memory B cells are not produced
2 ways to gain passive immunity
Transferred from mother to child across placenta (IgG) or breast milk (IgA)
Injecting the antibodies into the person
Primary vs. secondary immune response
1) Primary
Takes 10 days to reach peak Ab levels
Response lasts less than 2 weeks
Lower number of Ab produced
2) Secondary
Takes 2-3 days to reach peak Ab levels
Response lasts weeks to months
Higher number of Ab produced
Vaccination
Administration of weakened/dead pathogen or component of pathogen designed to trigger the primary immune response so when the pathogen is encountered in “real life,” the rapid secondary response takes care of it before illness results