Biology RNA Polymerase & Mitosis Phases Study Guide
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Nucleus houses
the nuclear DNA, along with the nucleolus and cytoplasm
Nucleic acid is formed by
repeating monomers called nucleotides
Nucleotides
building blocks of nucleic acids
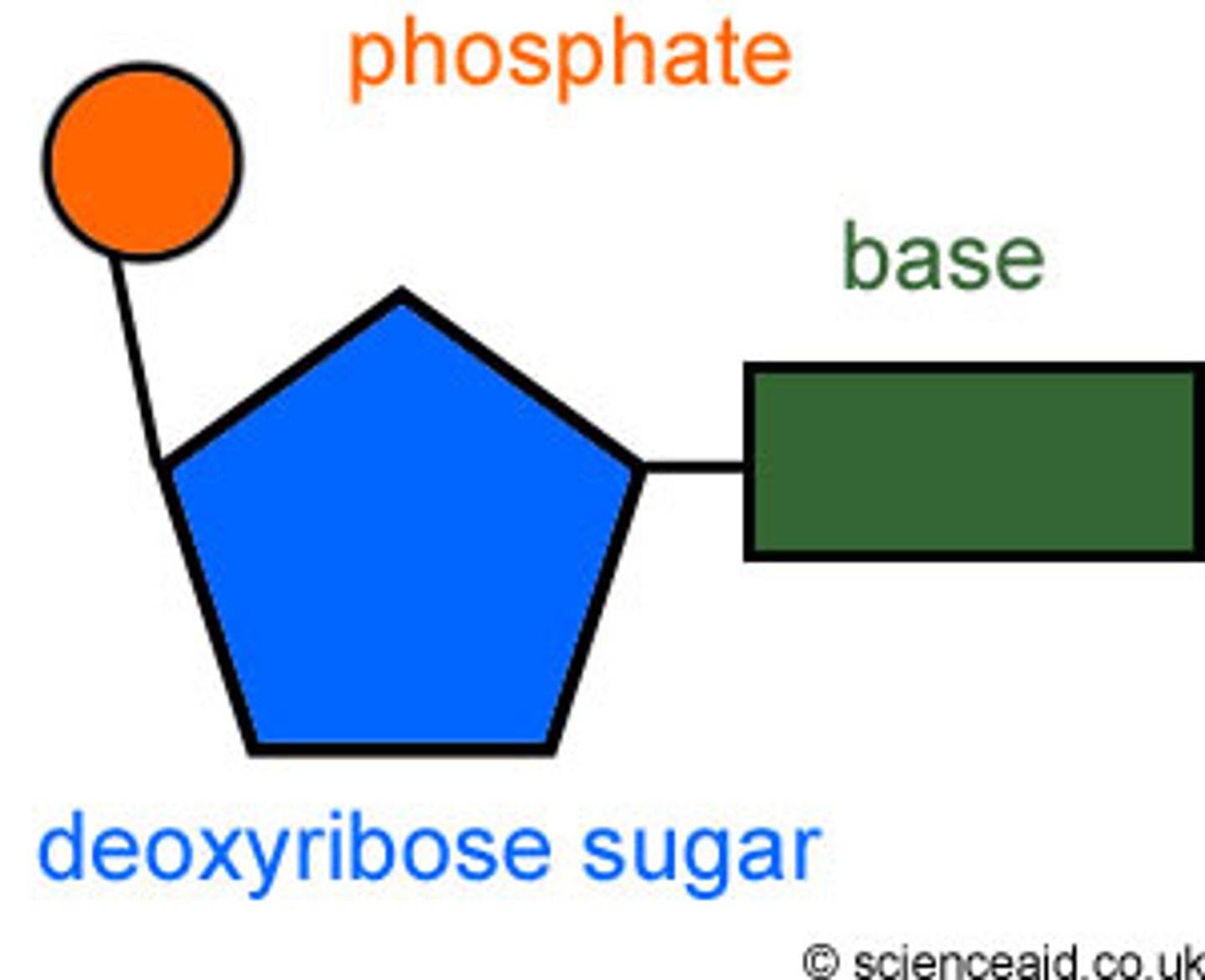
DNA is composed of
deoxyribonucleotides
which include five-carbon sugar deoxyribose, a phosphate, and one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, C, G, T)
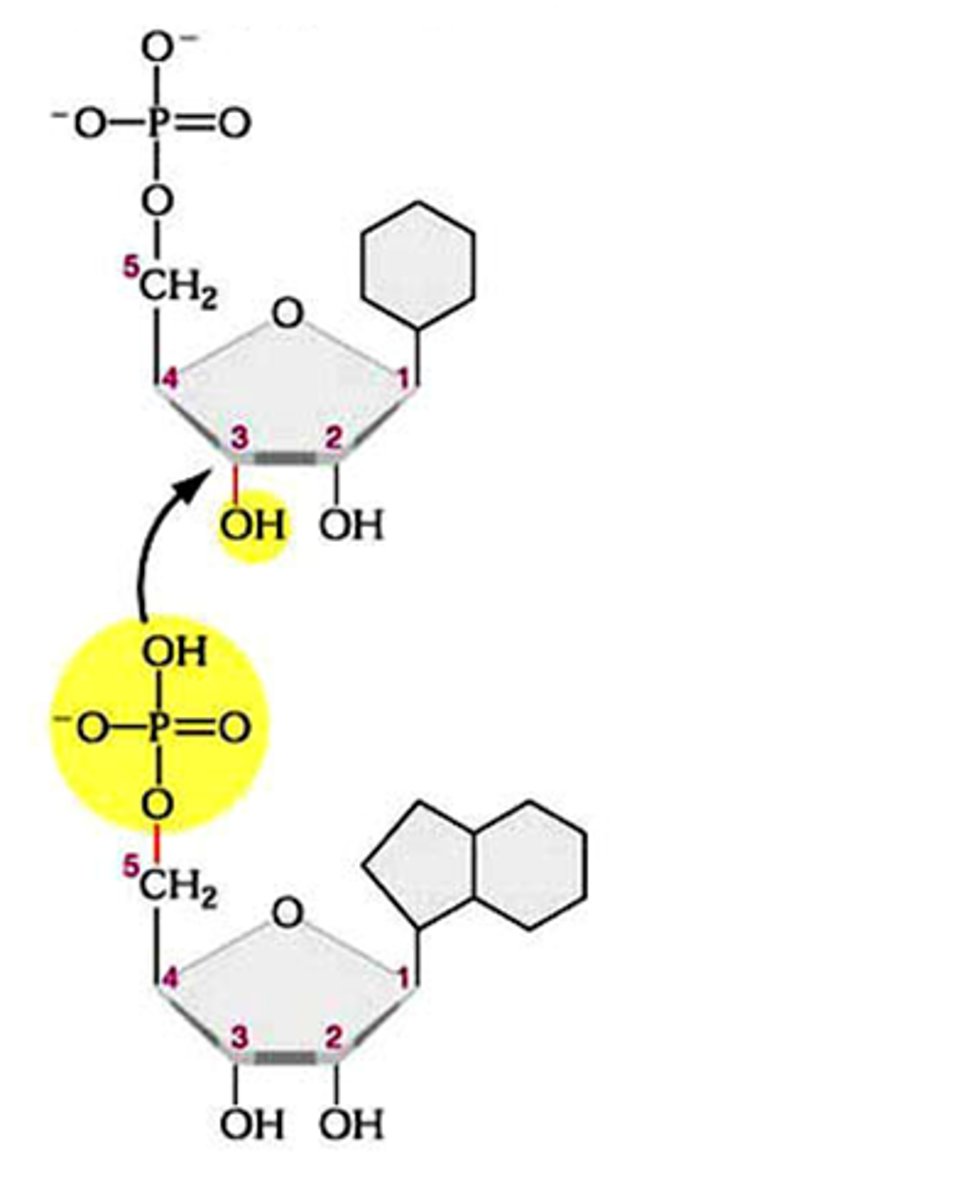
Phosphodiester Bonds
bonds between phosphate group and pentose sugar in nucleic acids.
Complementary Base Pairing
DNA, T pairs with A; G pairs with C
RNA, U pairs with A and G pairs with C
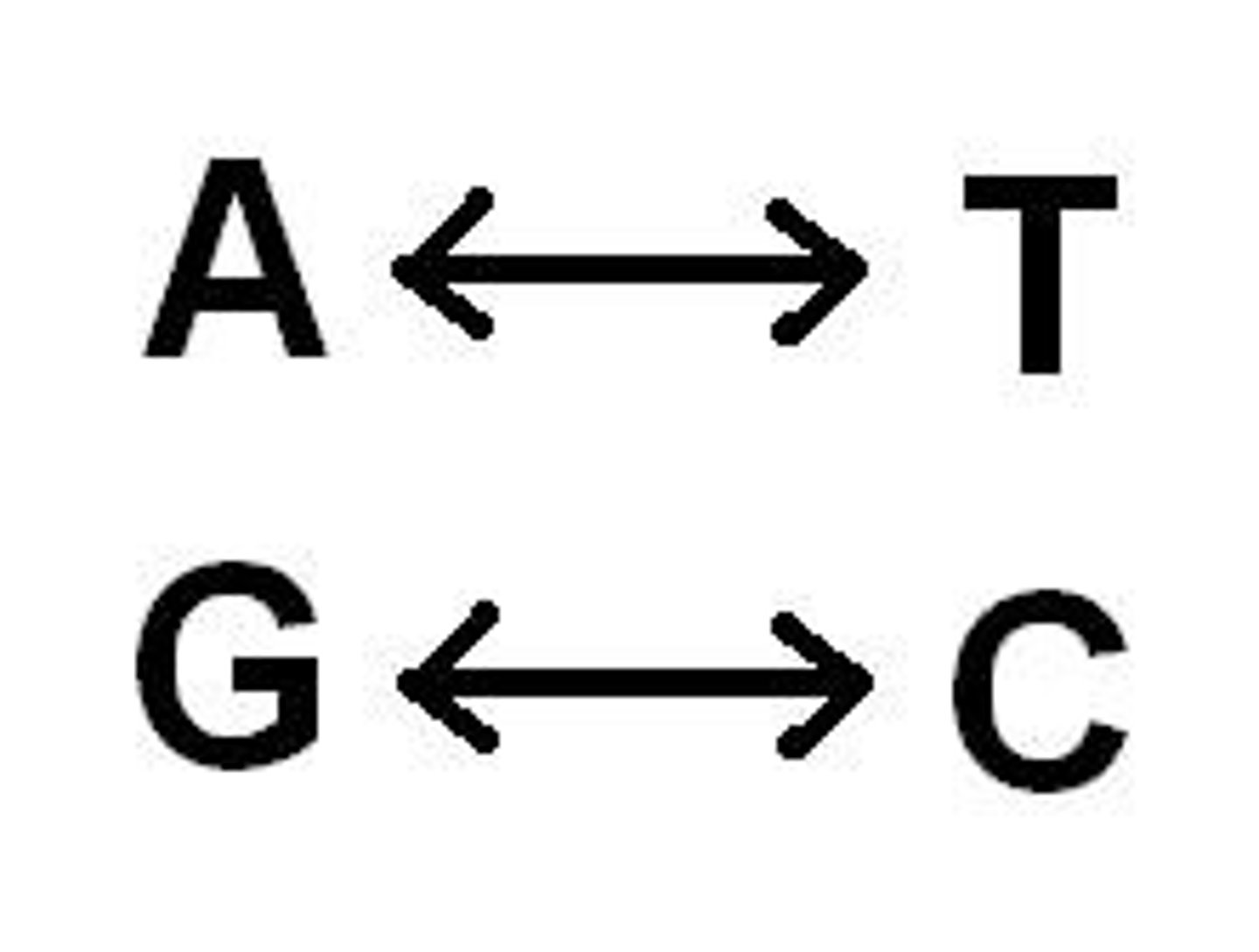
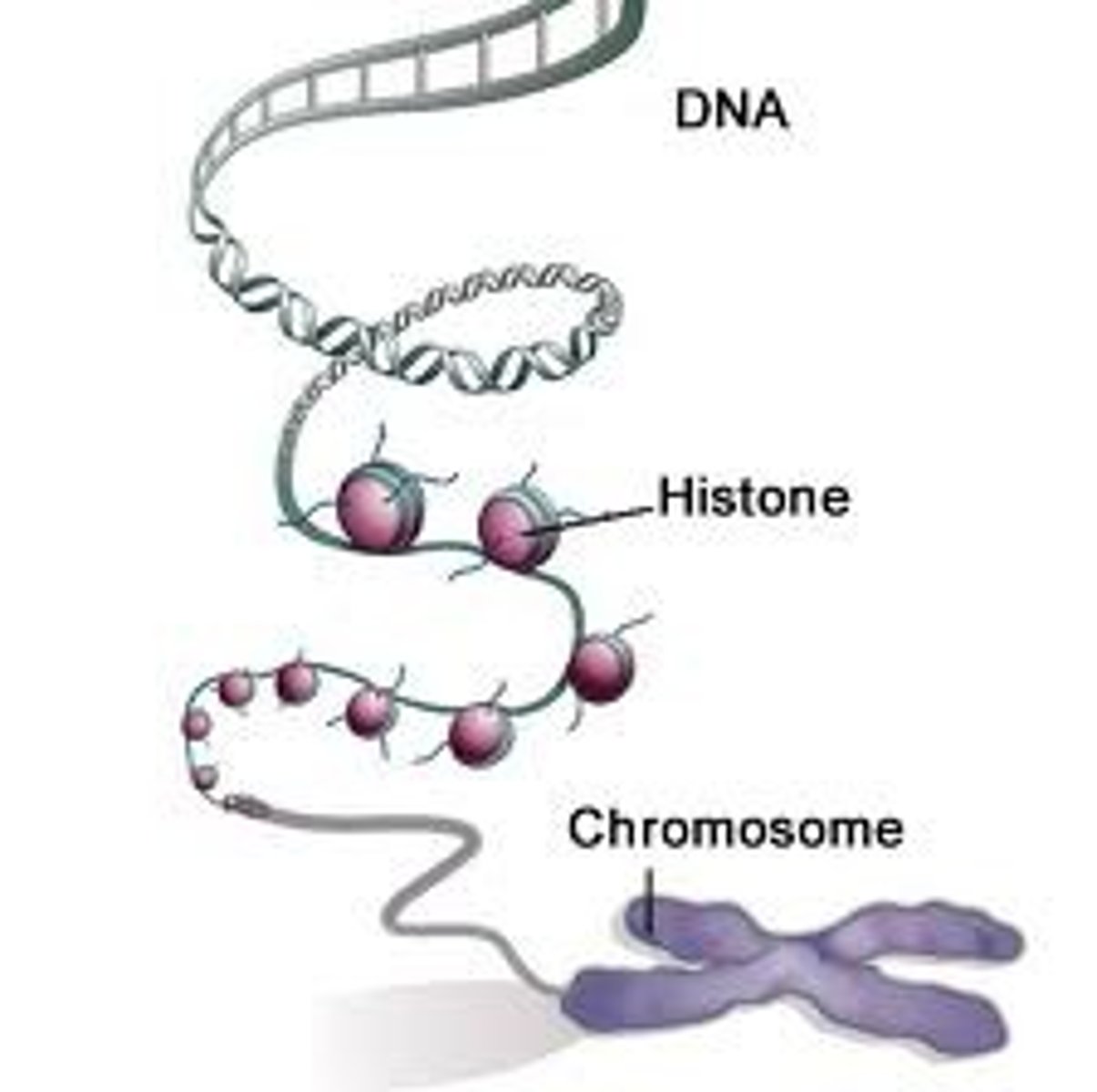
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
helps package DNA molecules within the nucleus
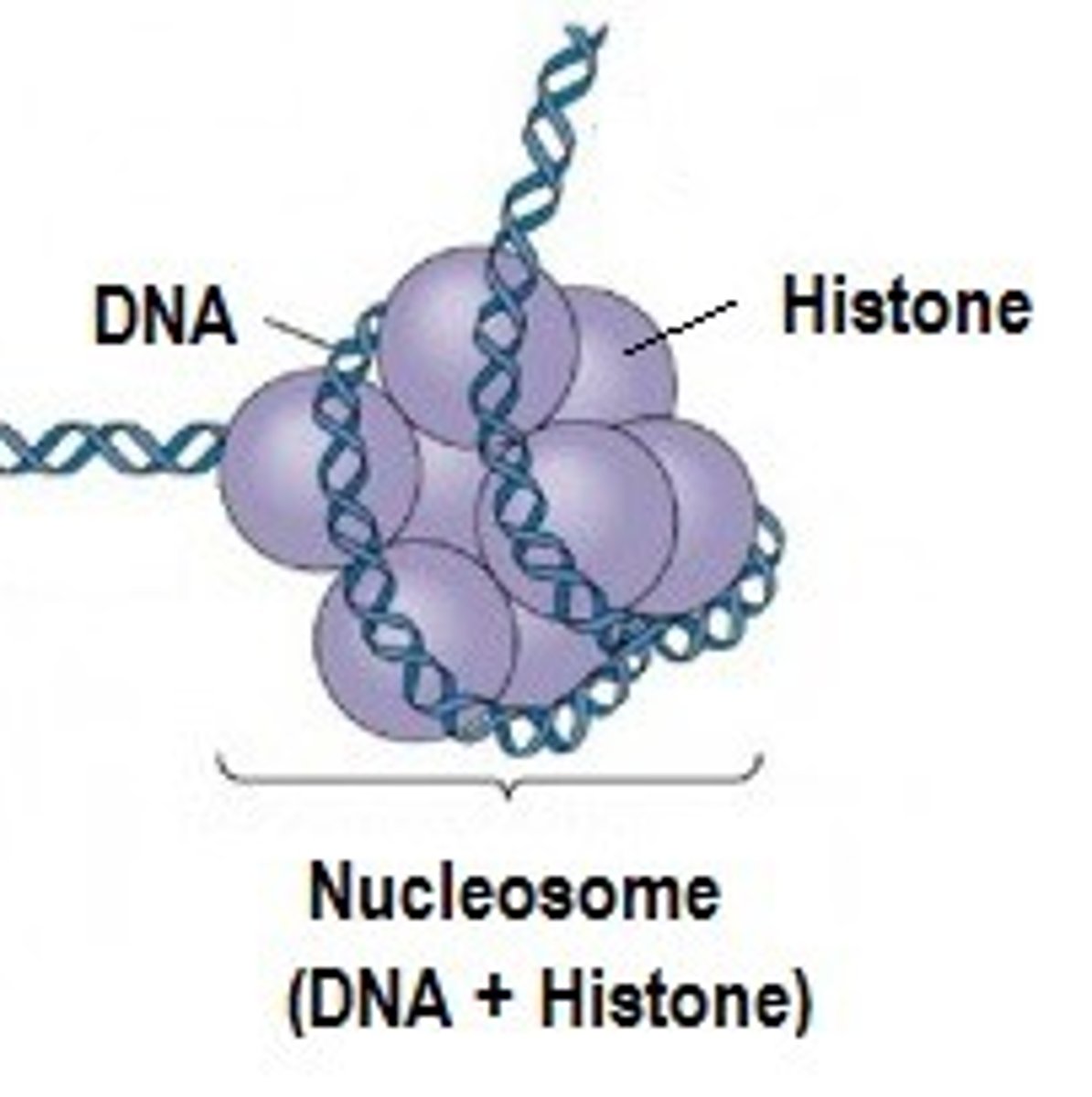
Nuclesome
repeating subunit of chromatin fibers, consisting of DNA coiled around histones
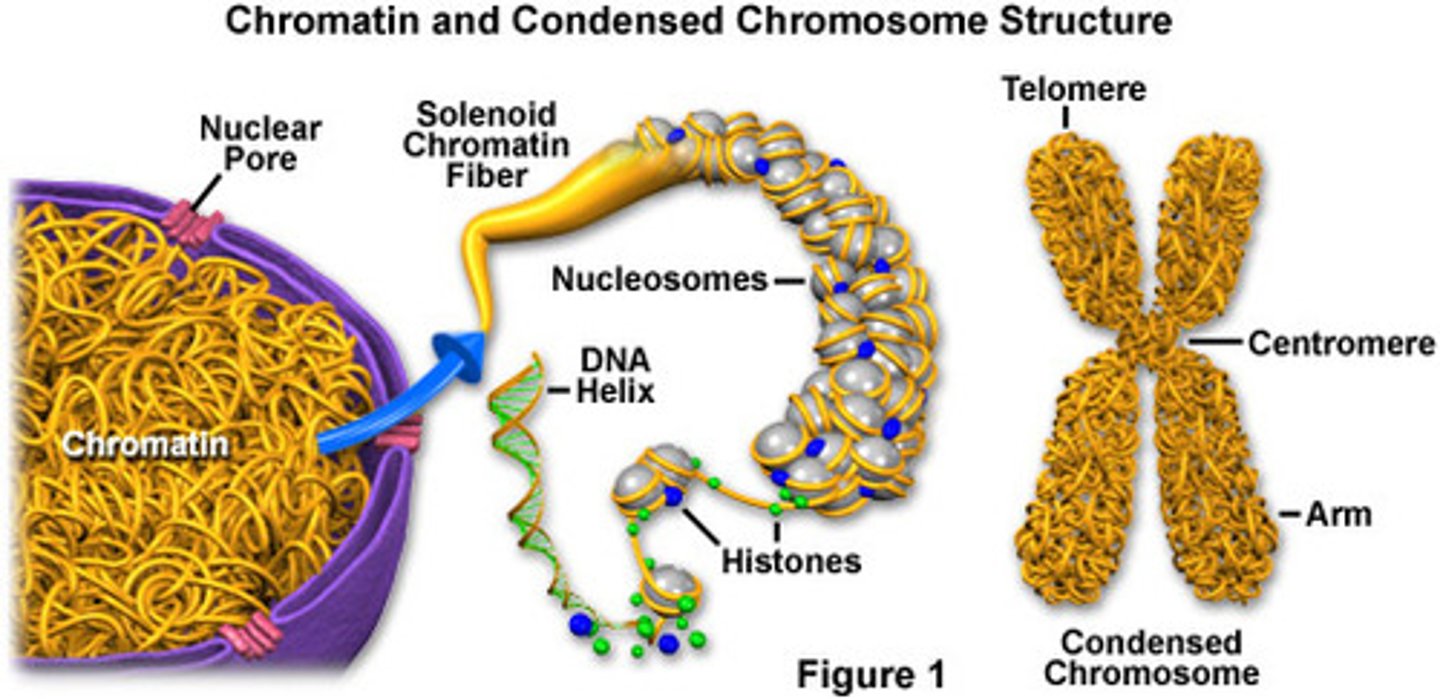
Chromatin
substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA tightly coiled around histones
our genetic DNA is typically present in our cells as chromatin
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
needed to prevent DNA from becoming tangled during cell division
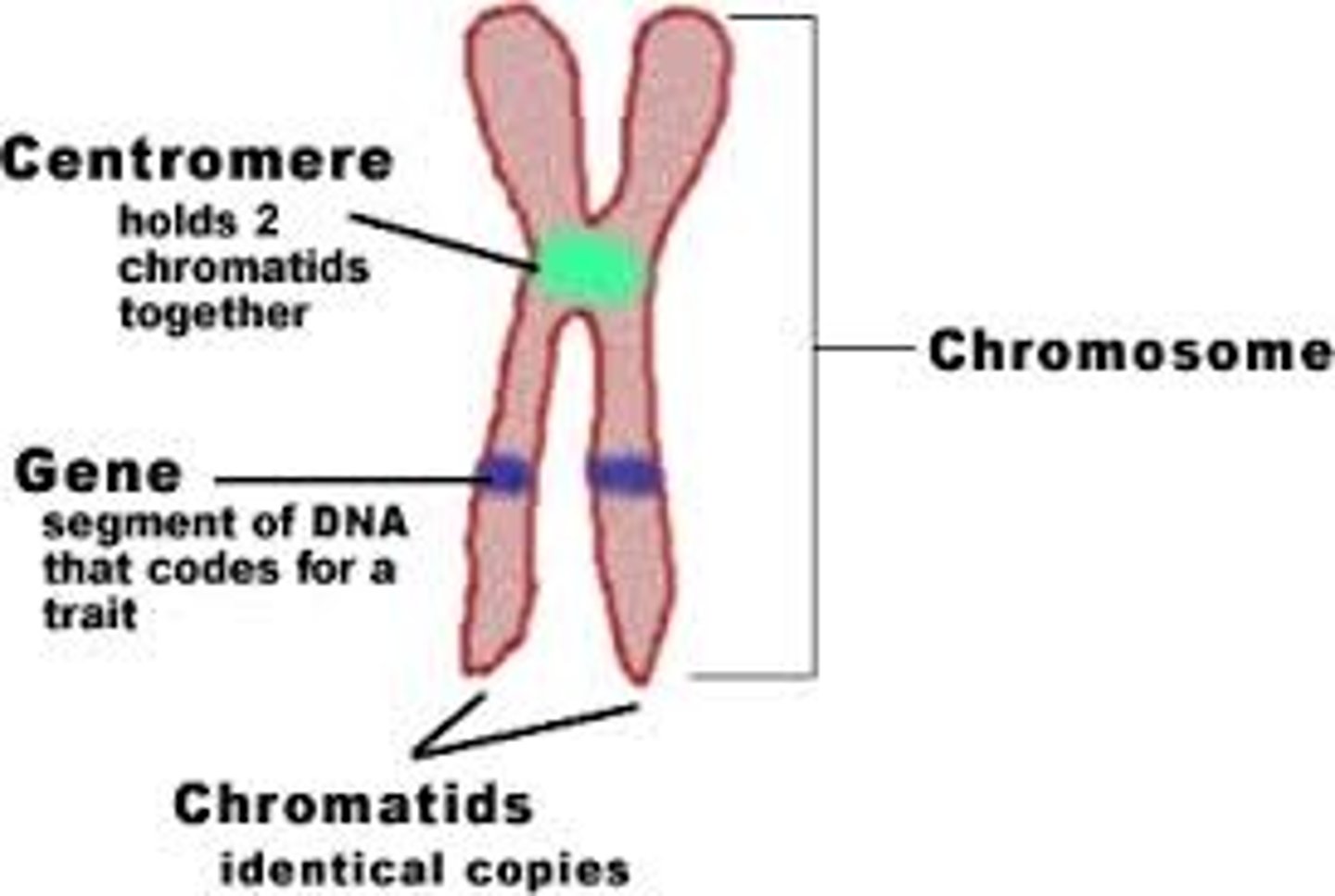
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission
provide instructions for the synthesis of very specific proteins
each gene has a promoter (start signal) and terminal (stop signal) for transcription, or copying, of a gene into an RNA molecule
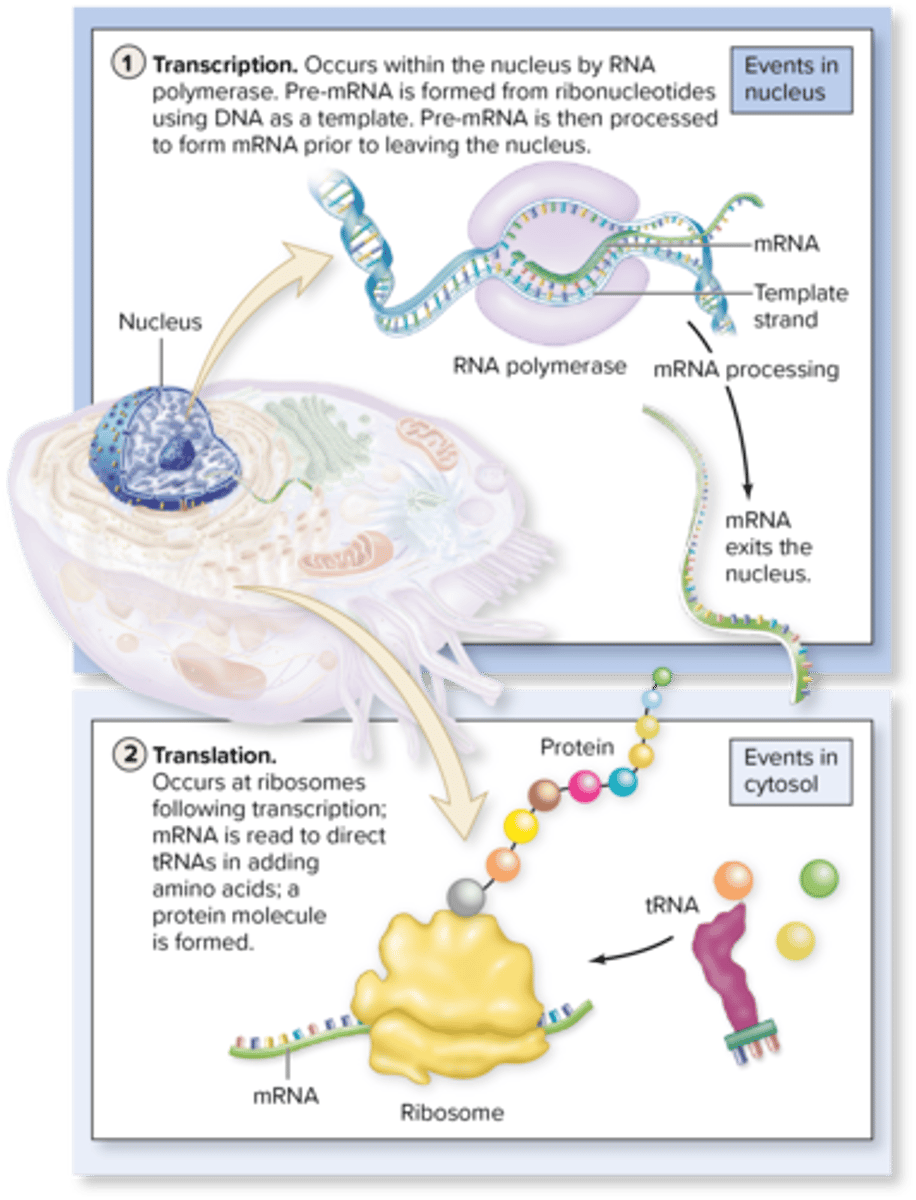
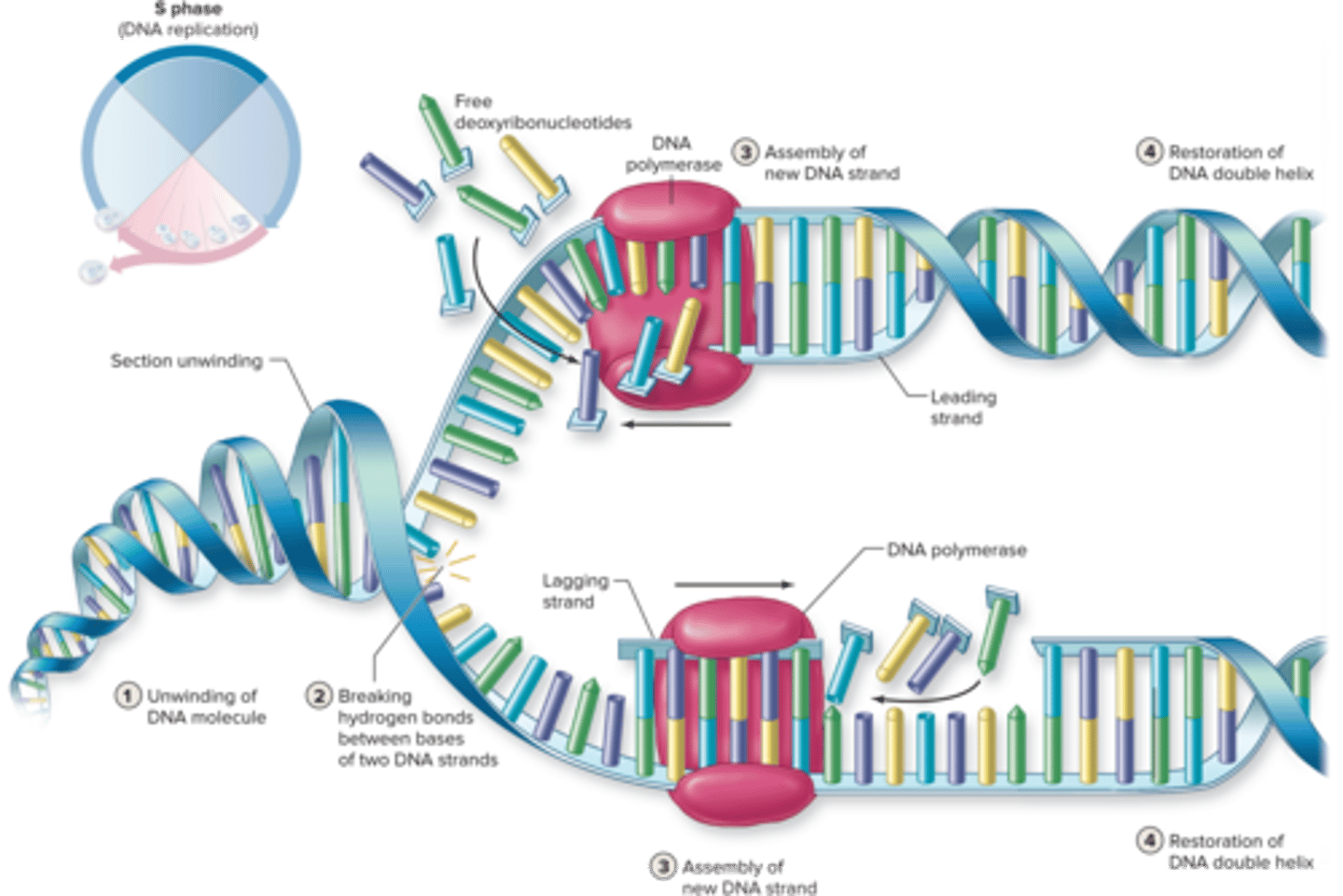
Transcription
the process happens in the nucleus, where the RNA polymerase enzyme creates an RNA molecule from ribonucleotides using DNA as a guide
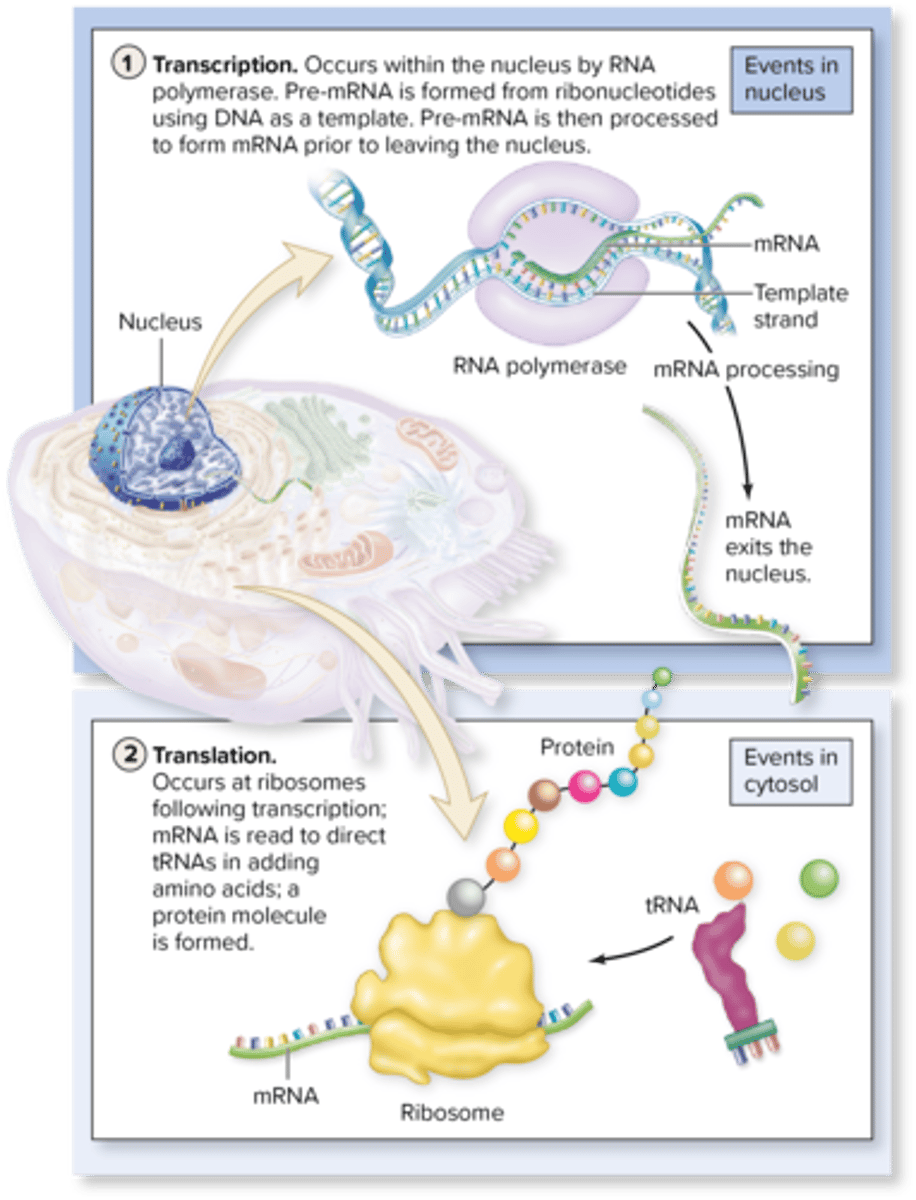
Translation
occurs within the cytoplasm by ribosomes, is the formation of a specific protein from amino acids as directed by the RNA molecule
Transcription Required Structures
DNA, ribonucleotides, RNA polymerase
In Transcription DNA is required because
a specific segment of DNA serves as the template to form an RNA molecule
In Transcription Ribonucleotides are required because
these are the monomers that will be used to synthesize the newly formed RNA polymer
Ribonucleotides Types One Nitrogenous Base
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil
In Transcription RNA Polymerase
is the enzyme that facilitates the placement of ribonucleotides with the bases of the DNA template as an RNA molecule is synthesized
RNA Polymerase assembles the ribonucleotides by
complementary-pairing nitrogenous bases of the ribonucleotides with nitrogenous bases of DNA

DNA, RNA Polymerase, and Ribonucleotides are located in the
nucleus
Three Functional Types of RNA are produced during transcription
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
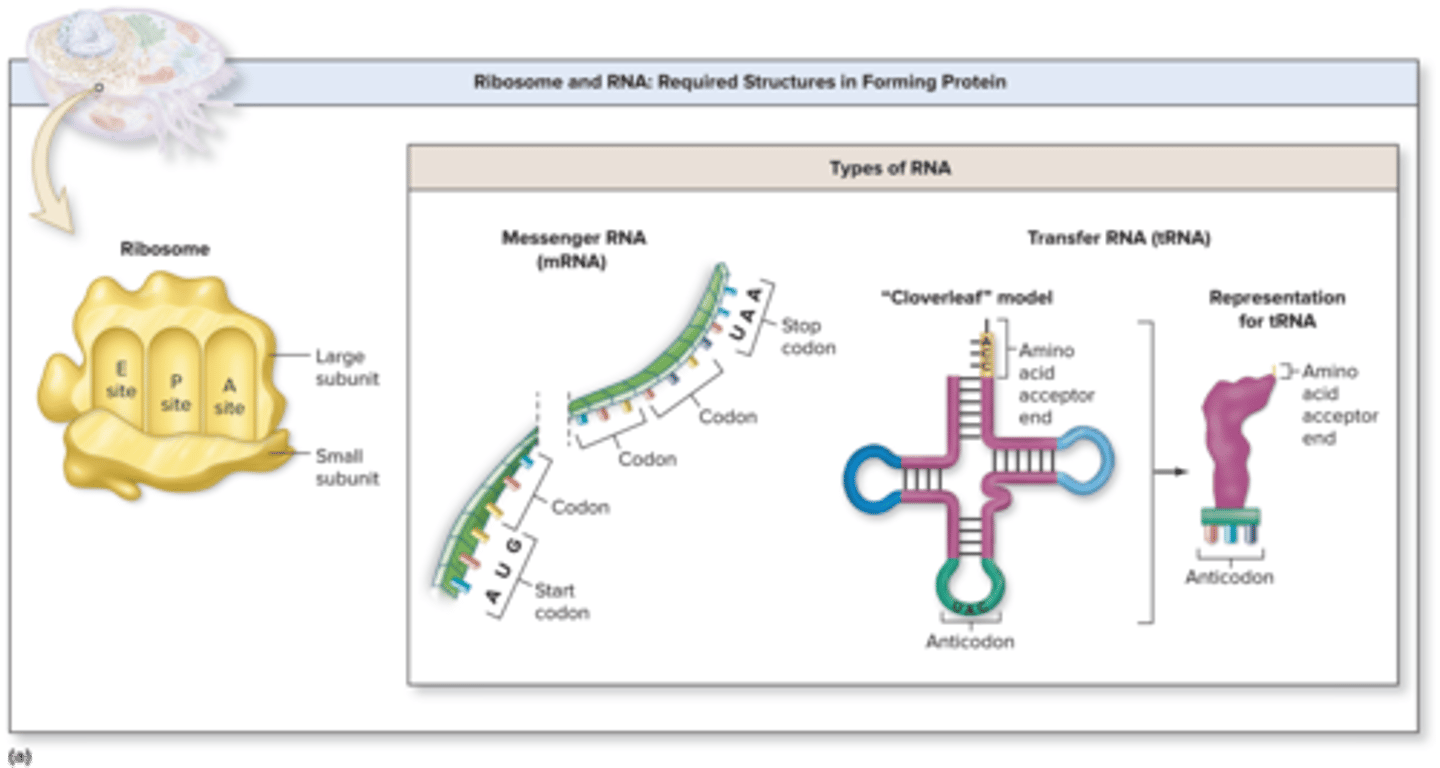
mRNA
messenger RNA, type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
transfer RNA, type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
rRNA
ribosomal RNA, type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
The process of transcription to form mRNA includes three major events
inititation, elongation, termination
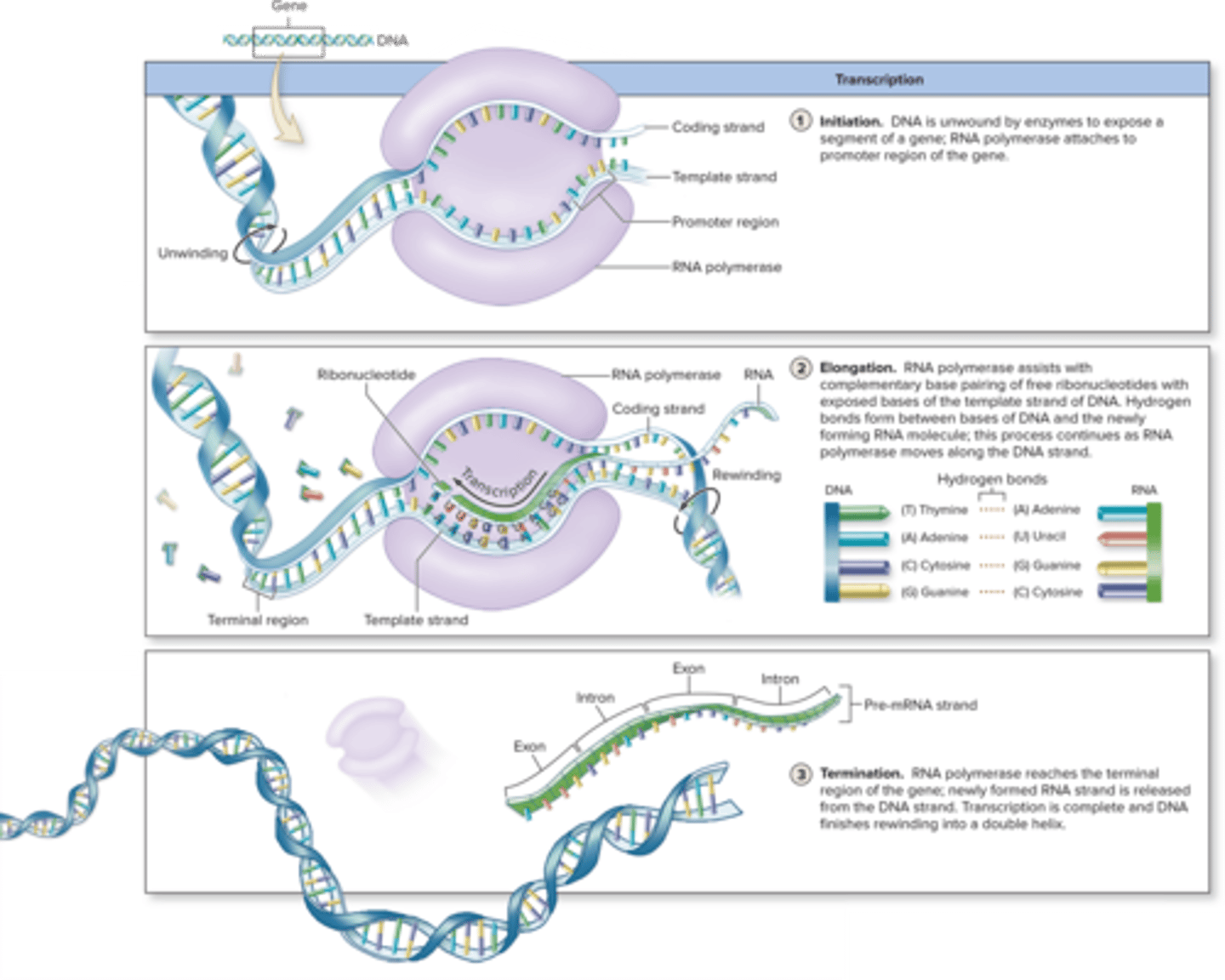
Template Strand
the strand of DNA that specifies the complementary mRNA molecule
Coding Strand
The strand of DNA that is not used as a template during transcription, also called the sense strand
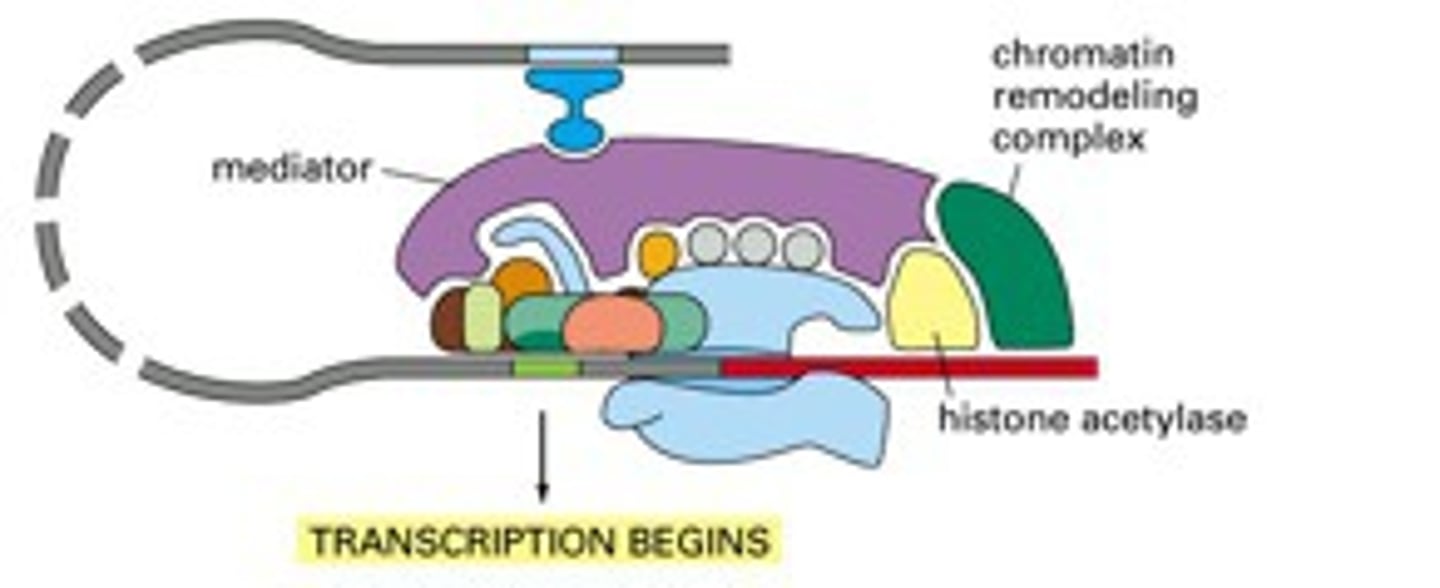
Transcription Initiation
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region of DNA strand, and synthesis begins
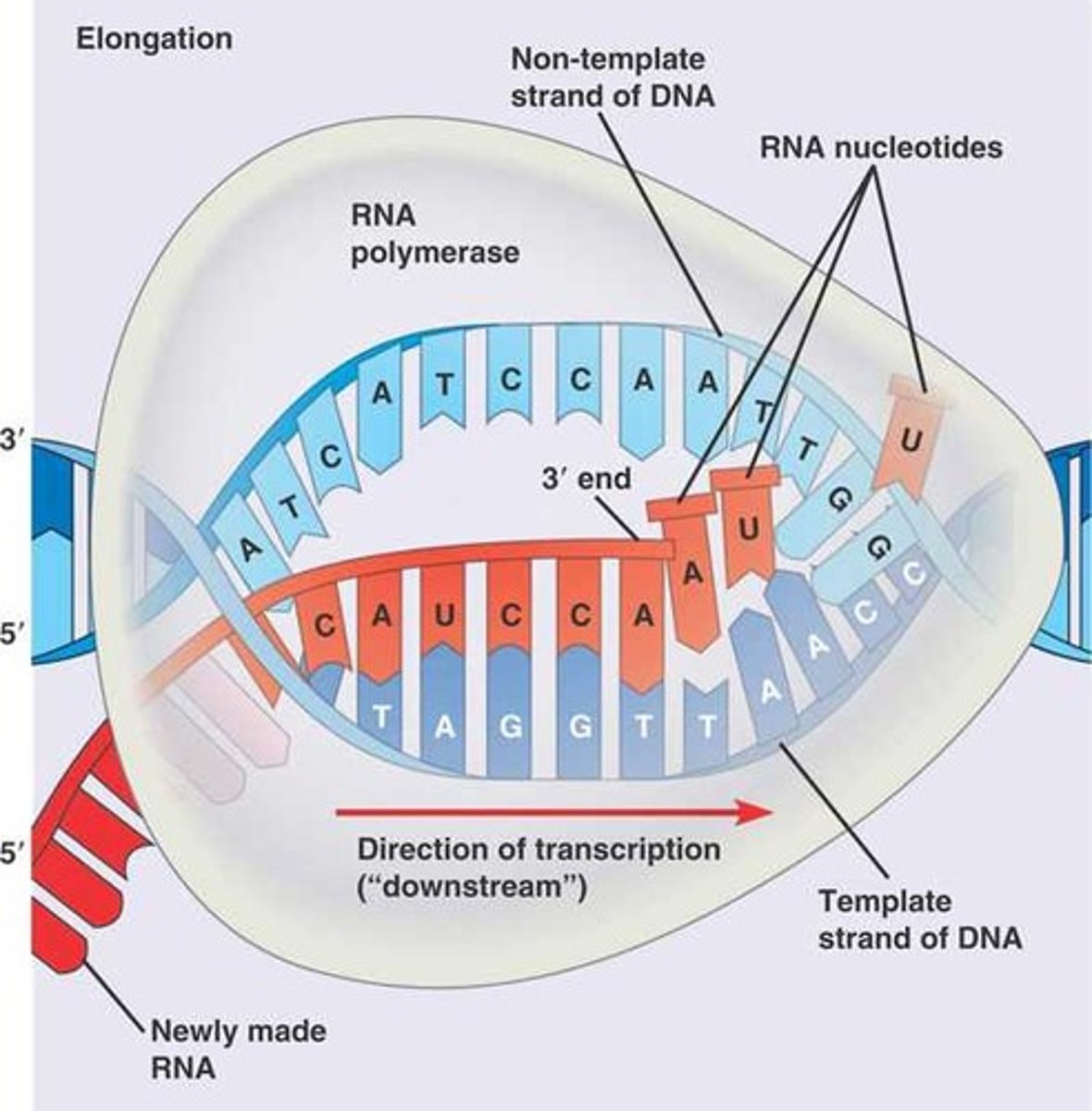
Transcription Elongation
mRNA is assembled by adding nucleotides complementary to DNA template strand - DNA rewinds once read
Transcription Termination
when the terminal region at the end of the gene is attached, RNA polymerase is released from the DNA as hydrogen bonds are broken between the DNA strand and newly formed mRNA
the newly formed mRNA strand is a recipe copied from DNA for synthesizing a specific protein (e.g insulin)
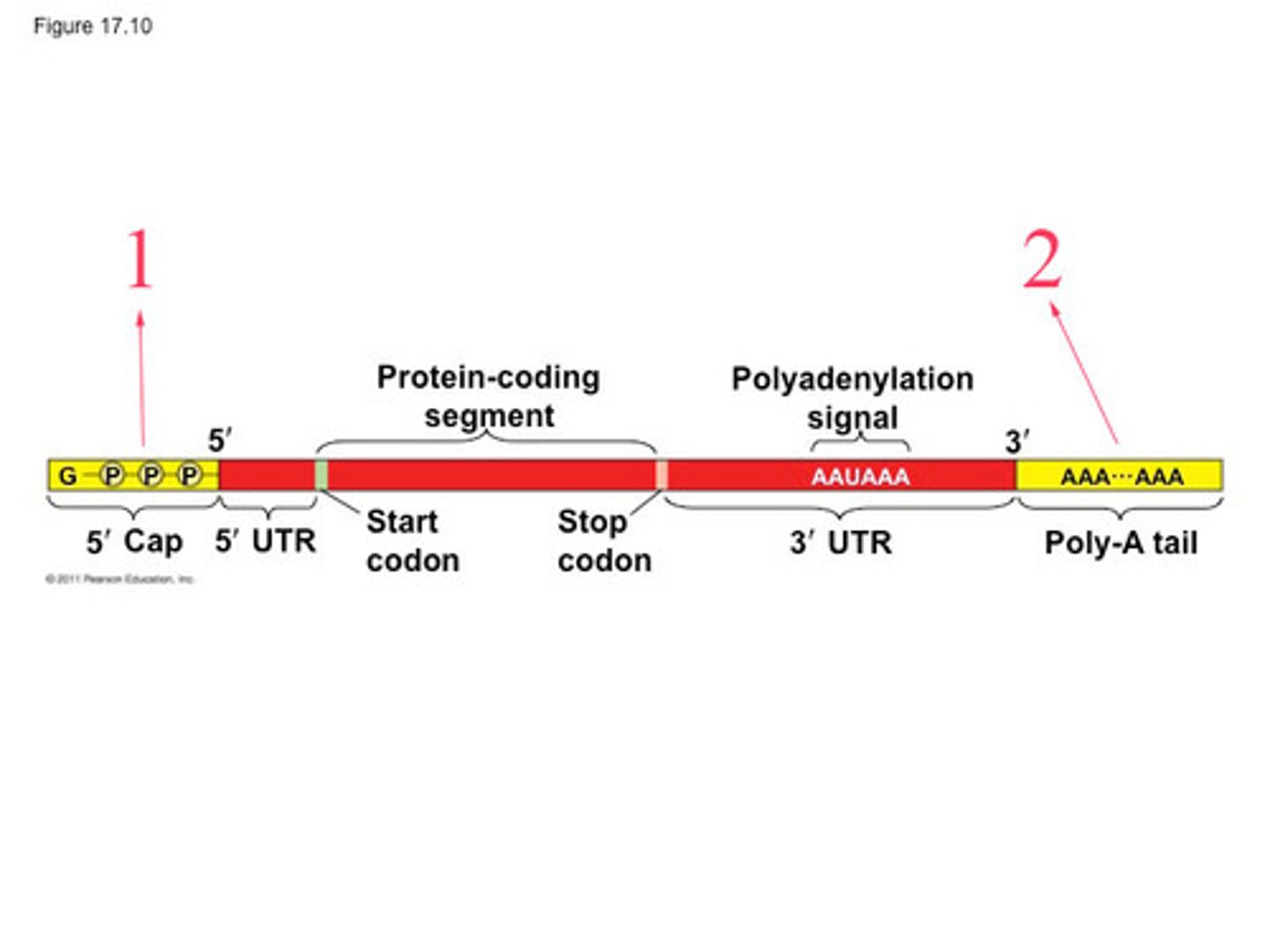
Modifications to mRNA
5'methyl cap and 3' poly A tail
splicing results in a mature mRNA, which can be used to make a protein
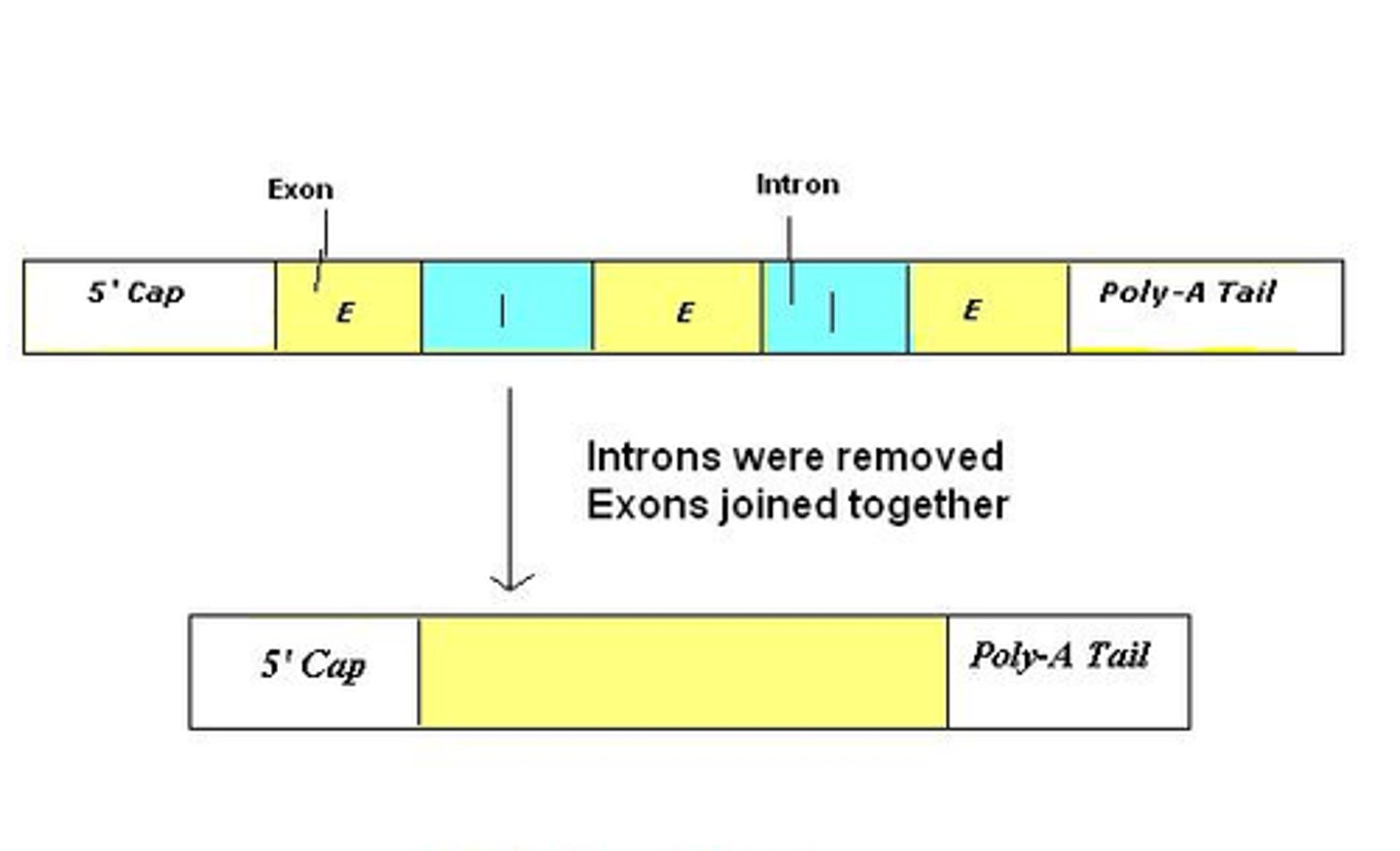
pre-mRNA
form of mRNA that contains both introns and exons
Introns
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
Exons
coding segments of eukaryotic DNA
Splicing
the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA
Capping
unique bonding of a ribonucleotide containing guanine to the lead end of the mRNA
increases stability of an mRNA strand, helping to prevent its digestion by nucleic acid digesting enzymes (in cytosol)
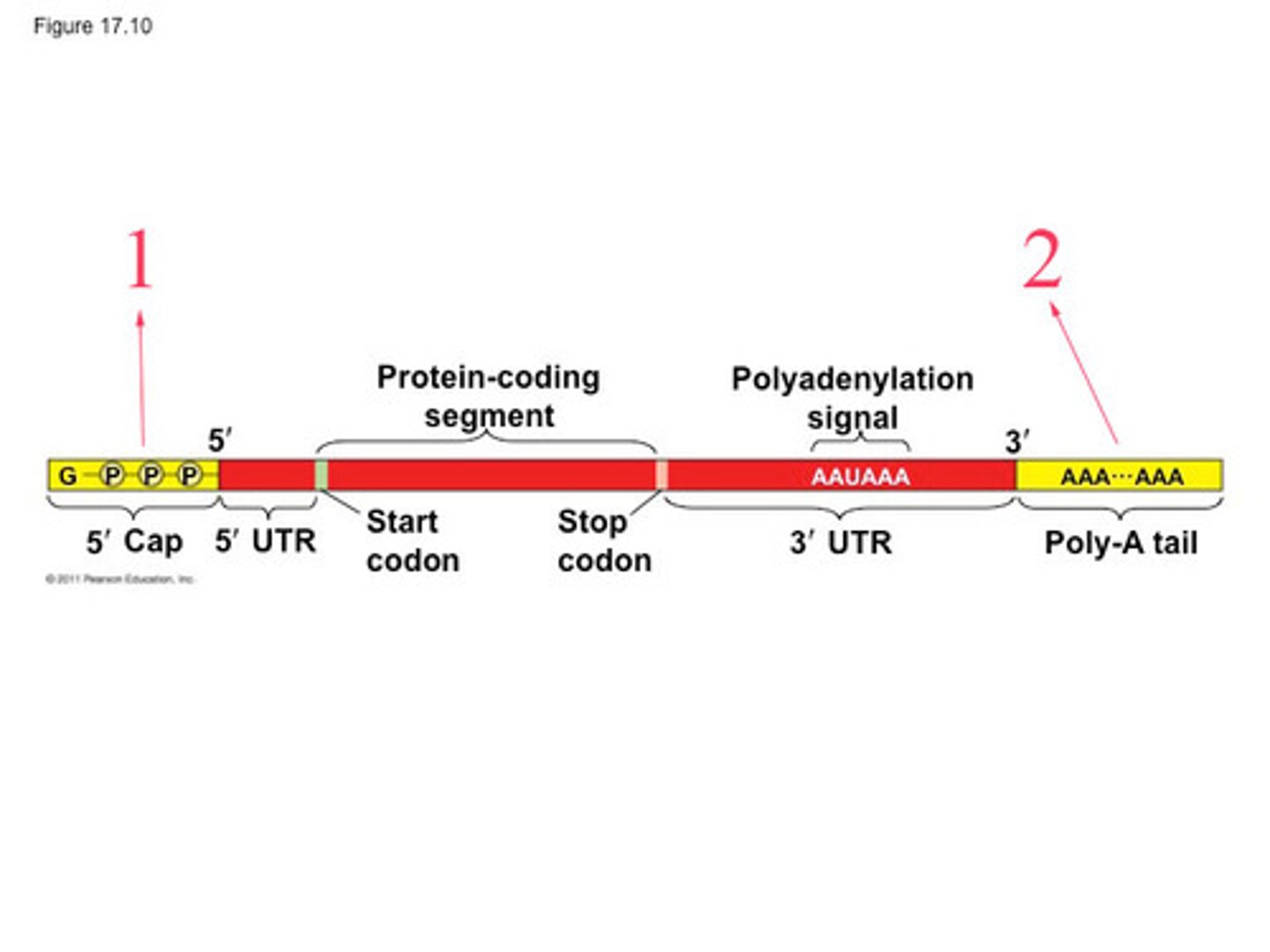
polyA tail
tail is a stretch of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
helps stabilize the mRNA, protects it from degradation, and aids in the export of the mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation
Translation Required Structures
ribosomes, mRNA, tRNA, amino acids
Translation Product
protein
Translation Ribosomes
composed up of a large subunit and a small subunit synthesized by the nucleolus
large subunits - A (aminoacyl) site, P (peptidyl) site, E (exit) site
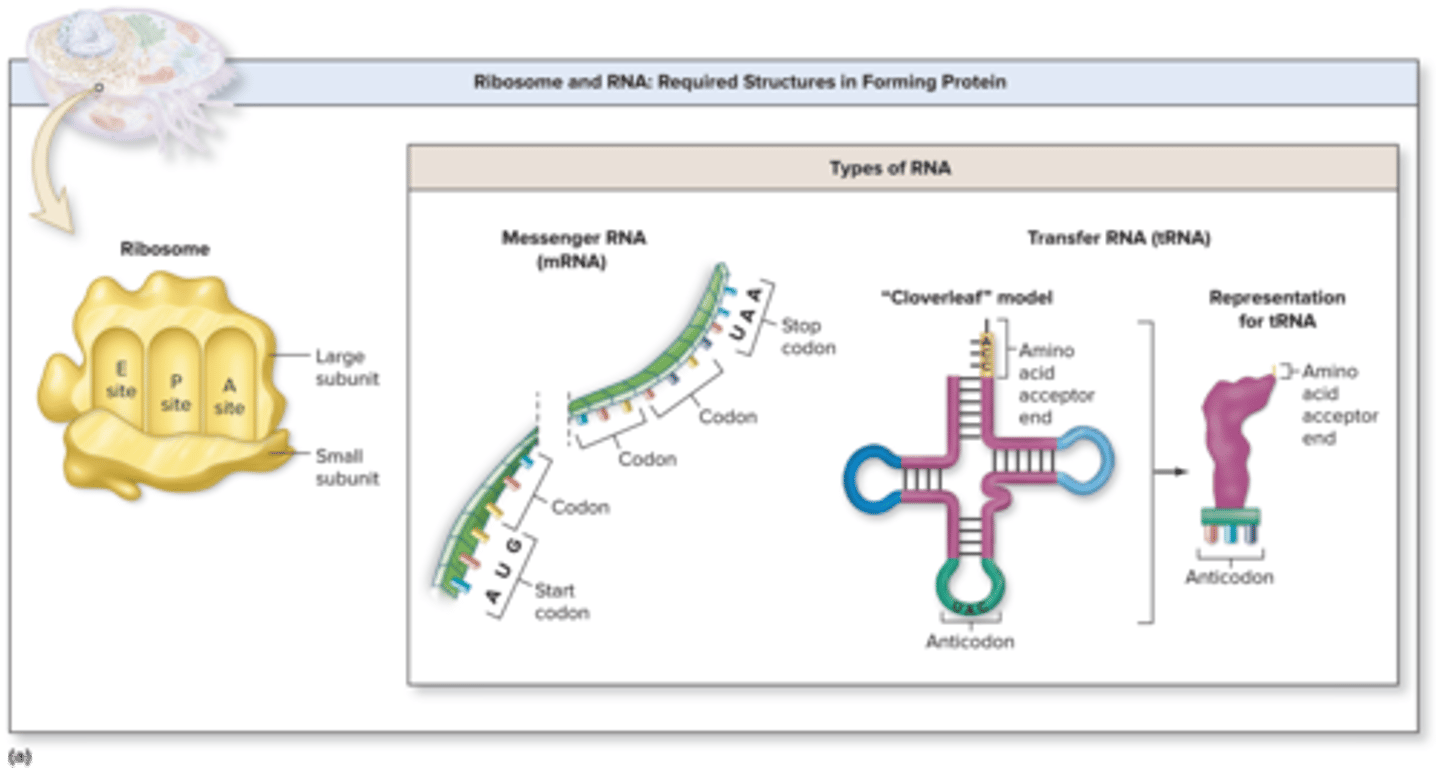
A (aminoacyl) site is where
new amino acids are added
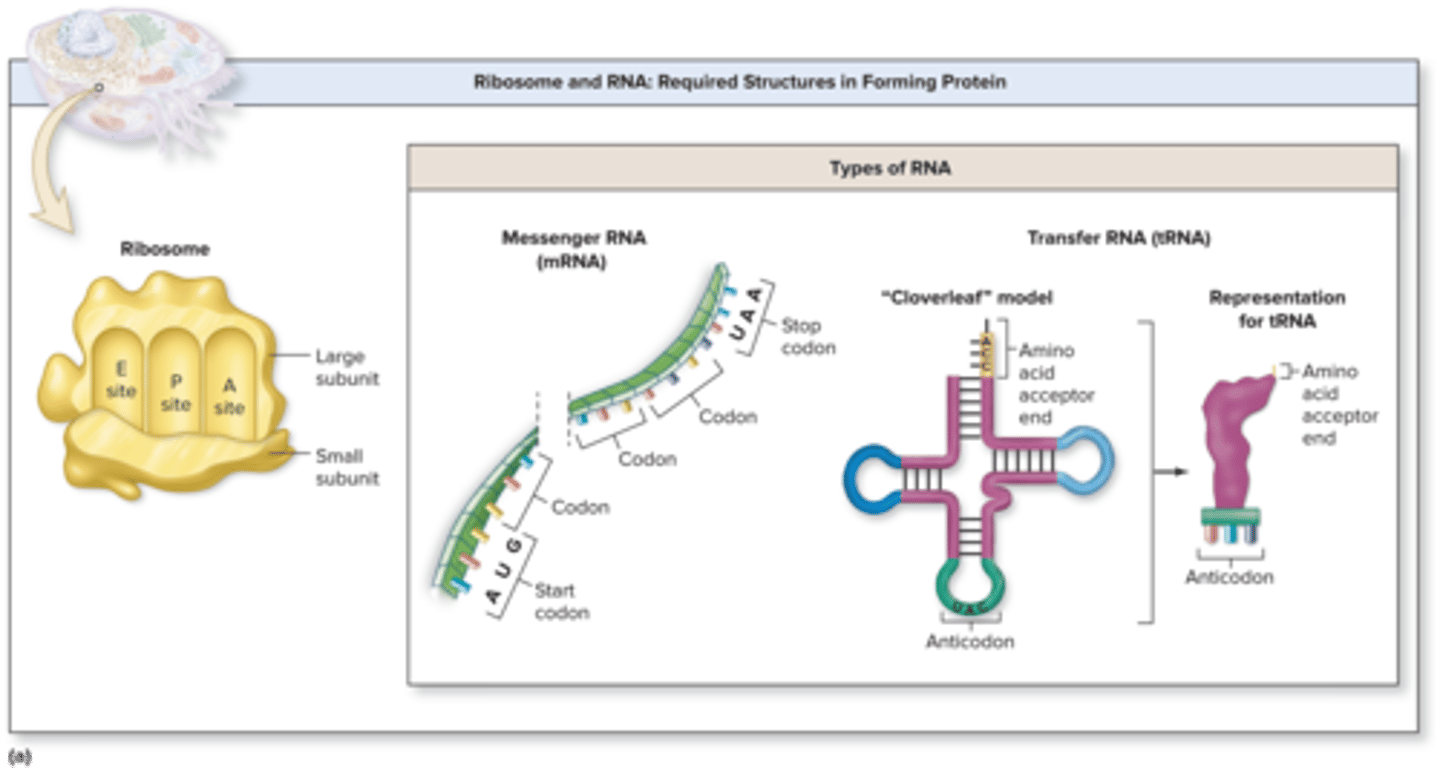
P (peptidyl) site holds the
newly forming polypeptide (protein)
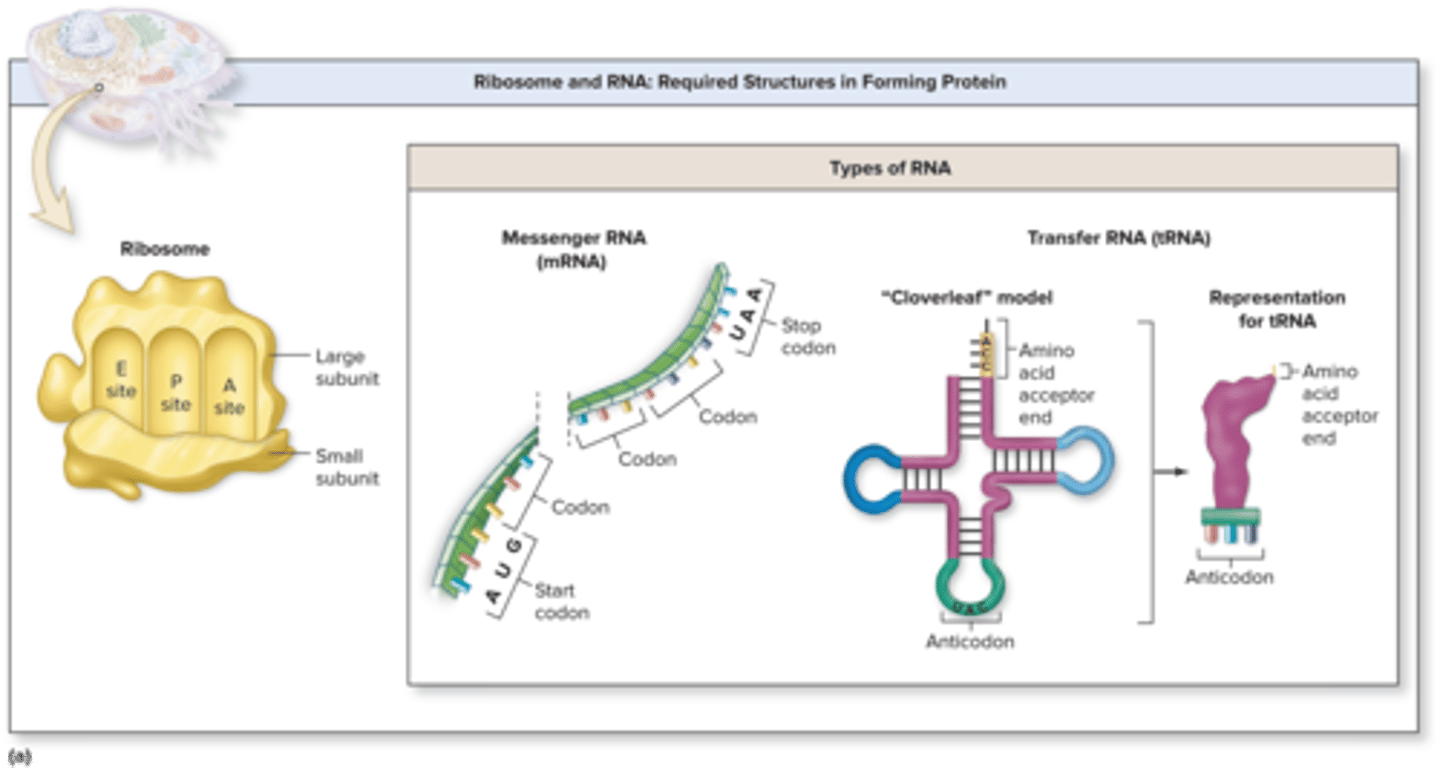
E (exit) site is
where tRNA sits before being released from the ribosome
Protein
an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
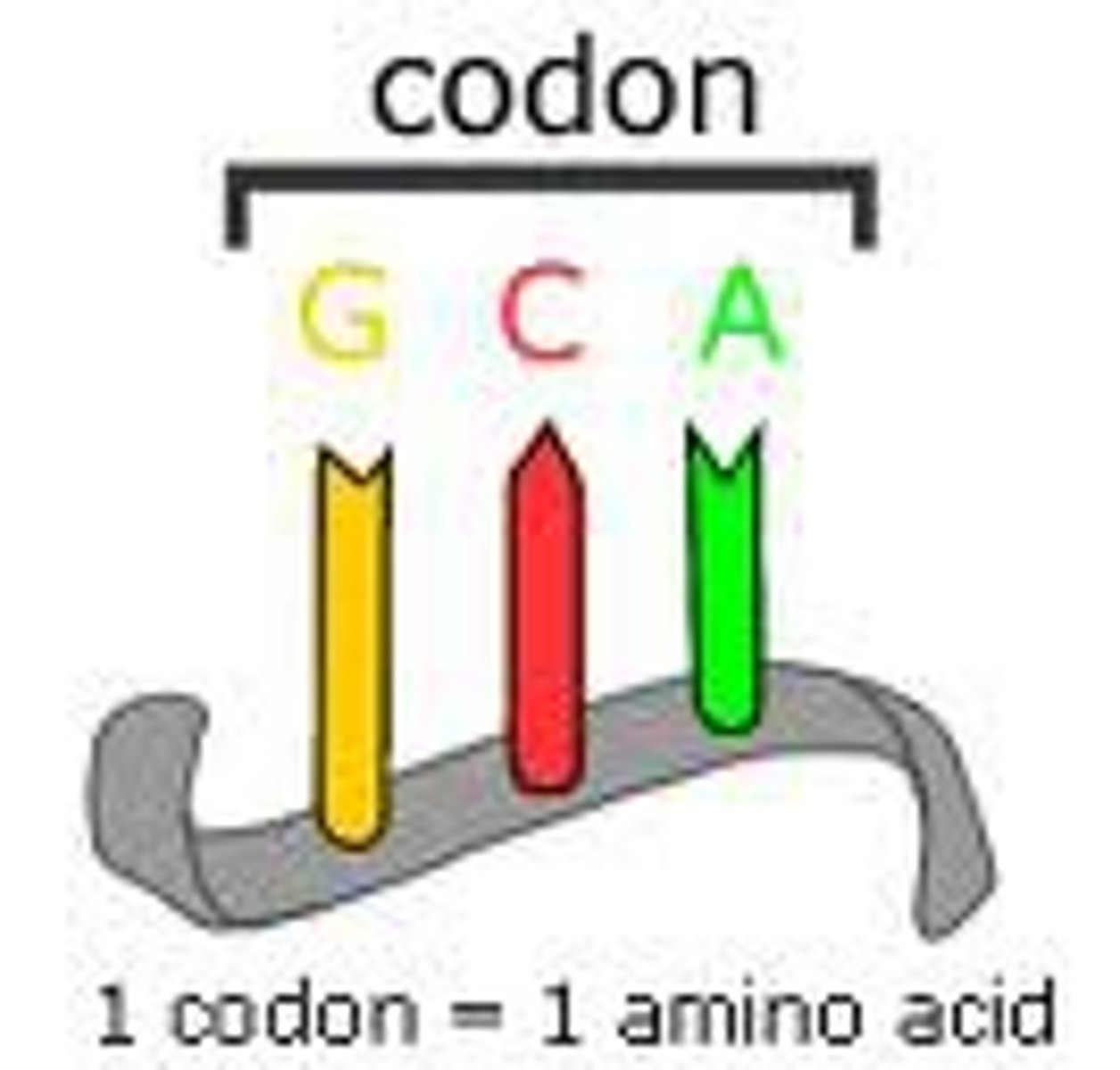
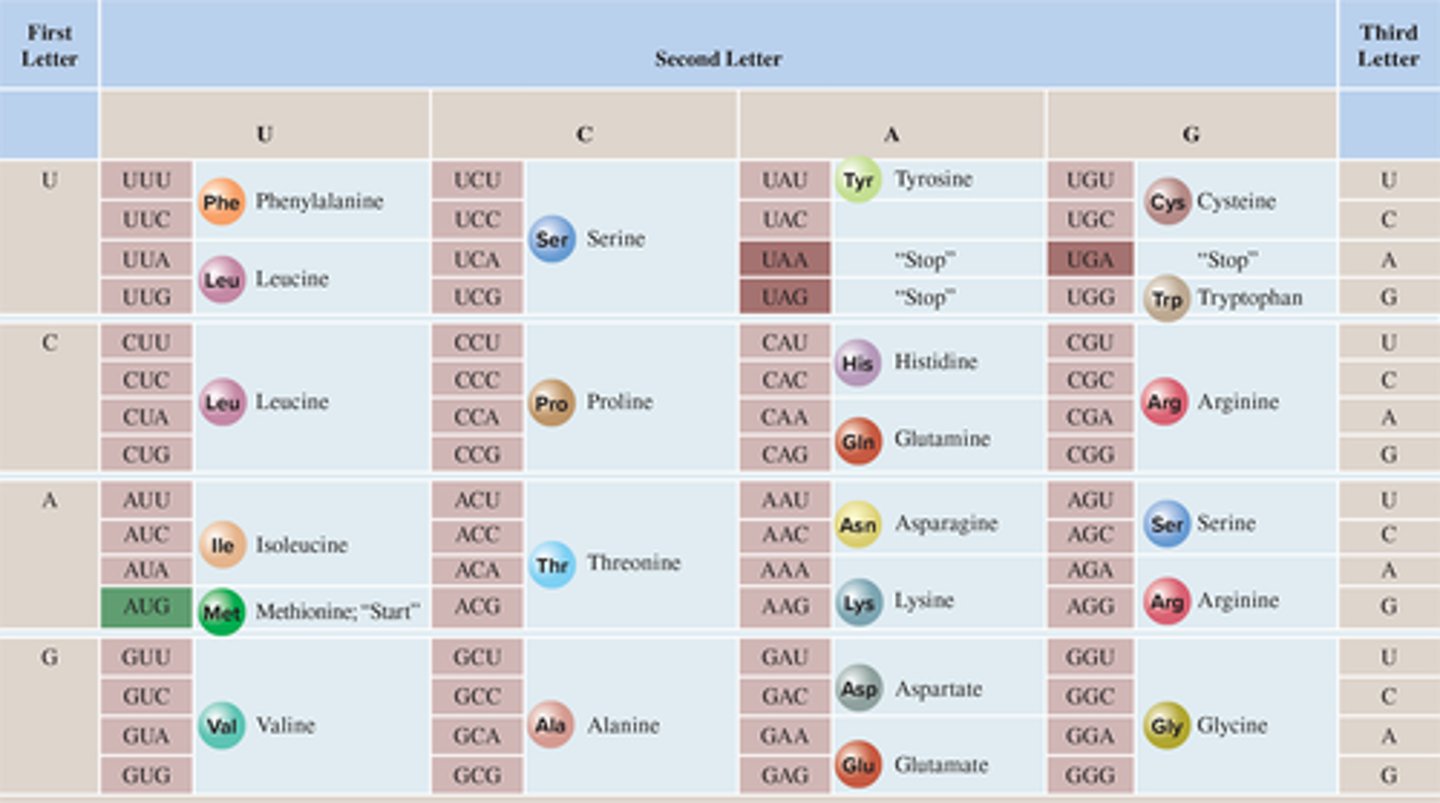
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Translation Start Codon
signals the start of translation and the amino acid methionine
AUG
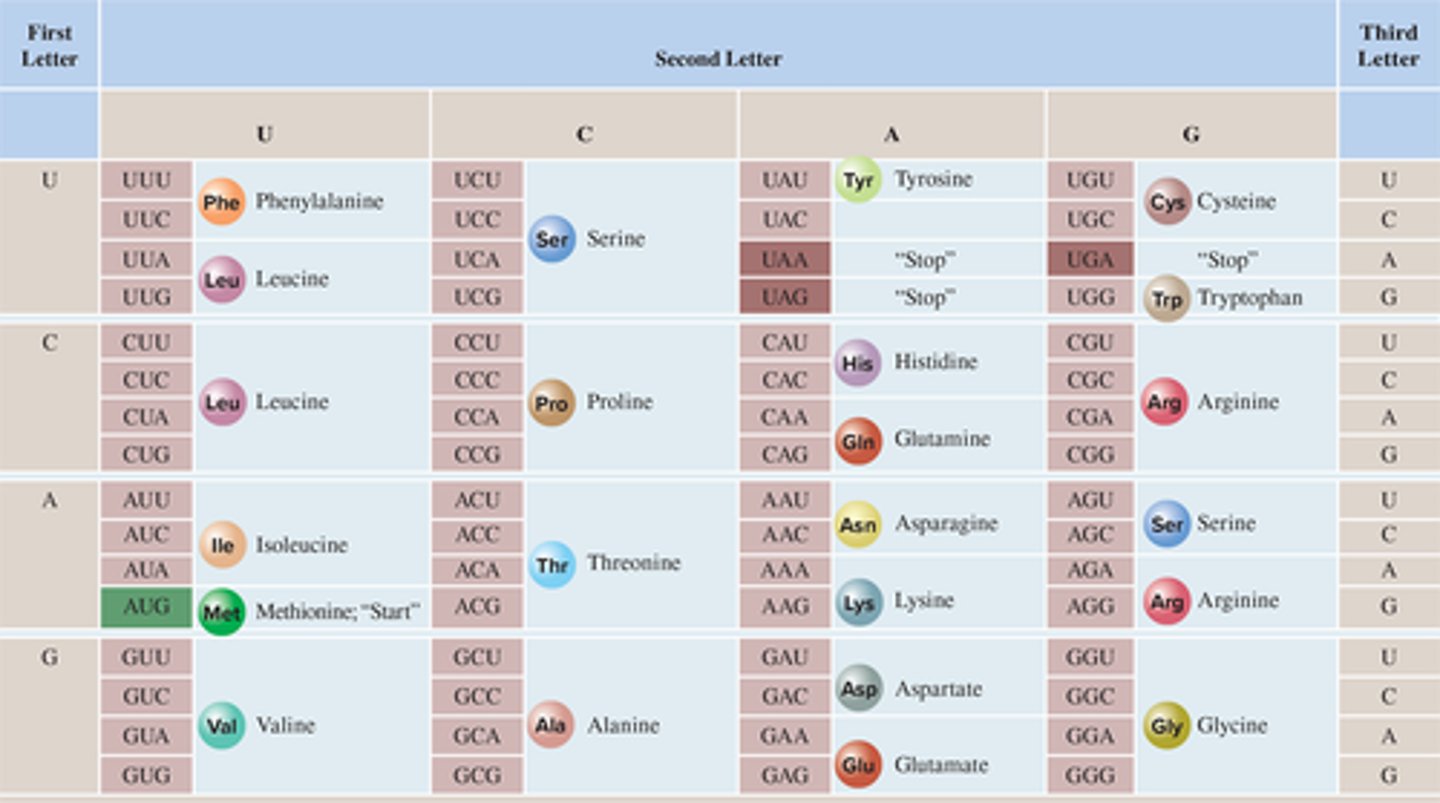
Translation End Codon
serve as the point where the reading of mRNA ends
UAA, UAG, UGA
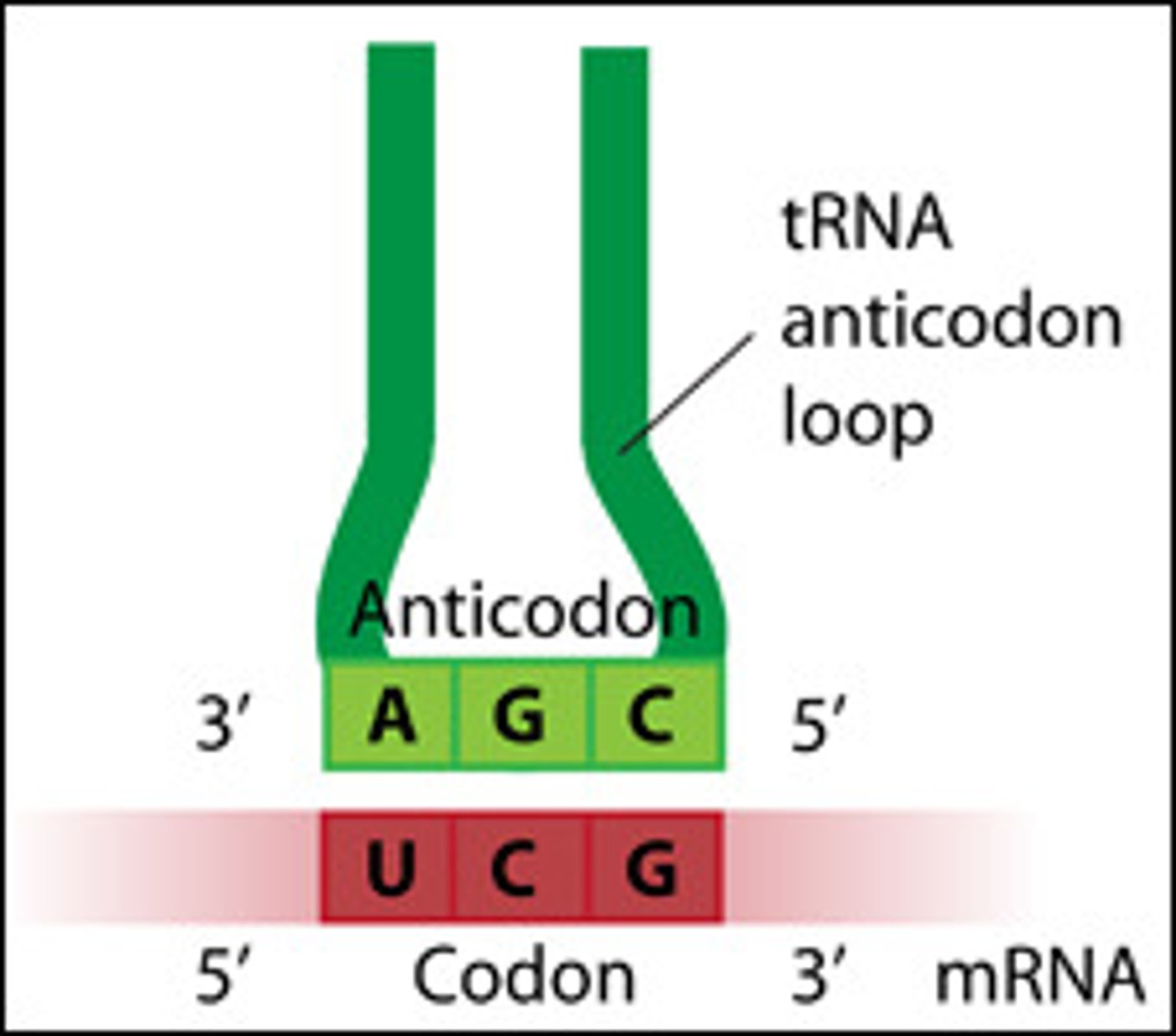
Translation Anticodon
pairs with complementary mRNA codon
tRNA Acceptor End
provides an attachment site for a specific amino acid
tRNA Anticodon
serve as an adapter site, complementary to mRNA codon
first sequence (e.g UAC) determines the specific amino acid to which a given tRNA attaches
Translation Steps
initiation, elongation, termination
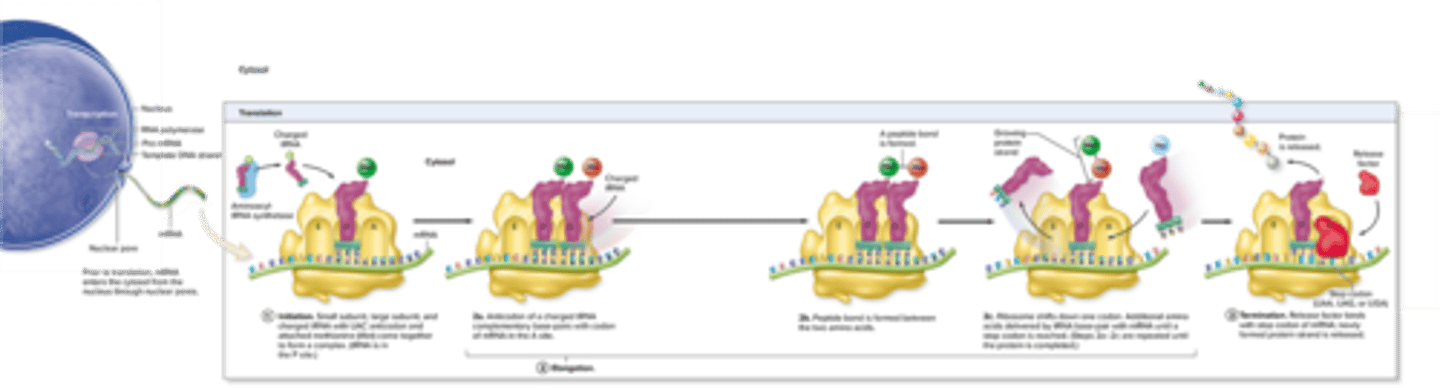
Translation Initiation
small subunit attaches to mRNA upstream of start codon (AUG), the large subunit joins complex and the tRNA in now in the P site
Translation Elongation
a charged tRNA with a complementary anticodon base-pairs with the codon of the mRNA in the A site bringing it with a specific amino acid
a peptide bond is formed between the amino acid in the P site and the amino acid in the A site (bond of amino acid to tRNA in P site breaks)
the ribosome then moves three nucleotides positions (same as codon) down the start codon on the mRNA
repeats until the entire mRNA sequence has been translated
Translation Termination
is when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) enters the A site to end translation
release factor enters the A site
ribosome hits release factor bound to mRNA start codon, two subunits of the ribosome are separated from mRNA and new synthesized protein is released
Polyribosome
string of ribosomes simultaneously synthesizing same protein
Why is DNA considered the cell's control center?
DNA is responsible for directing the synthesis of the proteins that carry out body functions
indirectly responsible for other metabolic changes that occur within a cell,
including synthesis of steroids and other lipids, and the enzymatic pathway of glucose oxidation
Mitosis occurs in
somatic (body) cells
Meiosis occurs in
germ (sex) cells
Somatic Cell Division
occurs when one cell divides to produce two genetically identical cells
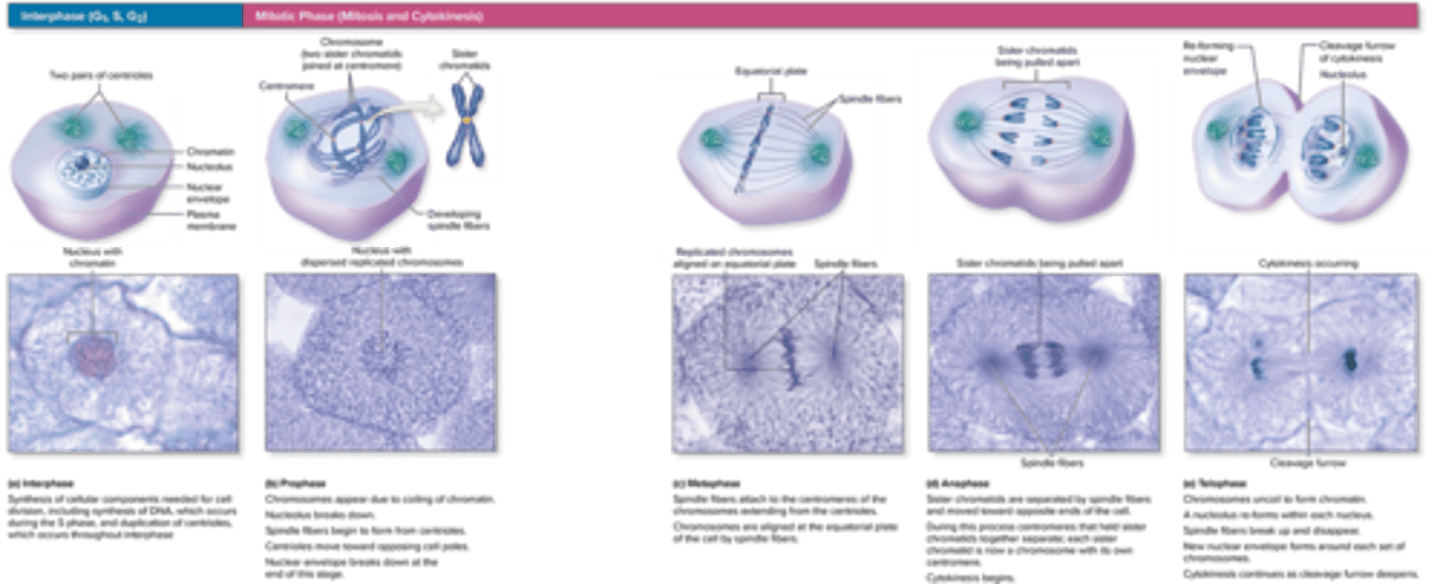
Cell Cycle Phases
G1, S, G2, mitosis, cytokinesis
Explain Cell Cycle
the cell cycle is a series of stages that a cell goes through to grow and divide
G1 phase
cell growth and preparation for DNA replication
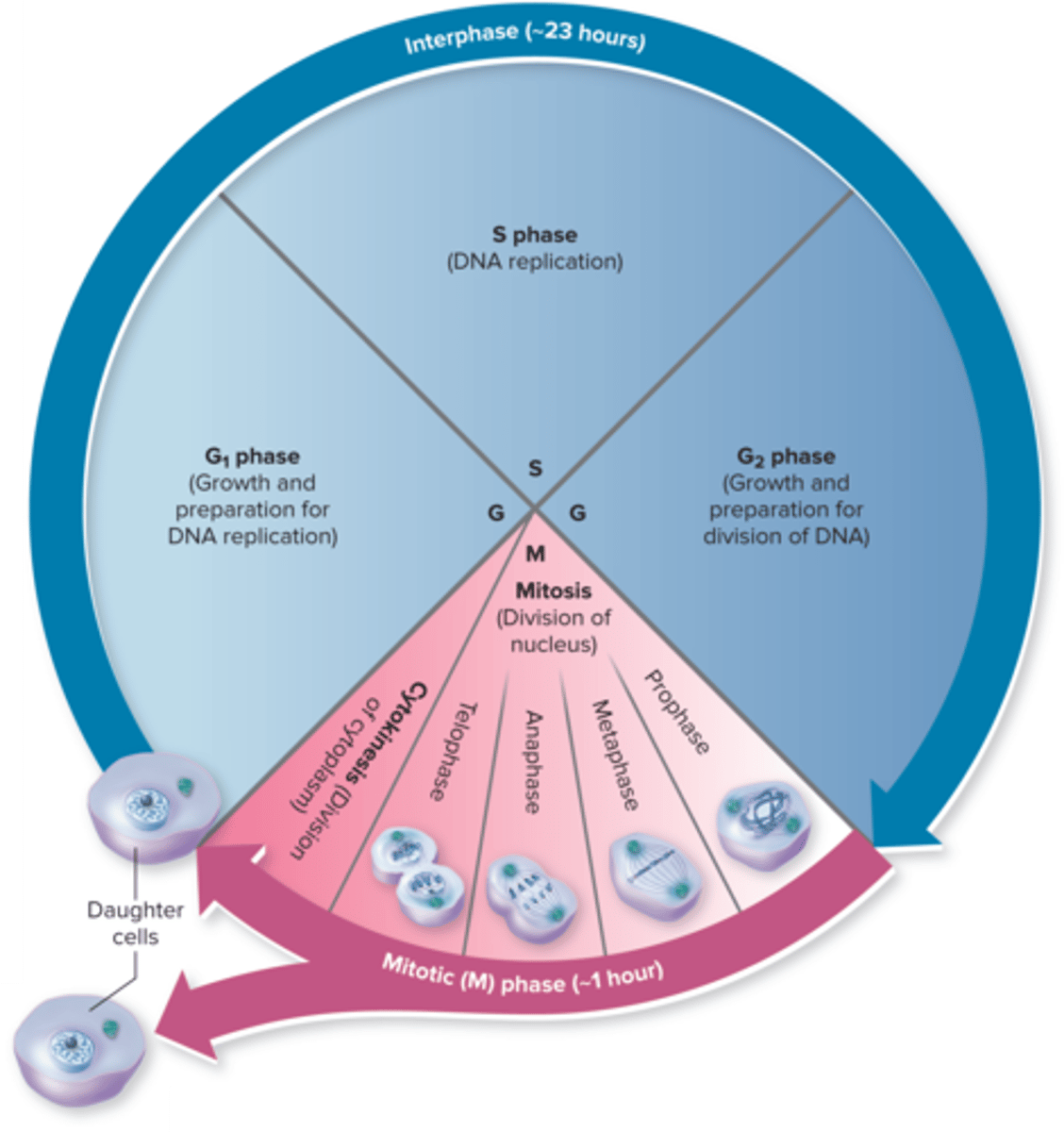
S phase
DNA replication
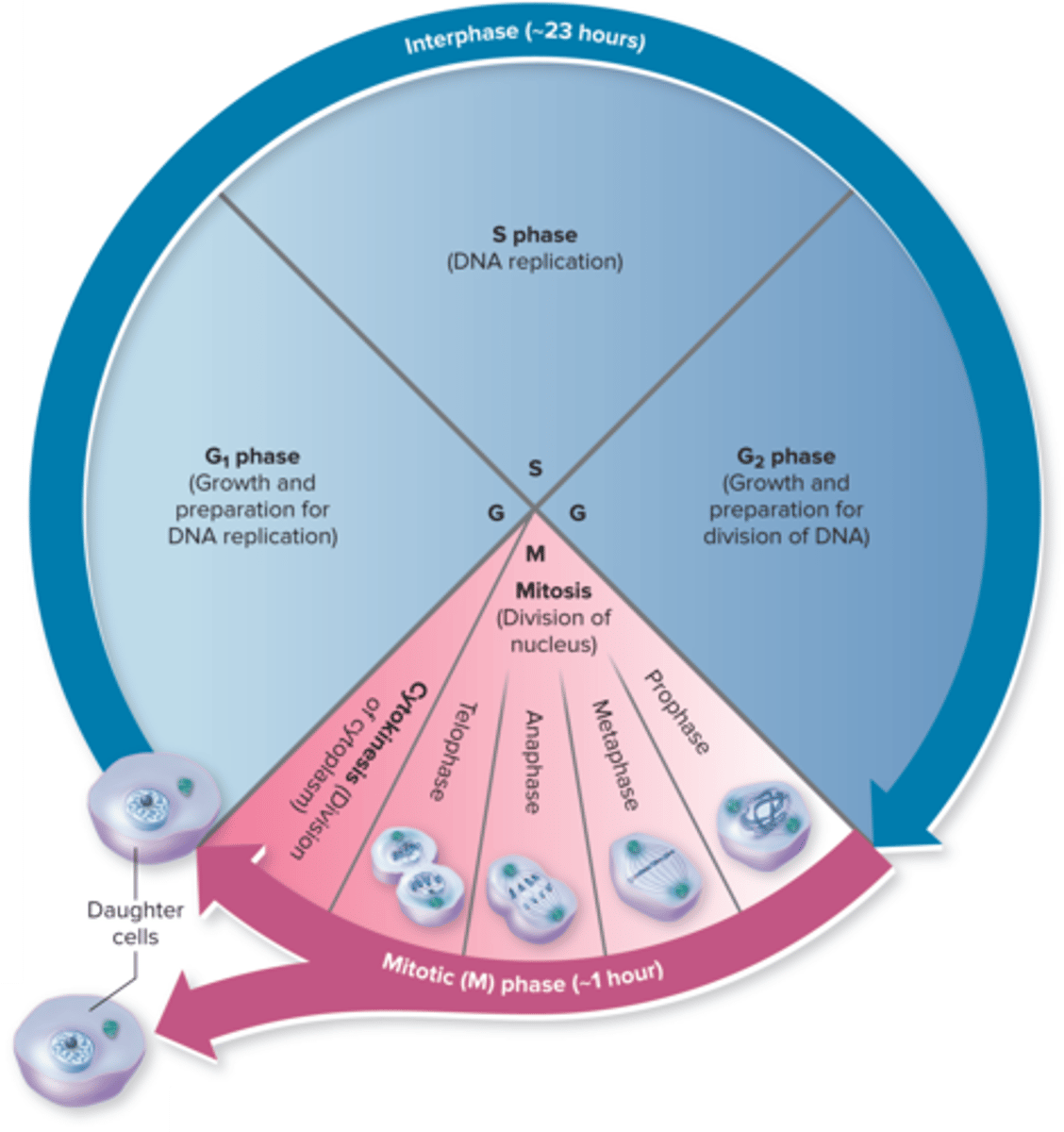
G2 phase
growth and preparation for divison of DNA
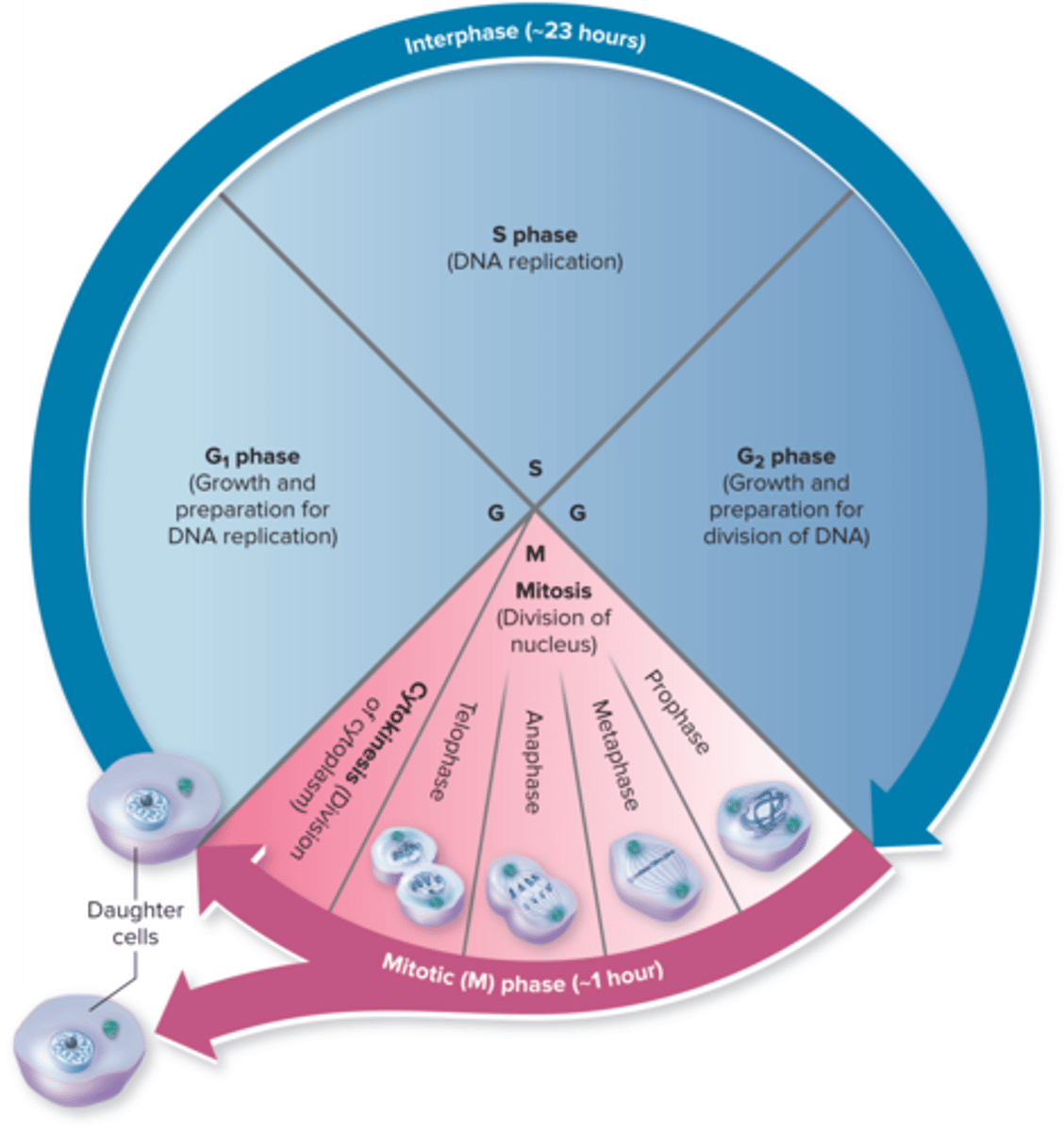
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
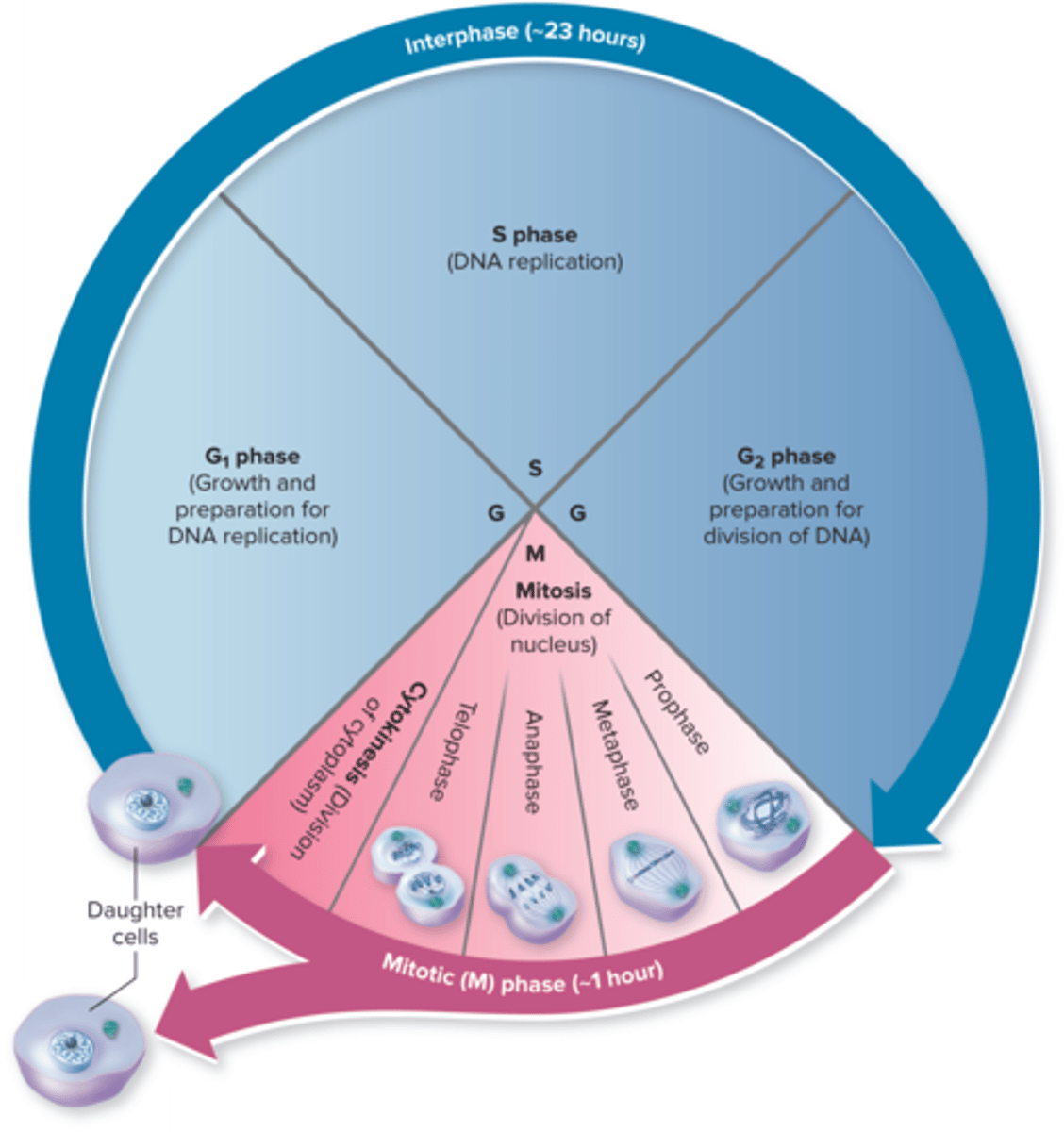
Mitosis Phases
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
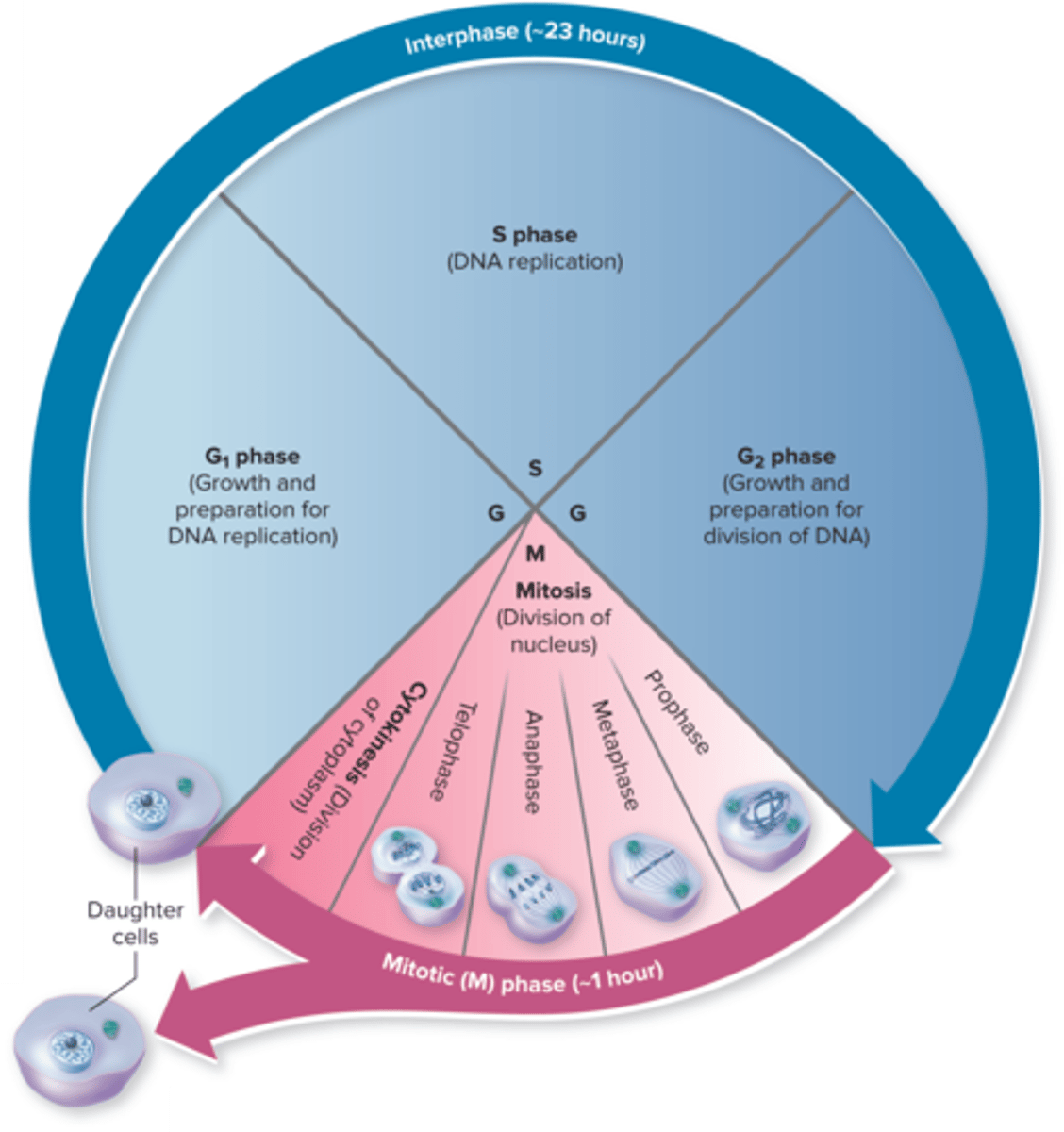
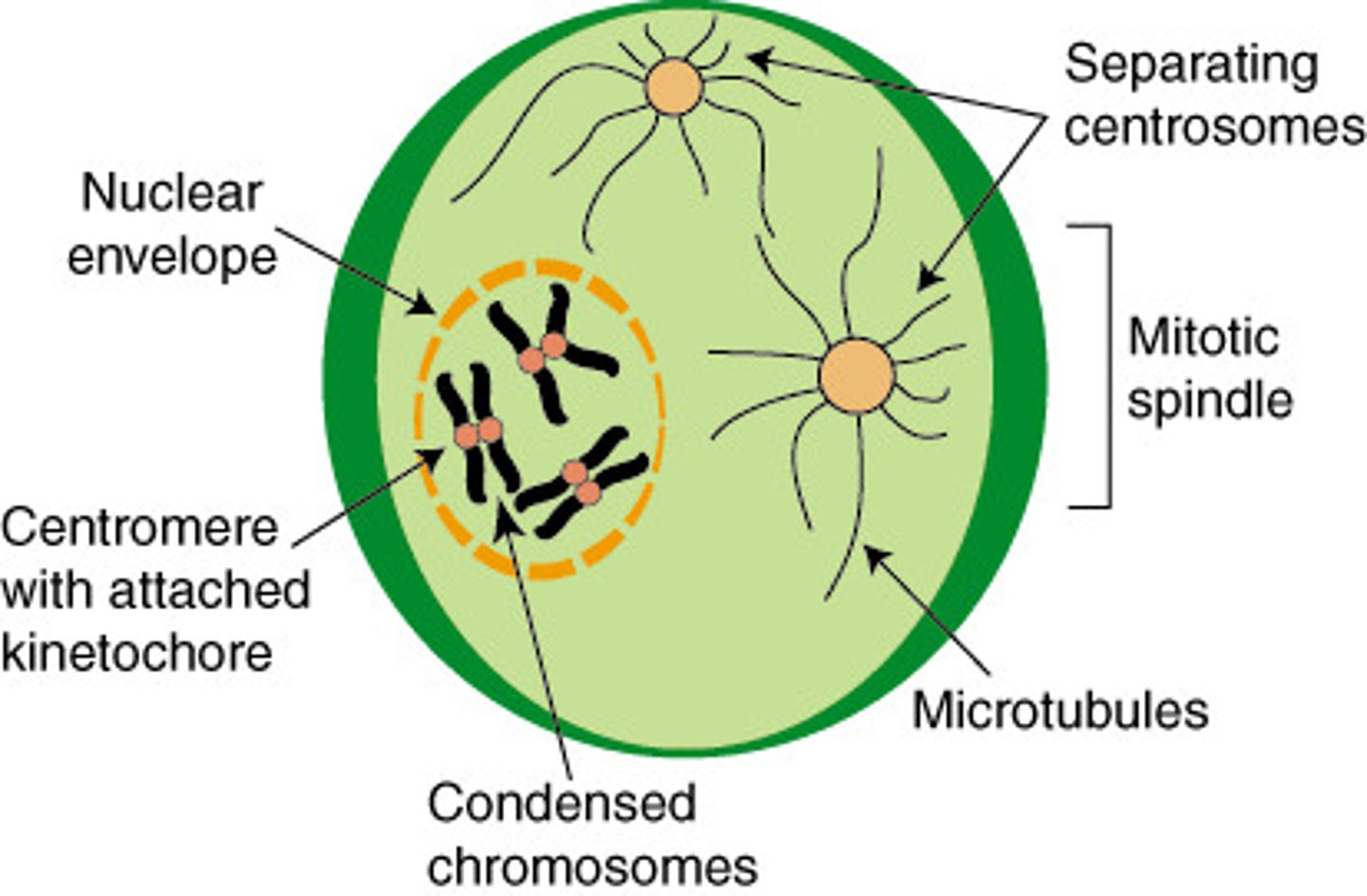
Mitosis Prophase
chromosomes condense become visible, the nuclear envelope begins to break down
Mitosis Metaphse
chromosomes align at the cell's equator
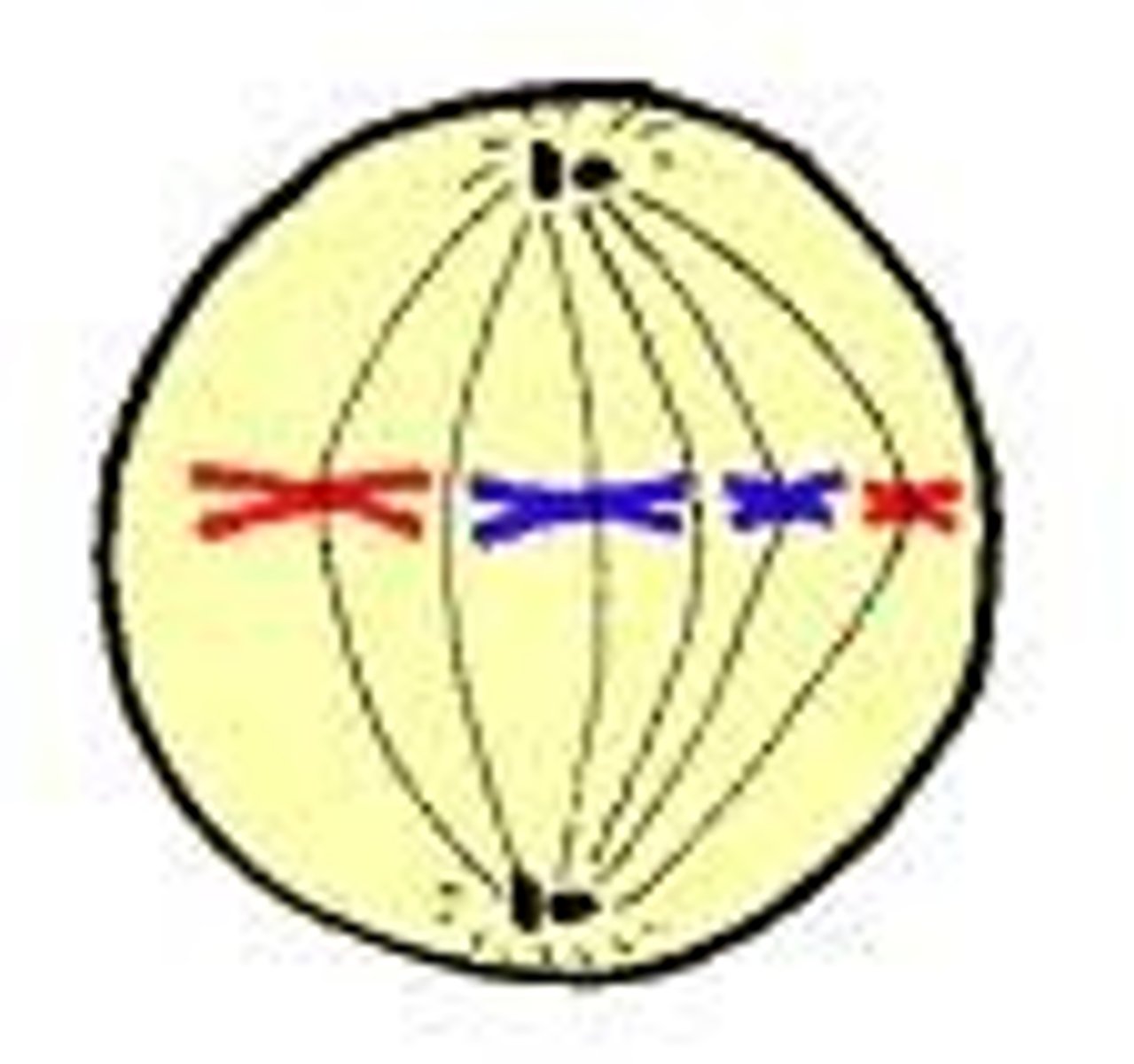
Mitosis Anaphase
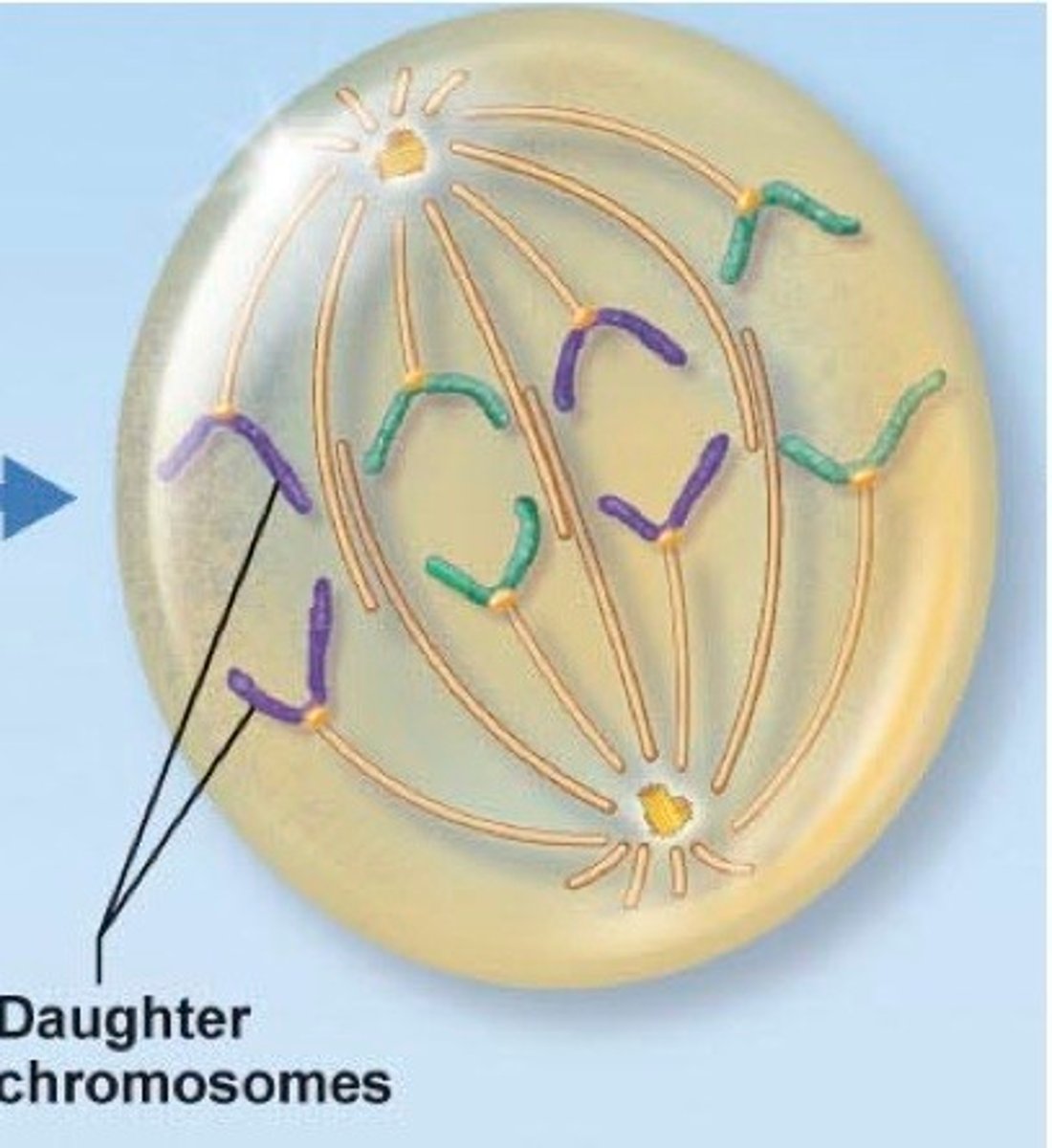
sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell
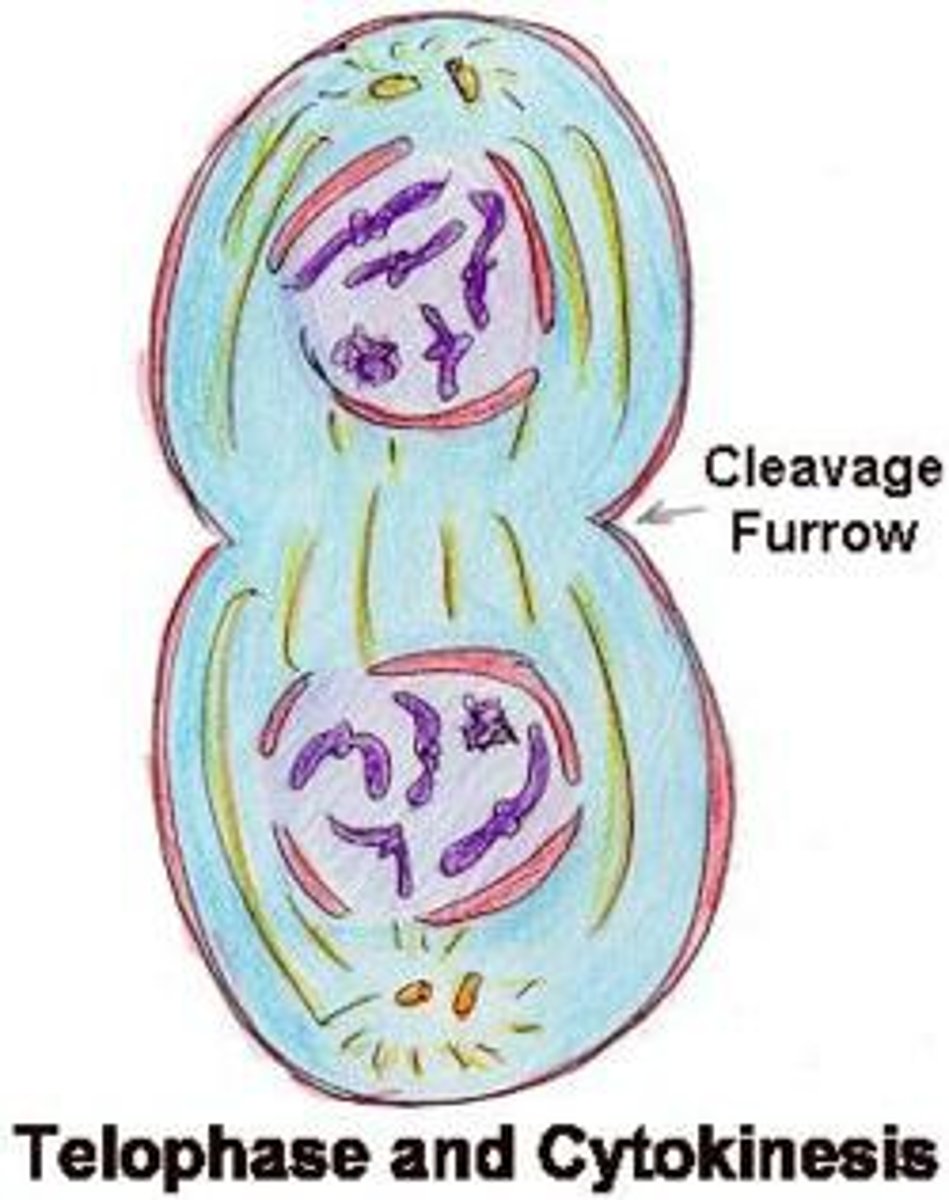
Mitosis Telophase
chromosomes gather on each side of the now separating cell
DNA replication
the process of making a copy of DNA
Apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
Apoptosis Process
destruction of DNA polymerase
digestion of the DNA into small fragments
digestion of cytoskeleton, cell shrinks
formation of blebs on plasma membrane surface
condensation of cytosol and destruction of organelles
release of proteins