1. Medicinal Chemistry 2
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Why were angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) developed?
ACE inhibitors lower BP but cause bradykinin build-up in the lungs, leading to a persistent dry cough.
ARBs block the angiotensin II receptor to lower BP without causing the cough.
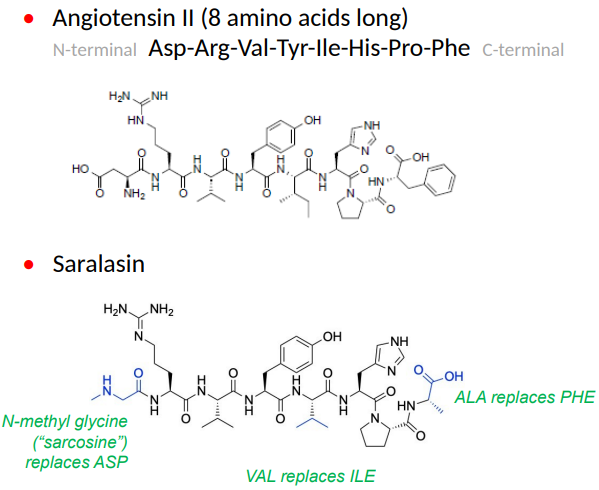
Why were peptides like Saralasin not ideal as angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)?
Peptides are polar and charged at intestinal pH, making them poorly bioavailable.
They have a short duration of action.
Saralasin, a peptide, has partial agonist activity, which is not ideal for ARBs.
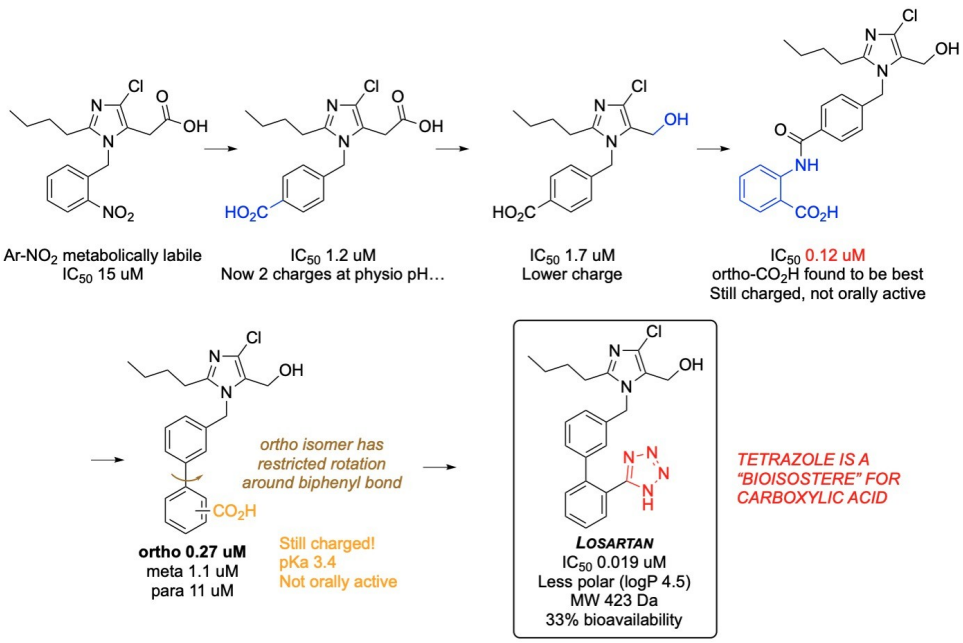
What did SAR studies reveal about Angiotensin II binding?
The C-terminal (RHS) region of Angiotensin II is the most important for binding.
Imidazole-5-acetic acid analogs, like S-8038, showed antihypertensive activity.
These analogs blocked the receptor without agonist activity by forming non-covalent interactions with the receptor.
How was S-8038 improved to Losartan?
Variants were made to improve potency, with the black part being less important.
A carboxylic acid at the para position increased potency but caused charge issues.
Converting the carboxylic acid to an alcohol reduced the charge.
Adding an amide group and using ortho isomers improved potency.
A bioisostere (tetrazole) mimicked the carboxylic acid, enhancing binding and bioavailability.
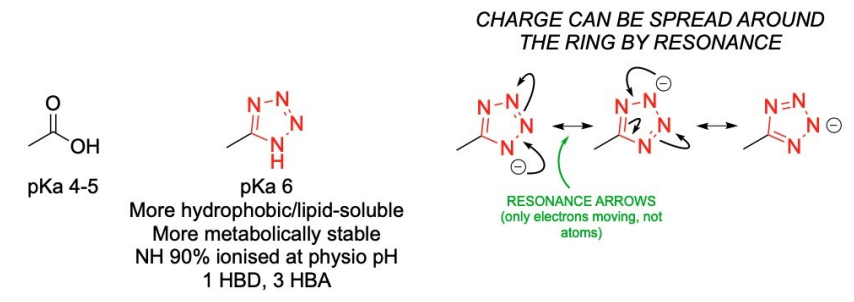
What is a bioisostere and how is it applied in drug design?
Bioisosteres are compounds or groups with similar molecular shapes, volumes, and electron distribution.
A replacement functional group mimics the original in shape and charge, maintaining the desired biological activity.
Example: A tetrazo ring replaces a carboxylic acid group, with subtle differences like charge delocalization over five atoms.
This modification improves bioavailability, stability, and reduces metabolism, making the drug more effective.
The change in properties (e.g., pKa) enhances the drug's performance while keeping its biological function.
What is significant about losartan's metabolite?
Losartan's metabolite, EXP-3174, is an active compound.
It is a potent receptor antagonist, with no partial agonism.
EXP-3174 is 40 times more potent than losartan itself.
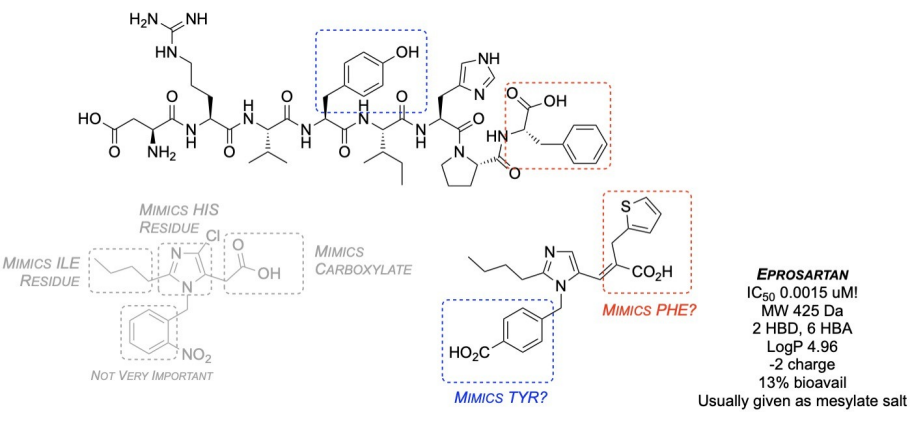
What are second-generation ARBs, and how are they improved compared to earlier versions?
Second-generation ARBs have structural modifications for better potency and receptor binding.
They keep the central scaffold but modify functional groups.
Example: A carboxylic acid is replaced by a theophany (a five-membered sulfur ring) to mimic the carboxylic acid group.
Improvements include:
Enhanced potency (low nanomolar range)
Better bioavailability
Molecular weight under 500 Dalton for oral absorption
Hydrogen bond donors/acceptors for receptor interaction
Often given as a salt to reduce charge and improve absorption.
What is sartan selectivity & why does it matter?
Sartans target angiotensin II AT₁ receptor (a 7-helix GPCR)
AT₁ → causes vasoconstriction
AT₂ → involved in growth & development
Drugs are ≥10,000× selective for AT₁ over AT₂
Selectivity matters to avoid side effects from similar receptors
High angiotensin II can activate other AT receptors if not controlled
How were ARBs like losartan developed & why?
Made after ACE inhibitors to avoid cough but keep ↓ BP effect
Based on receptor chemistry & angiotensin II interactions
Losartan uses a tetrazole instead of a carboxylic acid → better oral bioavailability