China stuff for the HWS final
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Last updated 5:17 PM on 1/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Buddha
Means "Enlightened One." He is said to have found a path for overcoming suffering. A prince who lived in India
2
New cards
Chiang Kai-shek
General and leader of Nationalist China after 1925. Although he succeeded Sun Yat-sen as head of the Guomindang, he became a military dictator whose major goal was to crush the communist movement led by Mao Zedong.
3
New cards
collective
large farm owned and operated by peasants as a group; used to increase crops and to give equal share of pay to all farmers
4
New cards
Confucius
(551-479 BCE) A Chinese philosopher known also as Kong Fuzi and created one of the most influential philosophers in Chinese history. Wanted people to follow the traditions and customs from the past to maintain order.
5
New cards
Dr. Sun Yat-sen
Educated in the West, and became a revolutionary. Led a rebellion against Qing Dynasty in 1911. Failed to establish a democratic government after the dynasties.
6
New cards
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress of China and mother of Emperor Guangxi. She put her son under house arrest, supported anti-foreign movements like the so-called Boxers, and resisted reforms of the Chinese government and armed forces. Son was 5 when he was crowned so she became "ruler".
7
New cards
Five Relationships
1. husband and wife 2. parent and child 3. elder and younger brother 4. ruler and Minister or subject 5. friend and friend
8
New cards
Four Olds
Old ideas, old culture, old customs, and old habits; the Red Guard's targets for destruction
9
New cards
Gang of Four
Jiang Qing and three political allies who attempted to seize control of Communist government in China from the pragmatists; arrested and sentenced to life imprisonment in 1976 following Mao Zedong's death. Arrested for trying to overthrow the government and for causing deaths during Cultural Revolution
10
New cards
Genghis Khan
Leader and founder of The Mongols (largest empire). (1206-1227)
11
New cards
Guomindang
Nationalist political party founded on democratic principles by Sun Yat-sen in 1912. After 1925, the party was headed by Chiang Kai-shek, who turned it into an increasingly authoritarian movement. The main government of Taiwan and was supported by more the gentry, less the peasants.
12
New cards
Han Dynasty
(202 BC - 220 AD) dynasty started by Lui Bang(peasant); a great and long-lasting rule, it discarded the harsh policies of the Qin dynasty and adopted Confucian principles; rulers chose officials who passed the civil service exams rather than birth; it was a time of prosperity(Golden Age); efficient bureaucracy
13
New cards
Kublai Khan
(1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China. Most info about him came from the writings of Marco Polo (maybe true, maybe not). Finished conquer of China after Genghis
14
New cards
Laozi
Chinese Daoist philosopher; founder of Daoism, taught that governments were of secondary importance and recommended retreat from society into nature. One with nature and to not strive for money, etc.
15
New cards
Loess hills
Hills made of unstratified, fertile, yellow-brown soil that is carried by the wind; of the Yellow River Valley in northern China.
16
New cards
Long March
A 6,000-mile journey made in 1934-1935 by Chinese Communists fleeing from Jiang Jieshi's(Chiang's) Nationalist forces; 90,000 people with only 7,000 survivors in the end
17
New cards
Mandate of Heaven/Dynastic Cycle
\
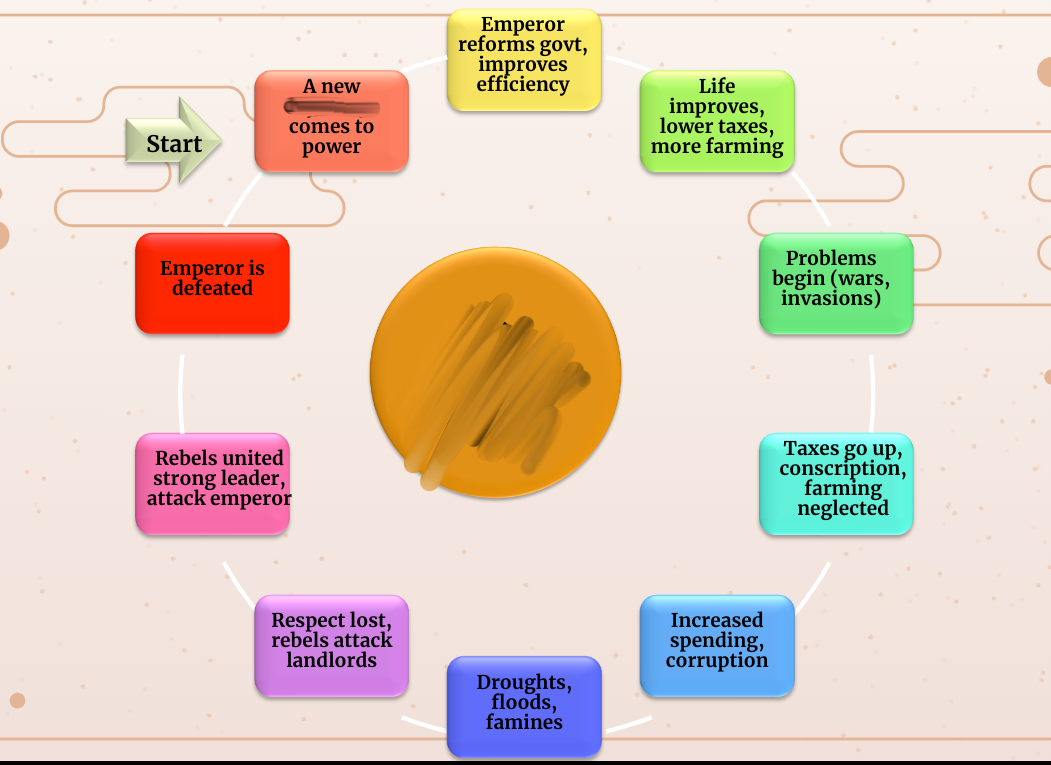
18
New cards
Mao Zedong
(1893-1976) Leader of the Communist Party in China that overthrew Jiang Jieshi(Chiang) and the Nationalists. Established China as the People's Republic of China and ruled from 1949 until 1976.
19
New cards
Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade. (1254-1324) Italian explorer and author. He made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys.
20
New cards
Ming Dynasty
Started by peasant Zhu. Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368; lasted until 1644; initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China. Imperialized and expanded through much of Asia. Golden age of culture, economy, etc. When Zheng He discovered America(we think)
21
New cards
Mongol Horde
led by the Khans. Took over large areas of Asia from the 1200's to 1700's. Was mostly undefeated.
22
New cards
People's Communes
The regional unit that comprised the collectivization system. It is an intentionally assembled community of people living together, sharing common interests, property, possessions, and even work and income. During the Great Leap Forward; failed
23
New cards
People's Liberation Army (PLA)
The combined armed forces of the People's Republic of China, which includes land, sea, air, and strategic missile forces. Was formed during the civil war between CCP and GMD
24
New cards
Qin Dynasty
the Chinese dynasty, founded by Qin Shi Huangdi, (from 226 BC to 206 BC) that established the first centralized imperial government and built much of the Great Wall
25
New cards
Qing Dynasty
the last imperial dynasty of China (from 1644 to 1911) which was overthrown by revolutionaries. Also known for its extreme isolationism; resisted foreign influence. Ruled by Manchus and had government structure similar to the Mongols.
26
New cards
Red Guards
the Radical youth of the Cultural Revolution in China starting in 1966. Often wore red armbands and carried Mao's Little Red Book. Terrorized Chinese citizens/cities and determined who went to camps.
27
New cards
Shang Dynasty
Second Chinese dynasty (about 1500 - 1100 B.C.) which was mostly a farming society ruled by an aristocracy mostly concerned with war. 30 kings ruled from 7 different capitals. They're best remembered for their art of bronze casting. Also implemented the ideas of the Mandate of Heaven
28
New cards
Tang Dynasty
(618-907 CE) The Chinese dynasty that was much like the Han, who used Confucianism. This dynasty had the equal-field system, a bureaucracy based on merit, and a Confucian education system; artistic golden age, Li Bai and other famous poets
29
New cards
Tiananmen Square
Site in Beijing where Chinese students and workers gathered to demand greater political openness in 1989. The demonstration was crushed by Chinese military with great loss of life.

30
New cards
Warlord
a local leader of an armed group; usually and old general from ancient dynasties
31
New cards
warlords
a military leader operating outside the control of the government
32
New cards
Xia Dynasty
This was the earliest known dynasty. There is no written evidence of this early time period, but artifacts have been found. The people of this time were farmers and made pottery. Probably not a realy dynasty.
33
New cards
Yuan Dynasty
(1279-1368 CE) The dynasty with Mongol rule in China; founded by Kublai Khan and had lots of wealth and prosperity; many, long trade routes; double up government (1 Chinese, 1 Mongol); centralized with bureaucracy but structure is different: Mongols on top-\>Persian bureaucrats-\>Chinese bureaucrats
34
New cards
Wendi
The Emperor Wen of (redacted), personal name Yang Jian, Xianbei name Puliuru Jian, alias Narayana deriving from Buddhist terms, was the founder and the first emperor of the Chinese (redacted) dynasty.
35
New cards
Dhali Lama
a title given by the Tibetan people to the foremost spiritual leader of the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" school of Tibetan Buddhism
36
New cards
Manchus
a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name.
37
New cards
Sui
a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The (redacted) unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and laying the foundations for the much longer lasting Tang dynasty.
38
New cards
The Emperor and the Royal family are…
Upper class
39
New cards
Scholars and Government Officials are…
Upper class
40
New cards
The Gentry (or gentiles if you know what I mean (yes you 8th period kiddos)) are…
Upper class
41
New cards
The peasants are…
lower class
42
New cards
Artisans and Merchants are…
Lower class
43
New cards
Soldiers were…
lower class
44
New cards
slaves are…
lower class
45
New cards
women
no class
46
New cards
Daoism
(redacted) or (redacted) refers to either a school of philosophical thought or to a religion, both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the Tao; the Tao is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality
47
New cards
\n \n Confucianism
(redacted) also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China.
48
New cards
\n Buddhism
(redacted), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha.
49
New cards
\n Communism
a political theory derived from Karl Marx, advocating class war and leading to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs.
50
New cards
\n WWII/ Japanese invasion (Second Sino-Japanese War)
The ( r e d a c t e d ) or War of Resistance was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War.
51
New cards
\n Formosa/ Taiwan
(redacted), 180 km east of China, is known for modern cities, traditional Chinese temples, hot springs resorts and dramatic mountainous terrain.
52
New cards
\n Four modernizations
goals first set forth by Deng Xiaoping to strengthen the fields of agriculture, industry, defense, and science and technology in China