Biological Anthropology Final
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
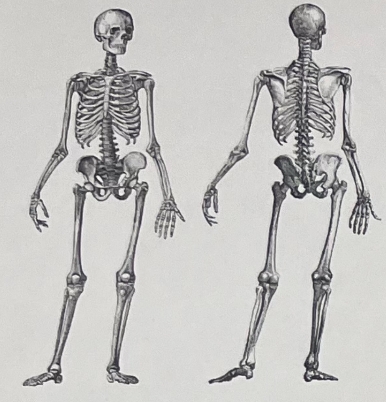
What characteristics demonstrate the bipedality of this skeleton? What is the genus and species of this primate?
Human skeleton; centrally located foramen magnum, broad/wide hips, acetabulum forward, vulgas knee, knees at midline, two arches in the foot, no opposable toe. Homo sapiens
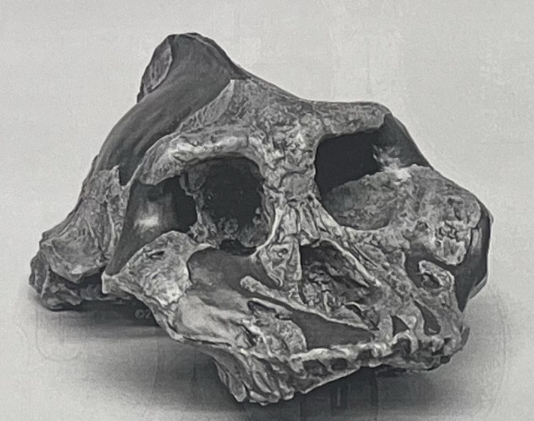
What is the genus and species of this skull?
a. In what area is this hominid found?
b. What time period?
Australopithecus aethiopicus
a. North East Africa
b. ~2.6 mya
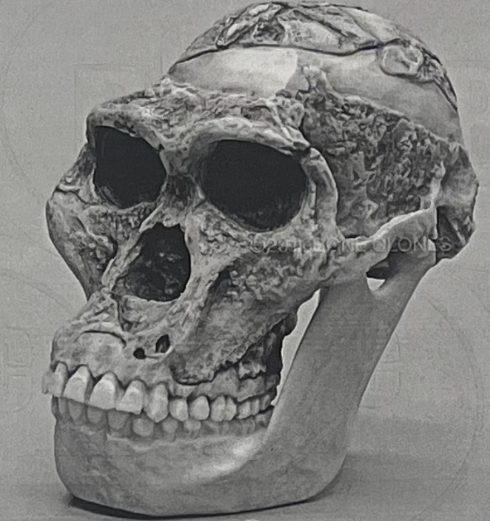
Genus & species
a. Location
b. Time period
Australopithecus africanus
a. South Africa
b. 3.5 - 2 mya
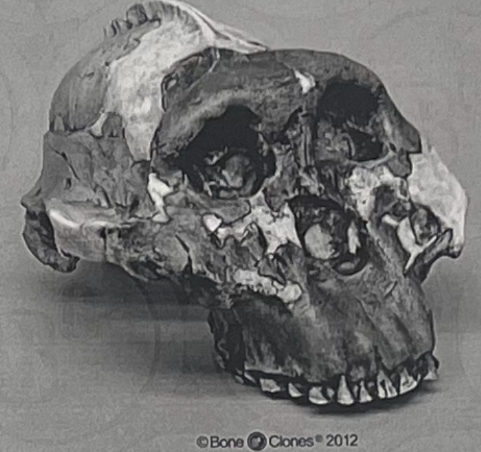
Genus & species
a. Location
b. Time
Australopithecus boisei
a. East Africa
b. 2.5 - 1 mya
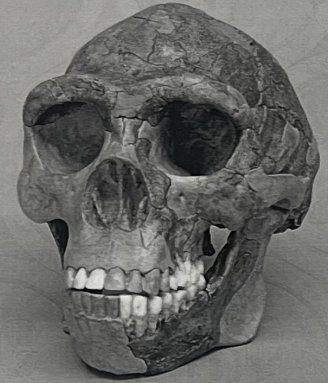
What geographic region is this species found in?
Homo erectus skull - found in Africa, Eastern Europe, and Asia
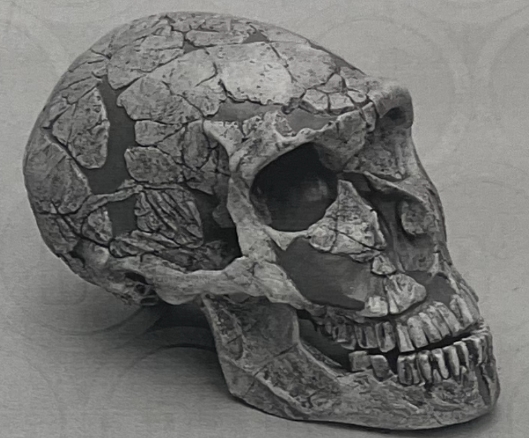
Describe the cultural advances of this species
Neandertal skull: practiced burials, evidence of pigmented body decoration, lived in caves, hunted large mammals, ate a wide variety of fruits/ vegetables/ seeds/ tubers, lived in groups, wore clothing, and used Acheulean, Mousterian, and Levelois tool making techniques,
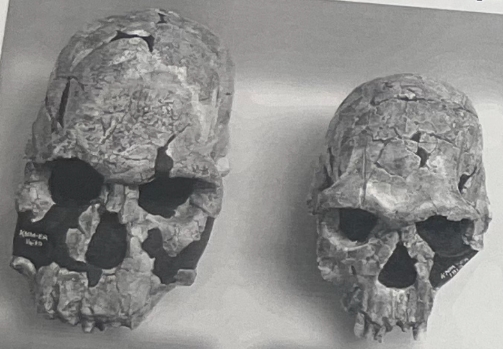
If you were a lumper, then these two skulls would belong to which taxa?
If you were a splitter, then these two skulls would belong to which taxa?
Lumper: Homo habilis
Splitter:
left: homo habilis
right: homo rudolfensis

What is this tool technology called? Which taxon(s) used this type of tool technology?
Oldowan; used by australopithecines and early homo habilis
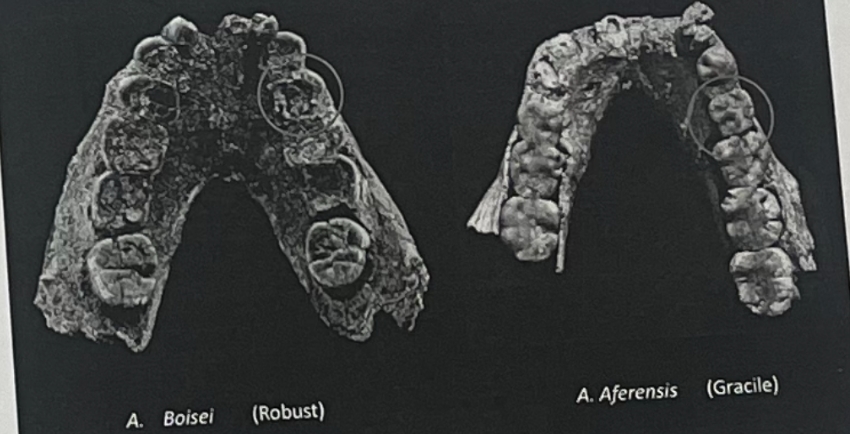
What do these mandibles tell us about the dietary flexibility of the species they are assigned too?
The more robust mandible is more specialized for earing tough roots and tubers. The more gracile one displays the ability to eat a larger variety of foods, greater dietary flexibility
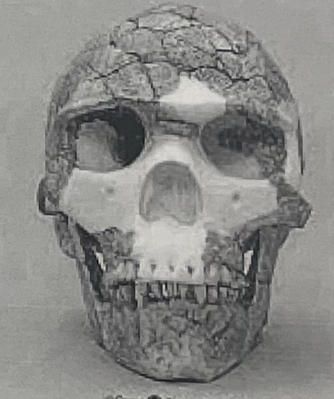
Genus & species
Homo sapien sapien