11 - Cytoskeleton: Intermediate Filaments; Cell-Cell Interactions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Intermediate filaments (IFs)
solid, unbranched, rope-like fibers that provide mechanical stress and are intermediate in size (~10nm diameter) compared to MTs and microfilaments.
Alpha-helical rod-shaped monomers that spontaneously form homodimers (do not bind ATP or GTP or any nucleotide).
Dimers have polarity and associate in same direction.
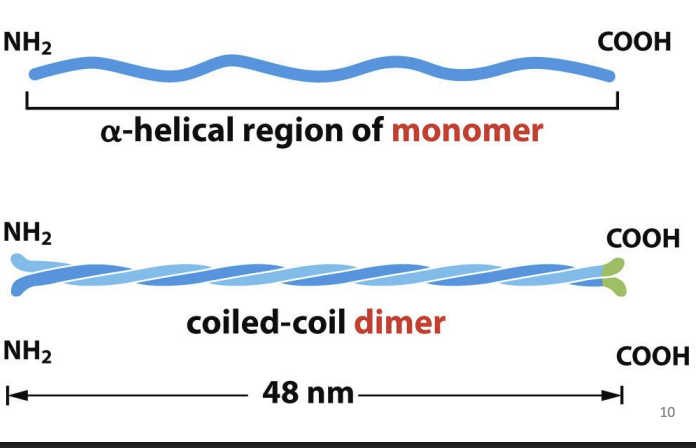
How do intermediate filament dimers assemble into tetramers, and what happens to polarity?
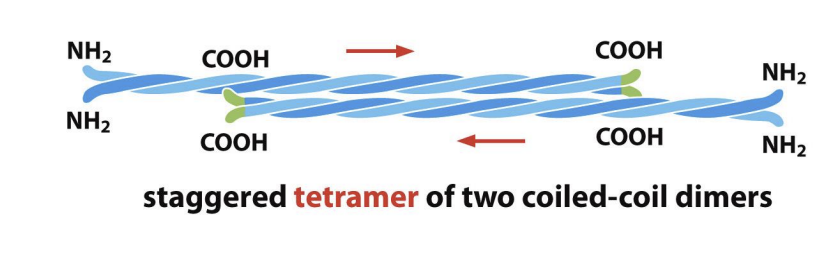
Dimers associate with each other in staggered formation that are in opposite orientations (form tetramers with no polarity).
are Intermediate Filaments easy to solubilize and where are new subnunits addrd
IFs are very difficult to solubilize = highly stable.
New subunits added to middle rather end!
Types of Intermediate Filaments
Very diverse, encoded by different gene families
eg nuclear, vimentin-like, epithelial, axonal
Which of the following statements are consistent with the structure and function
of intermediate filaments? Select all that apply.
A) Intermediate filaments protect cells from mechanical stress because they have
high tensile strength and resist stretching.
B) Each filament is made of eight strands, and each strand is made from
staggered tetramers linked end-to-end.
C) Intermediate filaments are constructed of identical subunits found in all
eukaryotic cells.
D) Intermediate filaments can connect cells at cell–cell junctions called
desmosomes.
a,b,d
IFs can be linked to other cytoskeletal elements through
bridges formed by plakin proteins = large, modular proteins e.g. Plectin.
Plectin can bundle IFs or link IFs to MTs, microfilaments or filaments of Myosin II.
Can also attach IF bundles to PM
What is the role of SUN and KASH proteins in the nuclear envelope?
SUN proteins = inner nuclear membrane proteins that bind to KASH proteins within nuclear envelope and nuclear lamina or chromosomes.
KASH proteins bind to actin filaments or indirectly to MTs/IFs.
Creates bridge between nucleus and cytoskeleton
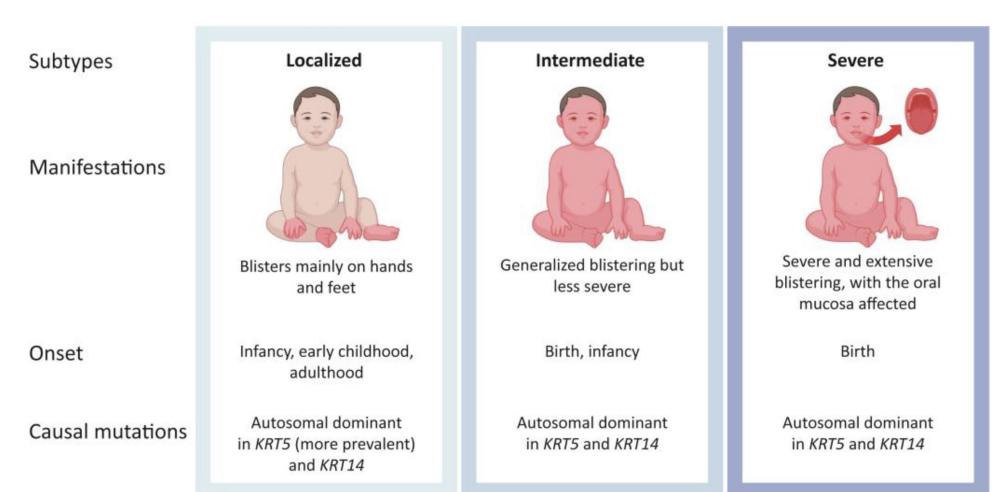
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex =
mutation in type of IFs (Keratins) that lead to skin blistering.
ALS/Lou Gehrig’s disease
accumulation or abnormal assembly of neurofilaments which disrupts axonal transport can contribute to disease.
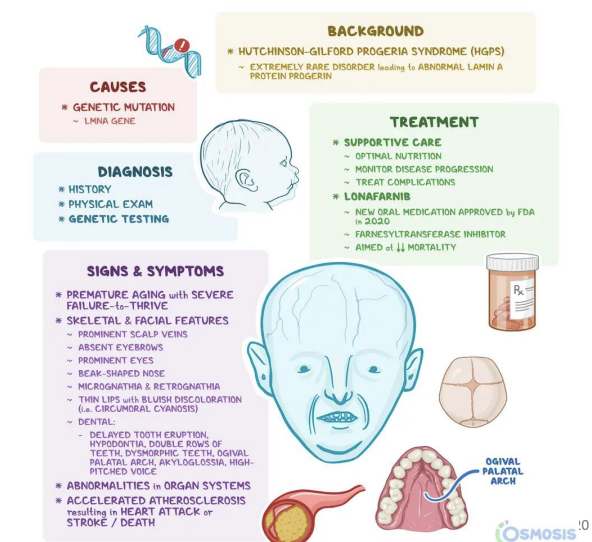
Hutchison-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS)
incorrectly modified nuclear lamin = deformed nuclei.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
complex network of proteins and polysaccharide chains that cells secrete
Cell-Cell Interactions
Cells can also linked by direct interactions, such as binding of integral membrane proteins on two cells, to create multicellular structures (e.g. tissues and organs)
epithelia
Epithelial tissues have cells tightly bound into sheets
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and connective tissue
Connective tissues (e.g. bone or tendon) are formed from ECM, with a very sparse amount of cells, that bear most of the mechanical stress to which the tissue is subjected.
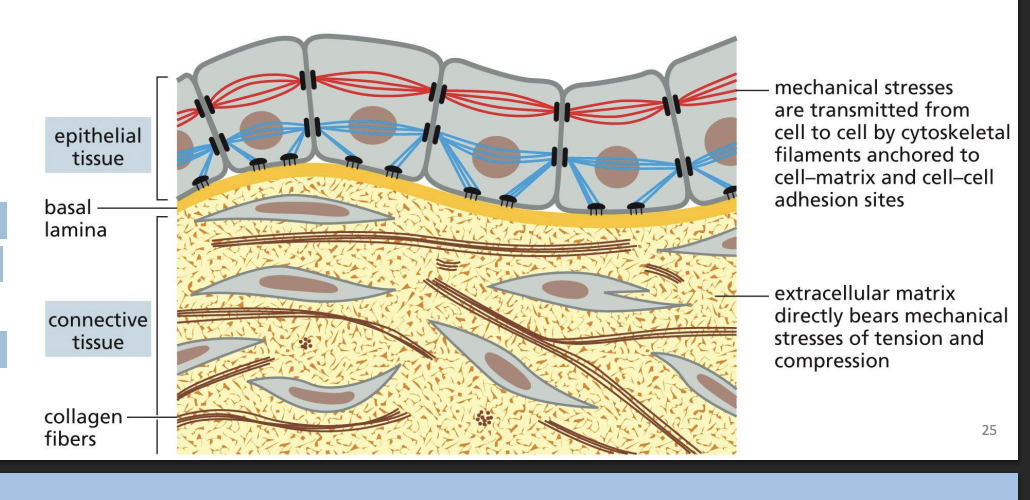
basal lamina
ECM is like “thin mat” = basal lamina (basement membrane).
Types of specialized structures at cell junctions:
• Desmosomes and
Hemidesmosomes
• Adherens junctions
• Gap junctions
• Tight junctions.
tight junctions
sealing of adjacent cells to prevent movement of molecules in space (paracellular pathway) between neighbouring epithelial cells.
Tight junctions allow for effective transport and act like fences to keep proteins confined to apical or basal sides.

What is the main function of intestinal epithelial cells?
Intestinal epithelia = absorptive cells (uptake nutrients from gut lumen).
Transcellular transport
transport of nutrients from apical side to basal side of cells.
Tight junctions form
sealing strands = branching network that encircles apical end of the cell.
Each sealing strand has transmembrane adhesion proteins embedded in neighbouring plasma membranes = occlude space.
Tight Junctions and Claudins and Occludins.
Occlusion occurs through transmembrane proteins, Claudins and Occludins.
Claudins can also form paracellular pores = selective channels to allow ions to pass between cells. Blood brain barrier is comprised of TJs!
adherens junctions
enormous protein complexes made up of 100s-1000s of cadherins and are important link between two epithelial cells.
Cadherins bind to cytosolic adaptor proteins that link to actin cytoskeleton.

Catenins
Cadherin linkage to cytoskeleton relies on adaptor proteins = Catenins. Catenins inhibit actin-myosin fiber formation which reduces tension.
mechanotransduction
Adherens junctions respond to tension inside of and outside of cells = mechanotransduction.
Adherens junctions are linked to contractile bundles of actin and myosin through Catenin proteins.
α-catenin is stretched from a folded to an extended conformation when contractile activity increases at junction = vinculin binding.
adhesion belt
Adherens junctions model shapes of multicellular structures in animal body.
Can form adhesion belt = continuous region that encircles each of the cells just beneath apical surface.
Creates transcellular network of actinmyosin bundles = coordinated contraction.
desmosome
found in tissues subjected to mechanical stress to provide strength. Contains cadherins that link cells with small extracellular gap. Cadherins in desmosomes are also linked to IF network inside of cells!

What is the molecular composition of desmosomes and how do they link to intermediate filaments?
Desmosomes have nonclassical cadehrins (Desmoglein and Desmocollin) that hold adjacent membranes together. Cytoplasmic tails of Desmoglein and Desmocollin interact with Plakoglobin and Plakophilin which bind to Desmoplakin. Desmoplakin binds IFs!
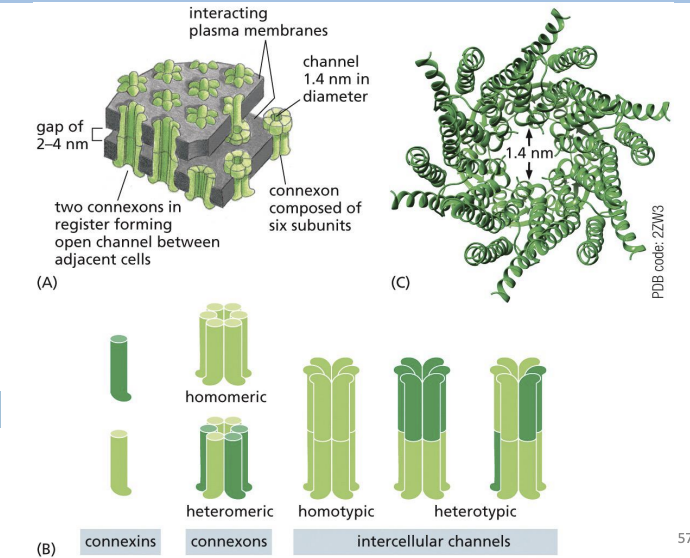
gap junction
specialized areas of intercellular communication, plasma membranes come close together between two cells to form channels of cytoplasm.
Channels have a pore that can share small molecules (e.g. ions) but not macromolecules.
Cardiac muscle = lots of gap junctions = ions pass through to allow for synchronized contraction!

Connexon
channel composed of 6 four-pass transmembrane Connexin proteins.
Connexons aligning between two cells = continuous channel formation
These channels can flip between open and closed states.
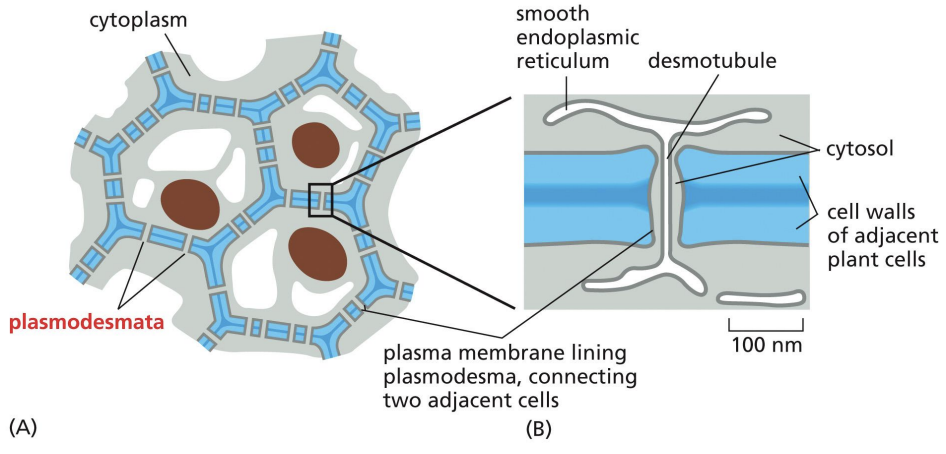
Plasmodesmata
Plants only have one class of intracellular junction = plasmodesmata, which act like gap junctions for cell to cell communication.
Plasmodesma = 20-40nm channel between two cells that contains desmotubule.
hemidesmosome
Keratins = type of IFs. Keratin network is connected to the basal lamina by
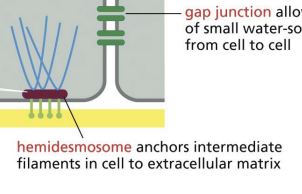
actin-linked cell-matrix j8unction
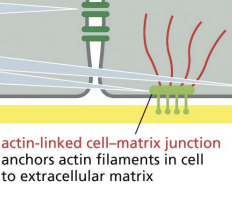
Apical surface =
cell surface that is exposed to lumen.
Basal surface =
cell surface tethered to basal lamina.
Lateral surfaces =
cell sides where junctions occur.
Transmembrane proteins that connect cytoskeleton to extracellular structures include …?
Transmembrane adhesion proteins mediate cell-cell interactions and link cytoskeleton to extracellular structures: • Integrins • Selectins • Cadherins
Cadherins
glycoproteins that join cells together and have modular construction of extracellular domains, which have calcium ions bound between them.
Act like “Velcro” = mediate strong cell-cell interactions
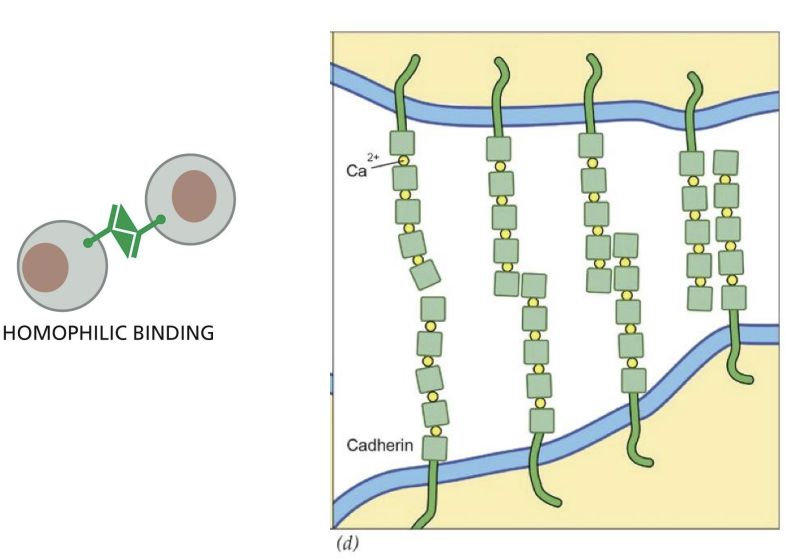
Classical cadherins
family of cadherin proteins that are closely related in sequence throughout extracellular and intracellular domains.
Nonclassical cadherins
cadherin proteins that are more distantly related in sequence.
Cadherins promote cell–cell adhesion by binding to cadherin molecules of the
same or closely related subtype on adjacent cells.
A) True
B) False
a
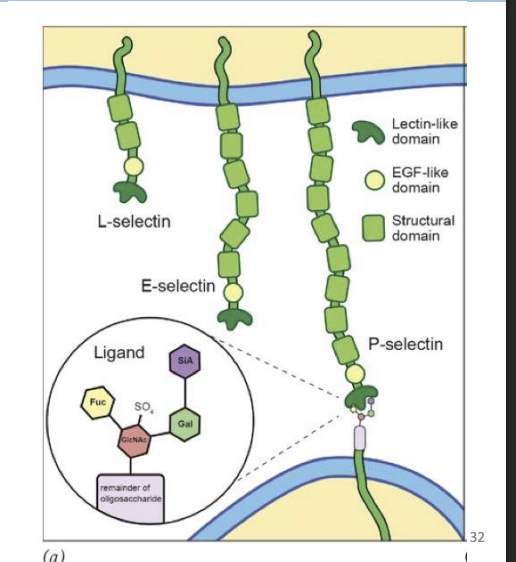
Selectins
carbohydrate-binding proteins that bind particular oligosaccharides on surface of cells and have a modular structure.
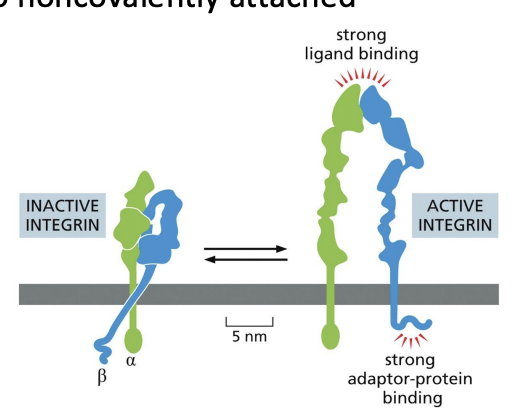
Integrins
proteins that are composed of two noncovalently attached glycoprotein subunits (alpha and beta).
N-terminals associate with ECM proteins or proteins on other cells, while short C-terminal tail interacts with actin through adaptor proteins
Cell-Cell Interactions: Selectins and Integrins
Selectins and integrins interact (heterophilic interactions) leading to transient
adhesion of white blood cells to blood vessels.
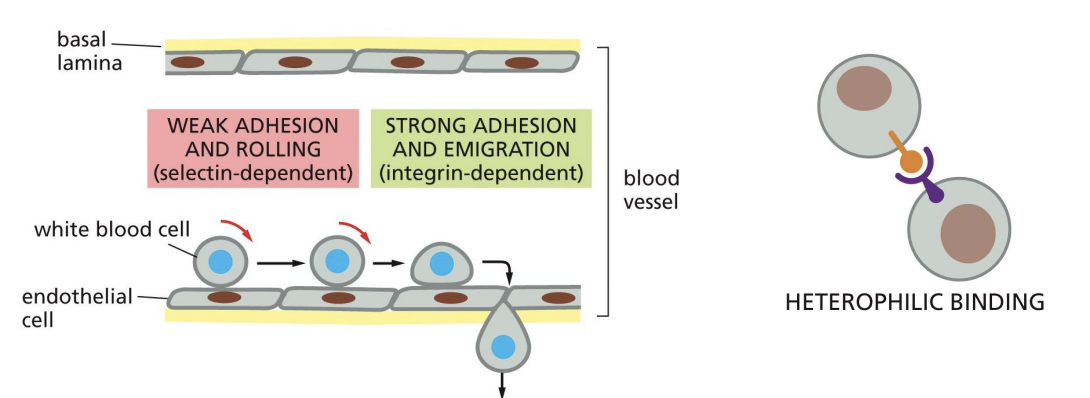
Ig superfamily proteins
proteins that contain one or more extracellular Ig-like domains reminiscent of antibody structure.
eg Ig superfamily proteins
NCAM = neural cell adhesion
molecules.
ICAM = intracellular cell
adhesion molecule.
VCAM = vascular cell adhesion
molecule
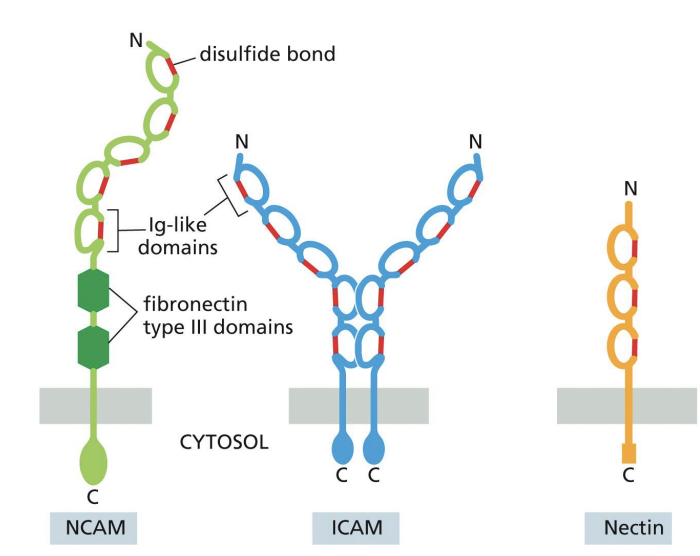
Although cadherins and Ig family members are frequently expressed on the same
cells, the adhesions mediated by Ig molecules are much stronger and, thus, are
largely responsible for holding cells together.
A) True
B) False
b
What is the term for the type of anchoring junction that links the intermediate
filaments in two adjoining cells?
A) Desmosome
B) Hemidesmosome
C) Adherens junction
D) Tight junction
a