Review Unit 1: Biological Bases for Behavior
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
day 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
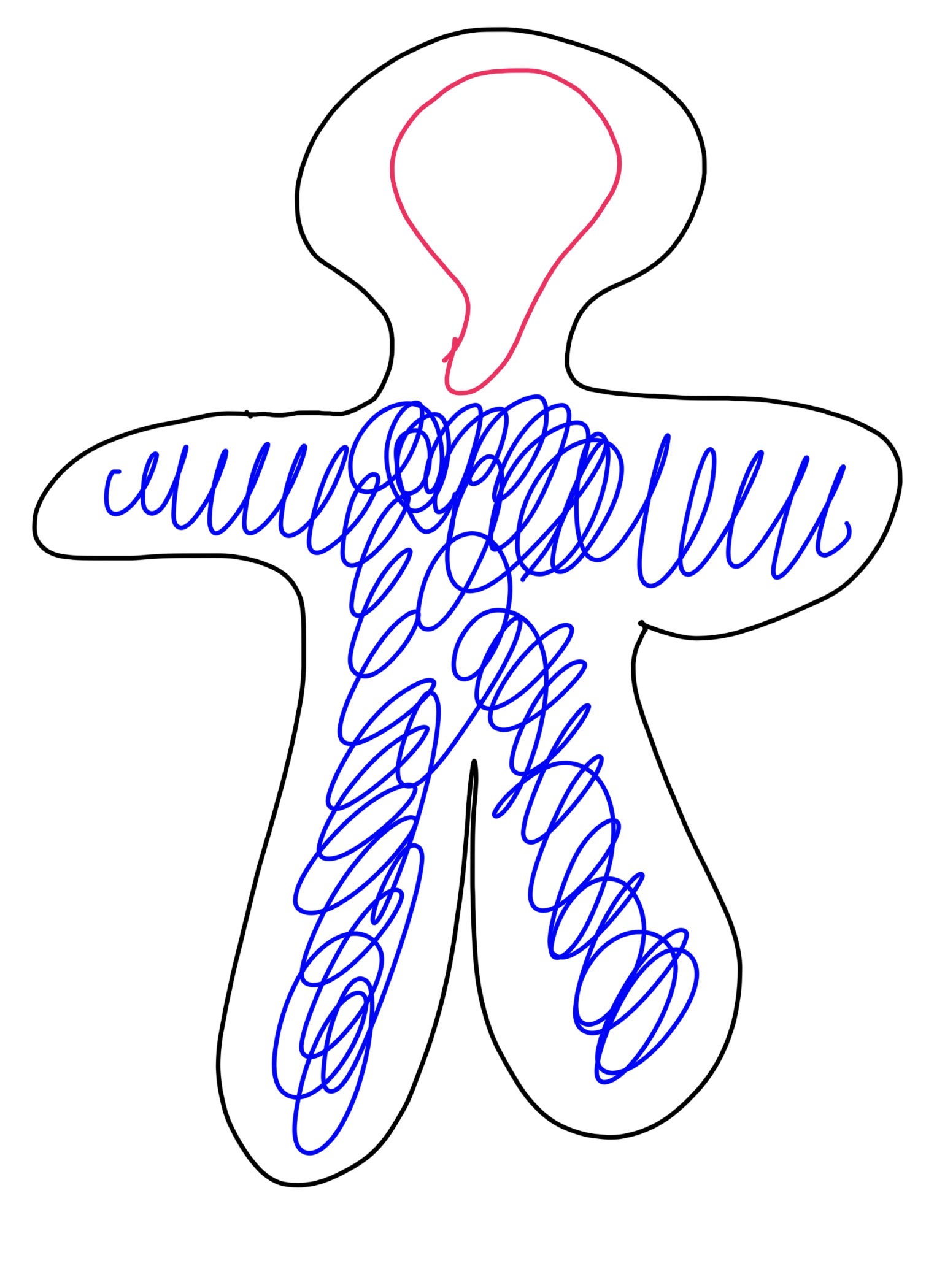
what is the blue on the man and what does it do
peripheral nervous system
sends info to the central nervous system and then to muscles and organs
controls voluntary and involuntary motives like breathing, digestion and heart rate
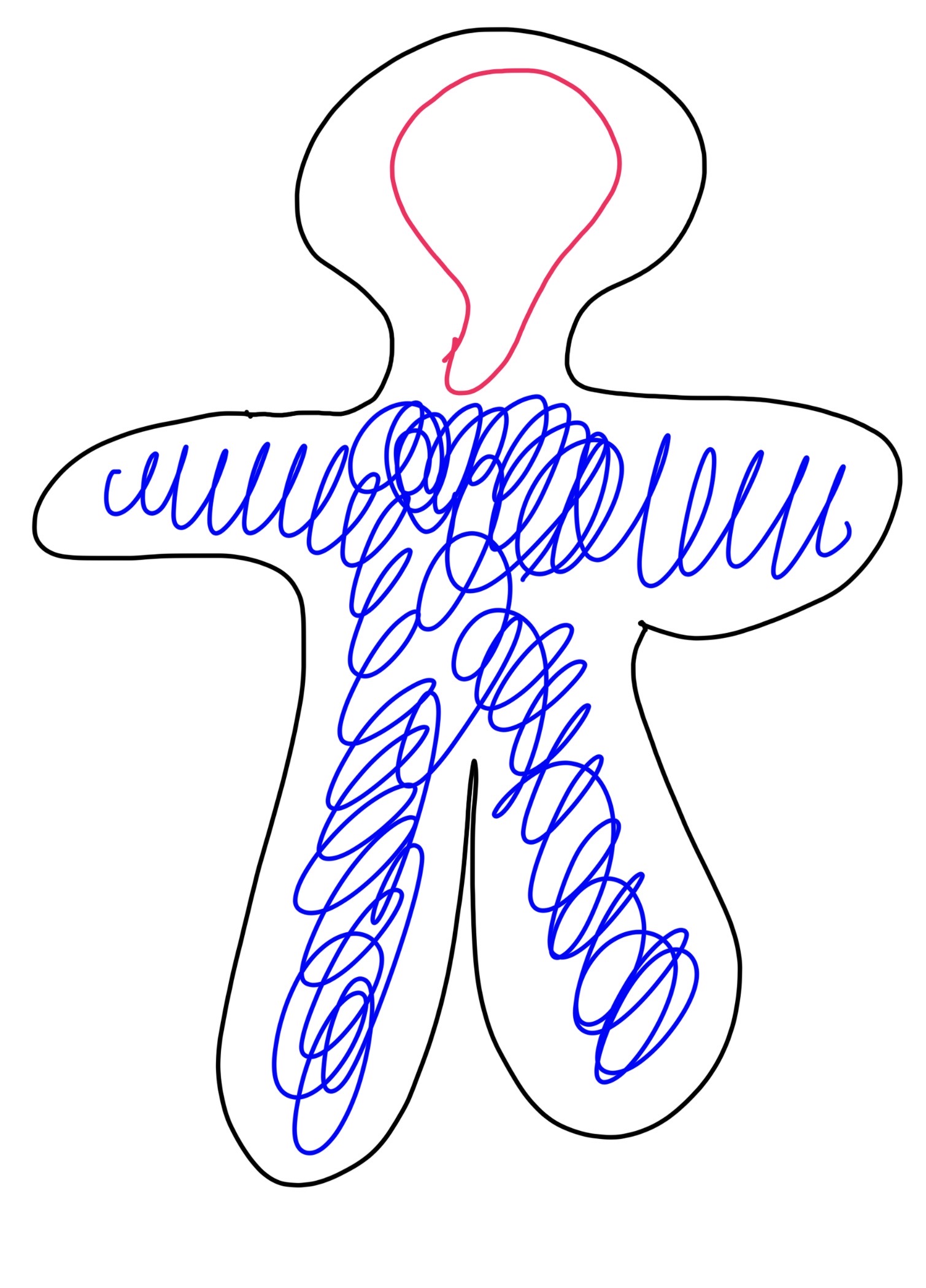
what is the pink on the man and what does it do
central nervous system
take info from senses and figures out what to do and sends orders to your body
what is the blue on the axon and what does it do
nodes of ranvier
allow action potentials to travel much faster by going from one node to another
what is the pink on the picture and what does it do
myelin sheath
protective sheet that forms around nerves
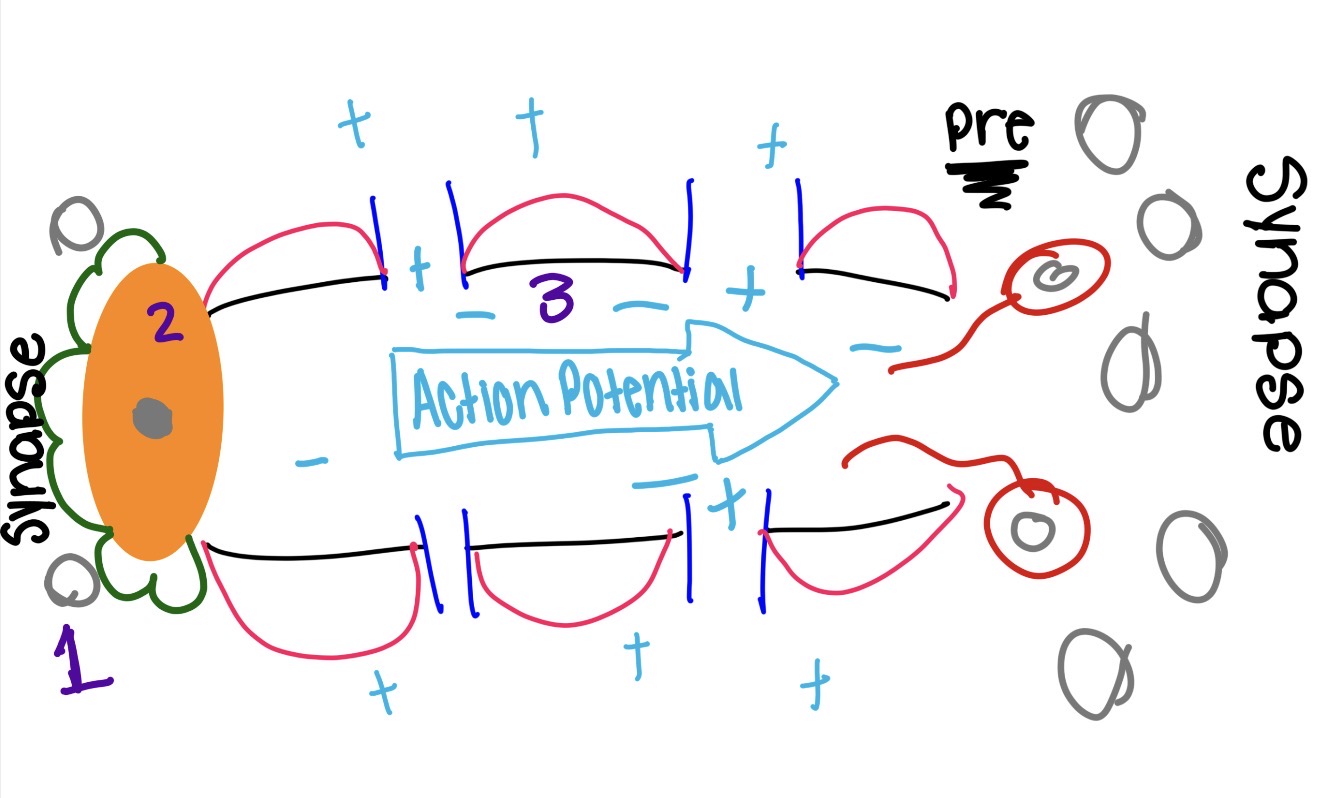
whats is the orange on the photo and what is it
the soma
houses nucleus of the cell
gets incoming signals from dendrites
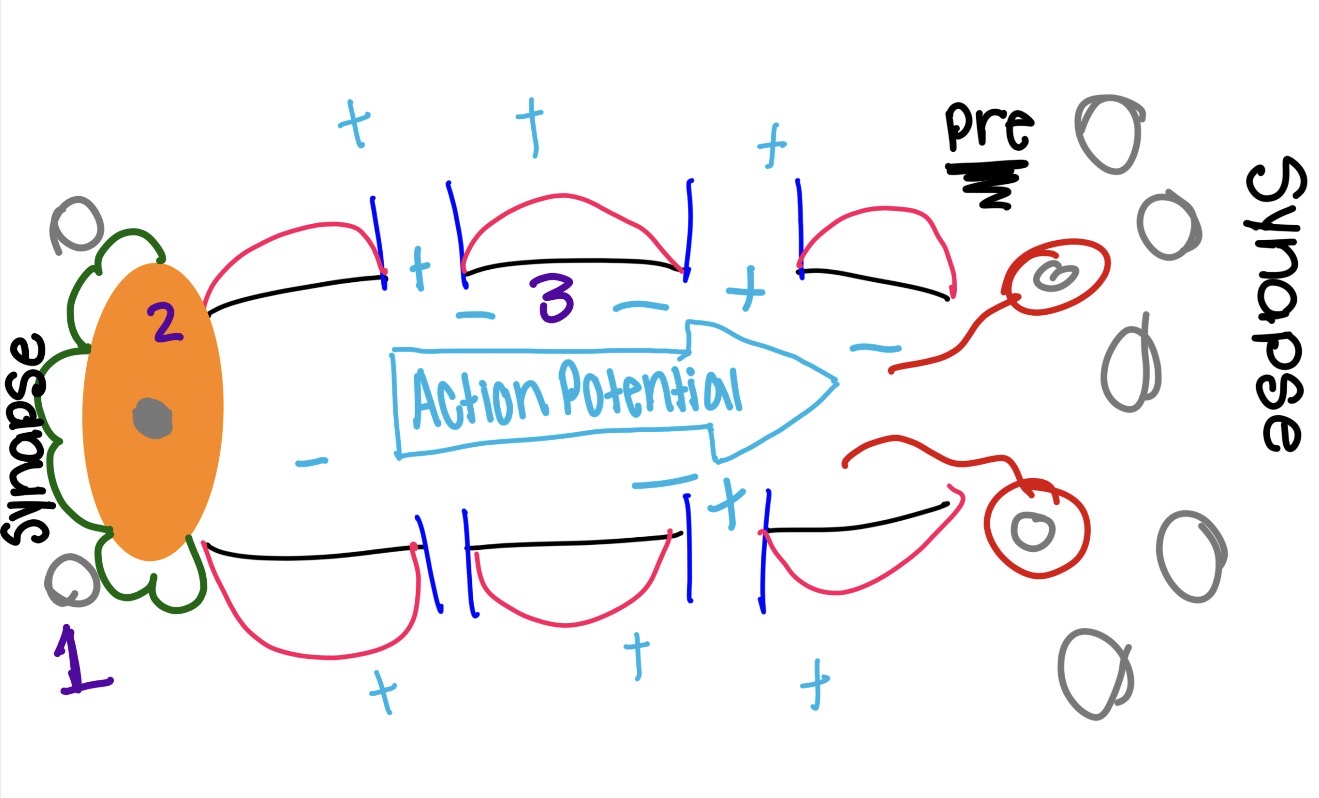
what is the red sperm looking things and what does it do
axon terminal
transmits signals to other cells
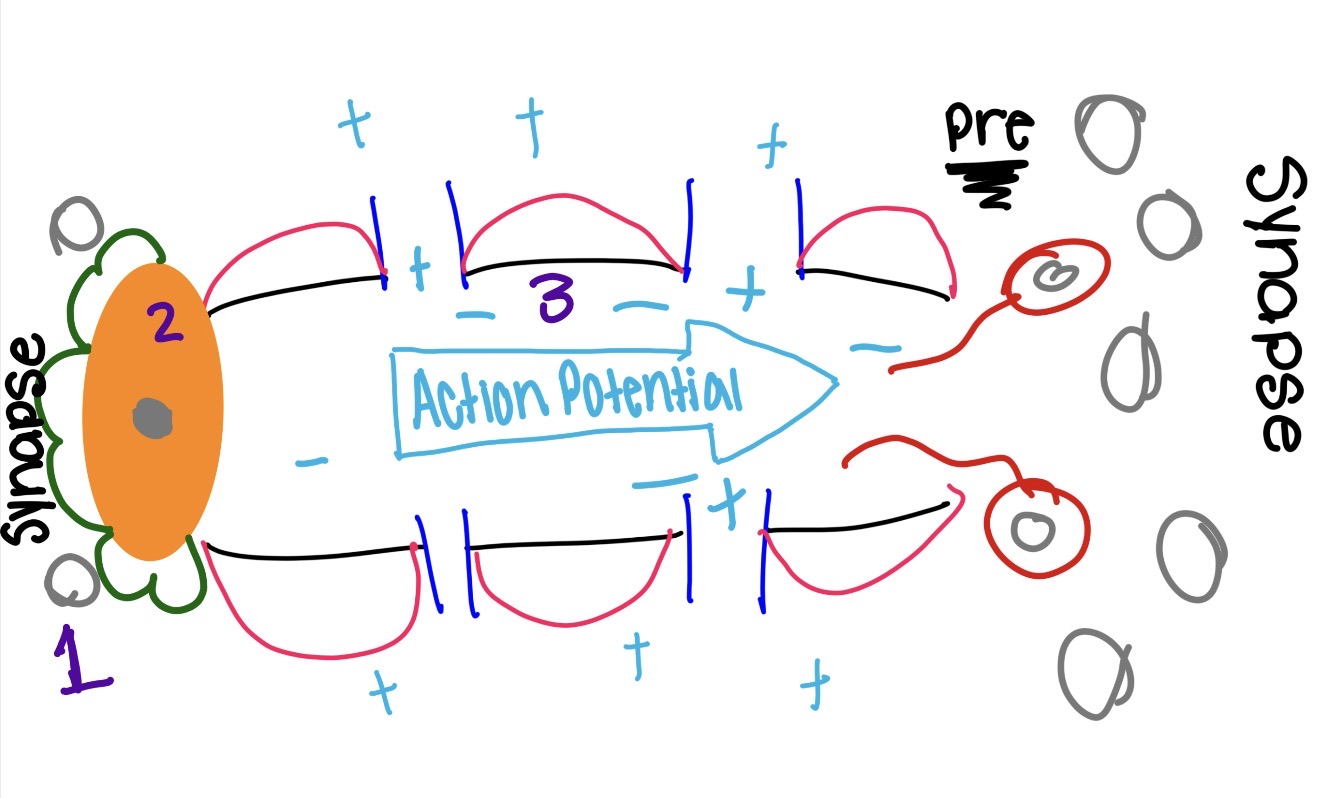
what is the green and what does it do
dendrite
catches neurotransmitters
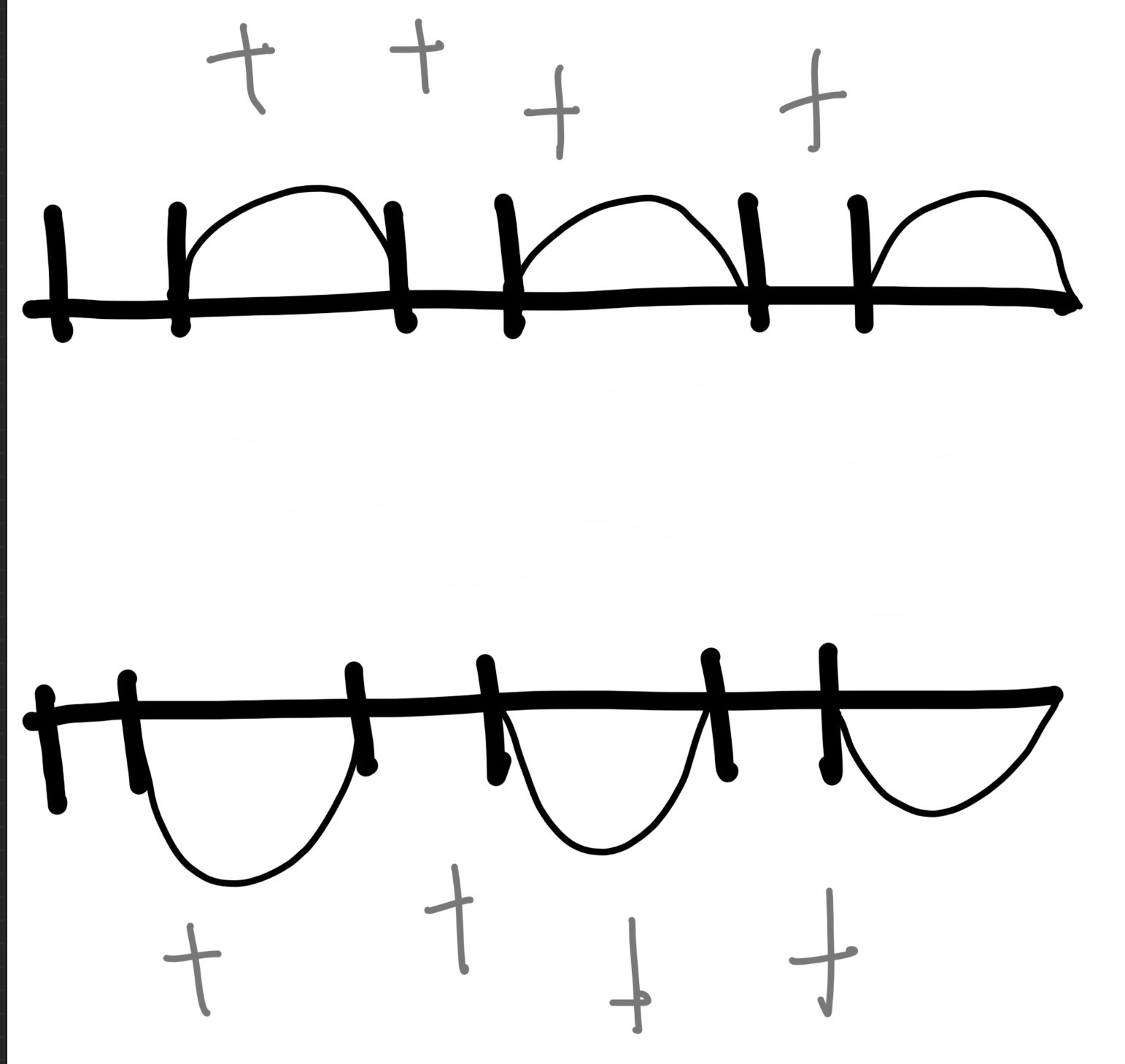
what phase is this
polarization/resting period
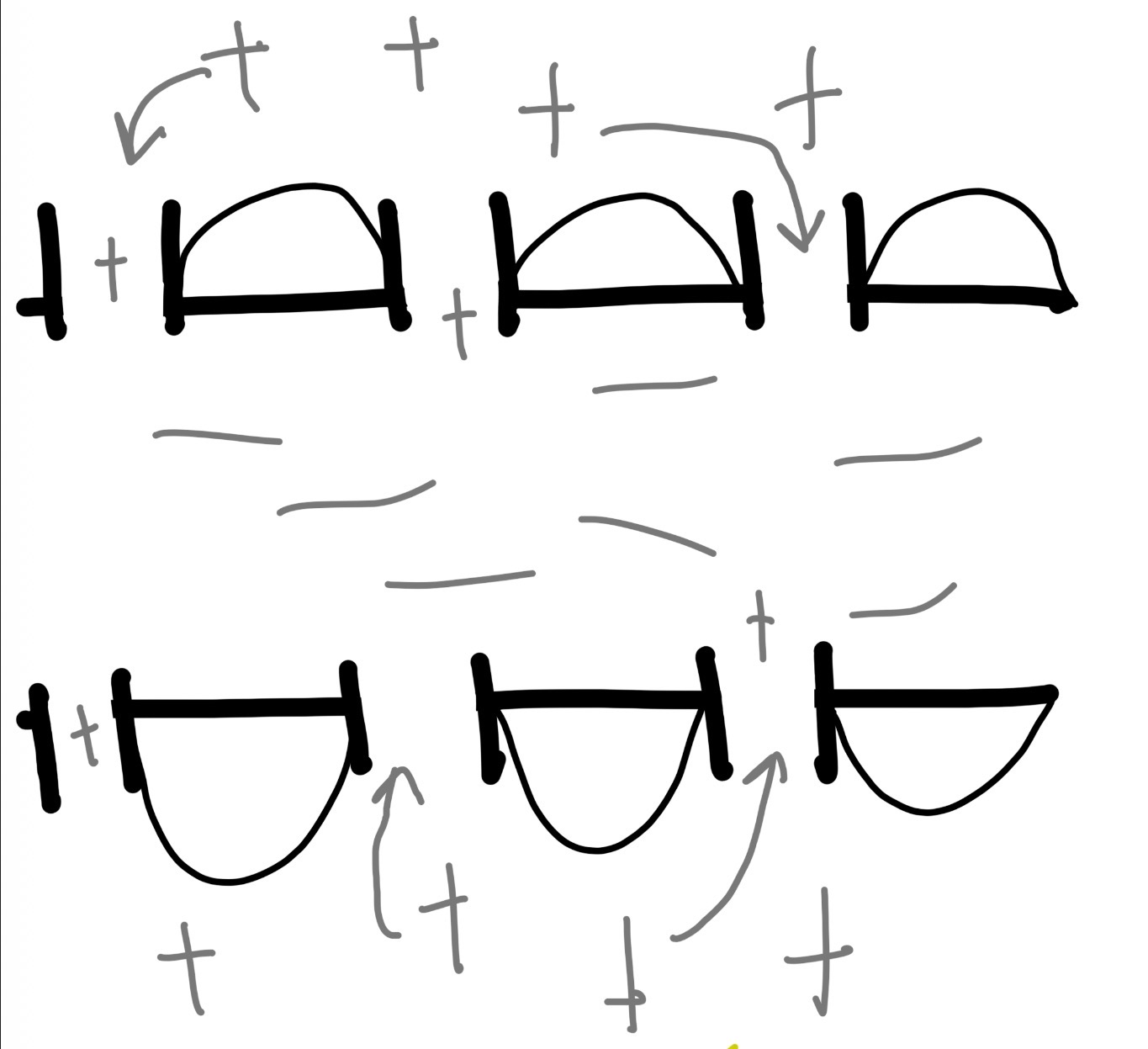
what phase is this
depolarization/ action potential
rapid positive shift in neurons electrical charge
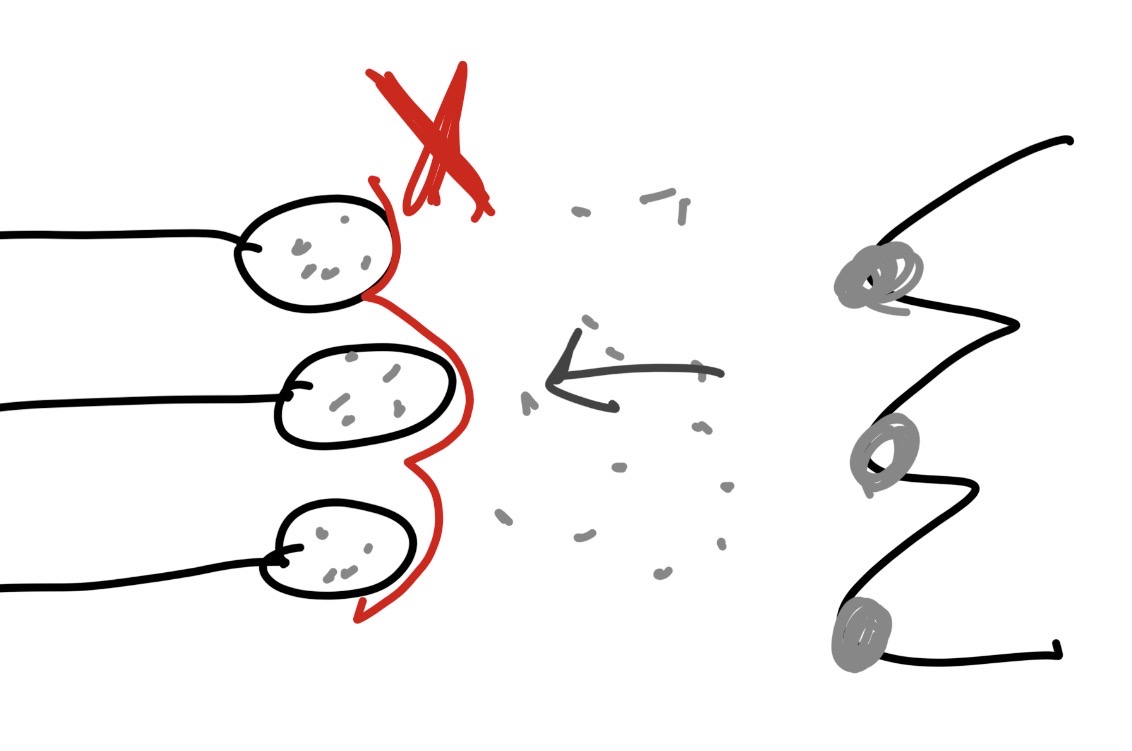
agonists
excite dendrite receptor
fires but it shouldn’t

antagonisits
inhibits/blocks the dendrite receptor

reuptake inhibitor
prevents reuptake from occurring in the axon terminal
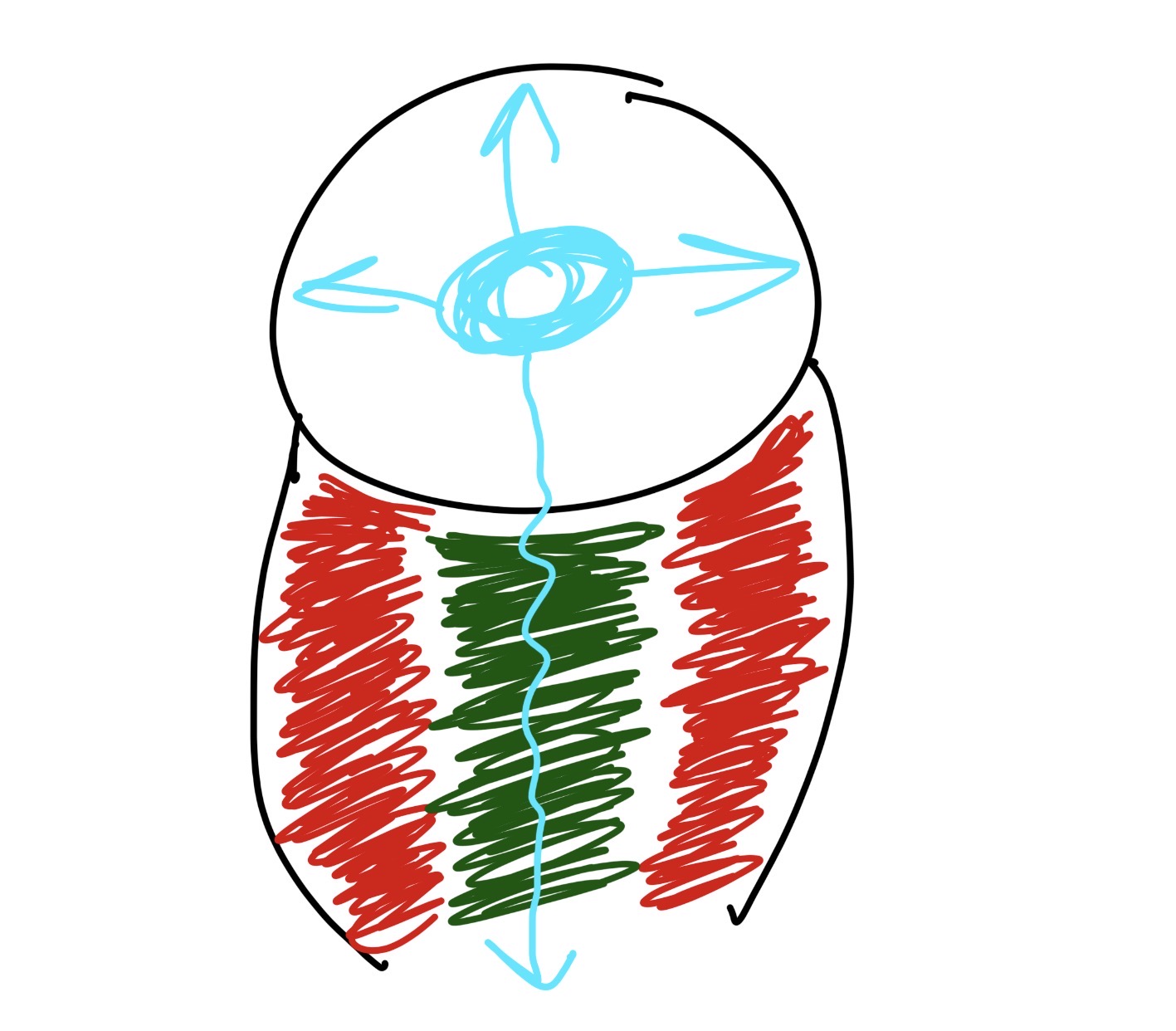
what is the red and what does it do
the medulla
controls involuntary functions
breathing, heart rate
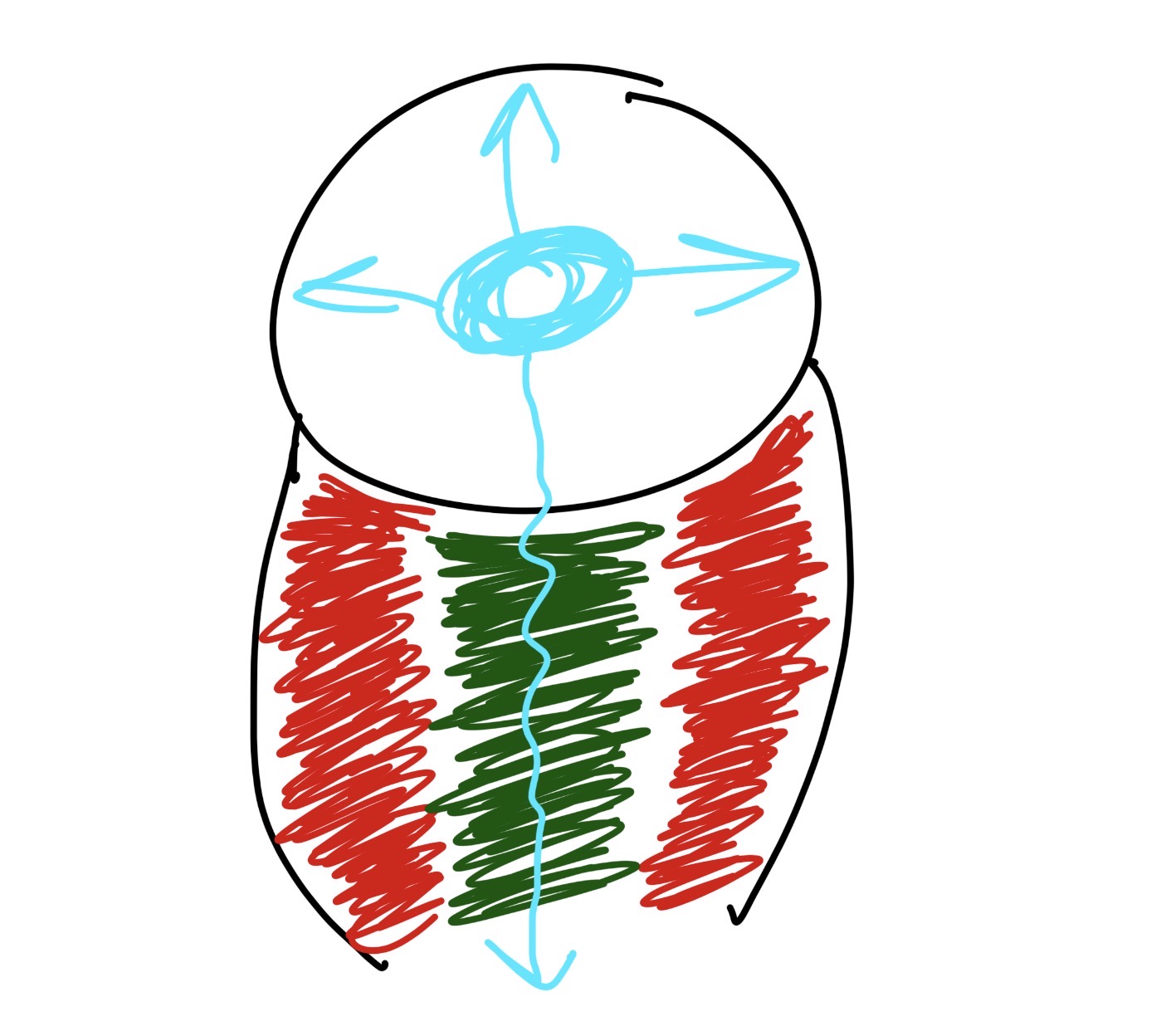
what is the green what what does it do
the cerebellum
controls balance, posture, and timing
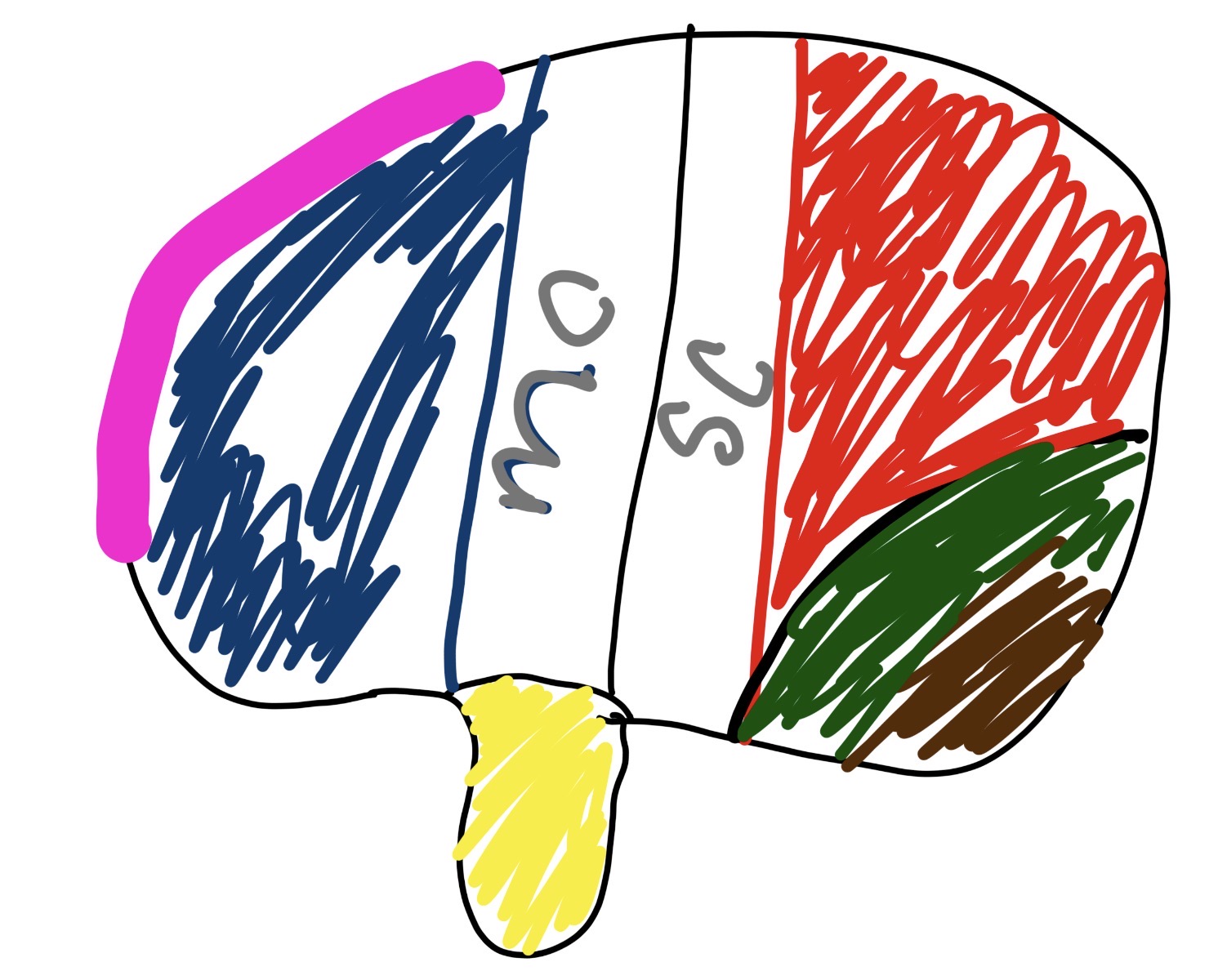
what section is the pink and blue and what does it do
frontal lobe
manages personality, movement, decision making,
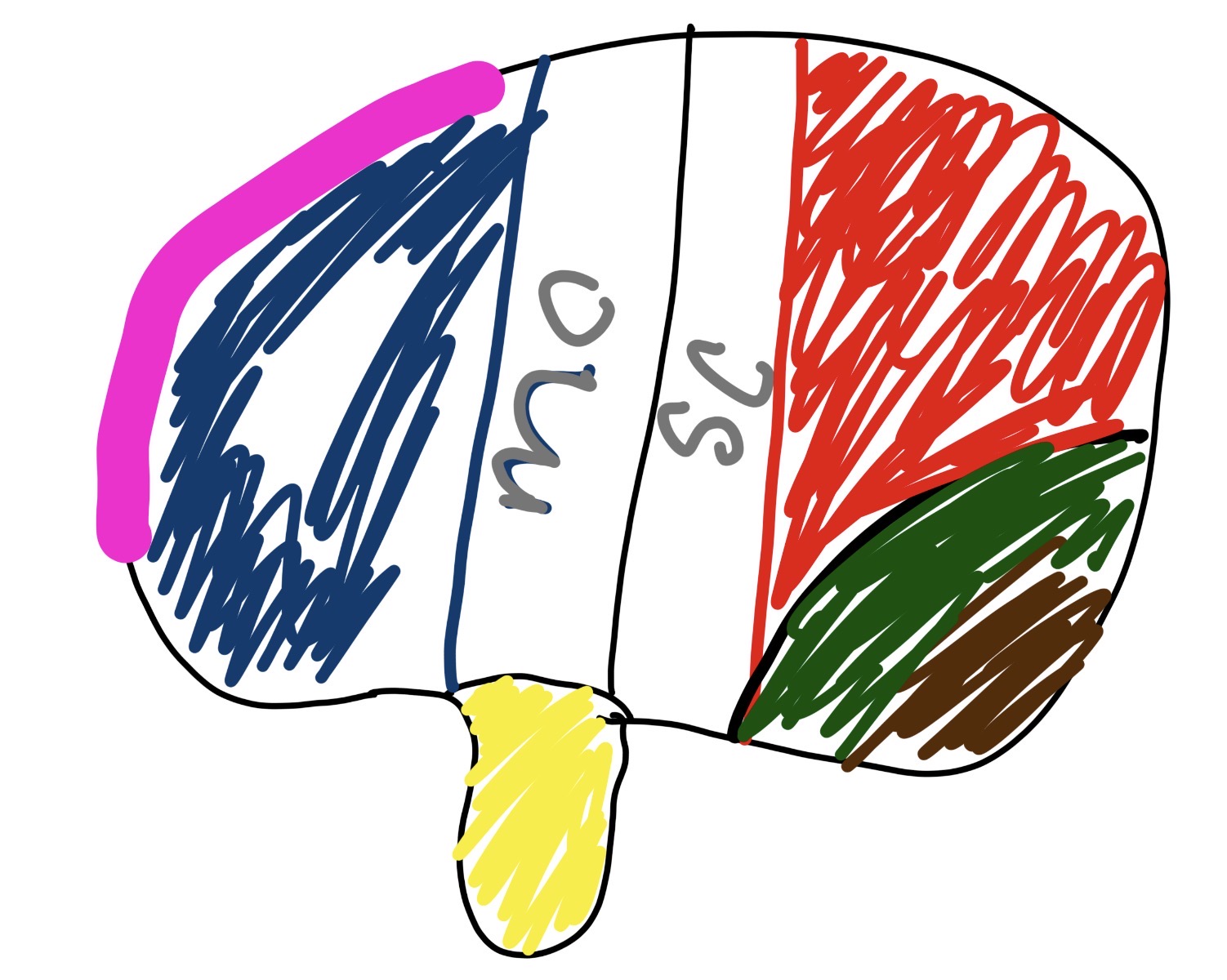
what section is the red and what does it do
parietal lobe
touch
taste
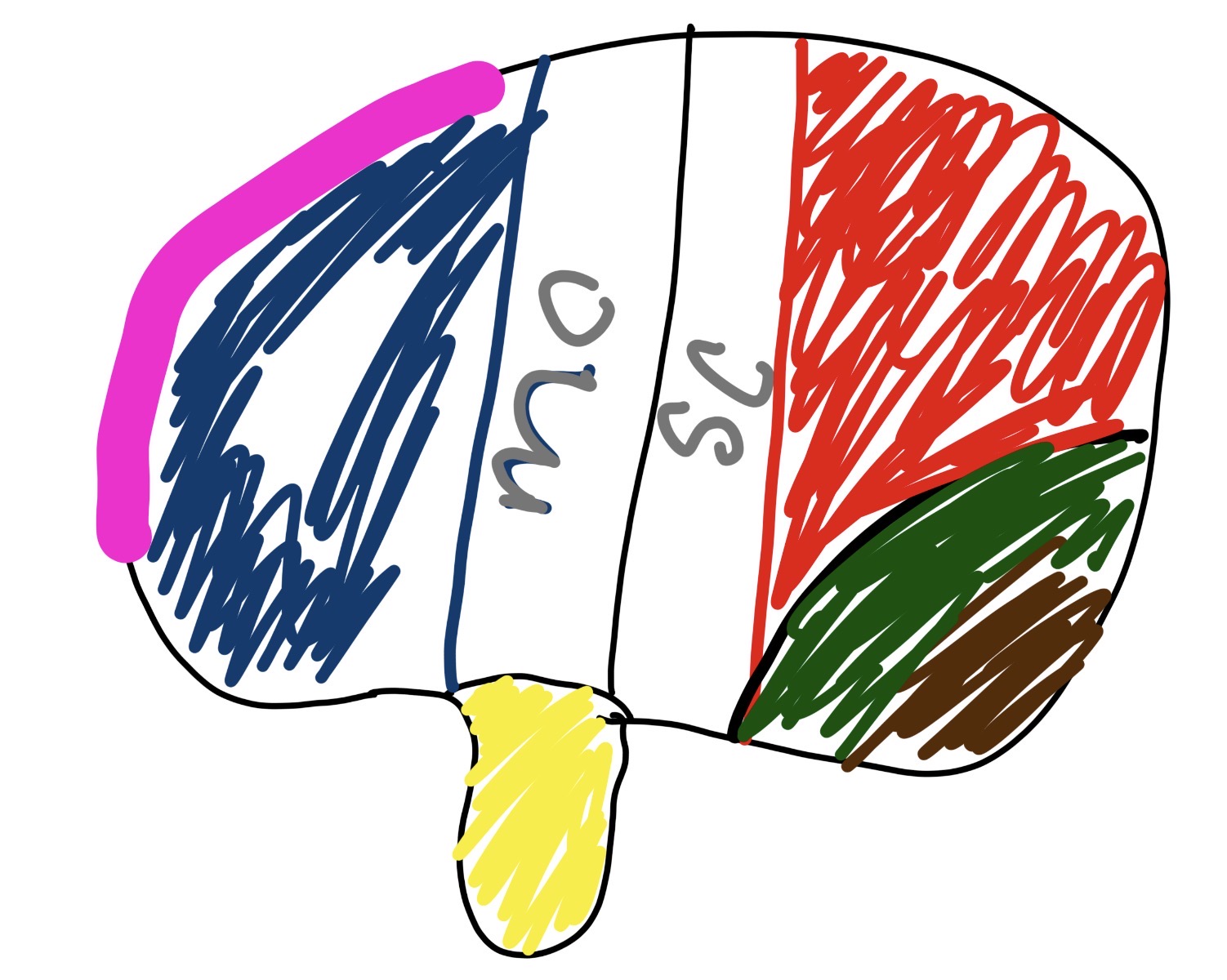
what section is the green and what does it do
occipital lobe
vision/sight
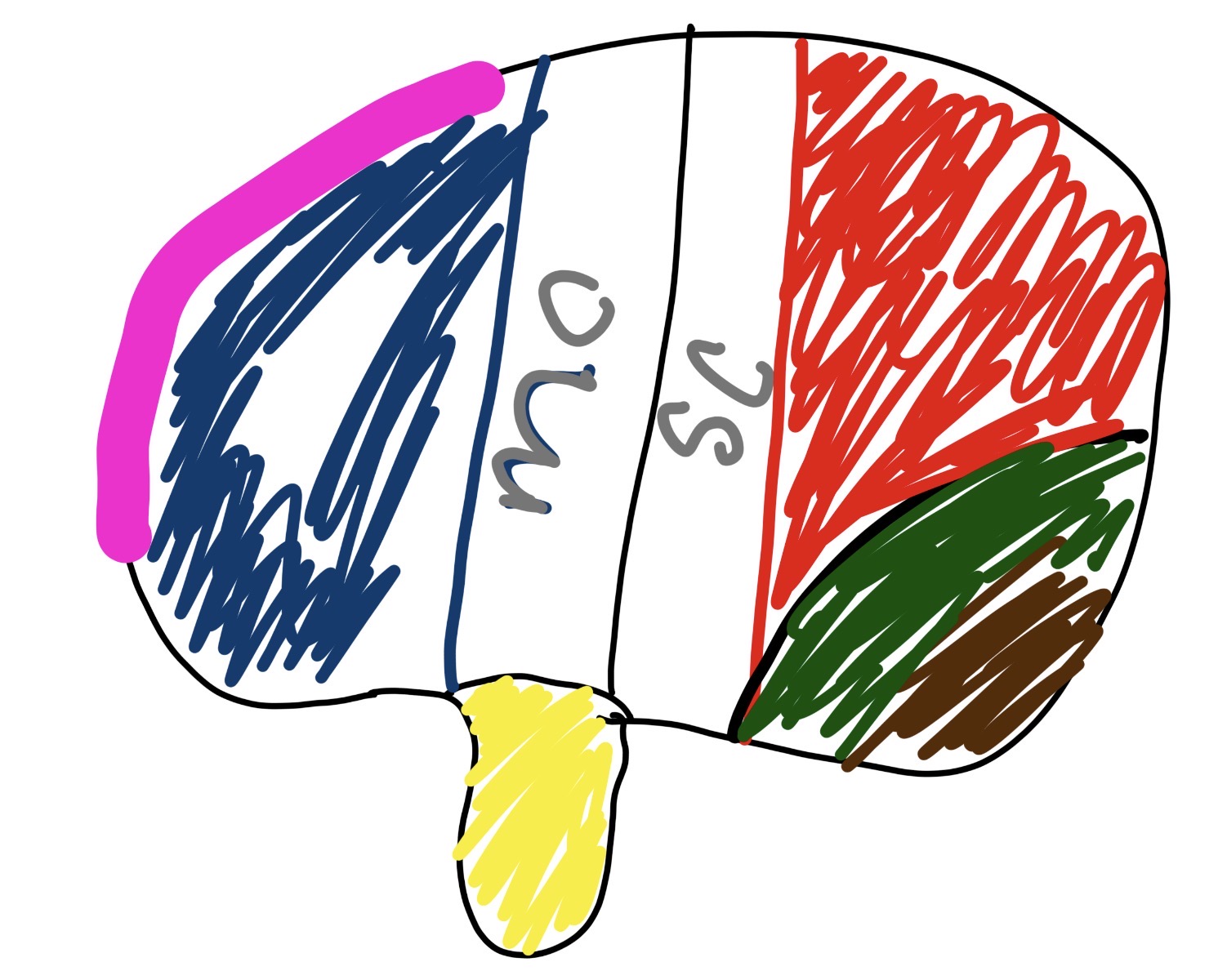
what section is the yellow and what does it do
temporal lobe
hearing
smell
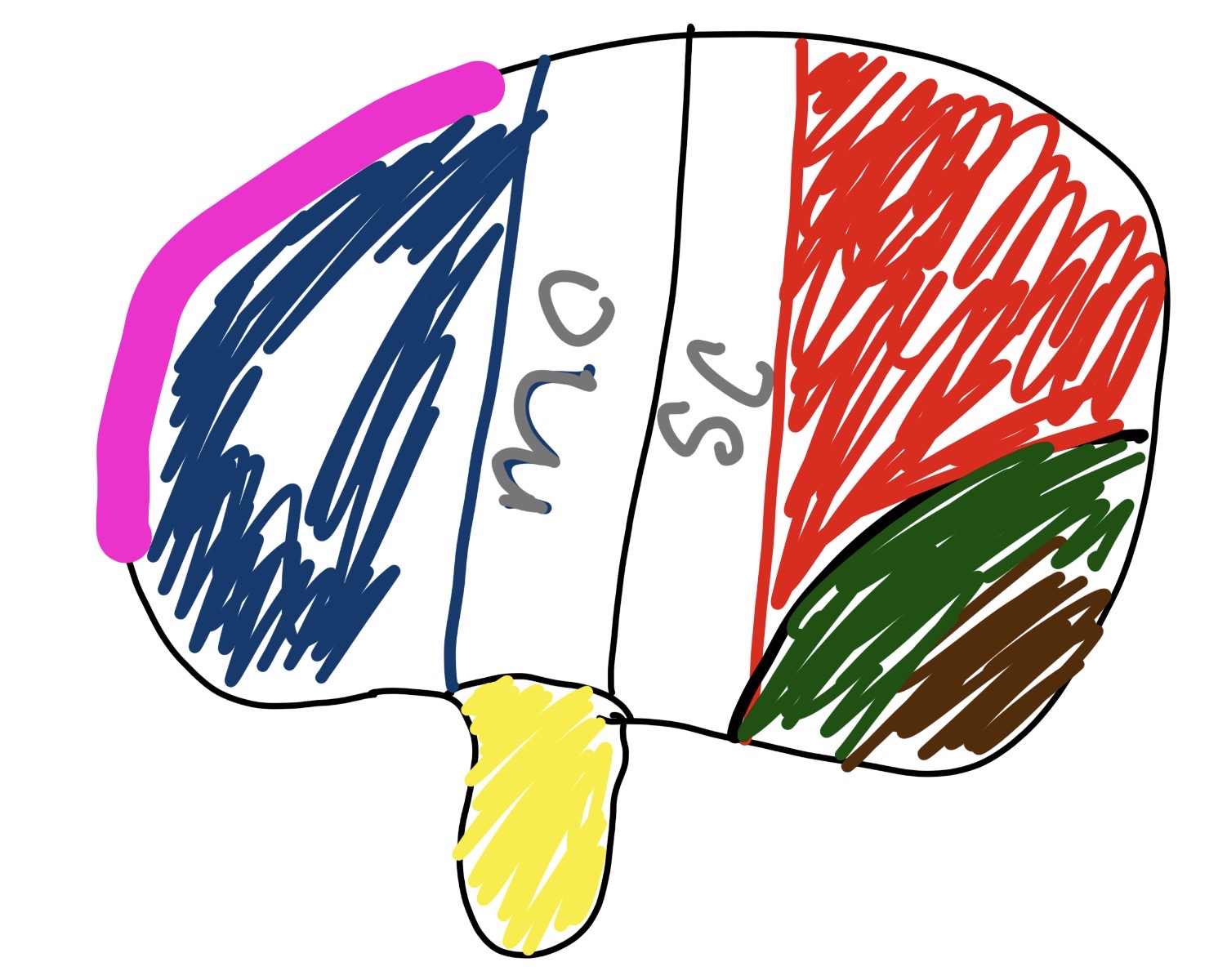
what is mc
middle cerebral artery
major artery supplying blood to large part of brain surfaces
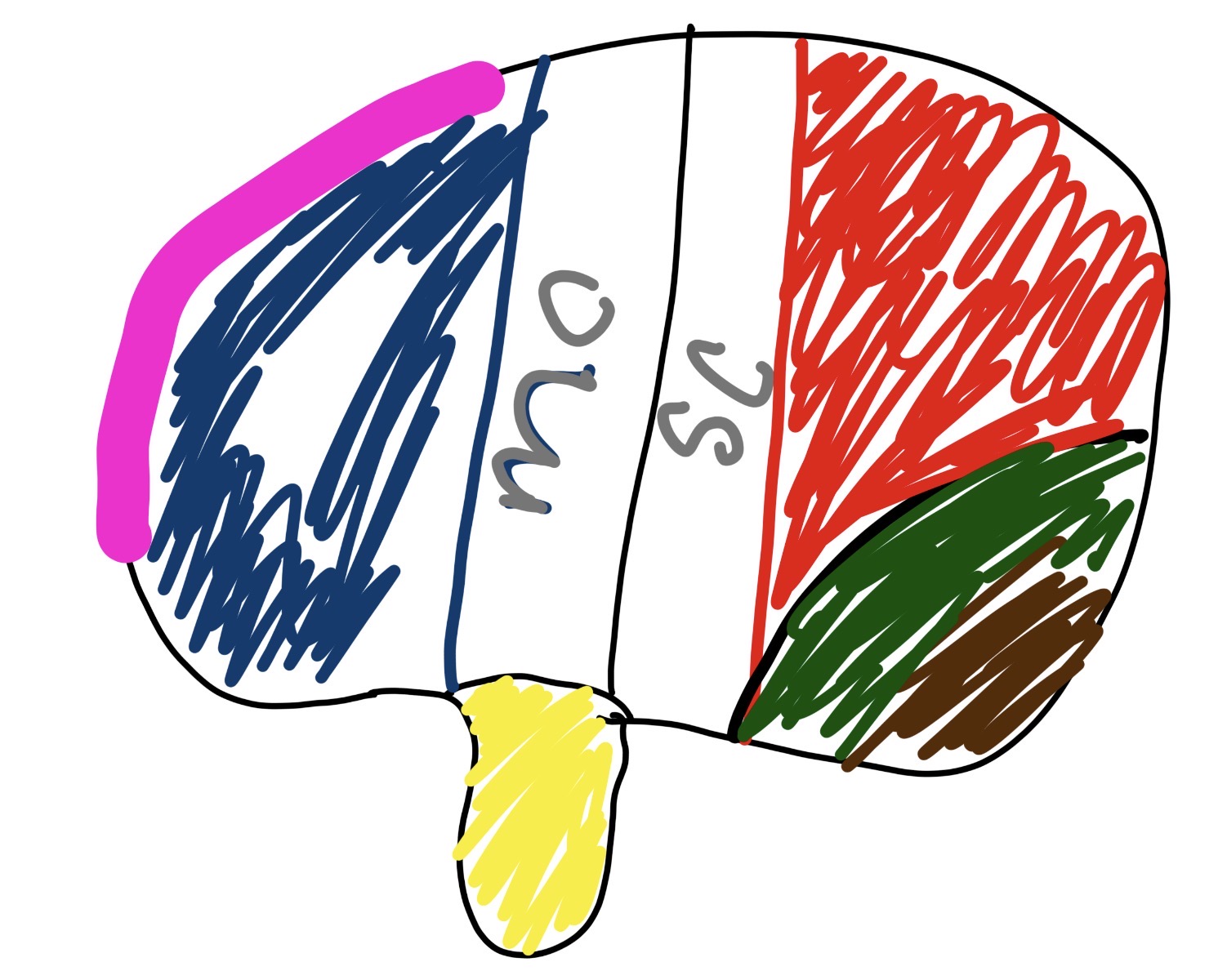
what is sc
Superior Colliculus
crucial for head eye movement
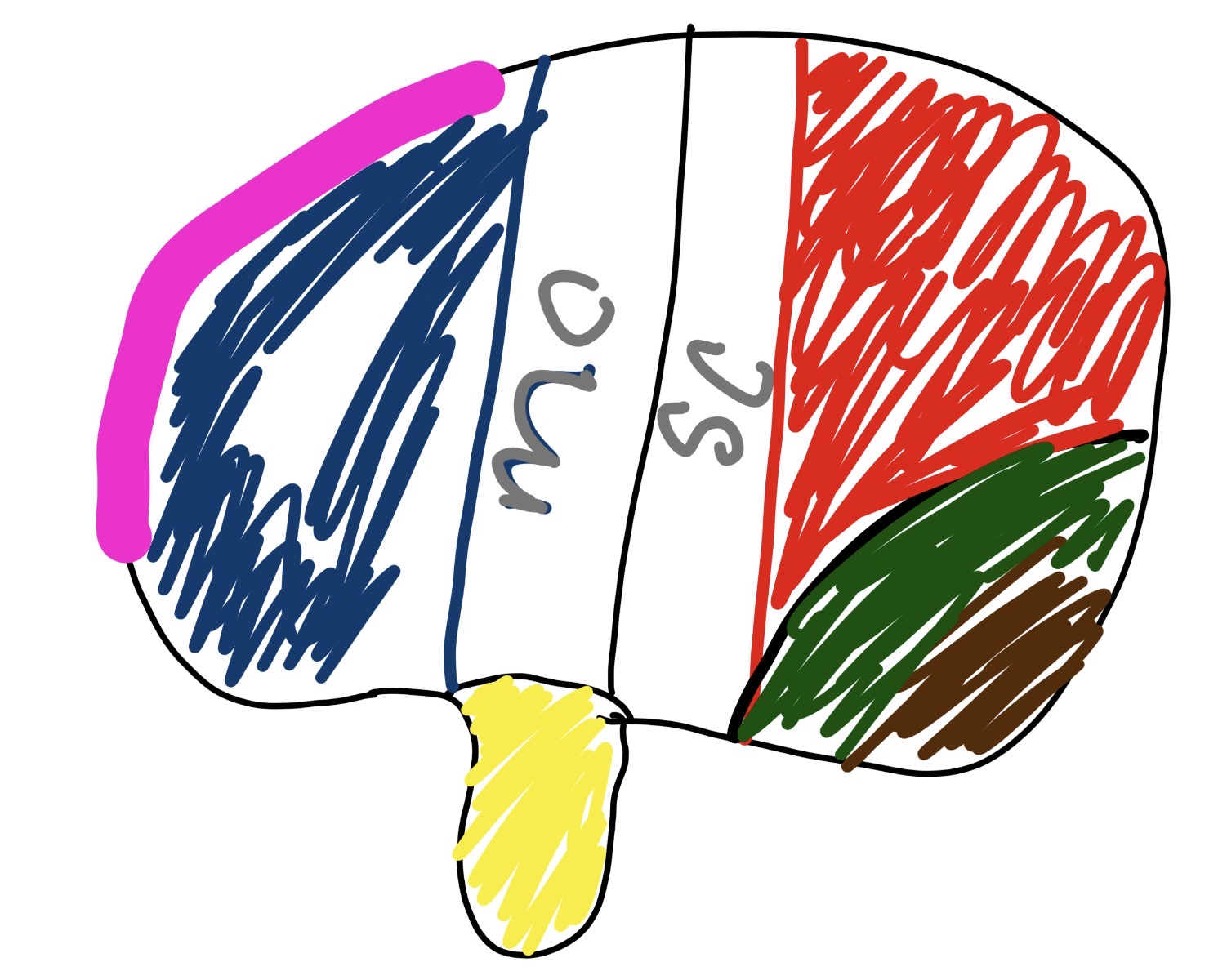
what is the pink and what does it do
pre-frontal
problem solving
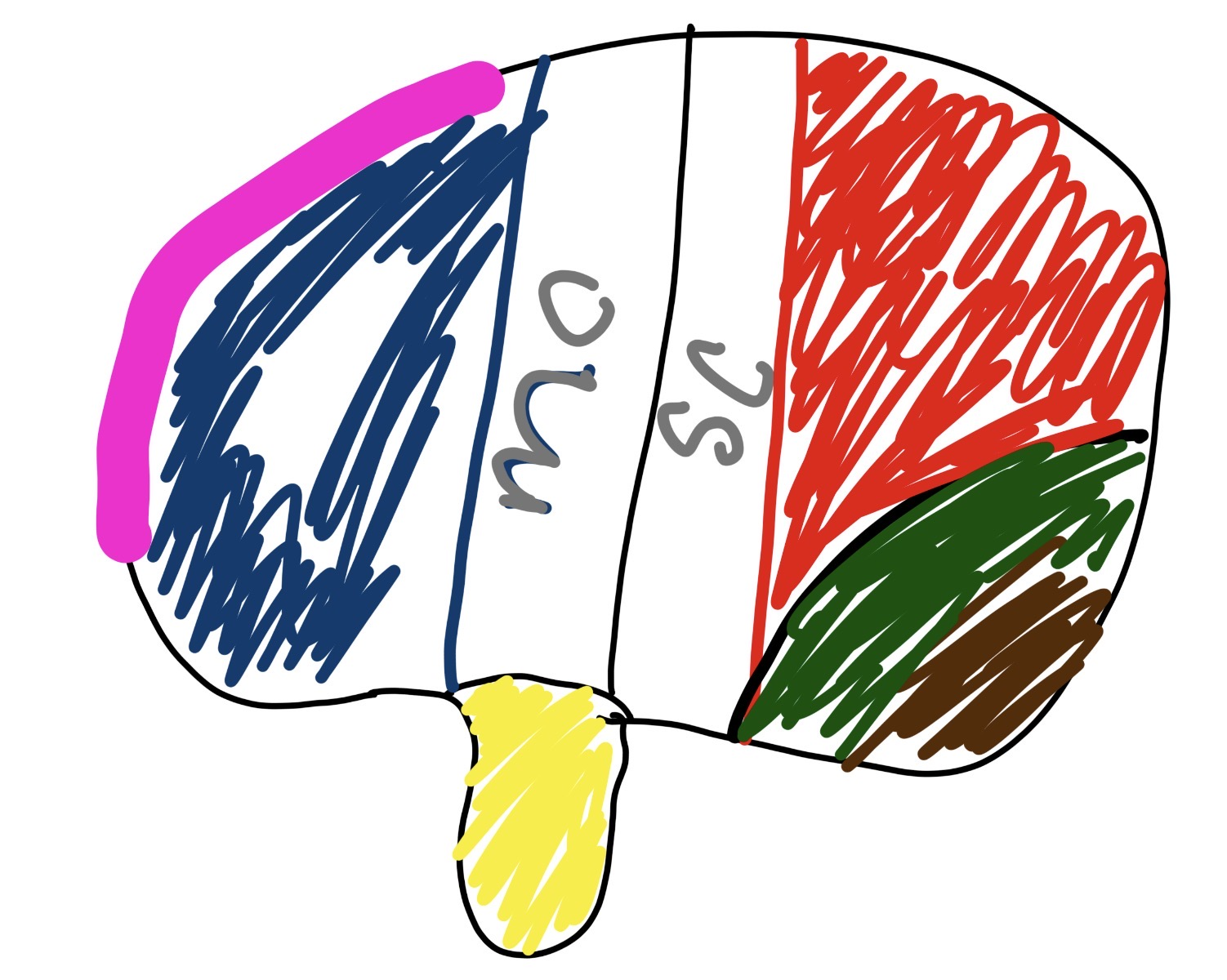
what is the blue and what does it do
brocas area
talking
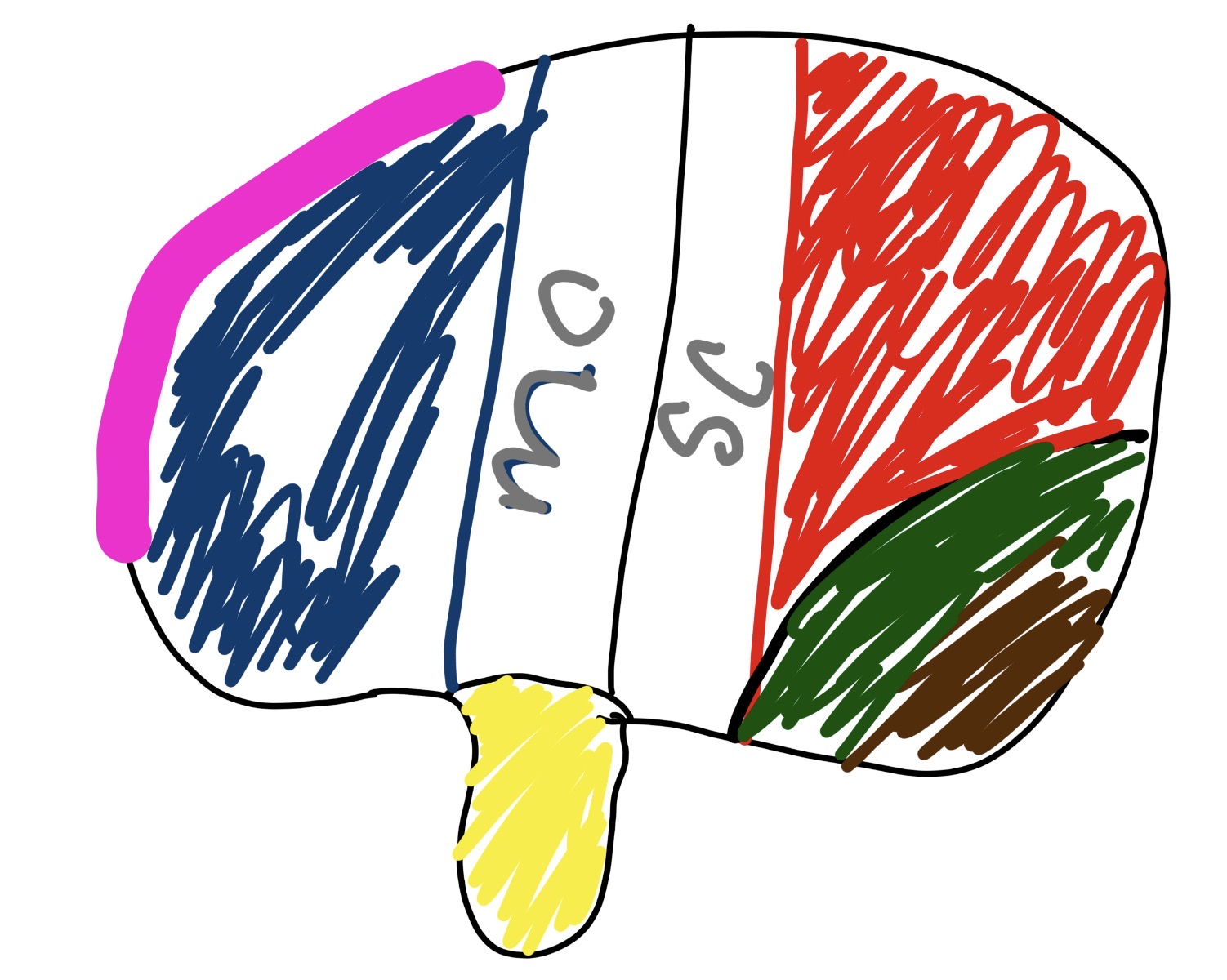
what is in the yellow section and what does it do
wernickies area
language comprehension
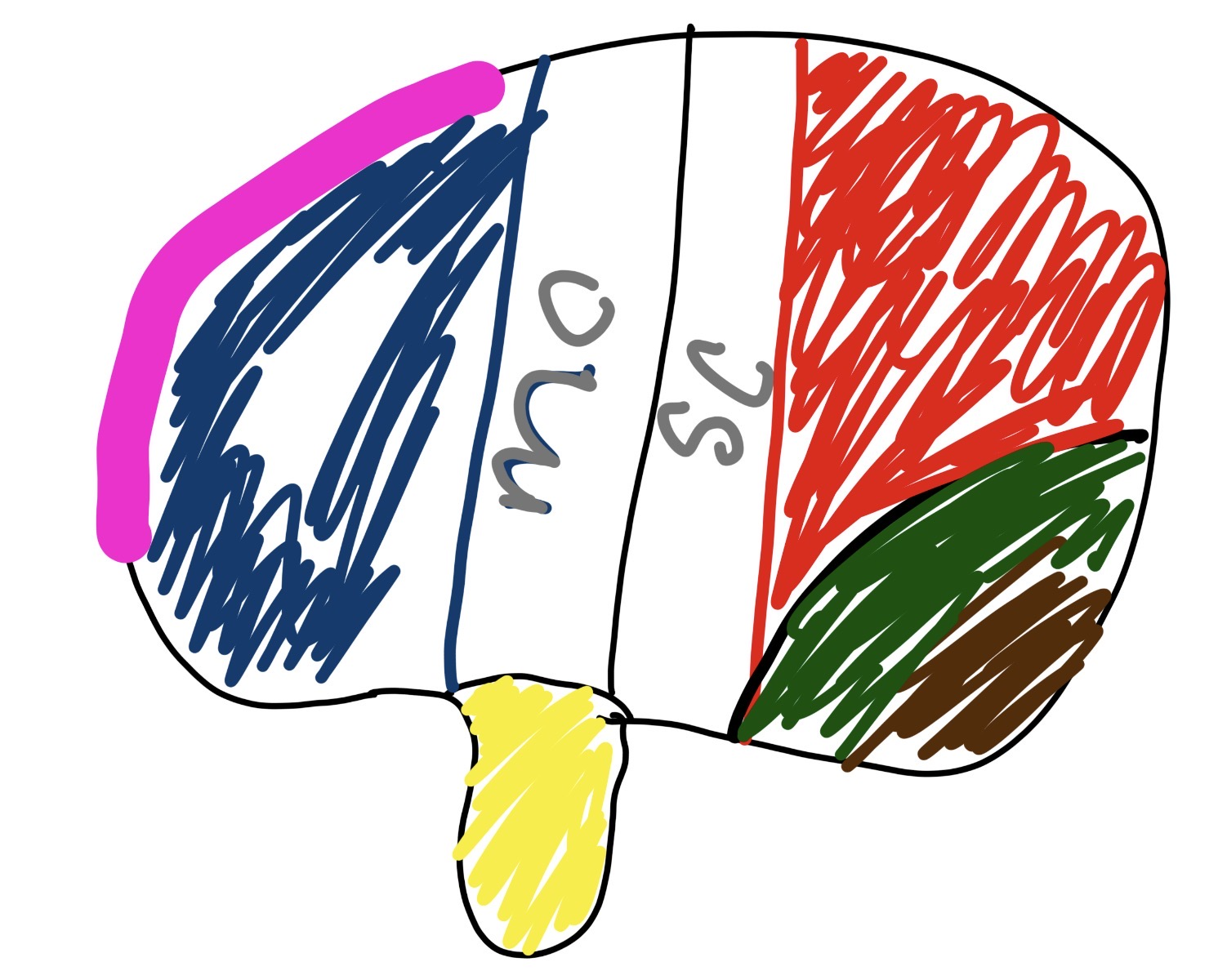
what is the brown and what does it do
visual cortex
handling sight (releasing “seeing fluid”)
sensory neurons
feels touch, pain, light, sound
inner neurons
transmits impulse between other neurons
motor neurons
transmits signals from brain/spinal cord to muscles and glands
autonomic N.S
sympathetic (fight/flight)
parasympathetic (calm down)
hyper polarization/ refectory period(recovery)
becomes more negative then the resting due to extra positives exiting
Acetylcholine (Ach)
memory
alzheimer’s (too little)
paralyzed (too much)
Dopamine
pleasure
schizophrenia (too much)
parkinson’s (too little)
serotonin
regulates hormones
depression (too little)
endorphins
pain killers
GABA
calm
insomnia (to much)
Glutamate
learning
Norepinephrine
adrenaline
mania/bipolar (to much)
outer brain
talking brain
CT or Cat scan (structural)
uses x-ray to show 2 dimensional slice of the brain
MRI (structural)
magnetic field and radio waves
PET (functional)
blood flow changes
FMRI (functional)
changes in oxygen
Taste
tastebuds
sweet
sour
salty
bitter
touch
pressure
temp
pain
smell
offaction
vestibular
balance
kinesthesis
receptors on joint, tendons, muscles to know where everything is
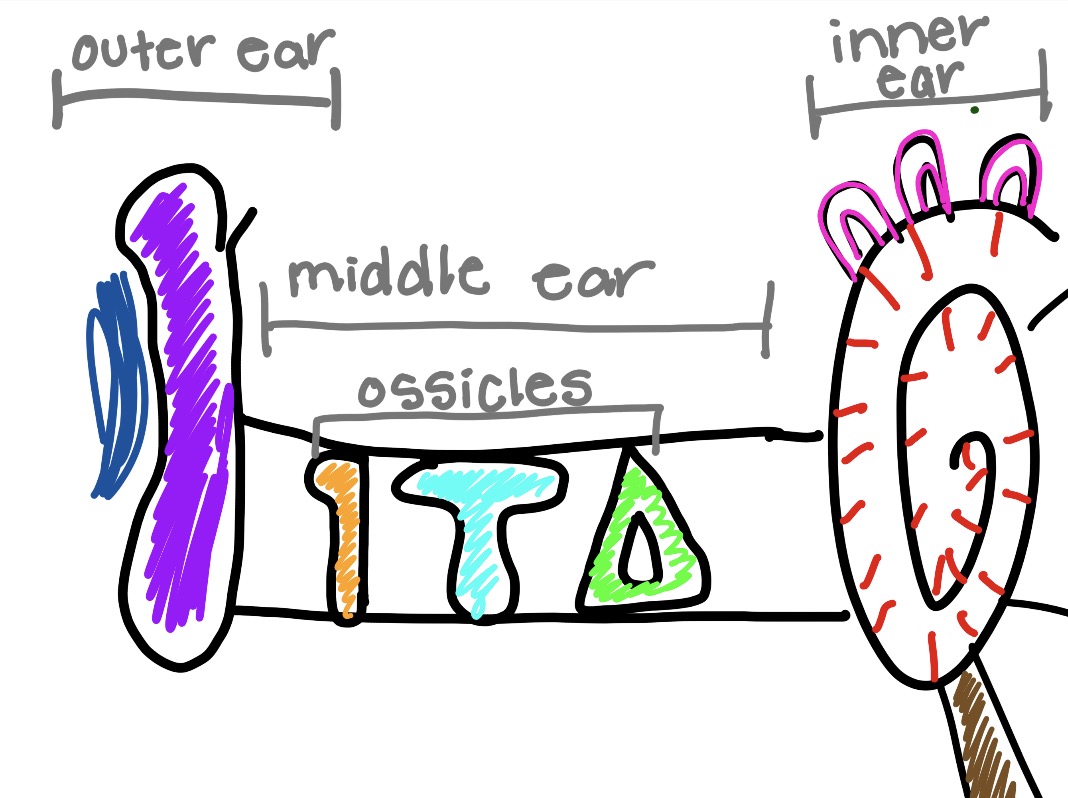
what is the blue and what does it do
auditory canal
the tube connecting to the outer ear to ear drum
pathway for sounds
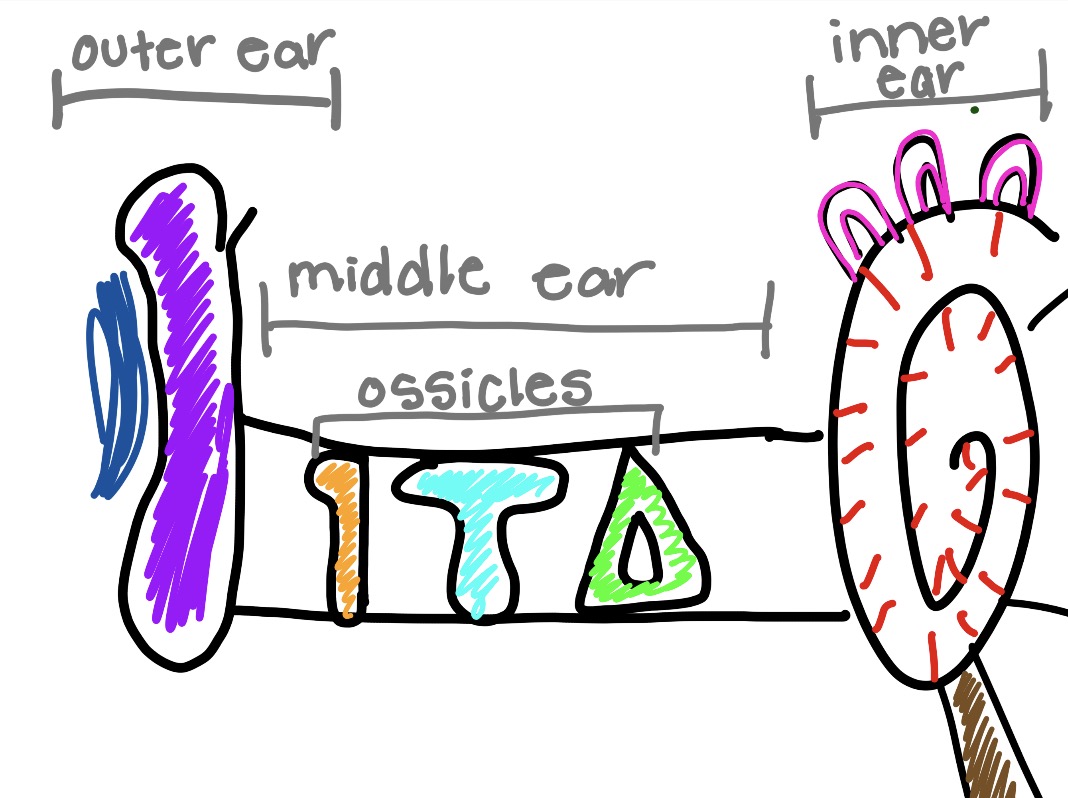
what is the purple and what does it do
pinna
outer ear
funnels sound waves into your ear
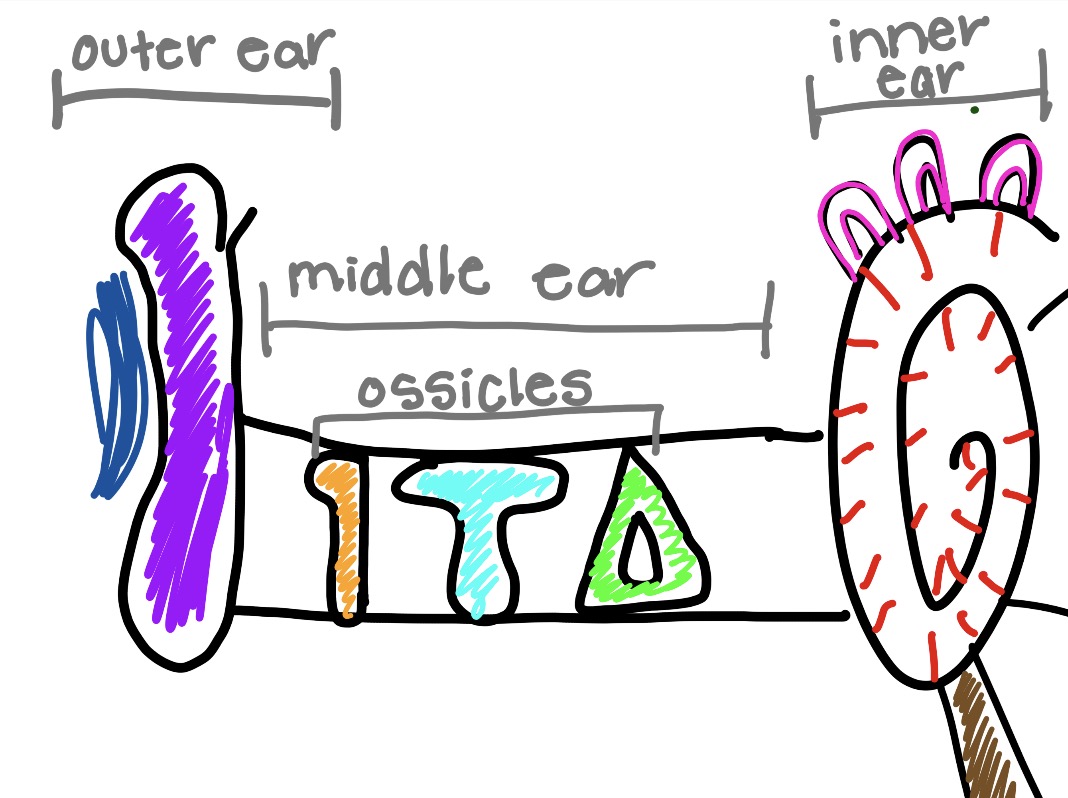
what is the orange and what does it do
malleus
hammer bone
captures sound vibrations and gives thme to incus
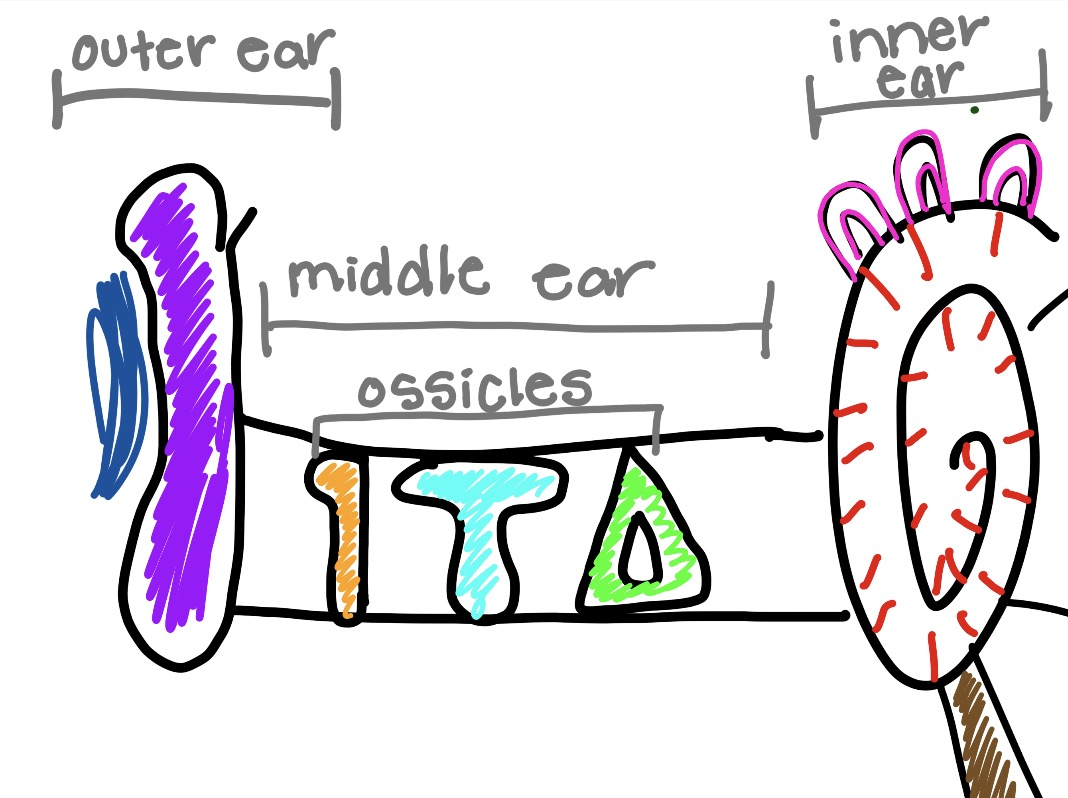
what is the teal and what does it do
incus
get sound vibrations and gives them to stapes
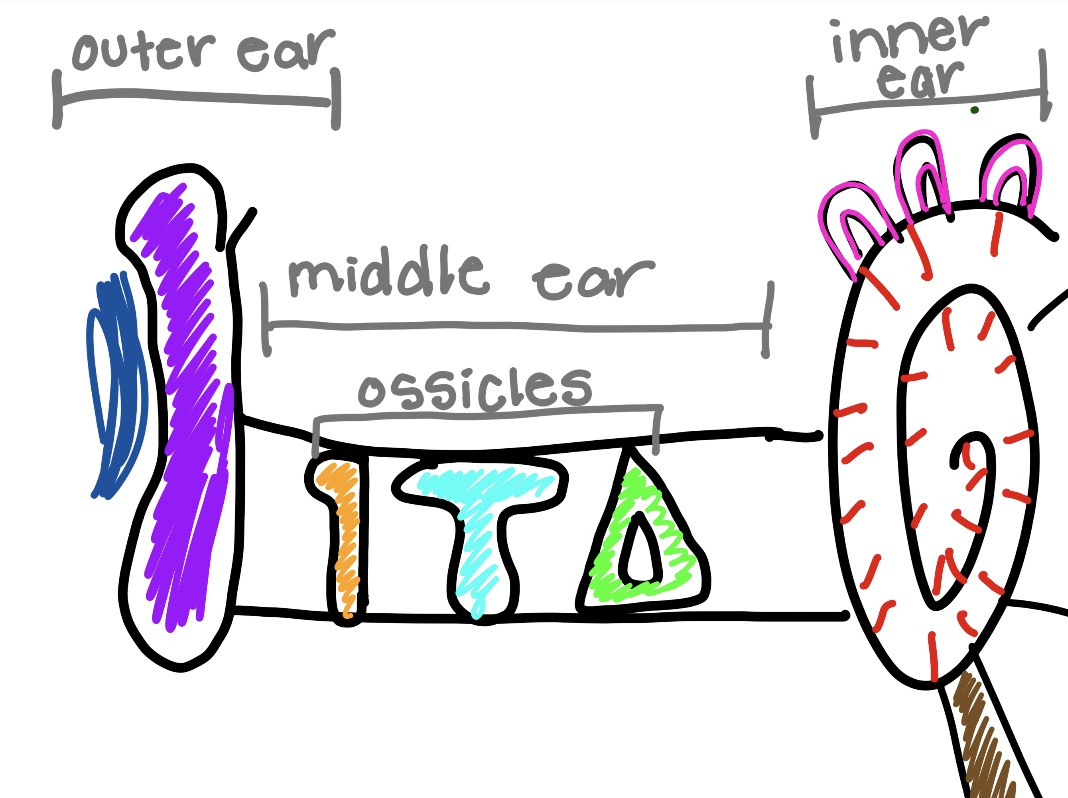
what is the green and what does it do
stapes
gives sound to cochlea
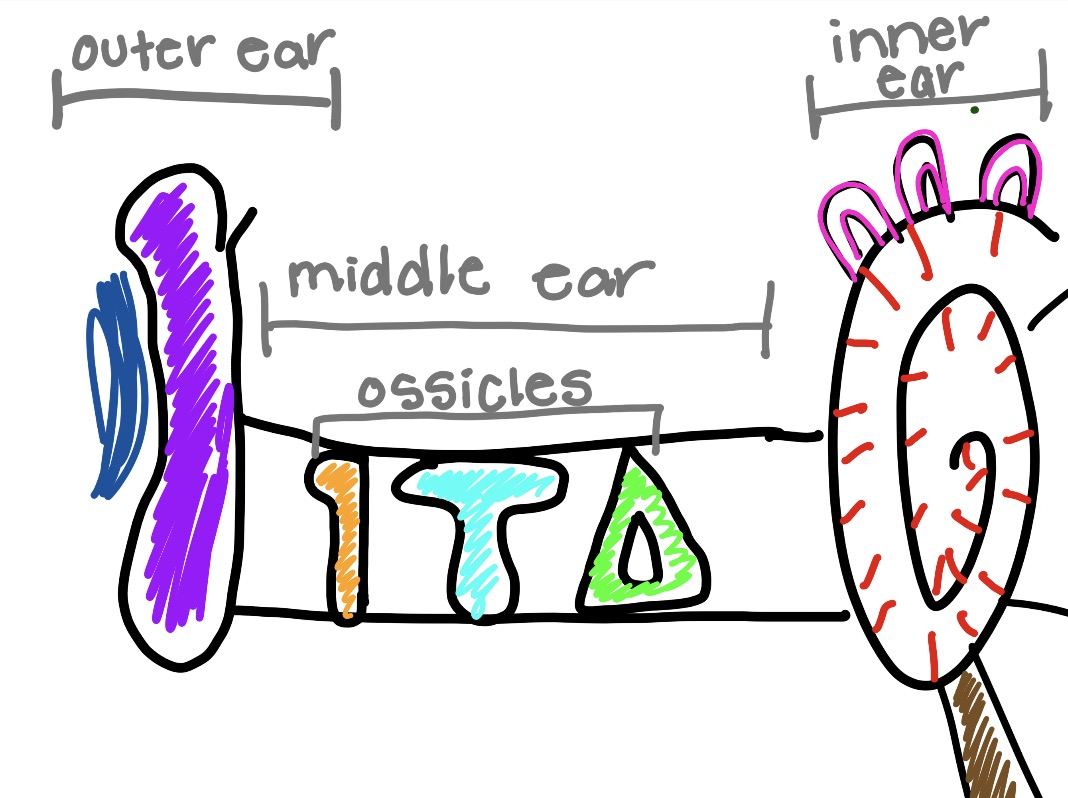
what is the circle thing and what does it do
cochlea
converts sound vibrations into electrical nerve signals that the brain interprets as sound
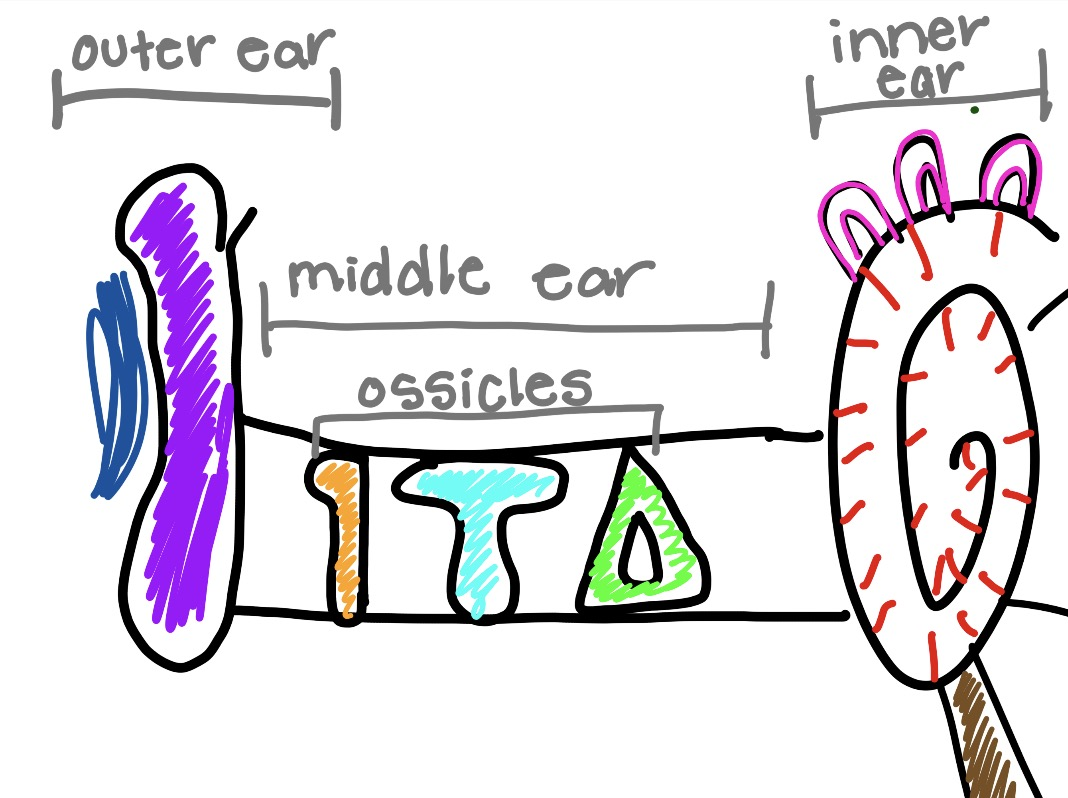
what is the pink and what does it do
semicircular cords
fluid filled loops that sense head movement and sends signals to your brain telling how to stay balanced
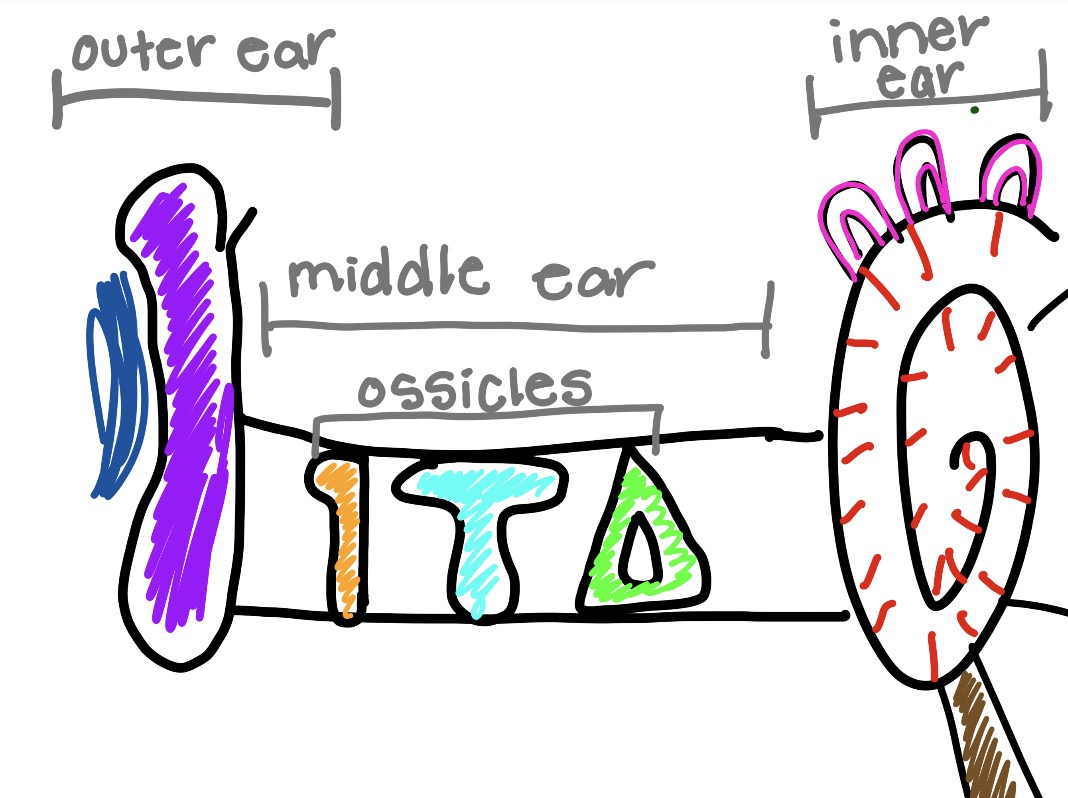
what is the red and what does it do
hair cell
convert sound vibrations into signals
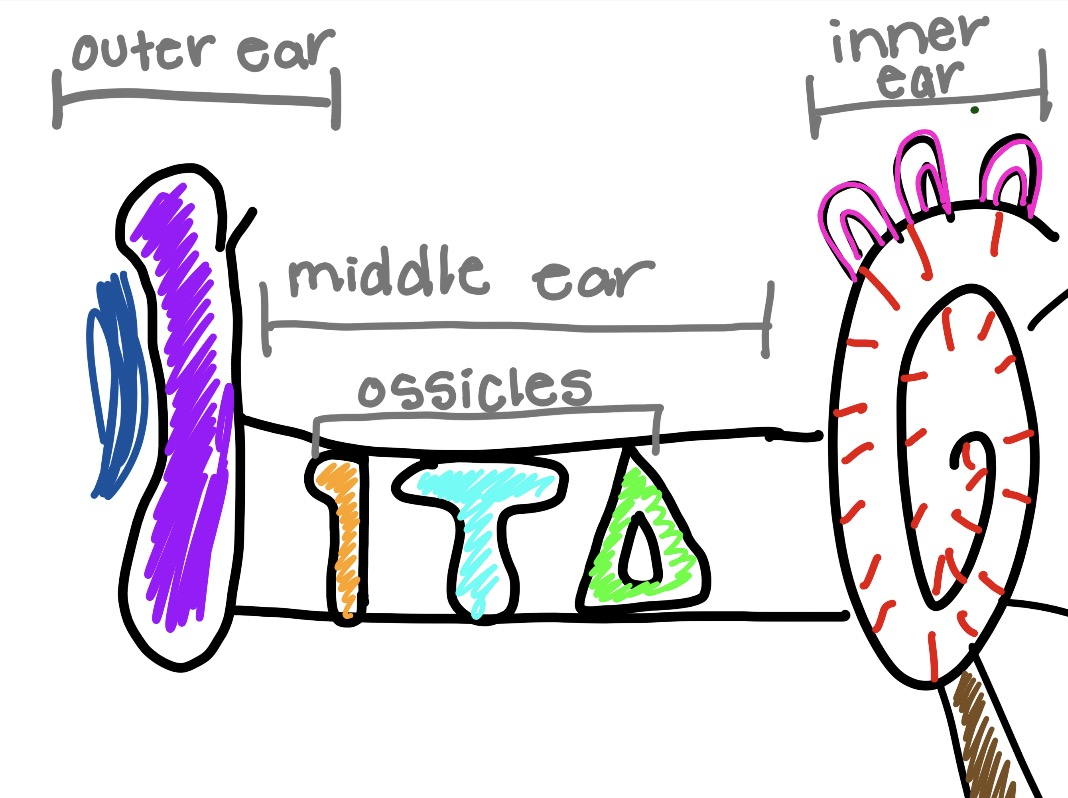
what is the brown and what does it do
eustachian tube
that equalizes air pressure, drains fluid, and protects the ear, usually opening with swallowing or yawning
beta waves
conscious
wide awake
alpha waves
subconscious
relaxed
day dreaming
theta wave (NREM)
light sleep
delta wave
deepest sleep
nightmares happen here
when rem happens when no supposed too
rem
dream state
recovery period
gets longer each time
right eye
goes to left side of brain and right arm
logical
language
verbal
left eye
goes to right side of brain and left arm
creative
non-verbal