Gen Chem 1: Chapters 1-2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
matter
anything that occupies space and has mass (solid, liquid, gas)
classifications of matter
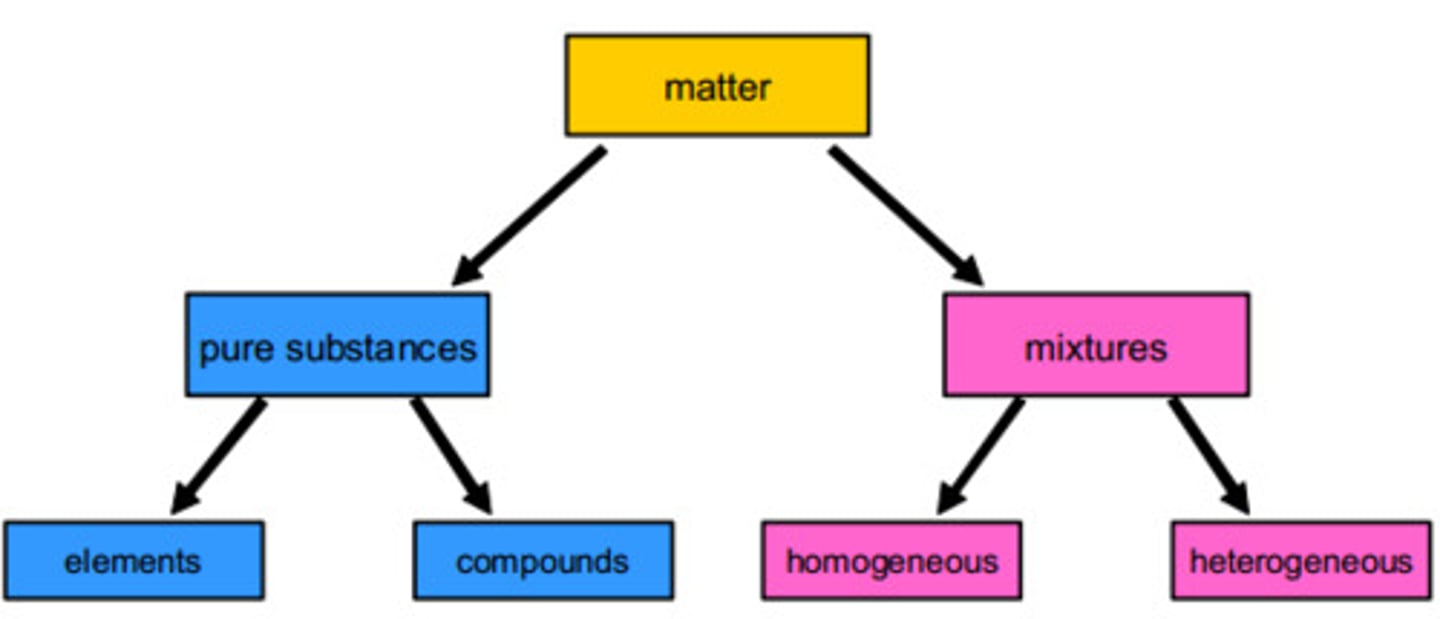
mixture
a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities (homogenous/heterogenous)
homogenous mixture
the composition of the mixture is the same throughout ("no chunks")
heterogenous mixture
the composition is not uniform ("has chunks")
substances
a form of matter that has a definite (constant) composition and distinct properties (elements/compounds)
element
a substance that cannot be separated further into simpler substances
compound
a substance composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically united in fixed proportions
molecule
consists of two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds (moves as one "unit")
atom
smallest particle of an element
physical property
can be observed without changing the composition of a substance (color, volume, mass, melting/freezing pt, length, opacity, pressure, boiling/condensation pt)
physical change
the form of matter changes, but NOT molecular composition (melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, deposition)
sublimation
solid to gas
deposition
gas to solid
chemical property
a property that is evident during a chemical reaction (toxicity, reactivity, heat of combustion, chemical stability, oxidation state, enthalpy of formation, chemical bonds, flammability)
chemical change
the molecular composition changes; a reaction
extensive property
depends on how much matter is being considered; can be added together (volume, mass, size, weight, length, heat)
intensive property
does NOT depend on how much matter is being considered; NOT additive (boiling point, color, temperature, luster, hardness)
how many m in 1 Gm (gigameter)
1 x 10^9 m
how many m in 1 Mm (megameter)
1 x 10^6 m
how many μm (micrometers) in 1 m
1 x 10^6 μm
how many nm (nanometers) in 1 m
1 x 10^9 nm
how many pm (picometers) in 1 m
1 x 10^12 pm
how many fm (femtometers) in 1 m
1 x 10^15 fm
volume
length x width x height (measured quantity with derived units: 1 mL = 1 cm^3) -- NOTE: when units are squared/cubed, the conversion factors themselves must also be squared/cubed
density
mass/volume
(solid and liquid units: g/mL; gas units: g/L)
when do leading zeroes count as sig figs?
never (ex: 0.0007 = 1 sig fig)
when do interior zeroes count as sig figs?
always (ex: 2075 = 4 sig figs)
when do trailing zeroes count as sig figs?
only when there is a decimal place (ex: 1450 = 3 sig figs, but 1450. = 4 sig figs)
how to determine amount of sig figs when multiplying/dividing
answer should have the same number of sig figs as the input with the SMALLEST number of sig figs (ex: 1.180 x 0.0078 should have 2 sig figs)
how to determine amount of sig figs when adding/subtracting
answer should be rounded to the same decimal place as the LEAST PRECISE input (fewest decimal places) (ex: 89.334 + 1.1 should be rounded to the tenths place (0.1))
Z
atomic number - # of protons in an element (defines the element)
A
mass number - # of protons + # of neutrons
ions
an atom that is electrically charged
anion
a negatively charged atom (more electrons than protons)
cation
a positively charged atom (less electrons than protons)
isotope
atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons
atomic mass
average mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element (measured in amu; found on periodic table)
molecular formula
shows the exact number of atoms of each element in one molecule
empirical formula
shows which elements are present and the simplest whole-number ratio of their elements
isomers
compounds with the same chemical formula but different molecular structures
structural isomers
compounds that differ in how the atoms are connected to each other
spatial isomers
compounds in which the relative orientations of the atoms in space can be different
mole (mol)
an amount in which there are 6.022 x 10^23 "things", such as atoms or molecules
molar mass
the mass (in grams) of 1 mole of atom/molecule of a substance
how to find molar mass of a compound
find the molar mass of each element in the compound, multiply each molar mass by the amount of each element in the compound, then add the products together
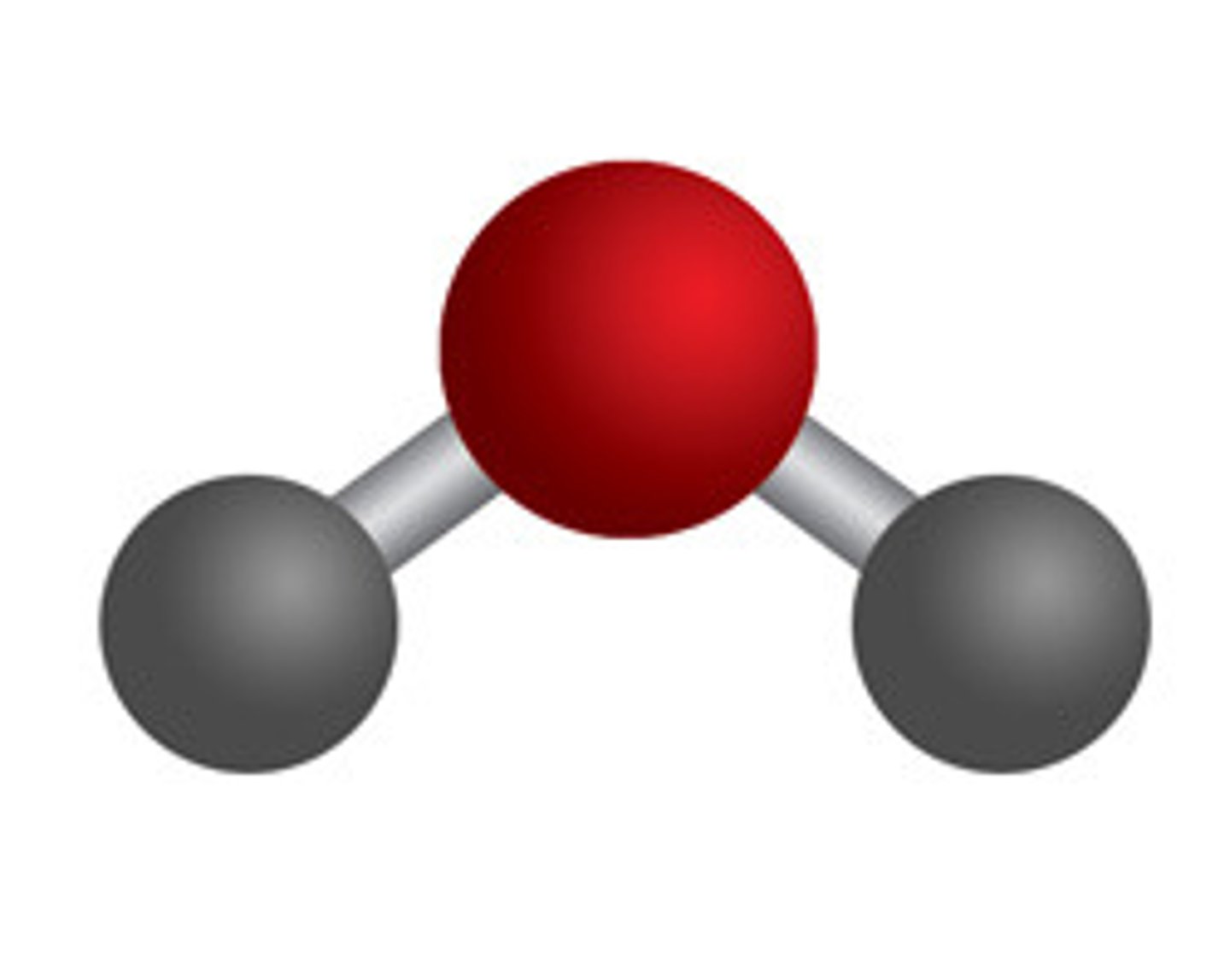
ball-and-stick model
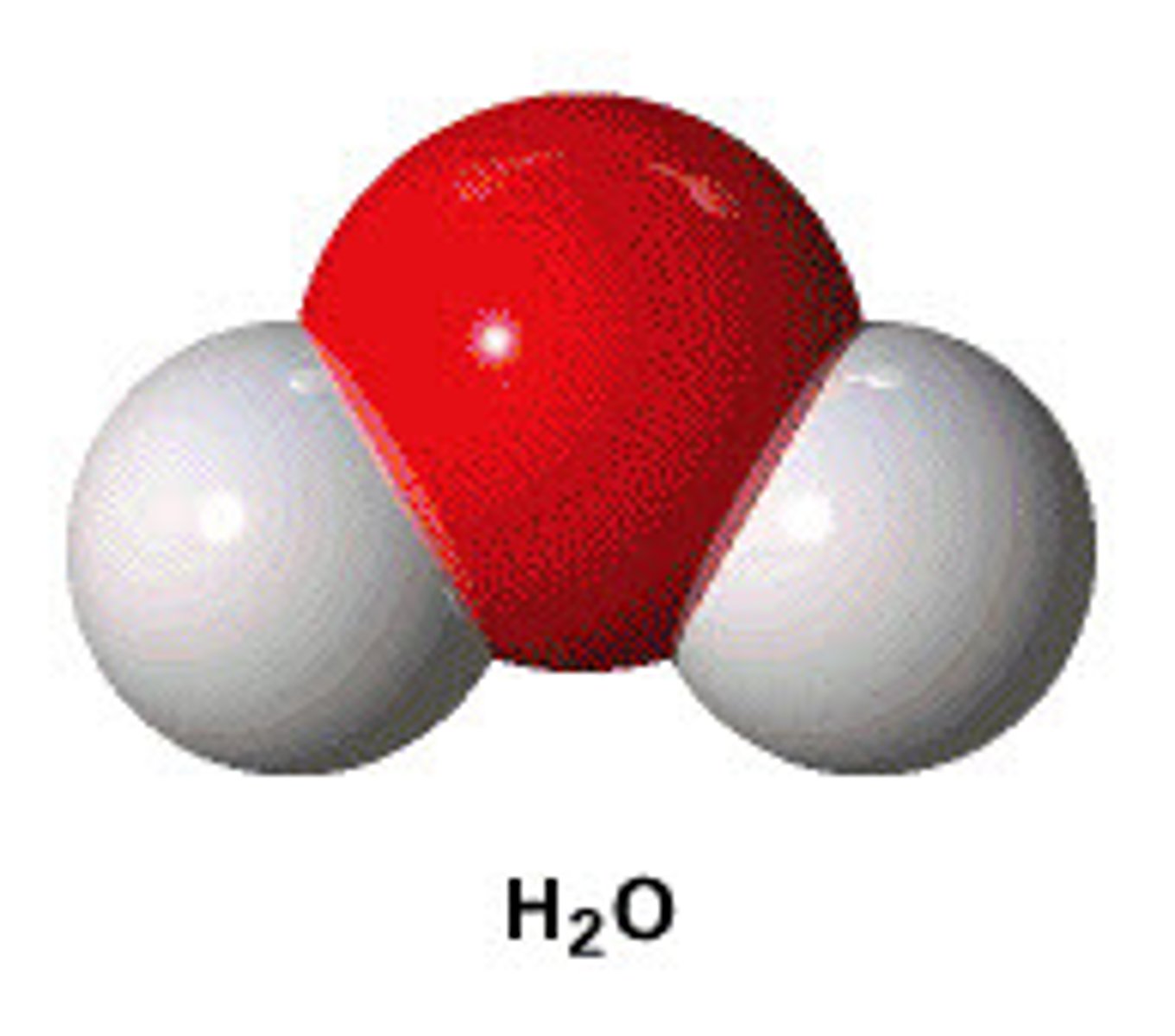
space filling model
Dalton's Postulates / The Atomic Theory
1. matter is composed of small particles called atoms. an atom is the smallest unit of an element.
2. all atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties (INCORRECT)
3. the atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements
4. compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element in a whole number ratio. for any given compound, the atoms present are always in the same ratio.
5. a chemical reaction involves only the separation, combination, or rearrangement or atoms; it does not result in the creation or destruction of atoms.