Business Management Unit 4 - AOS 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Define business change
Occurs when an organization improves, restructures or transforms a part of its operations in response to internal and or external pressures
Define change's role in business areas
change is an important part of a business's life; it allows a business to adapt to its environment and to improve its competitiveness.
Define reactive approach
a business is impacted by the business environments and is forced to change in order to protect or preserve its position in the market.
Define proactive approach
refers to a manager who foresees alterations in the business environments and looks to implement changes in order to take advantage.
Define key performance indicators (KPI)
Precise and measurable data which can be used to measure or evaluate the performance of organisations or individuals achieving objectives. KPIs can also be used to identify if there is a need for change AND they can be used to review if the change has been successful. They are particularly important to identify trends and as a benchmark against high performing competitors.
Define percentage of market share
A representation of the portion of sales that a business has compared to the total sales for the industry or product expressed as a percentage, it demonstrates a businesses competitiveness.
Define net profit figures
the amount of money that is left after expenses have been deducted from the revenue earned. If market share is high but net profit isn't it means pricing structure is not right.
Define the rate of productivity growth
a measure of efficiency for a business and compares the amount of outputs produced to the amount of inputs used in production an the right at which increases overtime, makes it more competitive.
Define number of sales
the amount of goods/services sold over a given period of time. If high, but low net profit then expenses too high and/or pricing structure is not right.
Define rate of staff absenteesim
The rate in which employees fail to attend work on a given day when they are scheduled to be there. 6 - 11% have for Australian businesses is regarded as high. Businesses in the health care, emergency services and manufacturing businesses tend to have a high rate of staff absenteeism, negatively impacting productivity.
Define levels of staff turnover
The rate in which employees are leaving the business and need to be replaced. Studies have shown that low levels of staff turnover relate to lower levels of performance. 15% level of staff turnover for Australian businesses is a moderate level,5% is low.
Define level of wastage
The amount of resources that are discarded by the business during the production process.
Define number of customer complaints
The amount of consumers that are dissatisfied with the business and/or its products and have expressed their concerns to the business.
Define number of website hits
measures each request to a server for a file from a website, including page content, images, and Scripts.
Define number of workplace accidents
The amount of unplanned or uncontrolled events that result in personal injury or property damage recorded to the business.
Define driving forces for change
those forces which initiate, encourage and support the change - they work to assist the business to achieve its goal.
What are the 11 driving forces for change?
- managers
-owners
-employees
-competitors
-legislation
-pursuit of profit
-reduction of costs
- globalization
-technology
-innovation
-societal attitudes
Define managers
are employees holding some form of responsibility within the business, they can be a driving force by initiating change that helps to position the business in future.
Define owners
looking for a return on their investment. In pursuit of increasing investment they can demand change.
Define employees
those that work in exchange for renumeration. They play a major role in the success of change by initiating or supporting it.
Define competitors
businesses competiting in the same market can initiate change given that there is an ongoing battle for market share. e.g. if one business introduces new product it typically has rival businesses to respond and initiate change.
Define legislation
Australian business need to be aware of legislation and if it changes then the business must adapt.
Define pursuit of profit
when the KPI of net profit is below benchmark levels it can initiate change in pursuit of higher profits
Define reduction of costs
if management decides costs are too high or there is a way it can reduce costs further to increase net profit they may change in pursuit of higher profits
Define globalization
the process where businesses develop international influence and begin operating on an international scale
Define technology
failing to stay with current and new technology can cause businesses to fall behind competitors
define innovation
drives change by introducing new ideas in the form of processes, products or methods.
define societal attitudes
as a society we have divergent attitudes towards things that will change overtime which can cause change
Define restraining forces for change
those forces which work against the change, thus creating resistance to the achievement of the goal.
What are the 6 restraining forces for change?
- managers
-employees
-time
-organisational inertia
- legislation
-financial considerations
define managers
manager who do not support or believe in change are unlikely to lead the business through successful change
define employees
employees are often the main stakeholders that resist the change and work against it. Employees may fear their job security and resist against it.
define time
insufficient time is given to those responsible to implementing change or it could be the wrong time of the year to change
define organizational inertia
tendency of a business to continue along its current path with people unenthusiastic towards change
define legislation
a business can plan to implement change but find there is some legislation preventing that
define financial considerations
costs associated with change may not be viable
Define lewis force field analysis
a tool used to compare forces for and against a particular change so that an informed decision can be made.
-they need to consider the state it is currently in and the forces that are working to keep the business in this state.
-Once the force field analysis is completed, the manager can make an informed decision about whether to pursue the change or not.
What are the 6 principles of the FFA theory?
1.Identify the goal or desired outcome ( new policy, launching project)
2.Identify driving forces and restraining forces.
3.Give a weighting to the forces (forces weak or strong influence?)
4.Rank the top driving and restraining forces.
5.Implement a response by allocating tasks to team members to strengthen the driving forces or weaken the restraining forces.
6.Evaluate the response.
- The change team should evaluate the outcome of the strategies to establish whether the strength of the driving and restraining forces has been altered.
Business example of bean bag business FFA theory
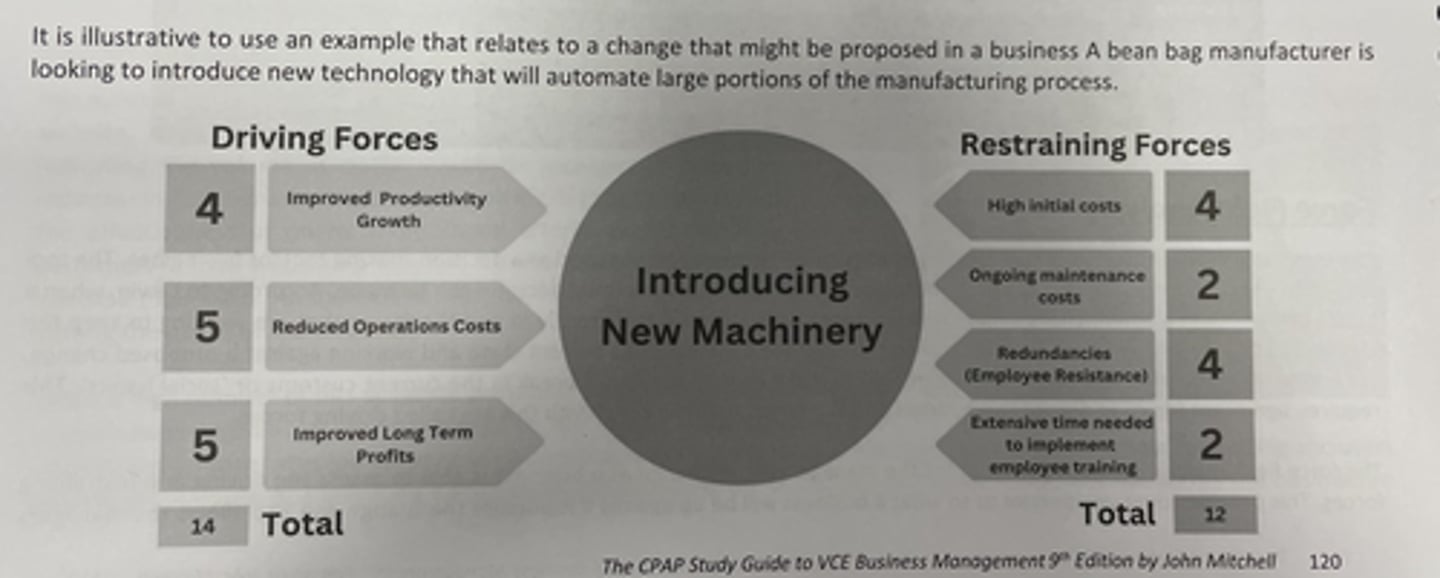
Benefits of FFA theory
- Being able to identify each of the forces
- Understanding those forces that will work for and against the change
- Enabling the managers to discuss ways to overcome the restraining forces
- The development of the action plan puts steps in place to reduce the strength of the restraining forces
- Helps make informed decisions about the change and if it is worth pursuing.
Limitations of using FFA theory
- may omit some forces that are not clearly identifiable at the time.
- The weightings of the forces are subjective. Biases can emerge.
- Timelines can also be subjective and may not consider unexpected events.
- Assigning responsibility to people to manage aspects of the change may result in a need for training as the skills of people may be lacking or overestimated
Define porters generic strategies
a strategic management theory describing how a business can seek to acquire a competitive advantage in its industry or market, and therefore dominate that industry or increase its market share in it. It is therefore a very proactive theory which has two underlying concepts lower costs and differentiation.
Other notes on porters generic strategies
Porter states that businesses should focus on one strategy rather than attempt to implement both. Businesses that implement both strategies risk being 'stuck in the middle' and being mediocre at both strategies.
Define lower cost
a strategy where a business aims to become the low-cost producer in its industry. It can do this in a variety of ways, however it is important that any cost reduction strategies do not significantly reduce the value to the end consumer.
- lower costs enable a business to gain a competitive advantage
- aim is to be a cost leader
How can a business lower costs?
- By using economies of scale
- By offering high volumes of standardised goods or services, and aiming for 'no frills'
- By implementing automated production lines to produce goods and services quicker and cheaper with less waste
- By implementing lean management strategies.
- By buying raw materials from the lowest cost source in the world.
- By minimising labour costs with overseas manufacture, or outsourcing non-core tasks.
- By reviewing materials management strategies and use JIT strategies to reduce storage costs
Aldi example of lowering costs

Advantages of lowering costs
- By offering competitive prices, a company employing a low-cost strategy aims to gain significant market share. A larger market share can lead to increased brand recognition and stronger bargaining power with suppliers, among other benefits
- may broaden the market if the lower costs are passed onto customers through better prices, potentially increasing market share
- may increase the profit margins of the product by lowering costs
- are able to withstand price wars longer than competitors as the business has the lowest costs in the industry
Disadvantages of lower costs
- It is important that any cost reduction strategies do not have a significantly negative impact on the value to the end consumers.
- Businesses won't be successful with this strategy either by trying to reduce costs of supplies if suppliers have a lot of bargaining power
- If lower costs are passed onto consumers, they may see this as a sign of lower quality and be reluctant to purchase.
- It's important to note that the low-cost strategy is not suitable for every industry or business as profit margins become too thin to sustain the business in the long run.
- Low-cost strategy companies are vulnerable to price wars initiated by competitors, so careful strategic planning and monitoring of the market are essential for success.
Define differentiation
The differentiation strategy is where a business looks to offer something unique to its consumers. This allows the business to stand out from its competitors. By becoming unique, the business's good/service will be in demand from consumers as they will not be able to get these features elsewhere.By implementing the differentiation strategy, businesses are able to charge a premium price for their product.
What is procurement in business differentiation?
Purchasing premium inputs that greatly enhance the quality of the end product.
How do patents contribute to business differentiation?
They secure the uniqueness of a product or part of a product.
What role does marketing play in differentiating a business?
Highly effective sales and marketing campaigns can highlight the unique qualities of a product.
How can relationships help a business differentiate its products?
By associating with high profile or talented personnel.
What is the significance of innovation in business differentiation?
Introducing new or revised innovative processes.
How does training contribute to business differentiation?
New programs greatly enhance the skills and abilities of employees.
What is the impact of distribution on business differentiation?
Improved delivery systems allow the business to get their products faster.
Why is location important for business differentiation?
The location should stand out from its competitors.
IGA local example
- have used customer feedback and focus groups to retain information on what products consumers want
- constantly asking for feedback and product recommendations
- want to know all customers on a first name basis
- this all ensures for more inclusivity and quality experience
Advantages of differentiation
- able to charge a premium price making the product less susceptible to price wars
- may attract greater customer loyalty as the customers are attracted to the uniqueness of the business or product
- if the uniqueness can be protected legally it can make it difficult for competitors to compete
Disadvantages of differentiation
- some customers may not be able to afford the premium price, narrowing the market
- high costs come with this strategy, profit margins can be diminished
- rivalry among existing competitors as they all want 'unique' products
Similarities of both strategies
- Both aim to increase competitive advantage in their industry
- Both aim to increase profit margins.
- Both strategies can be applied to either manufactured goods or services
Differences of both strategies
- How they aim to achieve competitive advantage.
- Lower cost can increase market share by attracting price sensitive consumers who don't have brand loyalty whereas differentiation attracts customers who are more loyal to a brand,
- Lower cost often result in lower prices for consumers whereas differentiation often leads to premium (higher) prices
What are the key initiatives for McDonalds business change
AI-Powered Drive-Thru Systems (with IBM): - Uses robotic voice assistants, license plate recognition, and personalized recommendations. - Aims to speed up service, reduce errors, and improve customer experience.
CosMc’s Beverage-Led Store Format: - Focuses on customizable drinks and light snacks. - Targets convenience-driven consumers and competes with brands like Starbucks.
What is McDonalds to approach to change
Proactive: AI drive-thru implemented to meet rising demand for faster, contactless service.
Reactive: CosMc’s created in response to market trends showing increased demand for specialty beverages.
What is McDonalds KPI
AI Drive-Thru: Customer complaints, productivity, staff turnover, profit margins.
CosMc’s: Market share, sales figures, profitability, and wastage levels.
What is McDonalds driving and restraining forces
Driving Forces:
- Technology and profitability motivate AI adoption.
- Competition and consumer trends drive CosMc’s development.
Restraining Forces:
- Employee resistance, high installation costs, privacy concerns for AI systems.
- Financial risk and organizational inertia for CosMc’s.
What are change management strategies for McDonalds
Low-Risk: Clear communication, staff empowerment, training, and incentives used for AI rollout.
High-Risk: Hypothetical manipulation or threats were avoided to maintain trust.
Lewin’s Three-Step Model for McDonalds
Unfreeze: Highlighted inefficiencies and competitive pressure to justify change.
Change: Implemented AI and CosMc’s with training and support.
Refreeze: Standardized new processes and monitored KPIs to embed changes.
What is McDonalds leadership
- CEO Kempczinski championed AI and CosMc's, balancing innovation with service quality.
- He adapted quickly when AI faced issues, discontinuing the program to maintain standards.
- Emphasized clear communication, vision, and empathy for staff during transitions.
What is McDonalds alignment with business principles
- Provided direction and communicated vision clearly.
- Built confidence by addressing challenges proactively.
- Supported employees by recognizing the impact of change on their roles.