bio cell membrane pt 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
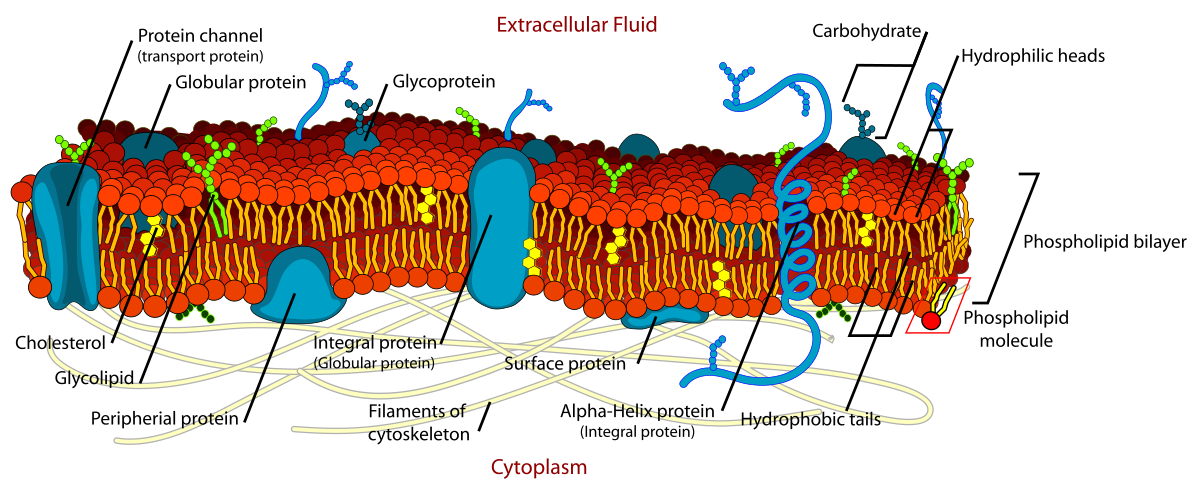
fluid mosaic model
cell membrane = flexible, consists of proteins scattered through membrane and molecules can move around
what does it mean that the cell membrane is selectively permeable?
it lets some substances (small, nonpolar) through but not others (large, polar)
passive transport
doesn’t need energy, moves down concentration gradient, can involve transport proteins
active transport
needs energy, moves up the concentration gradient, involves transport proteins
osmosis
water diffuses from area of high to low water concentration
what happens to animal cells in a hypertonic solution
the cells shrink and are crenated
what happens to animal cells in a hypotonic solution
the cells expand and burst (cytolysis)
what happens to plant cells in a hypertonic solution
vacuole shrinks, chloroplasts are in the center (plasmolyzed)
what happens to plant cells in hypotonic solution
cell pushes on wall, wall pushes back with turgor pressure (ideal situation)
what is the relationship between surface area to volume ratio
as a cell gets larger, the surface area to volume ratio decreases; there is less surface to get nutrients in the cell
how to nerve cells work
dentrites recieve the signals from neurons, the axon sends the signal away
purpose of facilitated diffusion
allow charged, polar molecules throughf
facilitated diffusion
done by protein channels not using energy, moving from high to low concentration
endocytosis
active transport of large substances into transport vesicles to outside the cell

phagocytosis
cell eating
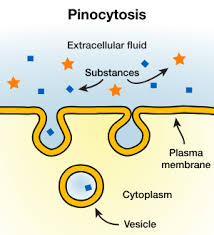
phinocytosis
cell drinking
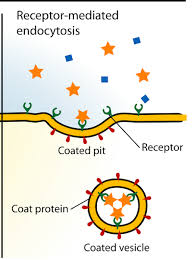
receptor-mediated endocytosis
receptors bind to specific substances
exocytosis
moves large amounts of substances out of the cell using vesicles
how does the sodium-potassium pump work
sodium leaves the cell and potassium enters using energy
endomembrane system
RER produces proteins and SER produces phospholipids, transported to Golgi in vesicle, then moves to cell membrane in another vesicle, membrane fuses and releases the products outside the cell
structure of a phospholipid
has a hydrophilic head that faces out and hydrophobic tails that face in