Organic Molecules and Biochemistry: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Organic Compound
A molecule that contains carbon.
Carbohydrates
Organic molecules made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
Lipids
Organic molecules made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
Proteins
Organic molecules made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen (and sometimes sulfur or Phosphorus).
Nucleic Acids
Organic molecules made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus.
Reactants
The starting materials on the left side of an arrow in a chemical reaction.
Products
The new substances formed on the right side of an arrow in a chemical reaction.
Dehydration Synthesis
The process that builds large molecules from smaller ones by removing a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
The process that breaks a large molecule into smaller ones by adding a water molecule.
Water's Polarity
Allows water to act as a universal solvent, building and breaking macromolecules and supporting chemical reactions.
Monomer of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharide, or simple sugar, with a general formula CH2O.
Simple Carbohydrates
Digest quickly, causing a rapid blood sugar spike, and have a basic structure of one or two sugar molecules.
Complex Carbohydrates
Digest slowly, providing a sustained release of energy, and have longer chains of sugar molecules.
Chemical Bonds and Energy
Bonds store chemical energy that is released when broken during cellular respiration.
Examples of Simple Carbohydrates
Sugars found in fruit like fructose, lactose, and table sugar, along with refined sugars in candy, soda, and syrup.
Examples of Complex Carbohydrates
Grains, vegetables with starch like potatoes or corn, or legumes like beans, lentils, and peas.
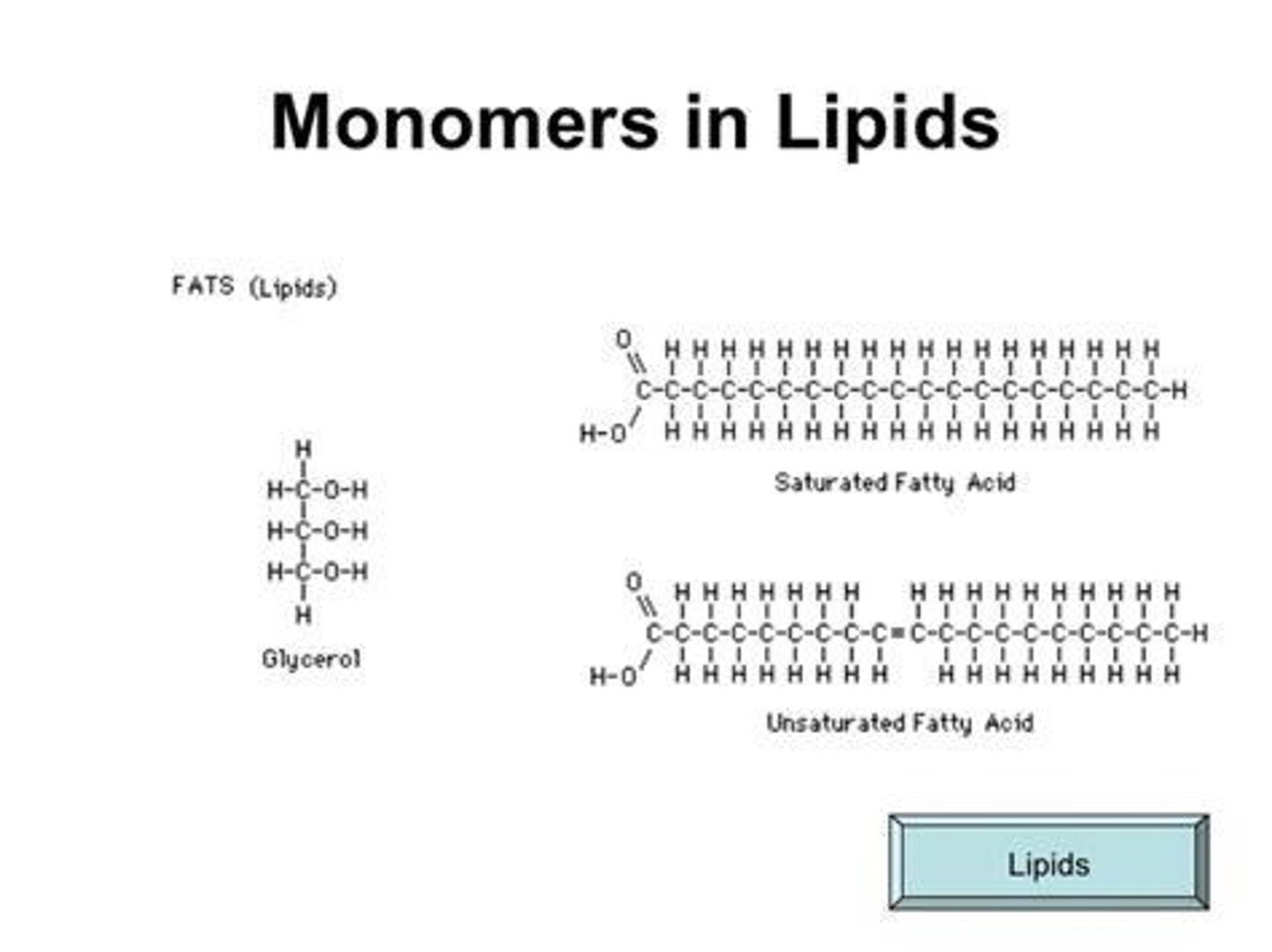
Monomer of Lipids
Fatty acids, which are long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group, and sometimes glycerol.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Found in animal products like red meat and butter, increase bad cholesterol, and are solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Found in sources like olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish; healthier because they can help lower bad cholesterol.
Omega 3 fatty acids
Healthy fats essential for heart and brain health.
Trans fats
Unhealthy fats that increase bad cholesterol and have no known health benefits.
Oils
Unsaturated fatty acid chain monomer with at least one double bond between carbons.
Fats
Saturated fatty acid chain monomer with all single bonds in carbon/hydrogen chain.
Steroids
Composed of 4 interlocking hydrocarbon rings, they keep cell membranes fluid even in cold temperatures.
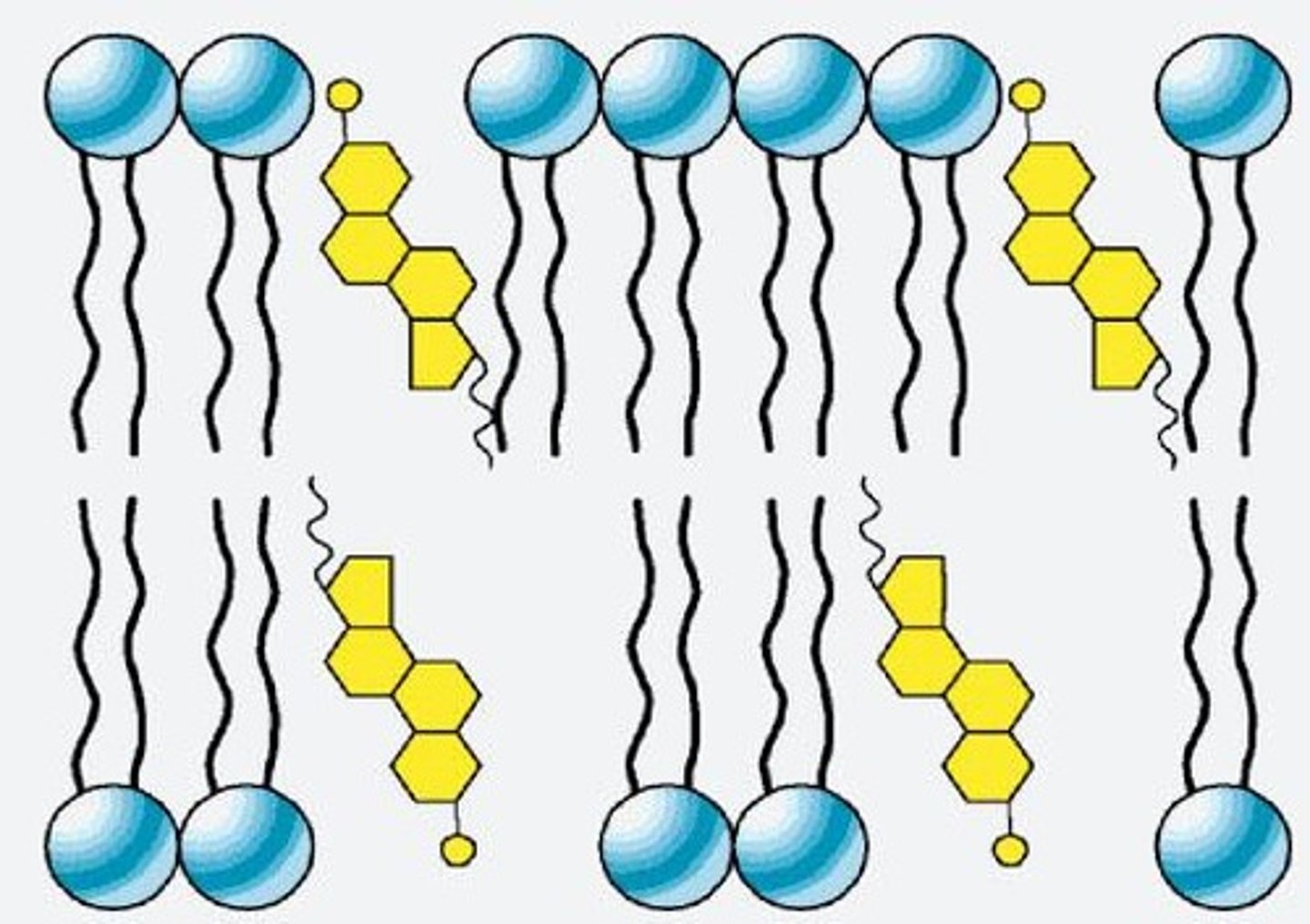
Phospholipids
Molecules that contain a polar and a nonpolar side, making up the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer).
Wax
Protective molecules secreted by ears to protect against dirt/infections.
Nonpolar lipids
Lipids are nonpolar due to their structure being dominated by nonpolar carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids, consisting of a phosphate group, a nitrogen-containing base, and deoxyribose (sugar).
DNA
Contains nucleobases cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine, and has a double helix/double-stranded sugar phosphate backbone.
RNA
Contains nucleobases cytosine, guanine, adenine, and uracil, usually single-stranded with a sugar phosphate backbone.
ATP
High energy molecule that releases energy when a bond is broken, converting food energy into usable energy.
ADP
Formed when a molecule of water breaks one of the high energy phosphate bonds in ATP.
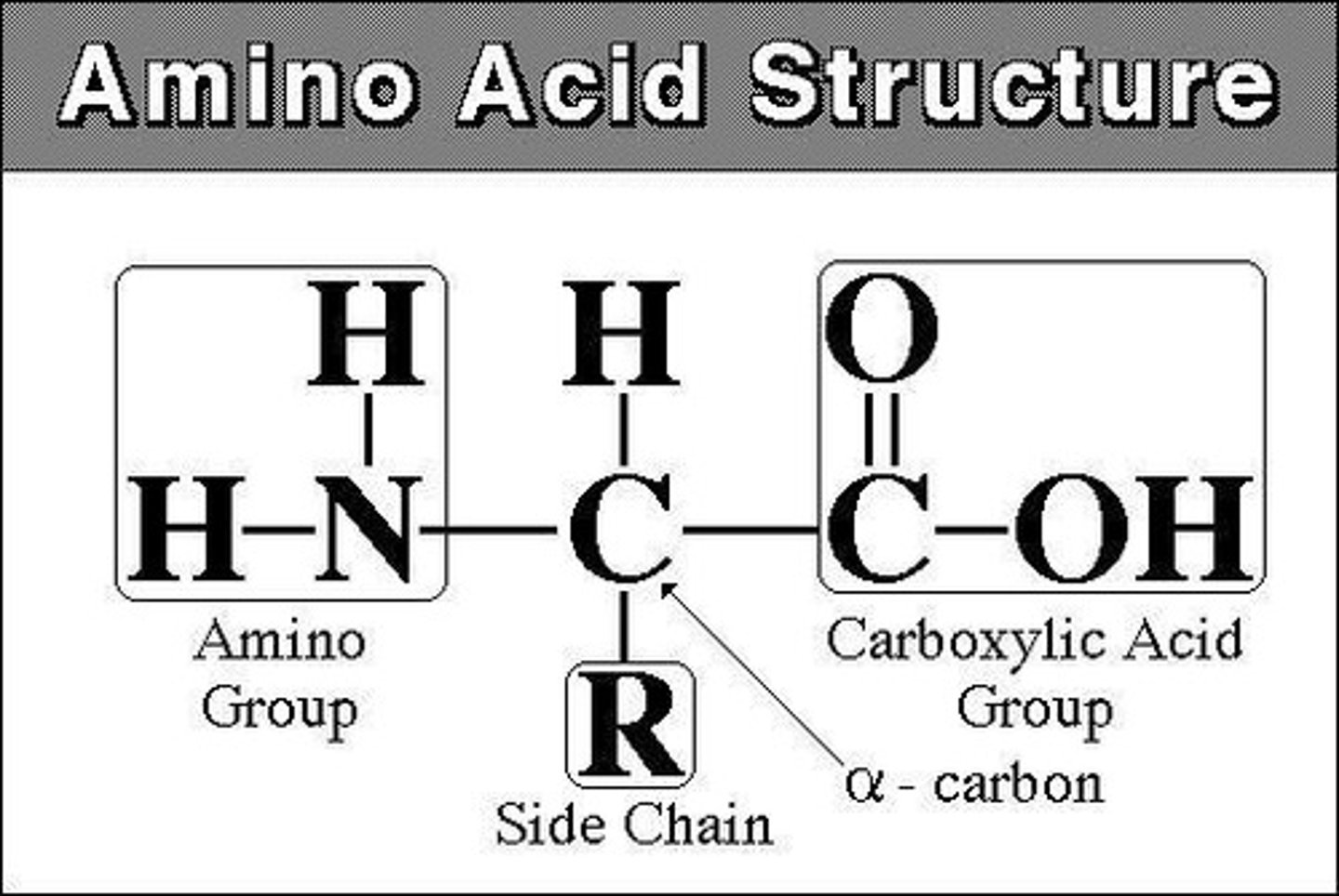
Amino Acid
Monomer of proteins, containing C, H, O, N, and sometimes S or P.
Denaturation
Process where changing temperature or pH alters the shape of a protein, affecting its function.
Collagen
Protein that provides support in tissues.
Keratin
Structural protein found in hair and nails.
Lactase
Enzyme that breaks down lactose.
Insulin
Hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
Hemoglobin
Protein that transports oxygen in the blood.
Antibodies
Proteins that defend against pathogens.
Primary protein structure
Polypeptide chain linked by peptide bonds.
Secondary protein structure
Includes A-helix (coil) and beta pleated sheet (zigzag).
Tertiary protein structure
More folding that combines both A-helix and beta pleated sheets into a final structure.
Quaternary protein structure
Not all proteins have this structure; it consists of 2+ polypeptides, including hemoglobin.