Bio 102 Richard Mccain Exam 4
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
last one before final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Invert Circulatory system
sponges,cnidarians, and nematodes lack seperate circulatory system
Arthropods and Mollusks have an open circulatory system
Larger animals require separate circulatory system for transport
Open circulatory system
no distinction between circulating and extracellular fluid
fluid called hemolymph
Closed Circulatory system
Distinct circulatory system enclosed in blood vessels
annelid worms and vertebrates
Vertebrate circulatory systems
Pulmonary circulation moves bllood between heart and lungs
Systemic Circulation moves blood betweent he heart and the rest of the body
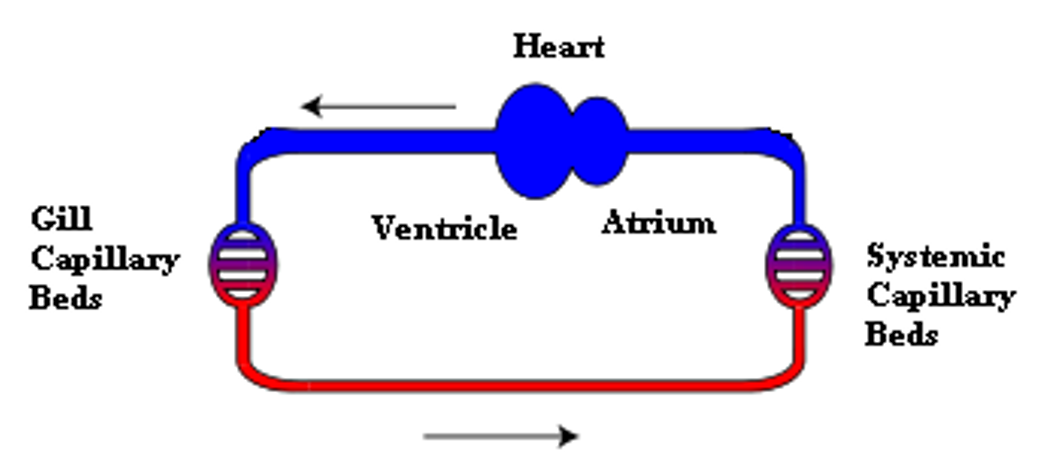
Vertebrate circulatory systems: fish
evolved a true chamber-pump heart
two chambers
blood pumped through gills and then to rest of the body
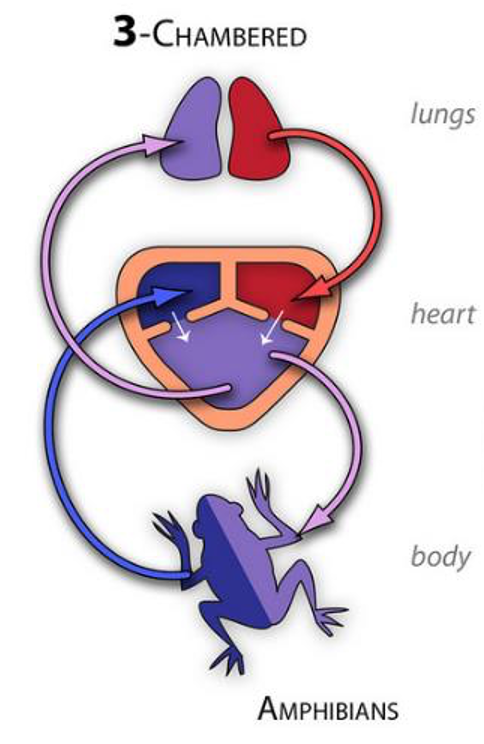
Vertebrate circulatory systems: Amphibians
advent of lungs required second pumping circuit
3 chambered heart
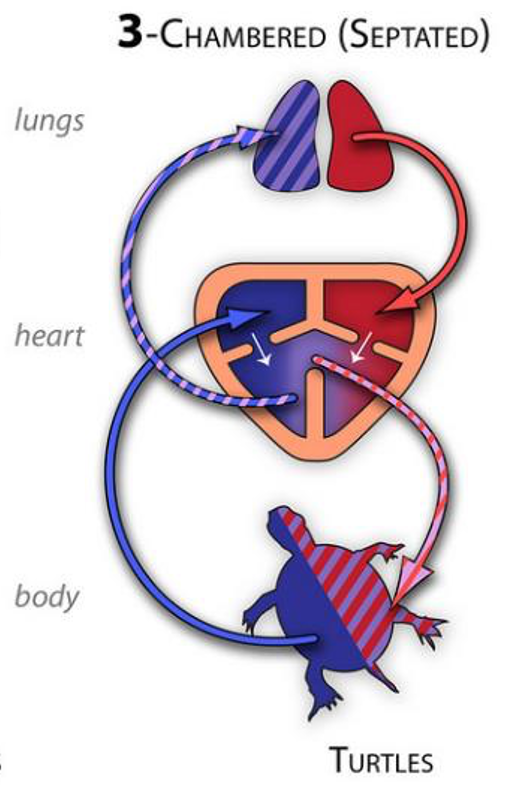
Vertebrate circulatory systems: Reptiles
3 chambered heart
2 atria and 2 ventricles
incomplete separation of ventricles(Septated
Vertebrate circulatory systems: Mammals, Birds, and crocs
4 chambered heart
2 atria and 2 ventricles
right atrium gets body blood which goes to right ventricle which pumps to lung
left atrium gets lung blood which goes to left ventricle which pumps to body
Blood
Connective tissue
extracellular matrix - plasma
cells - RBC, WBC, Platelets
Functions
transportation
regulation
protection
Blood plasma
92% water
contains solutes
nutrients
ions
Na, Cl, HCO3, Ca, Mg, Cu, K, Zn
proteins
Albumin, globulins
Fibrinogen
If removed, plasma is called serum
Ertthrocytes
5 mil per microliter
mature ones lack nuclei in mammals
live for 120 days
contain hemoglobin in verts
Blood types
Can have type A, B, both, or neither glycoproteins
these serve as antigens which is why you gotta do the matching game
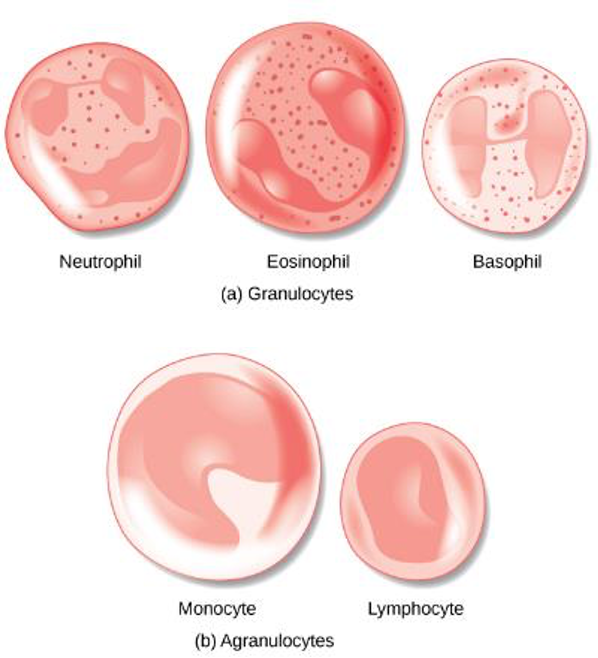
Leukocytes
>1% of blood cells
larger than erythrocytes and have nuclei
Granular Leukocytes
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
Agranular leukocytes
monocytes and lymphocytes
Granular Leukocytes
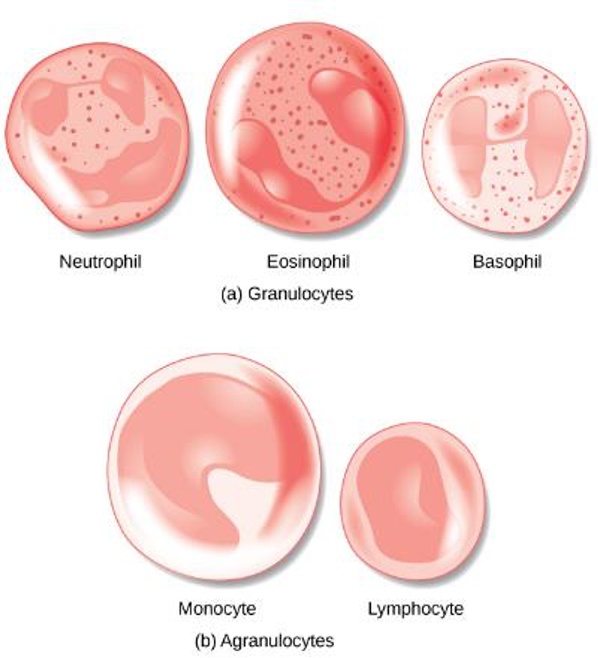
Agranular Leukocytes
Platelets
Function in formation of blood clots
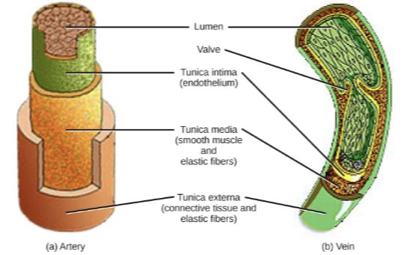
Characterisitcs of blood vessels
blood leaves heart through arteries
aterioles finest
blood goes from these to capillaries
blood collected in venules, which lead to larger vessels, veins
veins carry blood back to heart
Layers of blood vessels
ateries and veins have four layers
endothelium
elastic fibers
smooth muscle
connective tissue
Too thick for exchange
Capillaries have one layer of endothelial cells
allow rapid exchange of gases and other stuff
Filtering the blood
moves into interstitial space and lymph capillaries by diffusion
Lymphatic system
Significant amount of water and solutes in blood plasma filter through walls of capillaries
fluid that does not return to capillaries is returned by lymphatic system
a network of tissues, vessels, and organs that work together to move lymph back to blood stream
Structure of heart
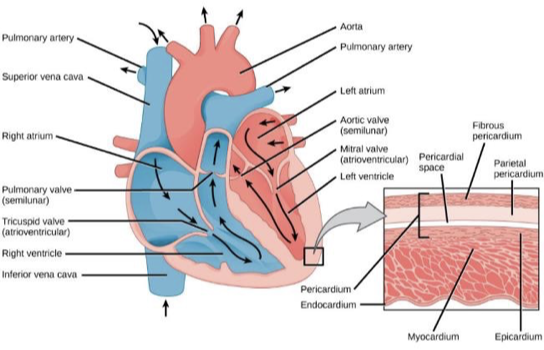
Coronary system
keep heart musculature oxygenated
mammal heart valves
Atrioventricular valves
maintain unidirectional blood flow from atria to ventricles
tricuspid on the right
bicuspid on the left
Semilunar valves
ensure one way flow from ventricles to vessels
Pulmonary valve to lungs
aortic valve to body
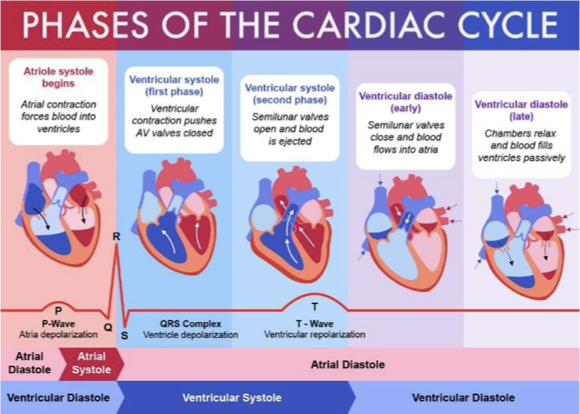
Cardiac Cycle
Valves open and close as heart cycles
Ventricles relaxed is diastole
Ventricles contracted is systole
Lub - AV valves closing
Dub- closing of other valves
Phases of Cardiac Cycle
Blood pressure
pressure exerted by blood on walls of blood vessel that helps to push blood through body
systolic blood pressure measures BP on beats
diastolic blood pressure measures BP off beats
Blood pressure effectors
Increases with blood volume
Blood volume is regulated by four hormones
1.Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
2.Aldosterone – encourages kidney to excrete potassium and retain sodium
3.Atrial natriuretic hormone – increases sodium excretion and decreases blood pressure
4.Nitric oxide (NO) – vasodilator
Osmoregulators
evolved mechanisms to adapt to a variety of environments
the cost is energy
Osmoconformers
internal environment is osmotic relation to the external environment
restricted to certain environs
spend less energy on osmo regulation
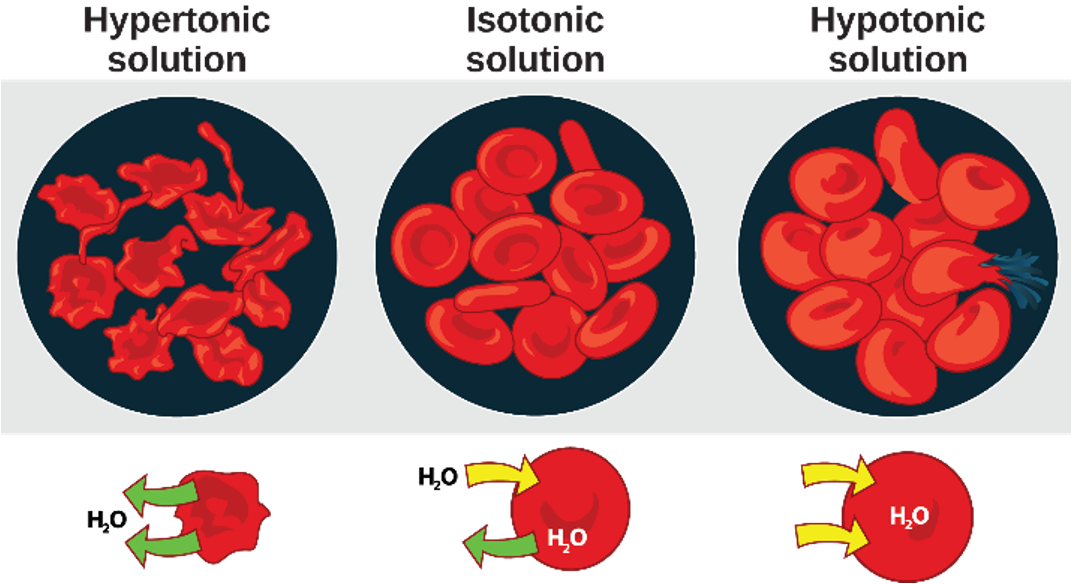
Osmoregulation
process of maintenance of salt and water balance(osmotic balance) across membranes within the body fluids
so that cells don’t shrink or swell
Important ions to Osmoregulation
NA, K, Ca, Mg
Cl, CO3, HCO3,PO3
Body fluid regulation
excretory system regulaes body fluid concentrations
key function: reabsorption
dependent on mineral ions
Body fluid regulation within aqua
marine environment
osmotic loss of water
gain of ions by drinking water
Fresh water
promote gain of water by osmosis
loss of ions as excess water is excreted
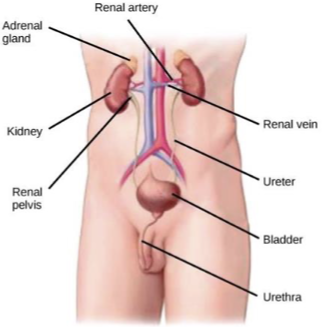
Urinary system
Kidneys makes
ureter moves
urinary bladder holds
urethra voids
Kidneys
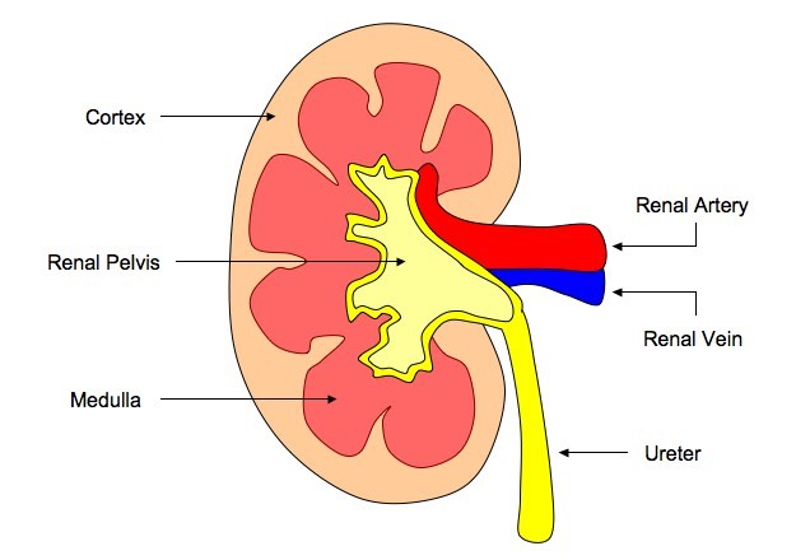
Renal Cortex
outer region
Renal medulla
cone shaped renal pyramids
Renal pelvis
hollow chambered innermost part
Kidney anatomy
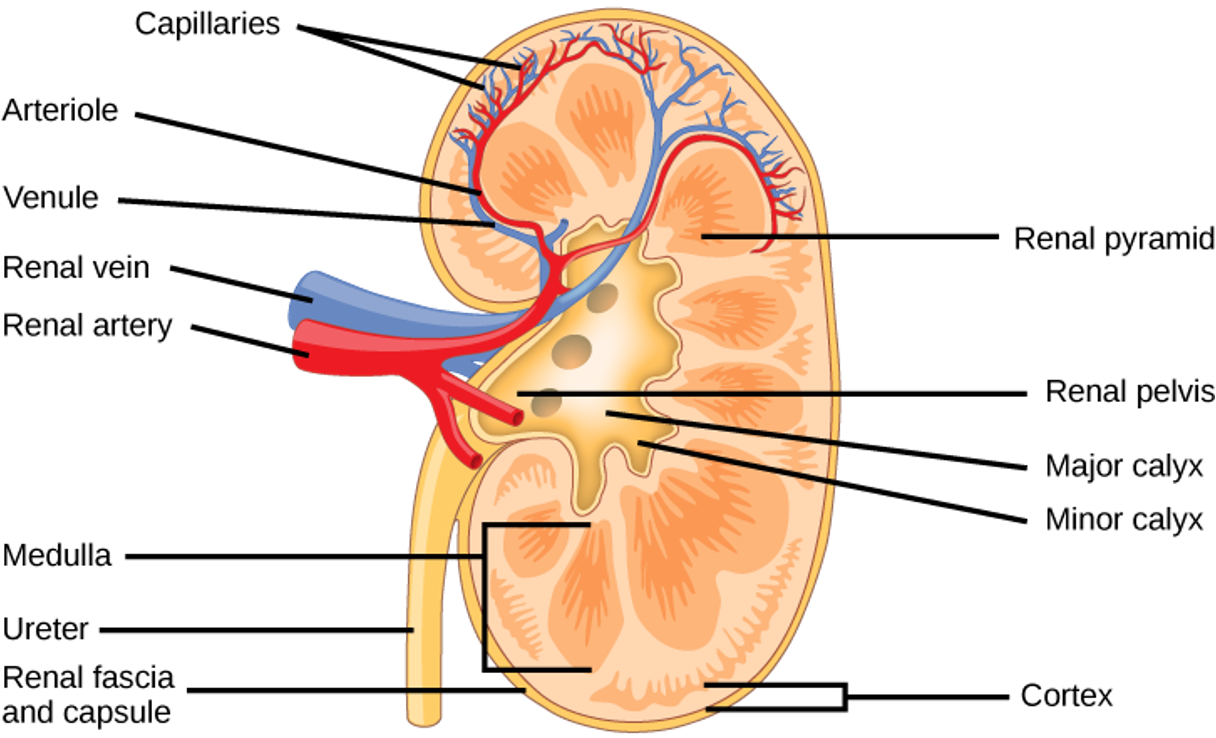
Nephron
Functional unit of kidney
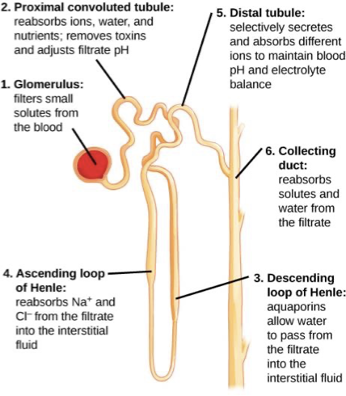
Nephron Anatomy
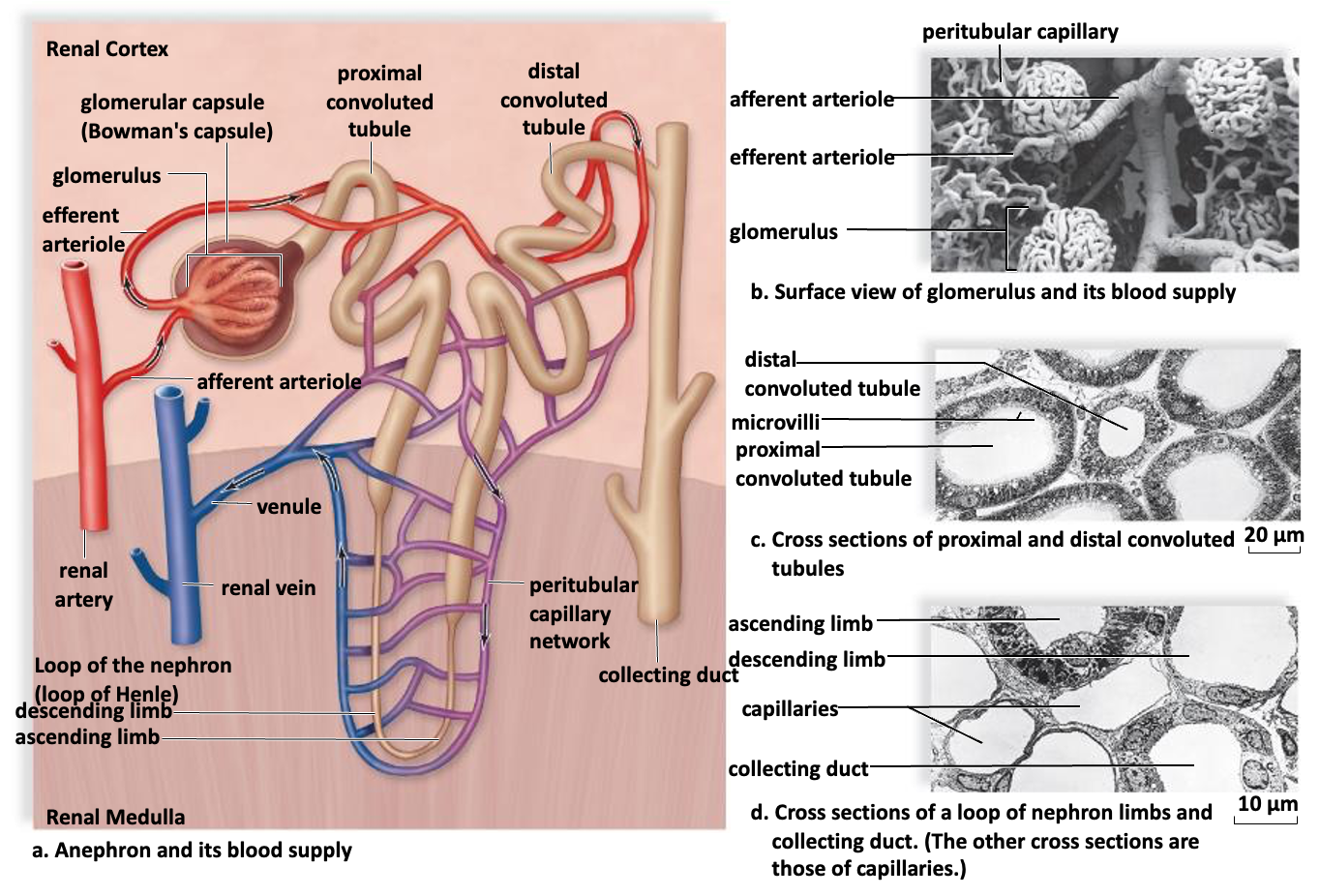
Urine formation
glomerular filtration in glomerular capsule
tubular reabsorption at proximal convoluted tube
tubular secretion at distal convoluted tubule
Urine Homeostasis
excretion of hypertonic urine
dependent on reabsorption of wate
absorbed from
loop of nephron
collecting duct
ADH plays a role in water reabsorption
Excretory organs in unicells
use exocytosis
Excretory organs in inverts
most animals have tubular excretory organs
Flame cells in planarians
Nephridia in earthwroms
Malpighian tubules in insects
Aqautic animals regulation
inverts
most isotonic with water
osmoconfromers
Bony fishes
body fluids of bony fishes with only moderate amount of salt
osmoregulators
some adjust to both, most cant’
Cartilaginous
achieve isotonicity by having organic compounds in blood
Terrestrial animals
lose water through excretion and respiration
must drink water to make up
some reduce this loss by excreting nitrogen
some ahve highly convoluted nasal passage
Maintenance of blood pH, Osmolarity, volume, and pressure
more than 99% of sodium filtered at glomerulus returned to blood
Reabsorption of sodium regulated by hormones
aldosterone
renin
atrial natriuretic peptide hormone
ph adjusted by either
reabsorption of bicarbonate ions
secretion of hydrogen ions
Nitrogenous waste products
Catabolism of amino acids and nucleic acids results in ammonia
high solubility allows to be execreted directly by many aqautic animals
terrestrial animals must convert to urea
urea causes loss of much water
mammals and amphibians
uric acid losses less water
reptiles, birds, and arthropods
Hormonol control of osmoregulation
Hormone | Where produced | Function |
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine | Adrenal medulla | Can decrease kidney function temporarily by vasoconstriction |
Renin | Kidney nephrons | Increases blood pressure by acting on angiotensinogen |
Angiotensin | Liver | Angiotensin II affects multiple processes and increases blood pressure |
Aldosterone | Adrenal cortex | Prevents loss of sodium and water |
Anti-diuretic hormone (vasopressin) | Hypothalamus (stored in the posterior pituitary) | Prevents water loss |
Atrial natriuretic peptide | Heart atrium | Decreases blood pressure by acting as a vasodilator and increasing glomerular filtration rate; decreases sodium reabsorption in kidneys |
Hormonal control: RAAS
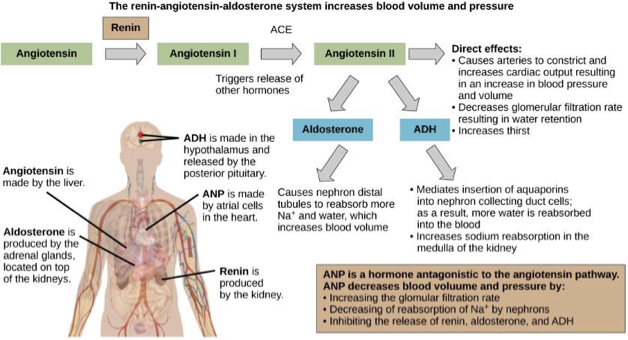
Innate immune system
found in all of animals, and some plants
nonspecfic
no memory
Physical/chemical barriers
skin
normal flora on the skin
mucous and cilia in the respiratory tract
low pH in stomach
antimicrobial peptides
Adaptive immune system
only in vertebrate
highly specific
has memory
Pathogen recognition
Microbes have different cell surface markers
anything foreign is antigen
cells recognize pathogen associated molecular patterns and phagocytize
markers not specfic
White blood cells
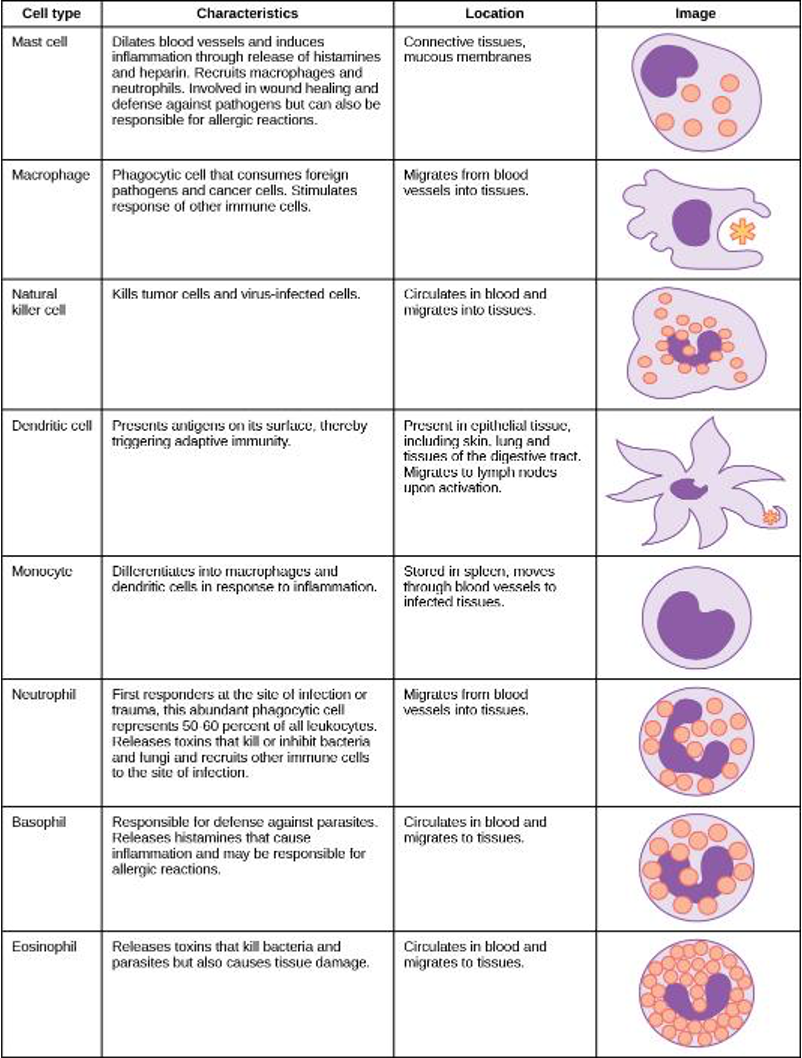
Inflammatory Response
Pain
heat
redness and swelling
due to increased vascular permeability to allow WBCs to leave capillaries and enter tissues
Natural KIller Cells
kill virus infected or alter self cells
Adaptive immune response
after exposure to an antigen and innate is insufficeient to deal with it
two types:
cell mediated immune response by T-cells
humoral immune response contrlled by B cells and antibodies
Can take days or weeks to start up
Antigen
macromolecule that reacts with immune system, contains a motif that is made of epitopes
memory of adaptive
highly specific antibodies made by B cells and T-cell Receptors made by T cells
b cells and t cells can distinguish between different motifs
Humoral immune response
B cells
mature in bone marrow
make antibodies
antibodies are proteins
each B cell produces antibodies with specfic variable region
can be secreted or membrane bound
Humoral antibodies
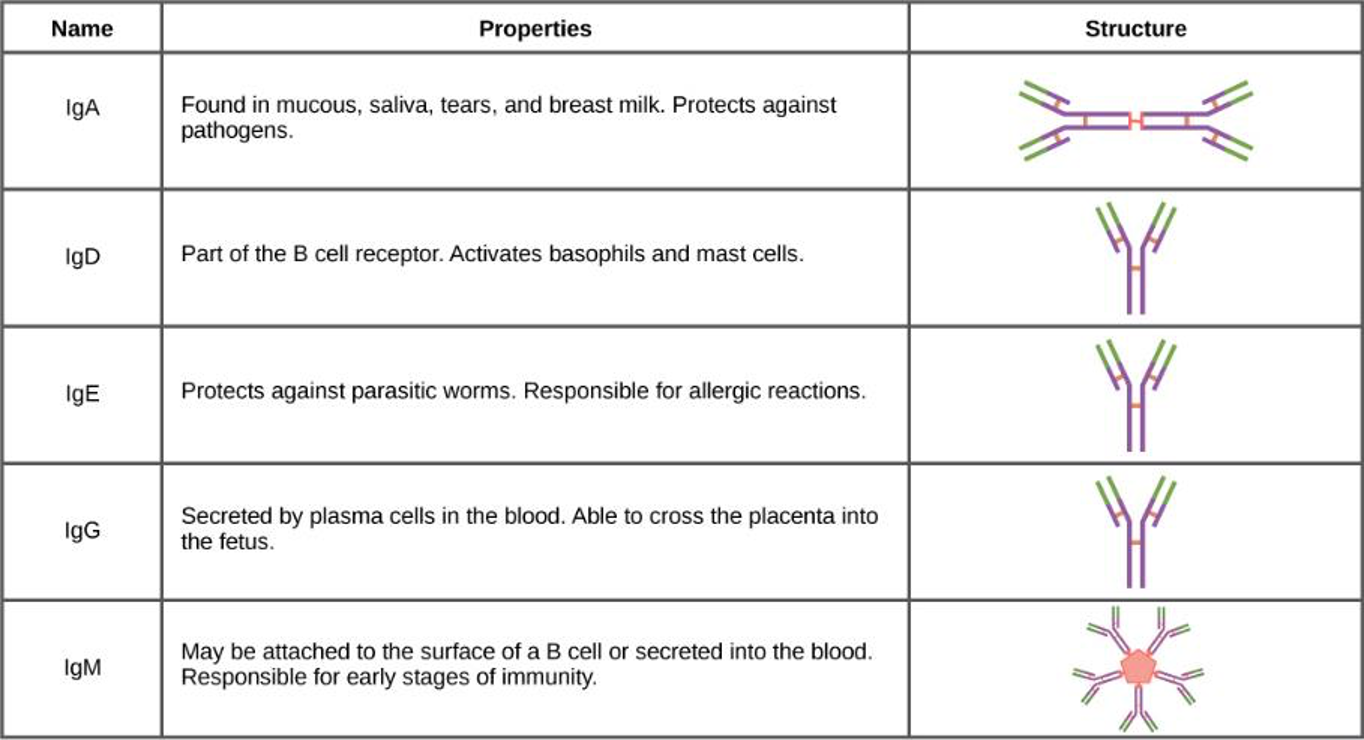
Antibody functions
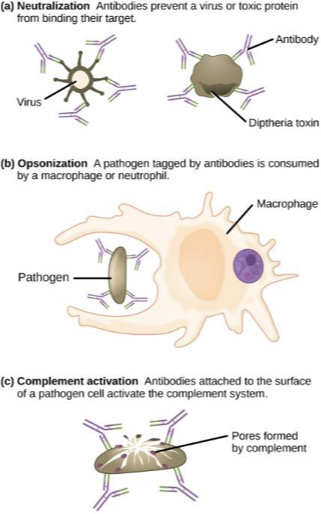
Neutralization
Antibodies precent virus or toxic protein from binding to target
Opsonization
pathogen tagged by antibodies is consumed by WBCs
Complement Activation
antibodies attached to the surface of a pathogen cell activate the complement system
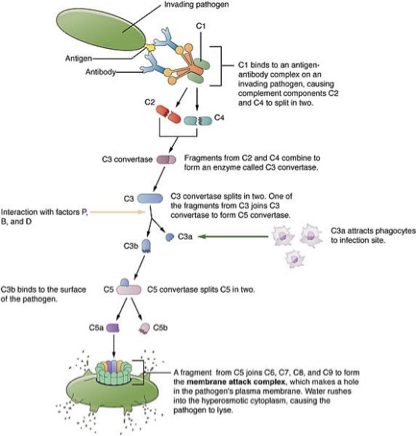
Major Histocompatability Complex
System that allows large proteins in immune system cells to identify compatible or foreign proteins
MHC clas 1
found on all of our nucleated cells
MHC class 2
found on antigen presenting cells
b cells
dendritic cells
macrophages
APCs
group of immune cells that process and present antigens for recognition by certain lymphocytes such as t cells
T cells
mature in thymus
T cell receptor is membrane bound
also encoded in our DNA
recognized specific antigens presented in MHC molecules
3 pops of T cells
helper t cells CD4
cytotoxic t cells CD8
t regulatory cells
Cell mediated response p. 1
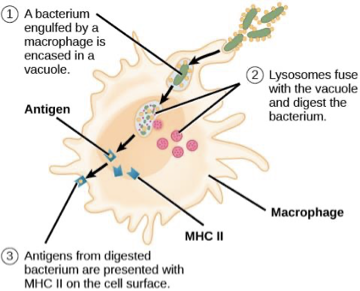
Cell mediated response p. 2
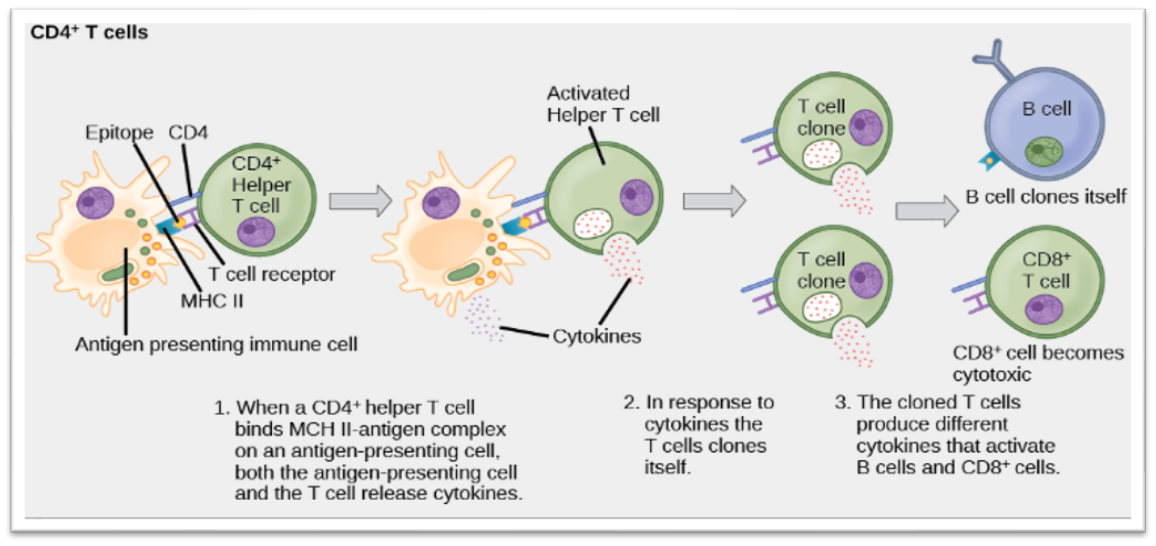
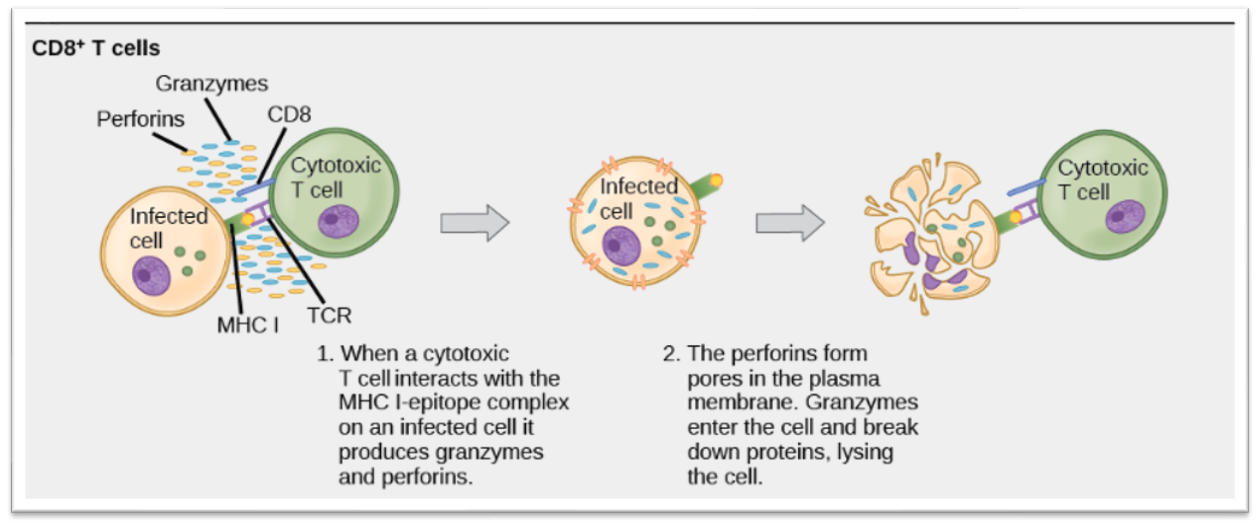
Cell mediated response p. 3
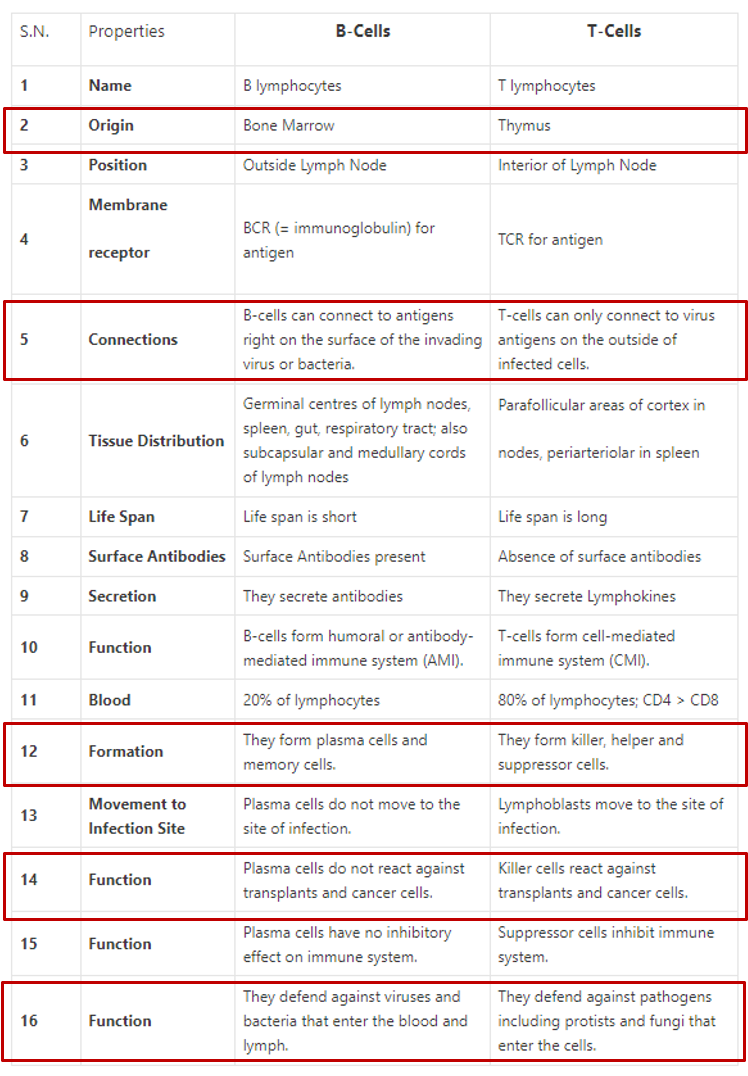
Variable region of B and t cells change
process called gene rearrangment
region of DNA that codes for variable region rearranges
results in high diversity
Difference between B and T cells
Lymphatic system
most blood cells erythrocytes
leukocytes have ability of migrating into the tissues
lymph nodes have congregation of B, T and other white blood cells there
when antigen goes through these, it is detected and more of it is found
Primary immune response
first exposure
days to weeks for B and T cells to upregulate and mount full response
after recovery, memory B and T cells will remain and circulate
Secondary immune response
second exposure
memory cells respond faster
either no sick or recover faster
Affinity vs Avidity, Cross reactivity
affinity is how strong a single bond is, avidity is the strength of all interactions
Cross reactivity is the being able ot react to multiple eptiopes
bad things immune system
Chronic inflammation
allergies
autoimmunity
Immunodeficiency
primary- genetic/developmental defect results in lacking od some component of immune system
Acquired- later in life
Ecology
is the study of interactions of living organisms with their environment
Organismal ecology
Study adaptations that enable individuals in specific habitats
Population ecology
Focus on the number of interbreeding individuals in an area and how and why population size changes.
Community Ecology
Study the processes driving interactions between species, as well as their consequences.
Ecosystem Ecology
Study the storage and movement of nutrients and energy among organisms and the surrounding atmosphere, soil, and water
Biogeography
study of geographic distribution of living things and the abiotic factors
Abiotic factors
ex. temp, rainfall
vary based on latitude and elevation
as they change, communities change
Species distribution
endemic species: only found in specific geographic region
generalists : live in a bunch of places
Abiotic factor examples
Energy sources
sunlight
ocean upwelling
Temperature
Water
freshwater
saltwater
frozen water
seasonal water changes
Nutrients and inorganic materials
Ocrean upwelling
process that recycles nutrients and energy in the ocean
wind from offshore brings nutrients from bottom of ocean
Seasonal lake cahnges
spring and fall turnover move nutrients and oxygen at the bottom of lake to the top
water has max density at 4 C
Terrestrial biomes
each of worlds major biomes distinguished by characteristic temps and amounts of precipitation
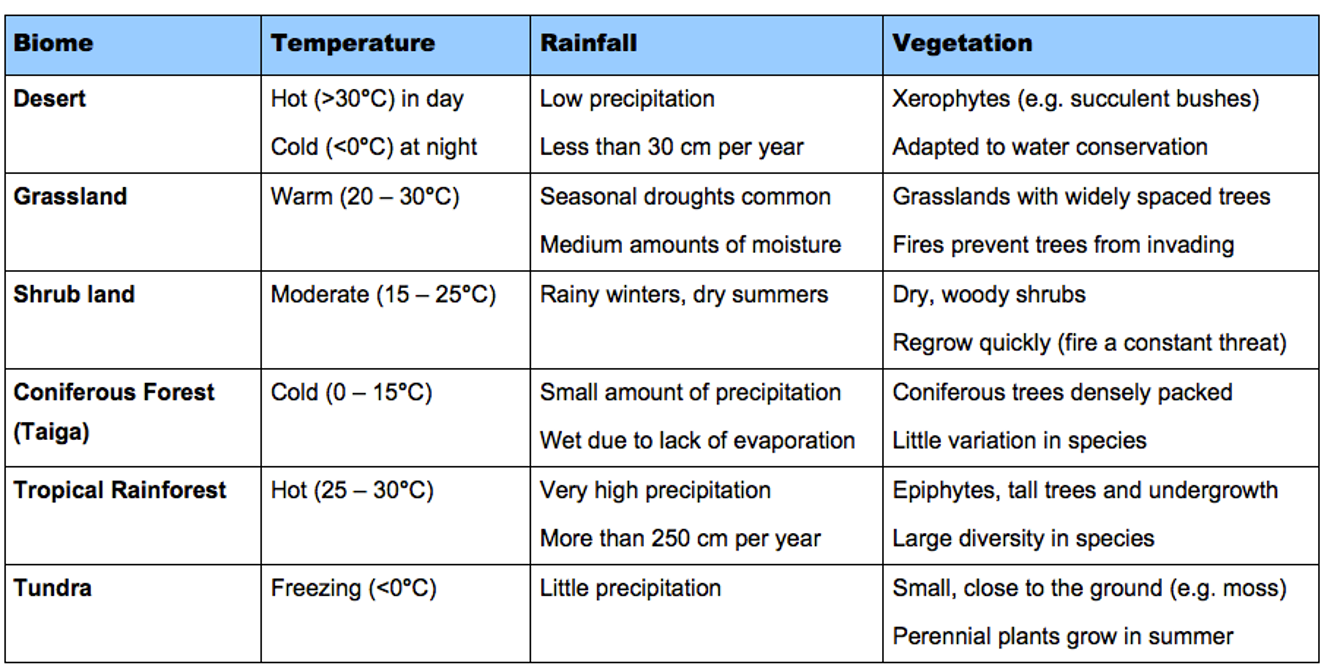
Tropical wet forests
high net primary productivity because precipiation and temp is ideal for plants
high species diversities
Savannas
grasslands with scattered trees
24 C to 29 C 10-40 cm
extensive dry season
plants well developed root system
Subtropical deserts
Low and unpredictable precipitation limits vegetation and animal diversity
Chaparral
65-75 cm of rain, mostly in winter
summers dry plants dormant
dominated by shrubs
adapted to periodic fires
Temperate grasslands
seasonal temps
vegetation is very dense and soils are fertile because of roots and rhizomes
Temperate forests
-30 to 30 C 75-150 cm
deciduous trees are the dominant plant in this biome
net productivity lower than tropical
soil is rich
Boreal forest
cold dry winters
short cool wet summers
evergreens
net primary production is lower than most forests
Artic tundra
plants have short growing season
biome cold and dry
little species diveristy, net primary productivty, and above ground mass
Characteristics of aquatic biomes
zones based on water depth and distance from shore line