Lecture 15 ATP structure cycle and coupling, Activation energy and enzymes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
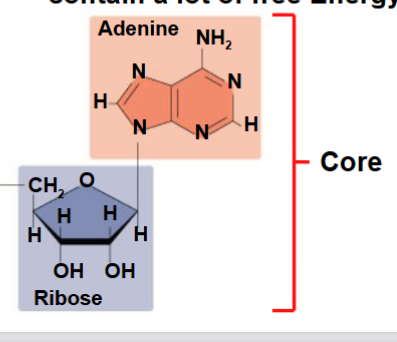
The core structure of ATP is..
Ribose(sugar)
Adenine( nitrogous base)
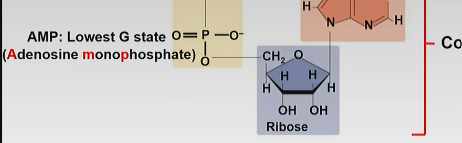
Adenosine monophosphate
-lowest G state
-one phosphate
Adenosine diphosphate..(ADP)
-second lowest G state
-two phosphates
Adenosine triphosphate..
-three phosphate
-highest G state
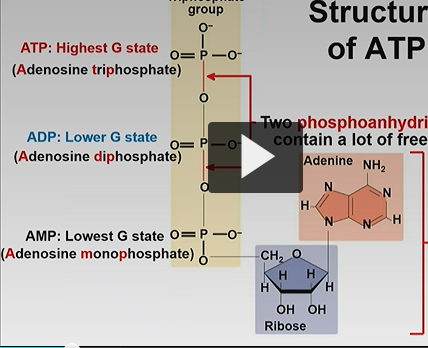
The breaking of …. bonds contain a lot of free energy
phosphoanhydride (covalent bonds) ( only 2)
*bonds occur between
-ATP-ADP
ADP-AMP
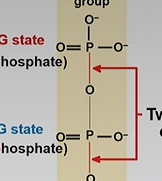
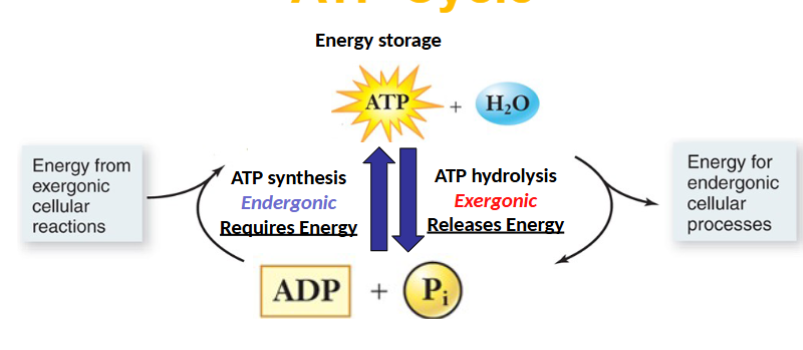
Exergonic ATP hydrolysis(breaking bonds)
-G state will decrease
Product: ADP
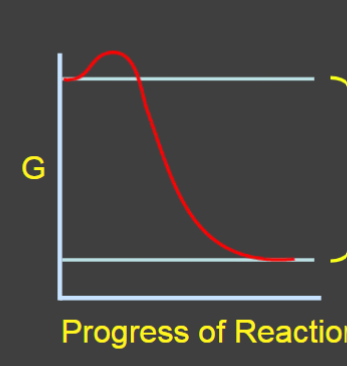
Energy released from an exergonic reaction can be used to power …
endergonic reaction
Kinetics of a reaction refers..
to the rate a reaction occurs
Rate of a reaction is affected by…
activation energy
Thermodynamics only refers to… …..not about the …… of a reaction
-whether energy is released or absorbed
-rate
Activation energy is…..
the amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Reaction with a high activation energy occur….
slowly
Reactions with a low activation energy occur..
fast
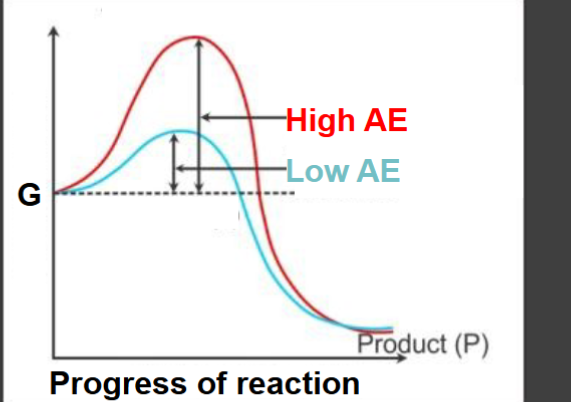
What is the significance of catalysts?
-lower activation energy
-increase the rate of reactions
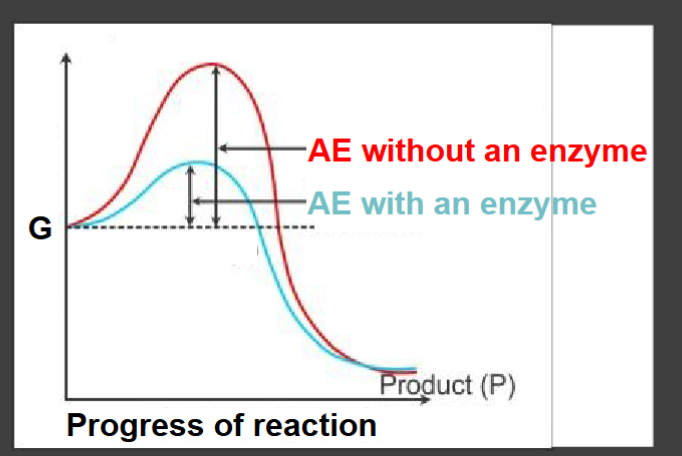
Enzymes are…
biological catalysts
Enzymes are important due to their ability to…
-stress chemical bonds(easier to break)
-Hold reactants in favorable orientations
ATP hydrolysis
Input: ATP+H2O
Output:ADP +Pi
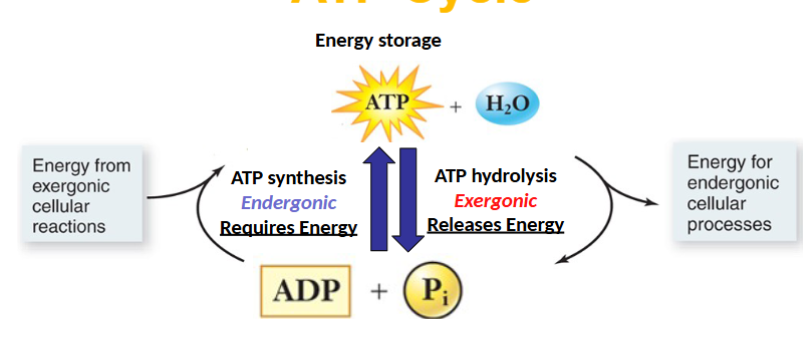
ATP synthesis
Input: ADP+Pi
Output: ATP +H2O