Biology Edexcel Topic 2 (The nervous system)
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
The brain and spinal cord
What is the spinal cord?
A long, thin structure composed of neurones that extend from the medulla oblongata down the spine
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Connects the peripheral nervous system (nerves outside the CNS) to the brain
Describe the structure of the brain
Consists of three main regions:
Cerebrum, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata
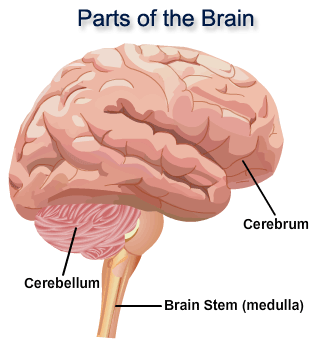
Where is the cerebrum located?
It covers the entire top of the brain
Describe structure of cerebrum
Largest region of brain, divided into two hemispheres
Function of cerebrum
Involved in consciousness, intelligence, language, memory, emotion, and visual and sensory processes
Function of each cerebral hemisphere
Left hemisphere receives sensory information from the right side of the body and controls muscle coordination on the right (vice versa for the right hemisphere)
Where is the cerebellum located?
Bottom of the brain, on the rear side
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Involved in fine muscle coordination, voluntary movement (e.g. walking) and involuntary movement (e.g. balance, posture)
Where is the medulla oblongata located?
The brain stem, at the base of the brain
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
Controls automatic processes in the body (e.g. breathing rate, heart rate)
What methods, other than surgery, are used by doctors to observe the brain?
CT scans and PET scans
What is a CT scan?
A procedure that uses X-rays to produce 3D cross-sectional images of the brain (CT stands for computed technology)
Describe how CT scans are useful to investigate brain function
CT scans show damaged regions of the brain (e.g. areas of swelling, bleeding), observations of the patient's symptoms can enable scientists to determine the function of the damaged region
What does a PET scan involve?
Radioactive substance injected into a patient's bloodstream and taken up by tissues in the brain, radiation is emitted by active tissues, enabling the identification of active and inactive regions of the brain (PET stands for positron emission topography)
Describe how PET scans are useful to investigate brain function
They show which areas of the brain are active and which are not, and comparisons of brain activity in healthy patients and patients with brain damage allow scientists to determine the functions of inactive regions
Why is it difficult to treat brain damage and disease?
The brain is complex and delicate so it can be easily damaged, drugs given to treat the diseases can't always reach the brain because of the membranes that surround it, and it is not fully understood which part of the brain does what
Why is it difficult to treat damage to the CNS?
Damage to neurones is permanent and cannot be repaired (nerve cells don't divide by mitosis), it is hard to reach some areas of the brain, and there is risk of further permanent damage to other areas of the CNS during surgery
Function of the nervous system
Allows an organism to rapidly react to environmental and internal changes
What are neurones?
Nerve cells adapted to quickly transmit nerve impulses, they are the functional units of the nervous system
What is the function of the axon?
It carries impulses away from the cell body of the neurone, and enables the transmission of nerve impulses over long distances
Function of dendrites and dendrons
Carries impulses towards the cell body, the dendrites provide a large surface area to receive impulses
Role of myelin sheath
Electrically insulating layer which surrounds the axon and increases the speed of impulses (allows the nerve transmission/action potential to travel faster)
Where is myelin produced?
In Schwann cells
Function of a sensory neurone
Carries impulses from receptors to the central nervous system
Structure of a sensory neurone
Long dendron carries impulses from receptors to the cell body, cell body found part way along the neurone, short axon carries impulses from cell body to the CNS
Function of motor neurone
Carries impulses from the central nervous system to effectors (a part of the body that can respond to a stimulus sent from the CNS)
Structure of motor neurone
Short dendrites carry impulses from CNS to cell body, cell body found at one end of the neurone, long axon carried impulses from the cell body to the effectors
Function of a relay neurone
Carries impulses from the sensory neurones to motor neurones within the CNS (found within the spinal cord)
Structure of a relay neurone
Short dendrites carry impulses from sensory neurones to the cell body, short axon carries impulses from the cell body to the motor neurones
Describe how the CNS system coordinates a response to a stimulus
Stimulus - Sensory receptor detects stimulus - sensory receptor sends impulses along sensory neurones to CNS - CNS coordinates response - CNS sends information to effector along motor neurone - effector produces a response to the stimulus
What is a synapse?
A small gap between neurones across which a nerve impulse is transmitted via neurotransmitters
How are nerve impulses transmitted across a synapse?
Nerve impulse reaches presynaptic neurone - triggers the release of neurotransmitters - neurotransmitters diffuse across synapse - bind to receptors on postsynaptic neurone - stimulates an impulse in the postsynaptic neurone
Why do synapses slow down the transmission of nerve impulses?
It takes time for the neurotransmitters to diffuse across the synapse and bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic neurone
What is a reflex?
An involuntary (doesn't involve the conscious part of the brain), automatic response to a stimulus by the body which is used as a protective mechanism (e.g. a withdrawal reflex is initiated when a hot object is touched to prevent burns)
Describe the reflex arc
Stimulus - sensory receptor - sensory neurone - relay neurone - motor neurone - effector - response