Bromination of E-Stilbene Theory
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what happens after you set up the glassware?
lightly capping the reaction by resting the glass stopper on top of the keck clip.
Make sure that the reaction is not sealed because you don't want pressure to build during the reaction; air should be able to flow around the stopper.
When bromine is added to an alkene, the result is…
an addition reaction with one or more brominated products
the number of brominated products made by an addition reaction depends on
the structure of the starting alkene
The distribution of the isomers in the reaction depends upon
the cation intermediate of the reaction.
what 2 cations can form in the experiement?
a cyclic bromonium cation and an acyclic carbocation.
The acyclic carbocation results in… while the cyclic cation results in
acyclic : 50/50 distribution of meso/d,l
cyclic = only meso product
functional group
an atom or group of atoms that governs the chemical and physical properties of a family of compounds
alkenes
organic compounds possessing a polarizable carbon-carbon double bond, a p-bond, as the functional group.
most common reaction that produces a carbon-carbon pi bond (double bond)
elimination reactions
most common mode of addition of X–Y across the p-bond of alkenes
involves
ionic stepwise mechanism
an electrophile, E+, first attacks the p-bond, functioning as a nucleophile, to produce a carbocation
markovnikov’s rule
the electrophile adds to the more substituted carbon of the double bond
alkene halogenation reaction
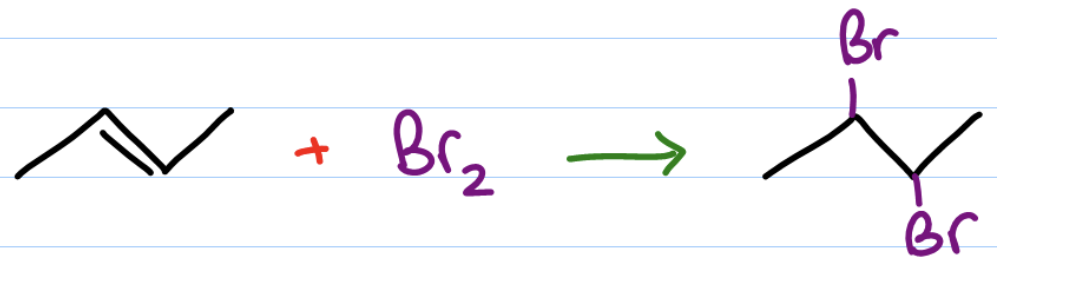
alkene halogenation product
vicinal dihalide