Human eye - Responding to the environment
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
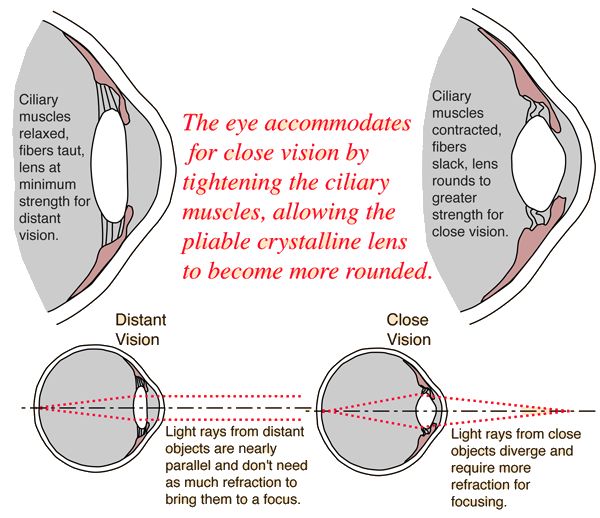
Accommodation
The ability to change the focal length of the object by changing the convex shape of the lens to assist with focussing on a near or distant object
Astigmatism
Uneven curvature of the lens or cornea resulting in distorted images
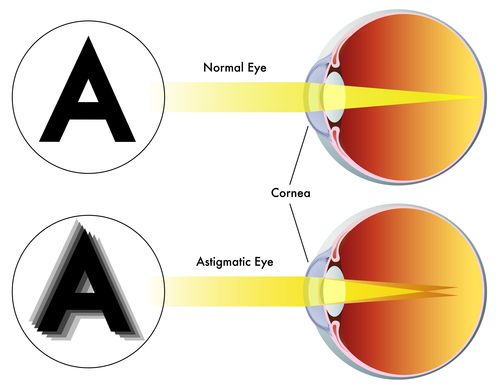
Astigmatism Treatment
Glasses or contacts
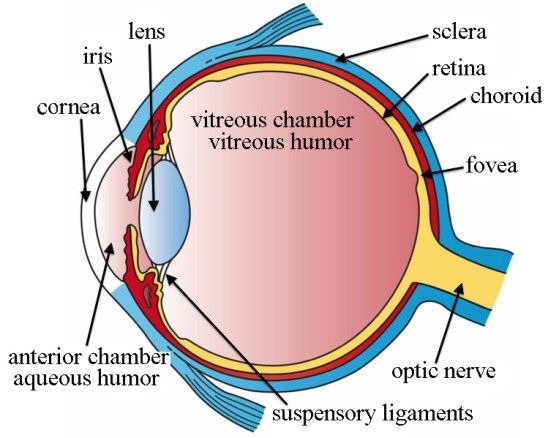
Aqueous humour
Watery liquid that protects the lens of the eye and supplies the cornea with nutrients
Long-sightedness
An eye condition in which close objects appear blurred. this is caused by a lens that cannot become rounded enough to refract light, so the image falls behind the retina
Long-sightedness treatment
convex lens or laser surgery
Short-sightedness (myopia)
The ability to see close objects clearly; distant objects appear blurry, this is caused by a lens that is too rounded, so the image falls short of the retina
short-sightedness treatment
concave lens or laser surgery
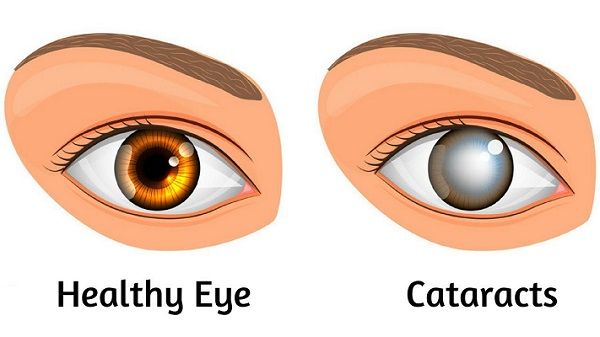
catatract and treatment
cloudiness of the lens and can be treated through surgery
Optic nerve
The nerve that carries impulses from the retina to the brain
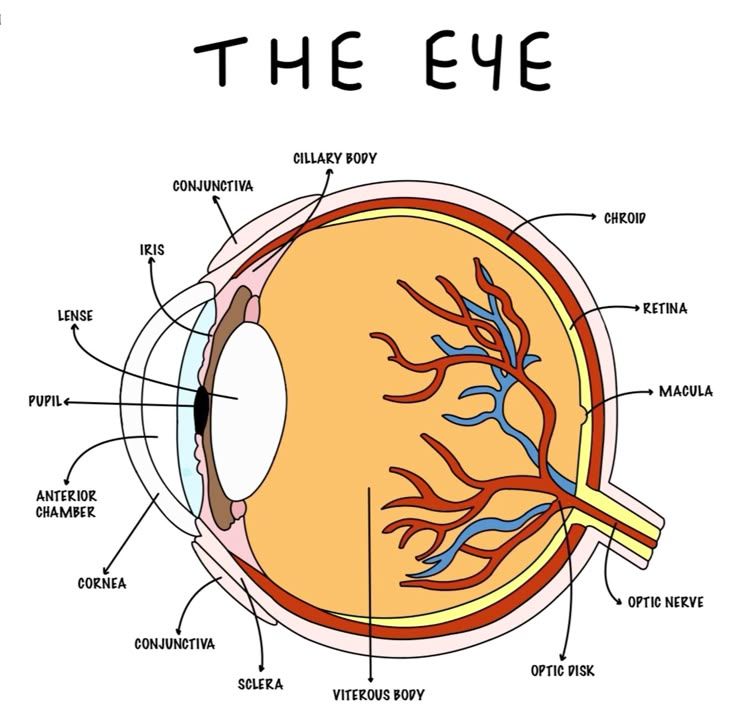
Photoreceptors
Specialized receptors to receive the stimulus of light and convert it to an impulse.
Refraction
To bend light-refraction takes place when light passes through a lens that is bent by a convex [()] shape or a concave [)(] shape
Binocular vision
The ability to focus the two eyes in a coordinated manner in order to see one image
Importance of binocular vision
allows for 3D dimensional vision
Sclera
outer white protective layer of the eye
sclera function
helps to maintain the shape of the eyeball and where eye muscles attach
cornea (function and location)
Clear layer on the front of the eye that helps focus light onto the retina
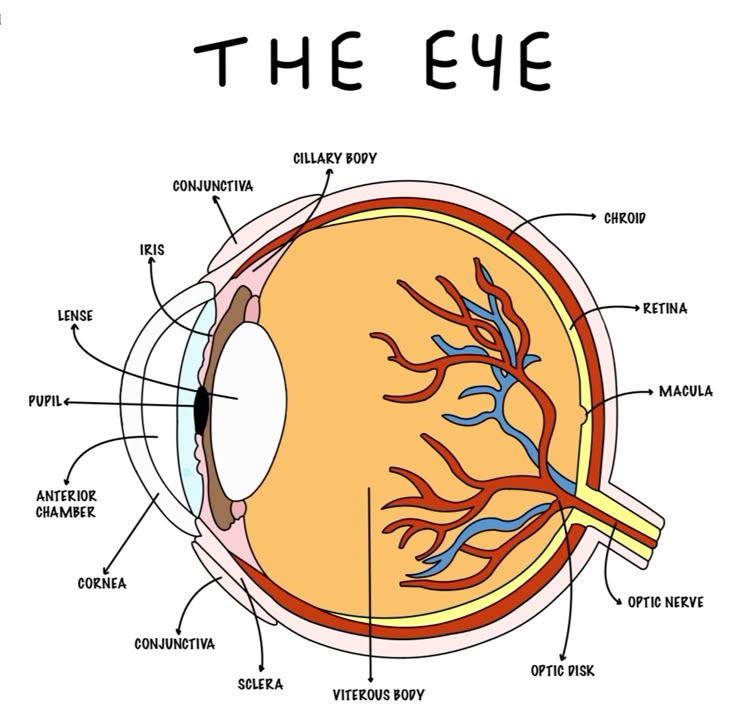
choroid
middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera
choroid function
the blood vessels nourish the other layers of the eye, and the melanin helps to absorb excess light
iris function
controls how much light enters the eye
pupil
The opening through which light enters the eye
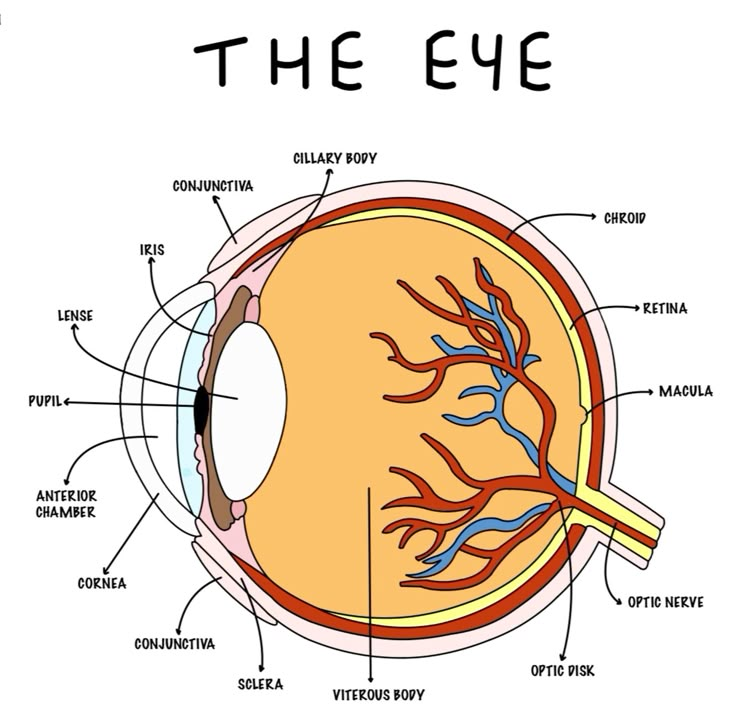
Retina
Light sensitive layer of the eye; contains rods and cones
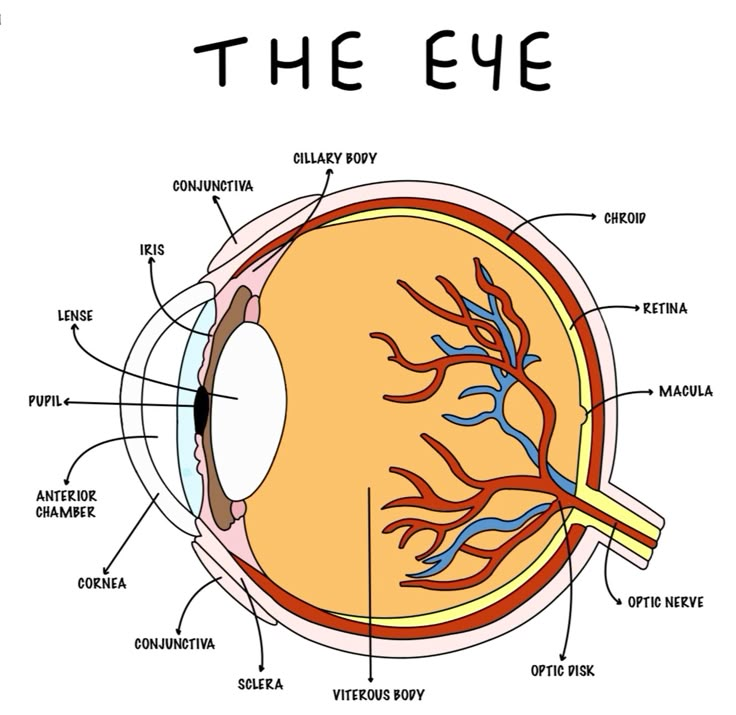
retina function
receive light that the lens has focused, convert the light into neural signals, and send these signals on to the brain for visual recognition
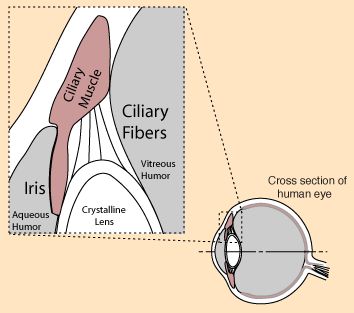
Cilairy Body
secretes aqueous humour
ciliary muscle
controls the shape of the lens for near or far vision
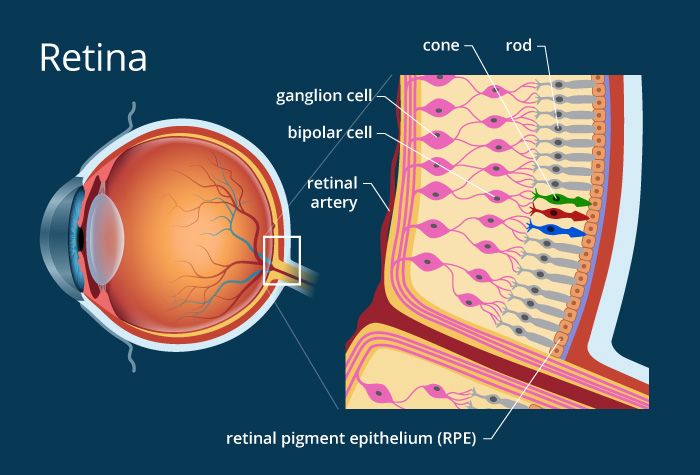
Photoreceptors function
convert light into nerve impulses
Rods
Sensory cells in the retina that are activated in dim light and allow us to see black and white
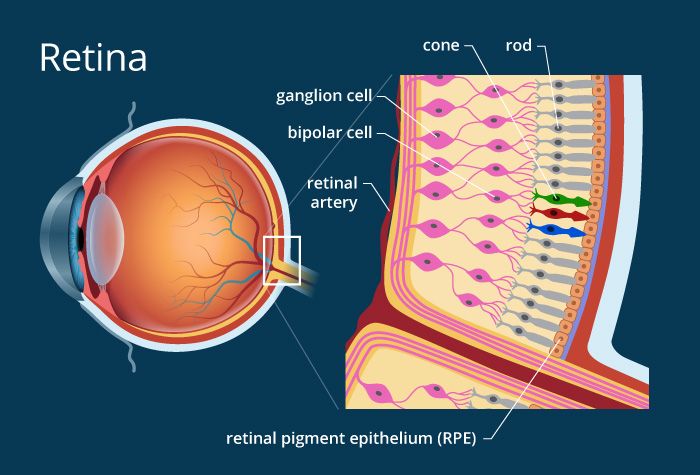
Cones
sensory cells in the retina that are sensitive to bright light and provide color vision.
Lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
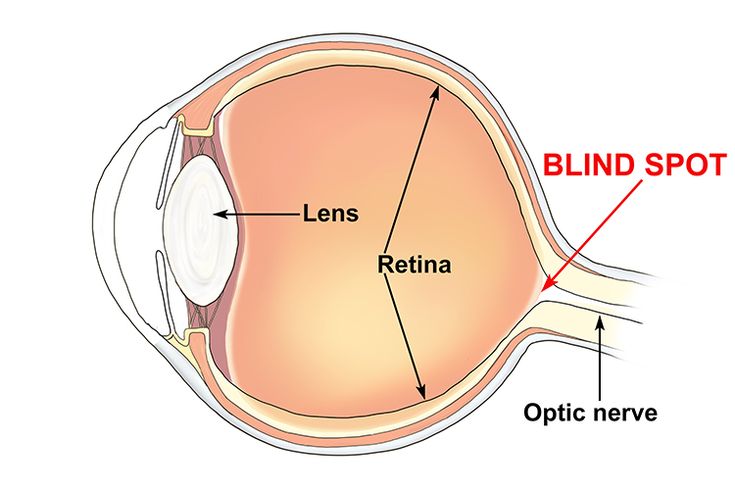
suspensory ligaments function
hold the lens in place
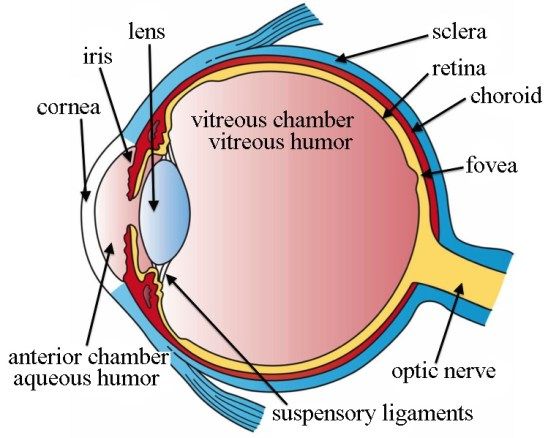
yellow spot function and location
small area on retina that contains only cones and responsible for sharp central vision
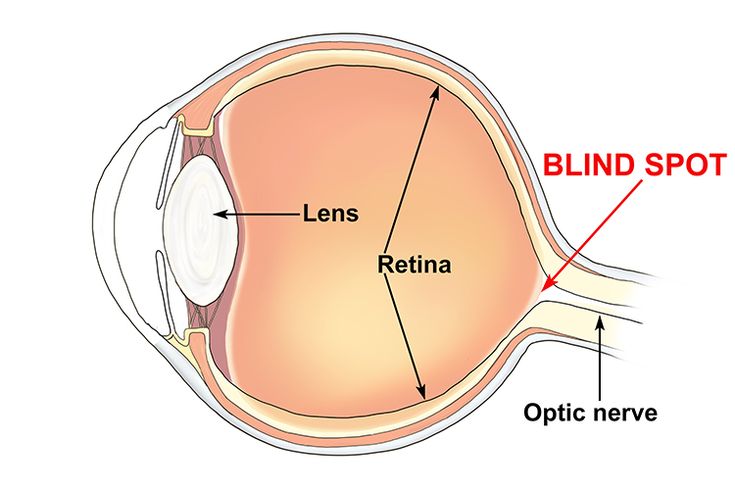
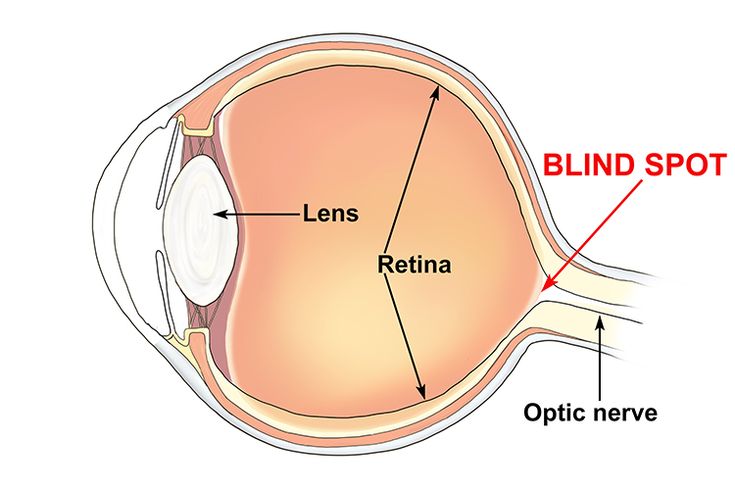
Blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
Pathway of light in the eye
cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina, optic nerve
Accommodation for near vision
ciliary muscles CONTRACT > ciliary body moves INWARDS > suspensory ligaments SLACKEN > elastic lens become more CONVEX/ROUNDED > clear image on retina
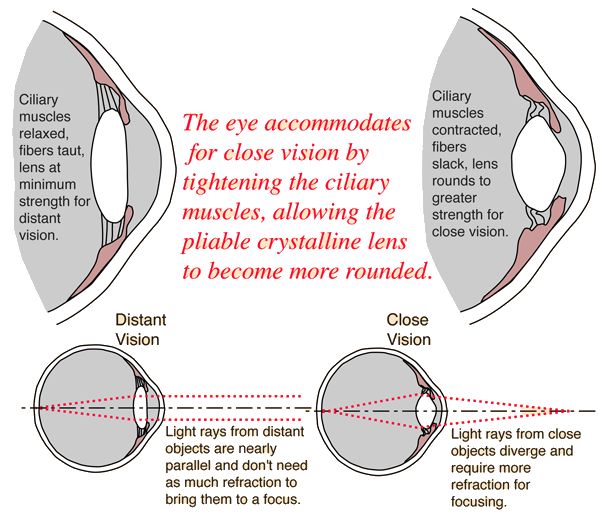
Accommodation for distance vision
ciliary muscles RELAX > ciliary body moves OUTWARDS > suspensory ligaments become TIGHT > elastic lens become more leas CONVEX/FLATTER > clear image on retina
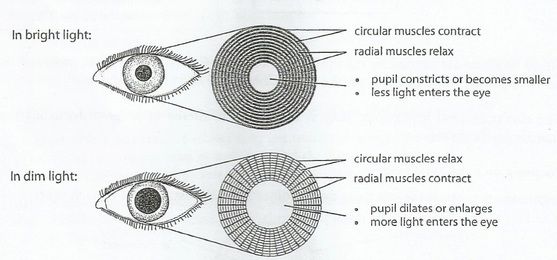
pupillary light reflex
Contraction of pupils in response to light.
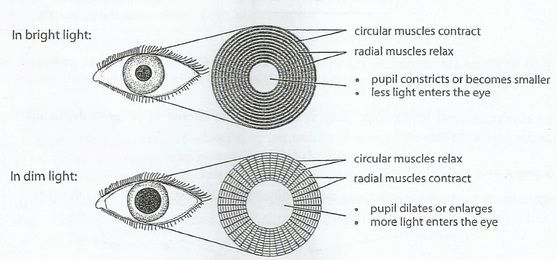
Pupils to Bright Light
RADIAL muscles RELAX
CIRCULAR muscles CONTRACT
pupils CONSTRICT
LESS light enters eye
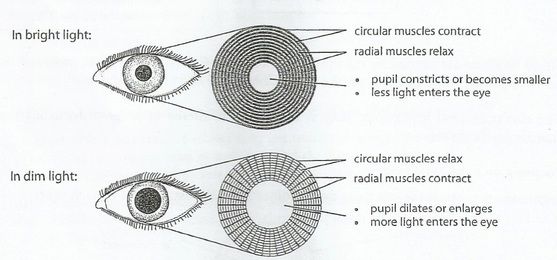
Pupils to Dim light
RADIAL muscles CONTRACT
CIRCULAR muscles RELAX
pupils DILATE
MORE light can enter the eye