physics 2 exam 4
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
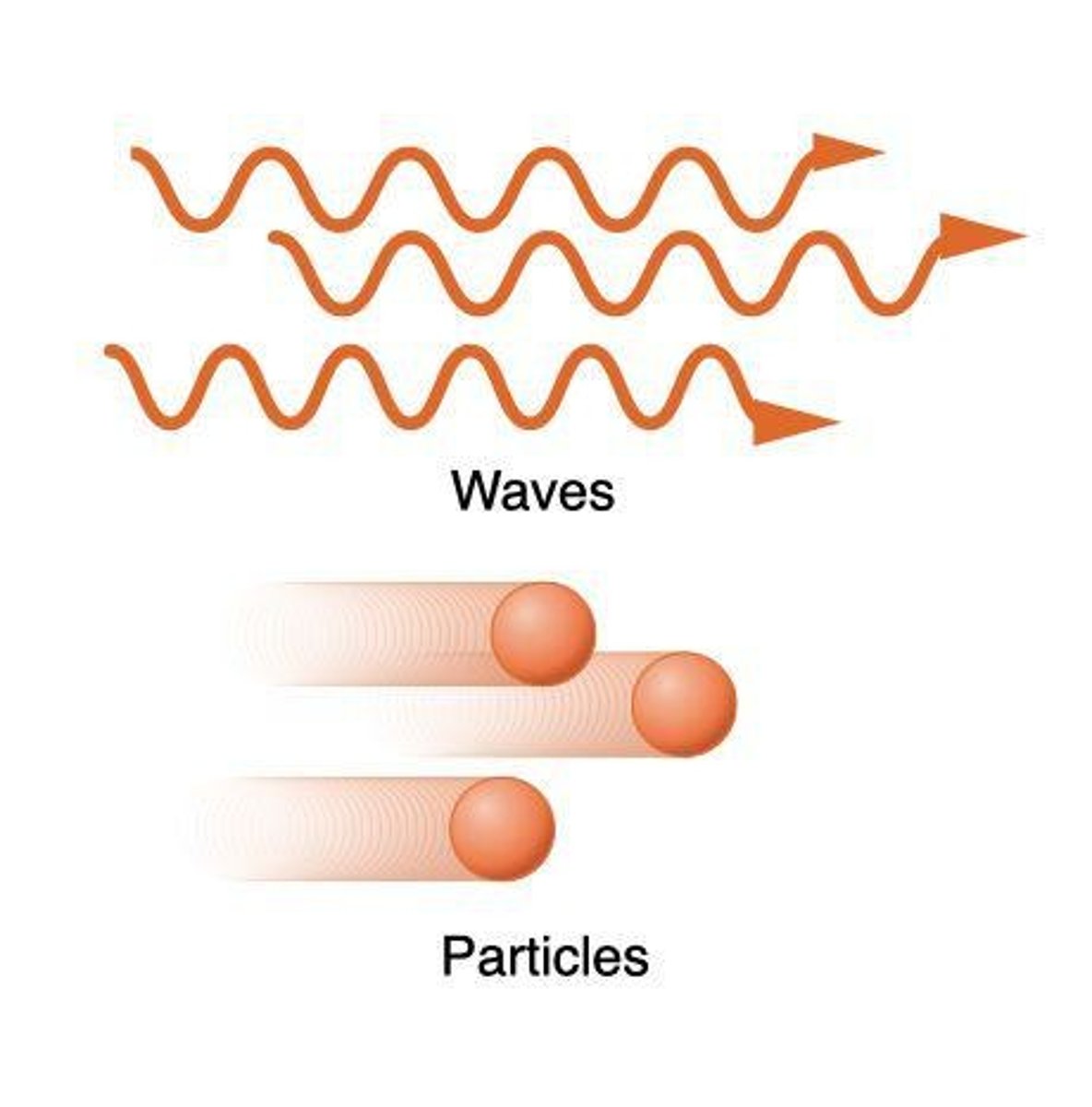
What is the duality principle of light?
Light behaves both as a wave and as a particle (photon).
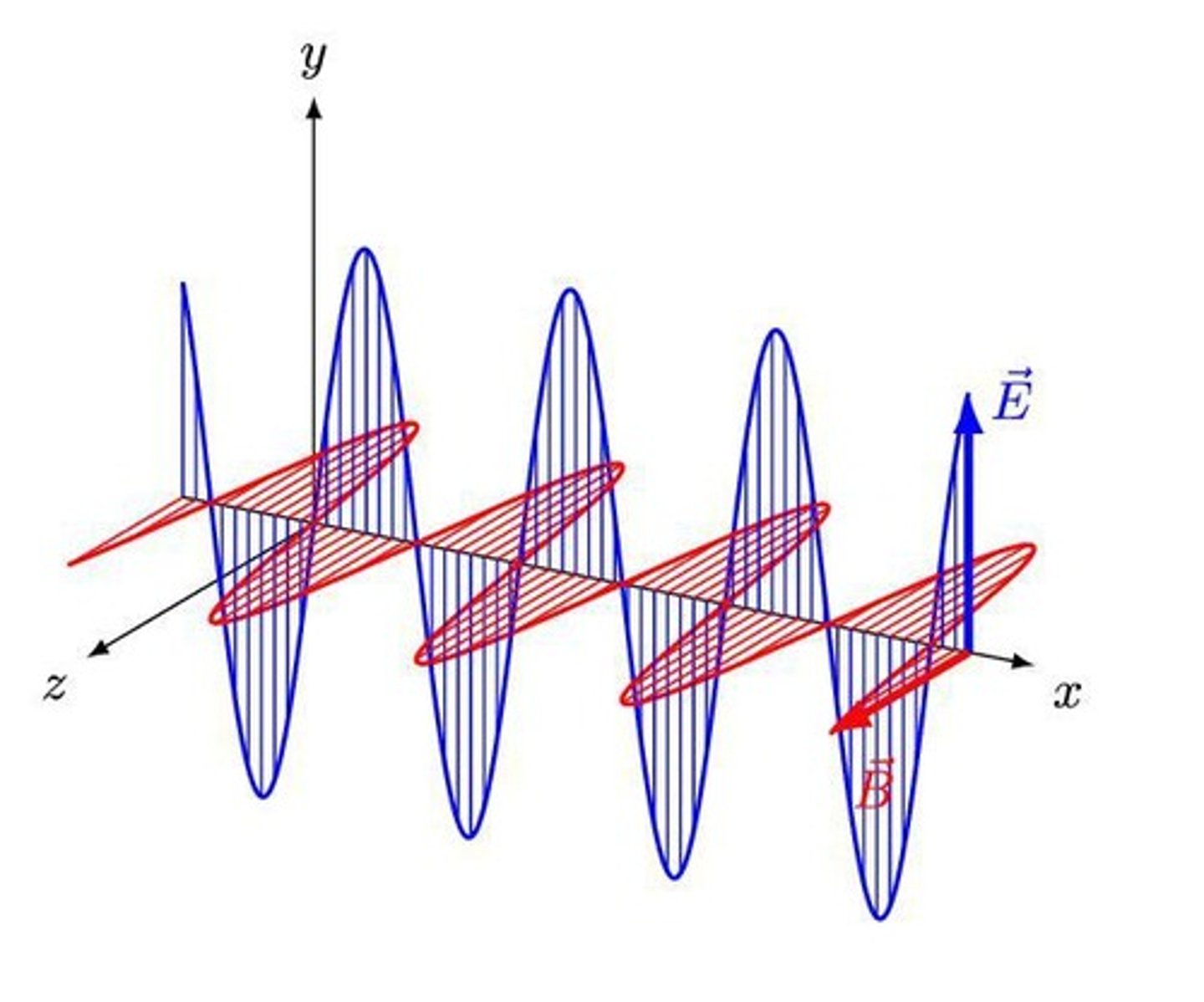
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
c = 3 x 10^8 m/s
What does the index of refraction represent?
It indicates how much light bends when entering a material.
What is the formula for the speed of light in materials?
n = c/v, where n is the index of refraction, c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and v is the speed of light in the material.
What is a photon?
An elementary particle of electromagnetic radiation, a packet of energy that moves at the speed of light.
What phenomenon occurs when light shines on certain metals and causes electrons to be emitted?
Photoelectric Effect
What is the relationship between energy and frequency of light?
Energy (E) is directly proportional to frequency (f), E = hf, where h is Planck's constant.
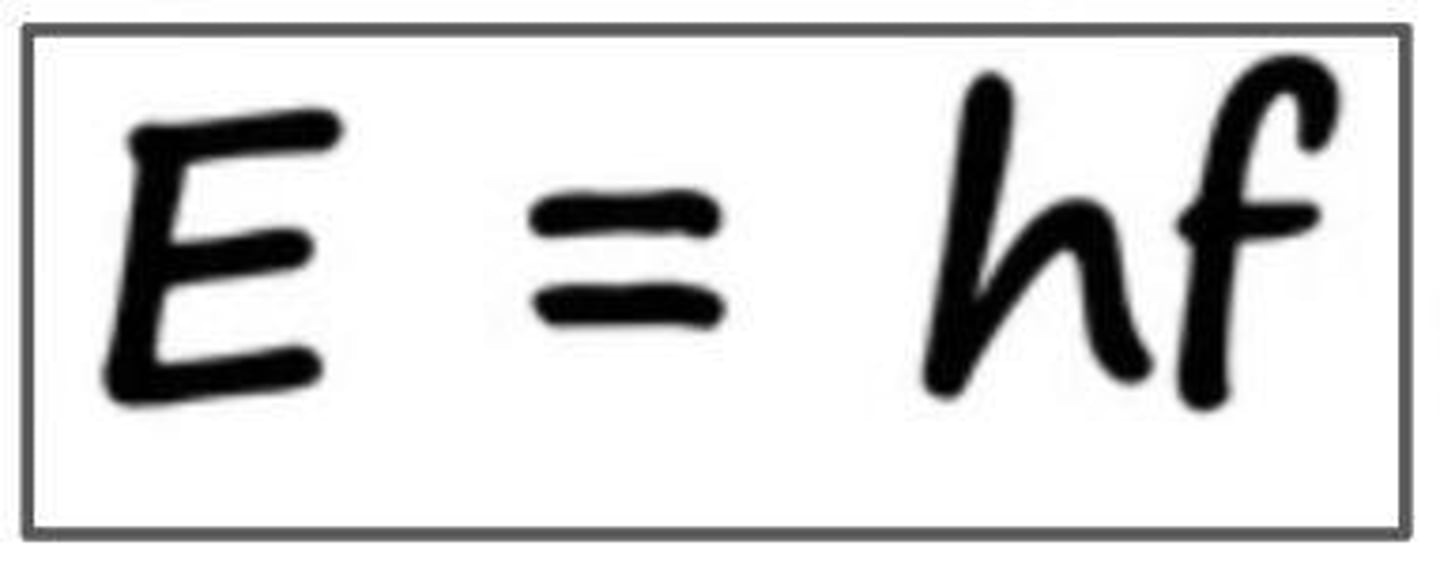
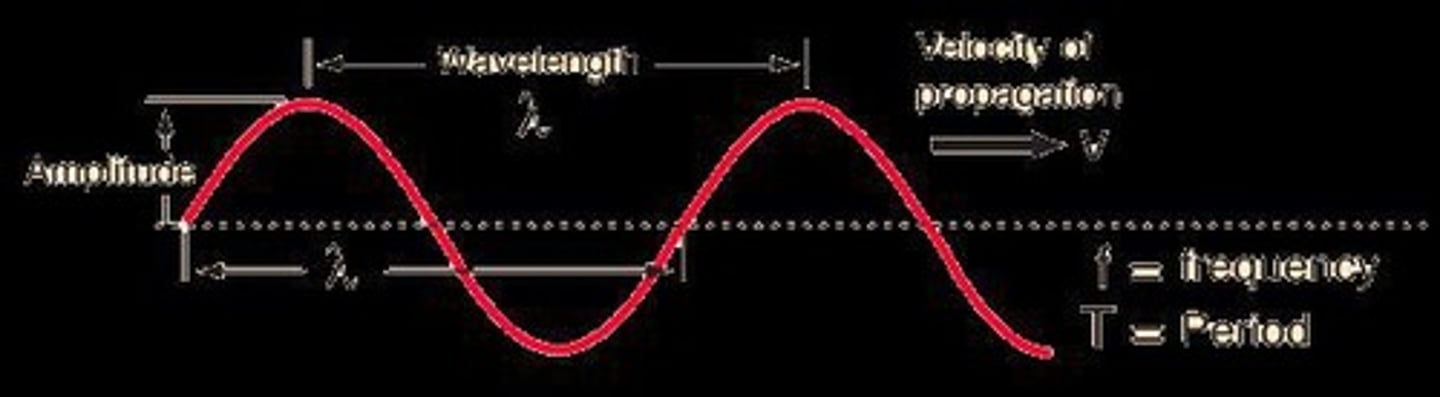
What does the amplitude of a light wave represent?
The maximum value from the equilibrium position, representing energy or intensity of light.
What is the formula for frequency?
f = 1/T, where T is the period.
What is dispersion in the context of light?
The separation of visible light into its different colors.
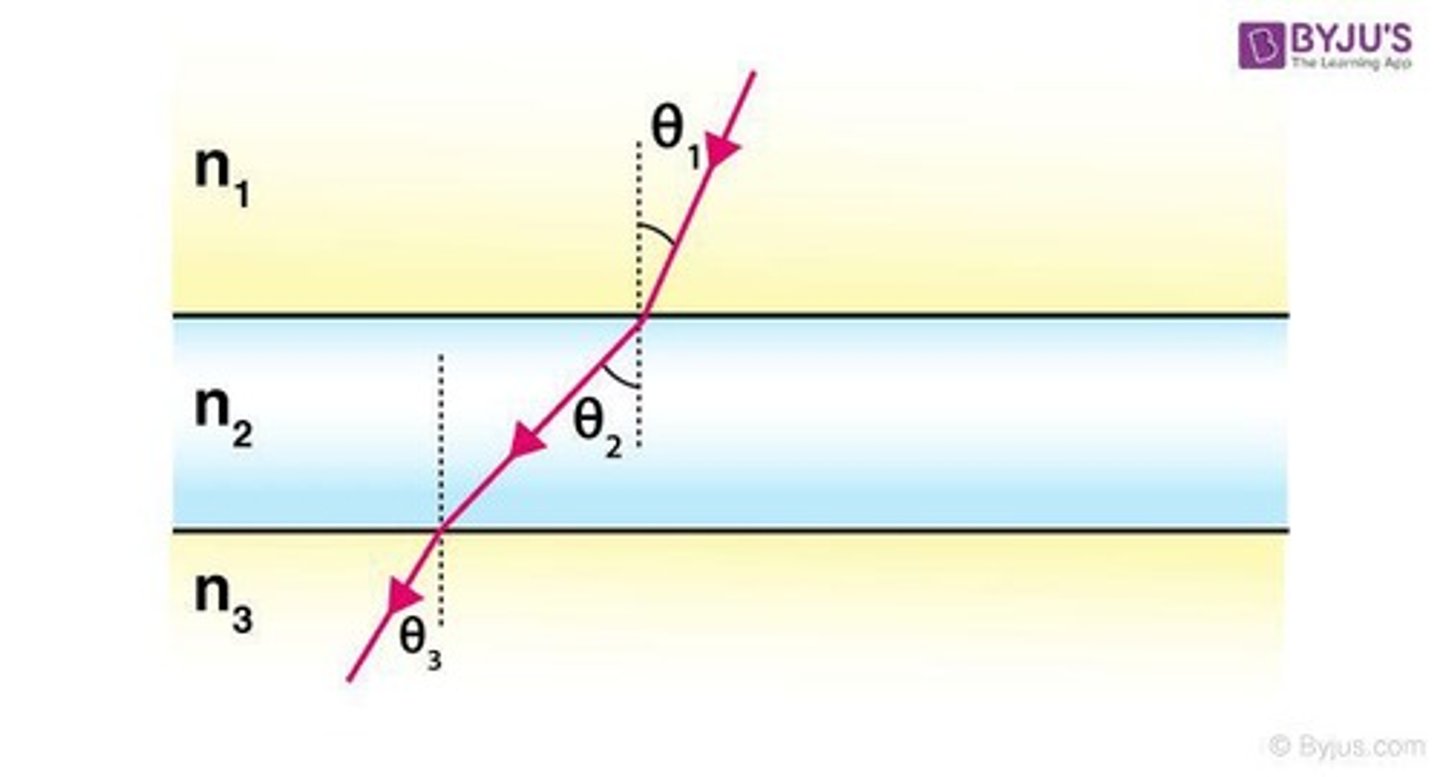
What is refraction?
The bending of light as it travels from one medium to another.
What is the critical angle?
The angle of incidence that creates a refracted angle of 90 degrees.
What happens during total internal reflection?
Light is completely reflected back into the denser medium when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
What is the formula for calculating the index of refraction?
n = c/v
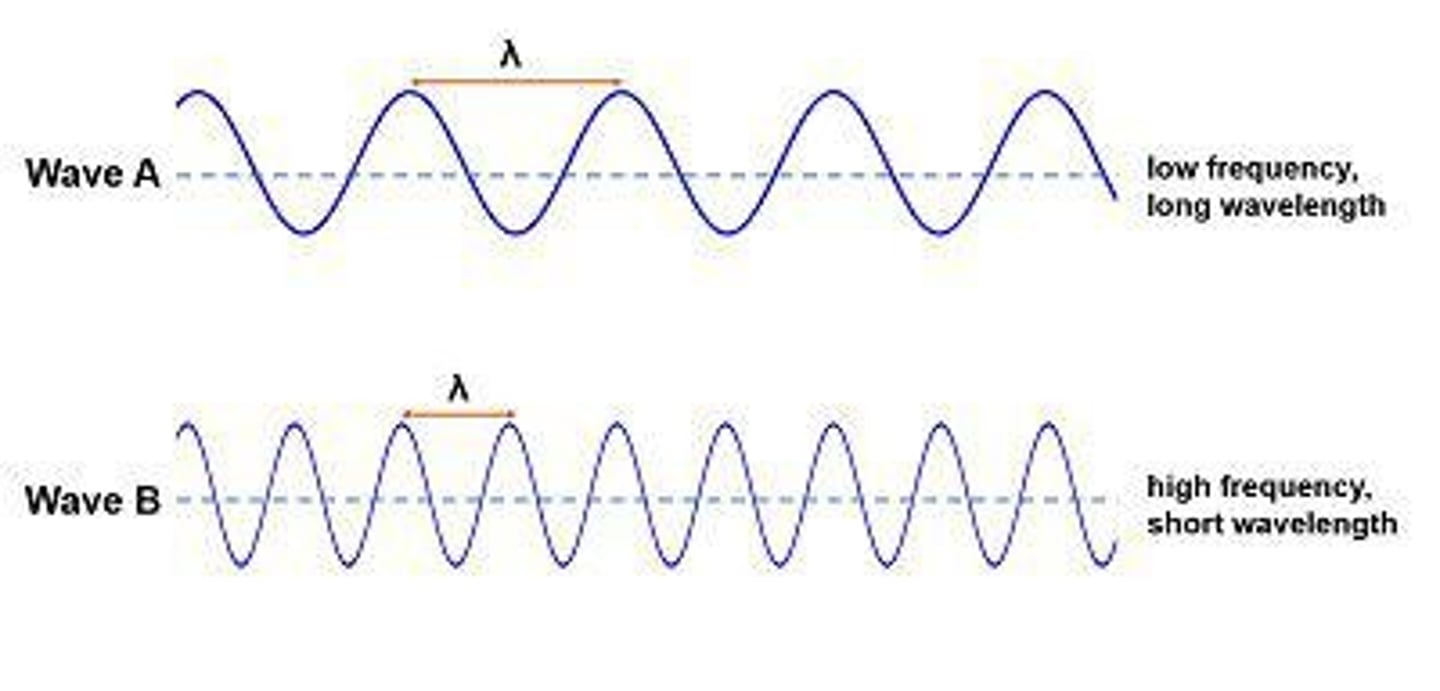
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
Higher frequency means shorter wavelength and vice versa.
What does the law of reflection state?
When light hits a surface, it is deflected at an angle equal to the angle of incidence.
What is the wavelength of light?
The length of one wave cycle, determining the color of visible light.
What is the amplitude of a light wave measured in?
Joules (energy) or Radiant Intensity (W/m²).
What does a high index of refraction indicate?
The material has a higher density than air and light travels slower through it.
What is the formula for photon energy?
E = hf, where h is Planck's constant and f is frequency.
What is the effect of light absorption?
An object takes in incoming light energy, converting it into another form of energy, typically heat.
What is the relationship between light frequency and energy?
Higher frequency light has more energy.
What does omni-directional propagation of light mean?
Light spreads out in all directions from its source.
What is the wave-particle duality nature of light?
Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties.
Define amplitude in the context of waves.
Amplitude is the maximum displacement of points on a wave, typically measured from the rest position.
What is the unit of measure for frequency?
Hertz (Hz), which is equivalent to cycles per second.
How is the period of a wave defined?
The period is the time taken for one complete cycle of the wave.
What does wavelength represent?
Wavelength is the distance between successive crests of a wave.
What is the energy of a photon with a wavelength of 450 nm?
Energy can be calculated using the formula E = hc/λ, where h is Planck's constant and c is the speed of light.
What is the Law of Reflection?
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection for a smooth surface.
Define the index of refraction.
The index of refraction is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium.
What is the speed of light in diamond (n = 2.42)?
The speed of light in diamond is approximately 1.24 x 10^8 m/s.
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection occurs when a light ray travels from a denser medium to a less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
How do you calculate the critical angle for total internal reflection?
The critical angle can be calculated using the formula θc = sin⁻¹(n2/n1), where n1 is the index of refraction of the denser medium and n2 is that of the less dense medium.
What happens when light travels from glass (n=1.50) into air (n=1.00)?
The angle of refraction can be determined using Snell's Law: n1sin(θ1) = n2sin(θ2).
What is the focal length of a lens?
The focal length is the distance from the lens to the focal point where parallel rays converge.
What is the relationship between object distance (do), image distance (di), and focal length (f) in lenses?
The lens formula is given by 1/f = 1/do + 1/di.
What is magnification in optics?
Magnification is the ratio of the height of the image (hi) to the height of the object (ho), given by the formula m = hi/ho.
What is Huygen's Principle?
Huygen's Principle states that every point on a wavefront can be considered a source of secondary wavelets, and the new wavefront is the envelope of these wavelets.
Define constructive interference.
Constructive interference occurs when two waves collide in phase, resulting in a wave of greater amplitude.
Define destructive interference.
Destructive interference occurs when two waves collide out of phase, resulting in a wave of reduced amplitude.
What is diffraction?
Diffraction is the bending of light around corners or edges.
What is the formula for calculating the distance between adjacent bright fringes in a double-slit experiment?
The distance can be calculated using y = (mλL)/d, where m is the order of the fringe, λ is the wavelength, L is the distance to the screen, and d is the slit separation.
What is the purpose of a diffraction grating?
A diffraction grating is used to separate light into its component wavelengths, creating a spectrum.
What happens to interference fringes if the slit separation increases?
The fringe spacing decreases, resulting in closer fringes.
What happens to interference fringes if the wavelength increases?
The fringe spacing increases, resulting in wider fringes.
What is the central fringe in interference patterns?
The central fringe is the brightest fringe and corresponds to the zeroth order (m=0) of the interference pattern.
How do you calculate the image distance for a concave mirror?
Use the mirror formula: 1/f = 1/do + 1/di, where f is the focal length, do is the object distance, and di is the image distance.
What is a virtual image?
A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to diverge from a point, and it cannot be projected onto a screen.
What is the significance of the focal point in lens optics?
The focal point is where parallel rays of light converge after passing through the lens.