Week 12: Energy Storing Molecule, Biological Oxidation and Reduction, and Cellular Respiration
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
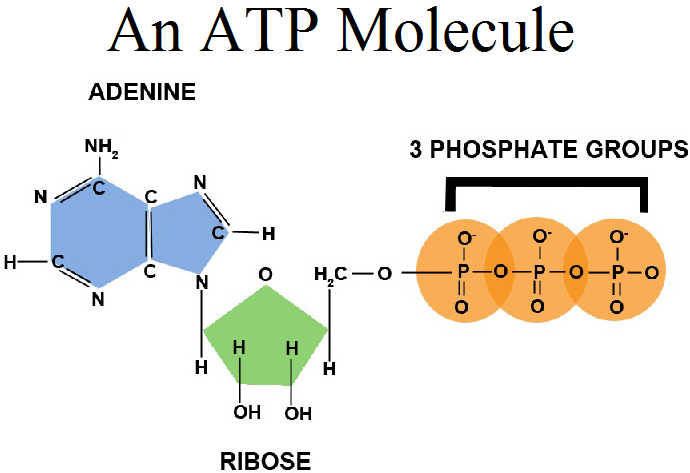
ATP structure
is a nucleotide composed of an
adenine ring
a ribose sugar
three phosphate groups (triphosphate).
ATP as an energy source and building block
known as the energy currency for living organisms.
is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells.
from oxidation
plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids
all cells use ATP, but differer in how its made (prokaryote vs eukaryote)
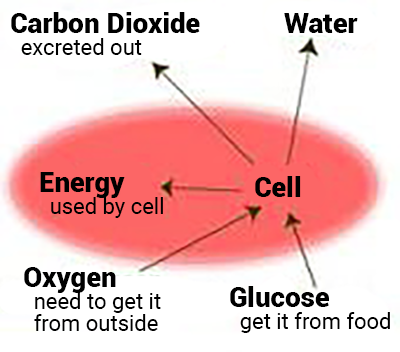
Glucose
is the molecule we know that is the provider of energy in the body
is obtained from the food we eat and the breakdown or digestion of this glucose
known as Glycolysis
produces a lot of energy in the form of ATP,
with the help of some enzymes and the oxidation-reduction reactions.
glucose from the food we eat along together with the oxygen we breathe, produce CO2, water and a lot of energy.
Biological oxidation in cells (1)
1)
related to the transfer of hydrogen atoms or electrons, where oxygen is the final acceptor of the hydrogen atoms
When this transfer of hydrogen atoms or electrons take place, it results in two processes known as Oxidation and Reduction.
primary function of biological oxidation is to provide usable energy in living cells.
Most of the energy liberated in biological oxidation is stored in high-energy compounds like Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism.
Energy comes from breaking bond and moving electrons
harvested as heat or ATP
Oxidoreductases
Biological oxidation is catalyzed by this enzymes
function in combination with coenzymes and/or electron carrier proteins
Oxidation
is the loss of electrons
The compound that loses electrons is said to be oxidized
lower energy state with loss of electrons
Loss of electron(s) or
Removal of Hydrogen, or
Addition of oxygen
During oxidation energy is released
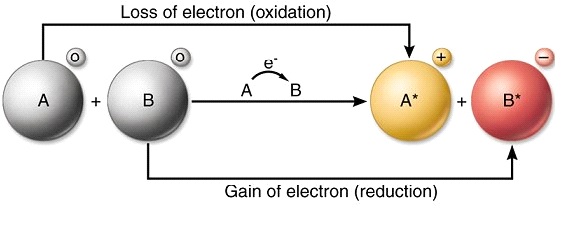
Reduction
is the gain of electrons
the compound that gains electrons is said to be reduced
now is more energy state
Gain of electron(s), or
Addition of hydrogen or
Removal of oxygen
During reduction, energy is gained
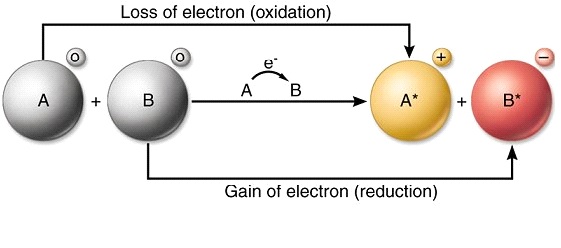
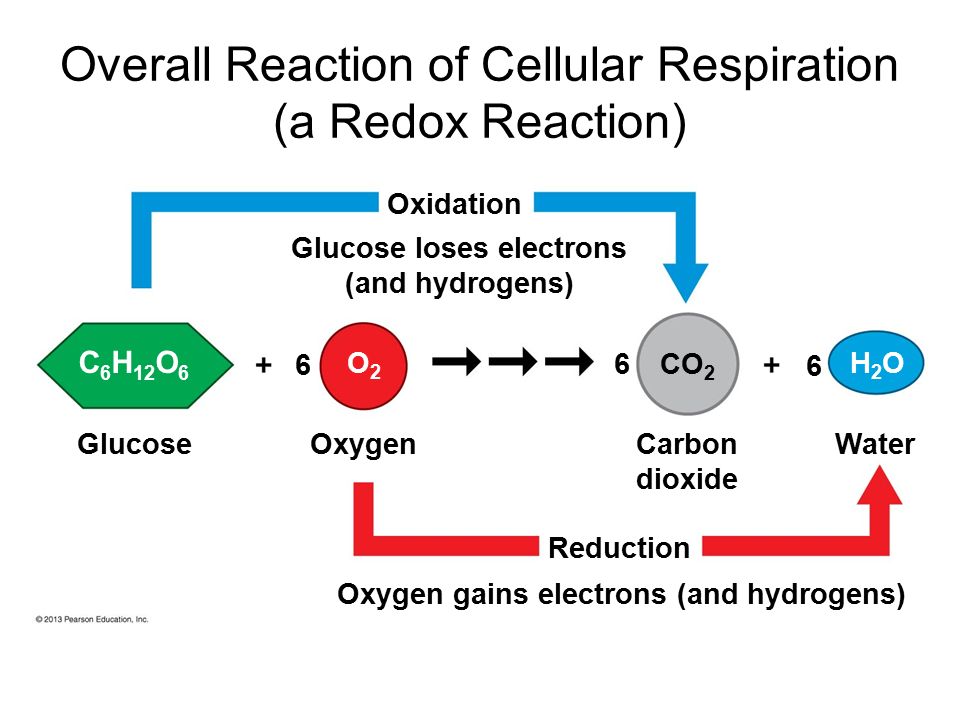
REDOX reaction of Glucose (glycolysis; aerobic cellular respiration )
1 Glucose reacts with 6 O2
producing 6 CO2 and 6 H20
opposite for photosynthesis
glucose loses hydrogens and electrons in the presence of oxygen, forming CO2.
This is an oxidation reaction.
On the other hand, oxygen gains hydrogens and electrons, forming water.
This is a reduction reaction.
As oxidation and reduction are happening simultaneously, it is a REDOX reaction.
Oxidation and reduction always happen side by side and hence the combination of the two is referred to as REDOX reaction, as displayed in the following image.
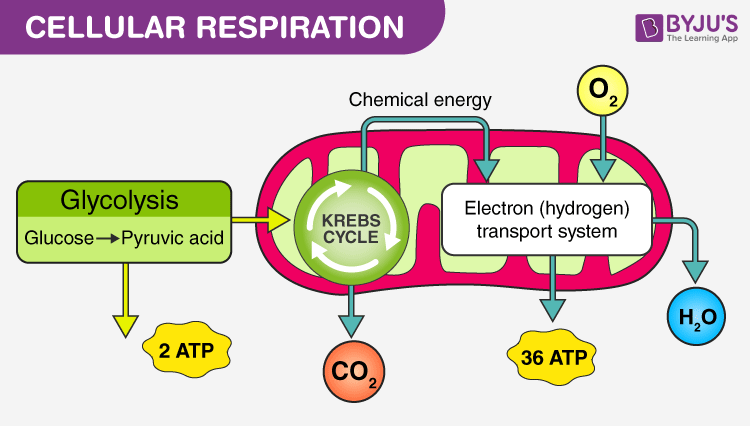
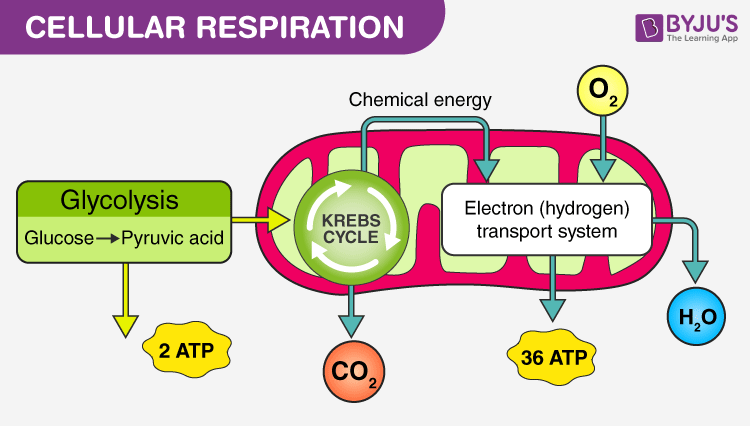
Cellular Respiration
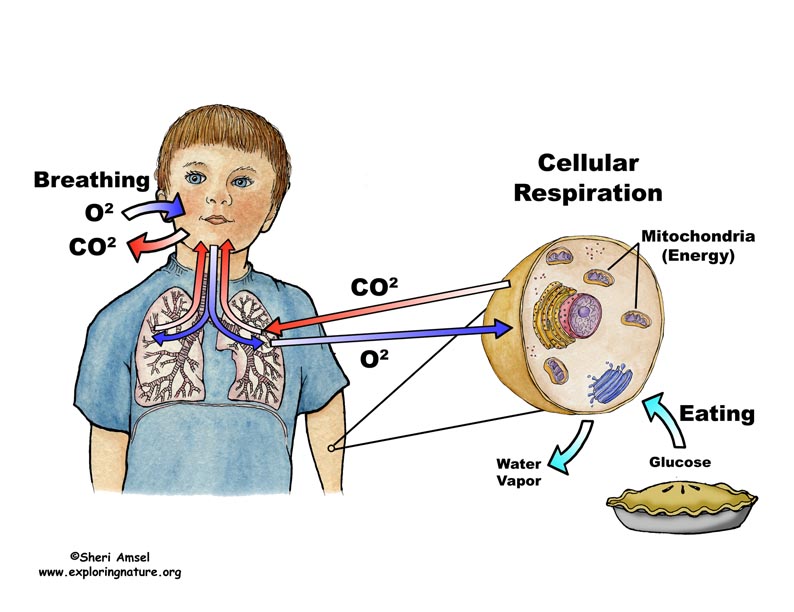
the process of breathing in oxygen and breathing out carbon dioxide that take place in the cells of the organism.
It is due to this exchange of gases that the cells take the energy from food and make it into ATP, and then release the waste products like CO2 and water.
Cellular respiration is a REDOX reaction.
When glucose and oxygen reach the cell, the process of cellular respiration is started.
We know that the food we eat is broken down into smaller units such as glucose molecules.
Also the oxygen from the air we breathe is carried from lungs through bloodstream into smaller blood vessels, until it reaches the cells.
This process starts in the cells’ cytoplasm and is completed in the mitochondria (the cellular power house).
Energy is stored as the following molecules:
ATP
NADH:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) +Hydrogen (H)
FADH2 : Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) + Hydrogen (H)
During the cellular respiration, hydrogen and electrons from various metabolic reactants are transferred to coenzymes NAD and FAD to produce NADH and FADH2 respectively.
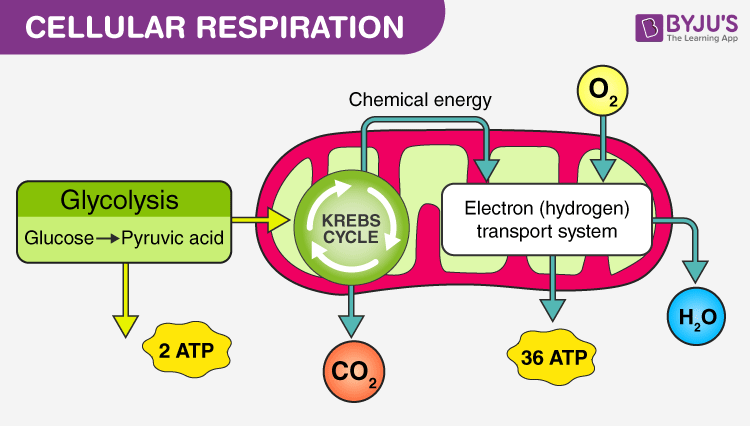
The process of cellular respiration may be divided into three stages:
Glycolysis
occurs in the cytoplasm
Oxygen is not essential for glycolysis
Krebs cycle
Oxygen is essential
Electron transport chain
Oxygen is essential
Glycolysis (first stage of cellular respiration)
is a series of reactions that take place in the cytoplasm.
This takes place in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic condition).
During this reactions, energy is produced due to the breakdown of glucose into two three-carbon molecules
called pyruvic acid, also known as pyruvate.
requires ATP to do so
This pyruvic acid, when further broken down, forms
Acetyl CoA (Acetyl Coenzyme A)
net gain of NADH ( co-enzyme)
net of gain 2 molecules of ATP.
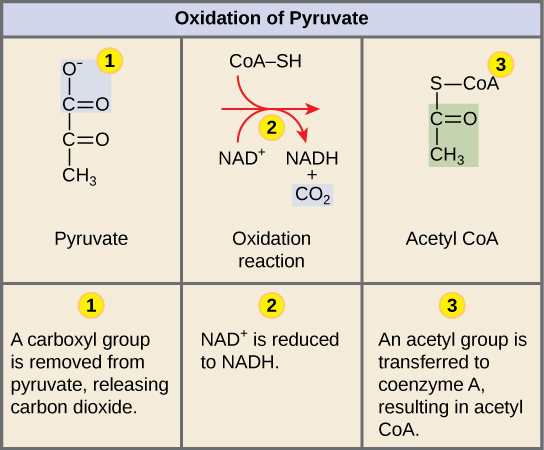
The image below shows the conversion of pyruvate into Acetyl-CoA.
This Acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs cycle.
Note that the two ATP molecules are not shown in this image.
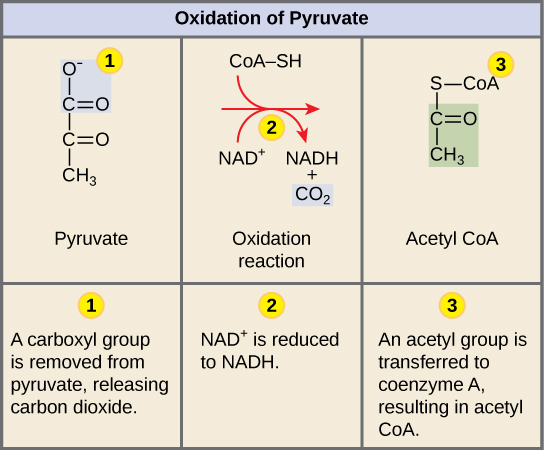
Order of operations for Glycolysis
A carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate, releasing carbon dioxide.
NAD+ is reduced to NADH
An acetyl group is transferred to coenzyme A, resulting in acetyl CoA
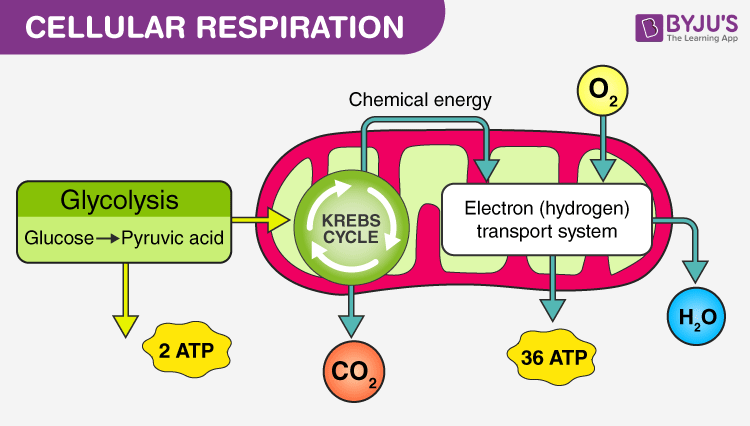
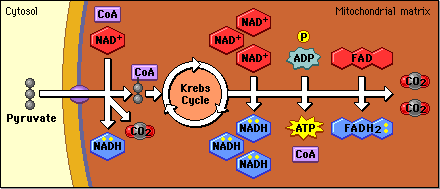
Krebs Cycle or citric cycle (second of cellular respiration)
takes place in the mitochondria of the cell, in the presence of oxygen (aerobic condition).
Pyruvate (Or pyruvic acid) enters the Krebs cycle as Acetyl CoA.
CO2 released as by product
When Acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide in the Krebs cycle, chemical energy is released and captured in the form of
6 NADH
2 FADH2, (coenzyme to transfer electrons)
2 ATP molecules.
This process is displayed in the above image. Note that in this image, CoA represents Acetyl CoA.
Electron Transport Chain (Third and final stage of cellular respiration)
Is the last stage of the respiration pathway.
It takes place in the mitochondria, in the presence of oxygen (aerobic condition).
It is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules.
This pathway takes place in the carrier proteins found in the inner membrane of mitochondria.
Oxygen if final electron acceptor, makes water
allows the release of the large amount of chemical energy stored in
reduced NAD+ (NADH)
reduced FAD (FADH2).
release their electrons to parts of ETC to create proton gradient
powers ATP synthase
The energy released is captured in the form of ATP
(3 ATP per NADH and 2 ATP per FADH2).
NADH and FADH2 are converted to ATP by the enzyme ATP synthase
In total
36 to 38 ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose.
Converts ADP with phosphate to ATP
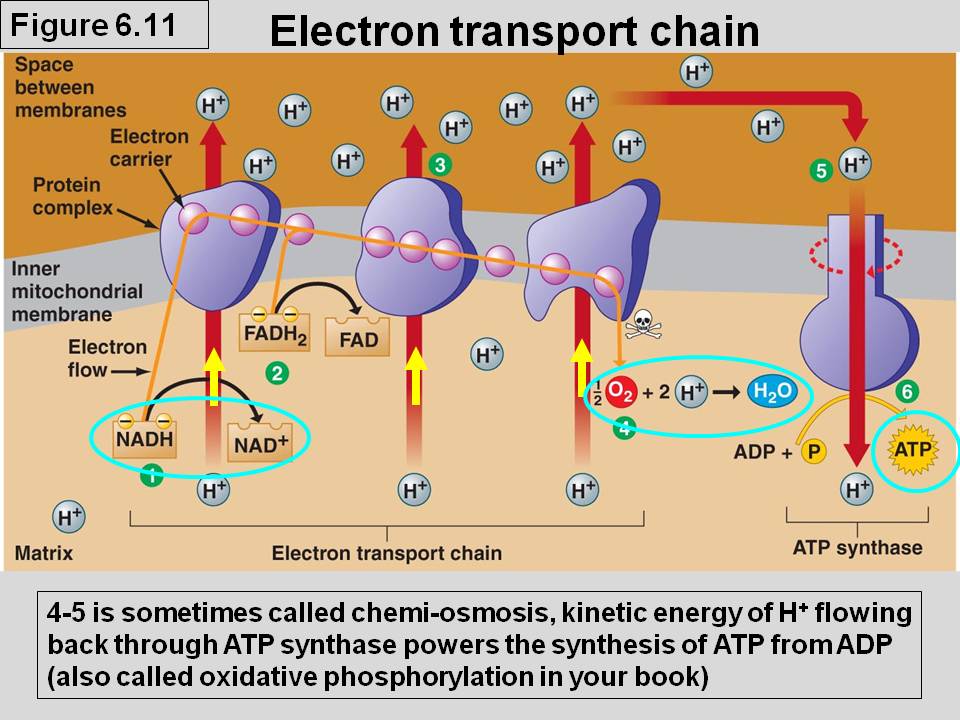
Cynaide poisiouns achieved due to
it blocking ETC
reduced ATP production, killing cell