Biology IGCSE Topic 8 Coordination and Response
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is sensitivity?
the ability to respond to changes in the environment - held by both humans/animals and plants
what is homeostasis?
maintenance of a constant internal environment e.g. body temperature (thermoregulation), water content (osmoregulation)
what is a coordinate response?
a response to a stimulus, carried out in the nervous system
what does a coordinated response require?
a stimulus, a receptor to detect this stimulus, and an effector to produce a response
what makes up the nervous system?
the CNS, the PNS and sense organs
what is the CNS?
the central nervous system - it is made up of the brain and the spinal cord
what is the PNS?
the peripheral nervous system - it is made up of nerves/neurons etc.
what are sense organs?
they are organs which contain receptor cells and respond to external stimuli by conveying electrical impulses to the nervous system (via nerves)
what are stimuli?
changes in surroundings
describe a basic nervous system response to a stimuli
receptor cells detect stimuli and send electrical impulses into the CNS via neurons. the brain coordinates the response and sends electrical impulses via neurons to a effector which carries out a response
what is a reflex action?
a nervous system response that bypasses the brain
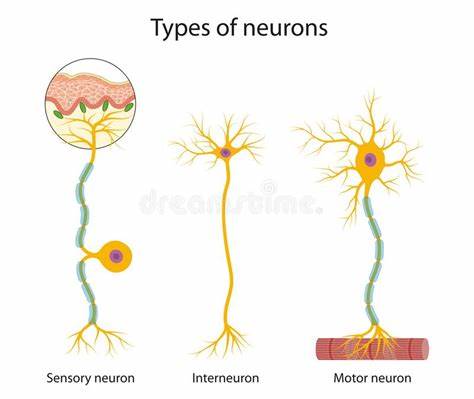
how many types of neuron are there?
3 - sensory, motor and relay
what are sensory neurons?
sensory neurons are neurons that transmit electrical impulses from a receptor to the CNS (brain)
what are motor neurons?
motor neurons are neurons that transmit electrical impulse from the CNS (brain) to an effector
what are relay neurons?
relay neurons are neurons that transmit electrical impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons in the CNS - they are only used in reflex actions
what are receptor cells?
cells adapted to detect stimuli
examples of receptor cells
rods (dim light) and cones (colour) in the eye
skin cells - pressure, heat, pain
taste receptors - tongue (taste buds)
what is an effector?
an effector is a muscle or gland that brings about a response to a stimuli e.g. contraction of a muscle, or secretion of hormones
what is a reflex arc?
a subconscious response to a usually dangerous stimuli. in a reflex arc, the electrical impulse do not go through the brain but instead the general CNS
why are reflex actions important?
they are important to protect the body from harm
describe a reflex arc
1) a stimulus is detected by a receptor cells e.g. extreme heat on skin
2) an electrical impulse is conducted along the sensory neuron
3) in the CNS, this passes to a relay neuron
4) The electrical impulse passes to a motor neuron and is transmitted to an effector
5) The effector carries out an appropriate response e.g. withdrawal of hand
how do the structures of motor and sensory neurons differ?
motor neurons have their cell body at the end of the axon, in the CNS
sensory neurons have their cell body in the middle of the axon, in the PNS
what is a synapse?
a gap between neurons where impulses are transmitted across chemically
what are neurotransmitters?
chemical messengers released at the end of a nerve fibre
describe the role of neurotransmitters at a synapse
1) an impulse arrives at the pre-synaptic neuron
2) neurotransmitters (chemical messengers( are contained in vesicles
3) neurotransmitters are released into the synapse
4) neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse
5) neurotransmitters bind with the receptor on the post-synaptic membrane
6) this binding stimulates the transmission of the impulse along the post-synaptic neuron
7) the neurotransmitters are reabsorbed into the pre-synaptic membrane, otherwise impulse would be repeatedly fired
learn the structure of the eye
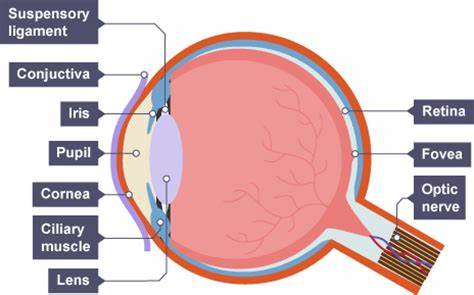
what is the function of the cornea?
transparent outer part of the eye which focuses light onto the retina and protects the eye
what is the function of the lens?
the lens is a transparent bioconvex disk that is attached to the ciliary muscles by the suspensory ligaments. It focusses/refracts light onto the retina
what is/the function of the iris?
the coloured part of the eye which does not allow light through - it contains 2 sets of muscles, circular and radial which control the size of the pupil
what is/the function of the ciliary muscles?
contract and relax to control the taughtness of the suspensory ligaments
what is/the function of the suspensory ligaments?
are taught or loose to control the shape - roundness/length - of the lens
what is/the function of the optic nerve?
transmits impulse between the optic nerve and the brain
what is/the function of the sclera?
the sclera is a tough, fibrous layer which is the supporting wall of the eyeball - transitions into the cornea
what is/the function of the retina?
the retina contains light receptors - rods and cones