3.3 Unemployment
Unemployment
Situation where people are willing and able to work, and actively seeking employment but are unable to find work
Unemployment Rate Formula
Total Unemployed/Total Labor Force *100
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Unemployment
Situation where people are willing and able to work, and actively seeking employment but are unable to find work
Unemployment Rate Formula
Total Unemployed/Total Labor Force *100
Labor Force
People of working age who are seeking work or are currently working
Cyclical Unemployment
Unemployment due to a lack of demand for goods/services in the economy (demand deficient)
Unemployment due to the fluctuations in the business cycle
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment due to a mismatch of skills demanded and supplied
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment due to workers in between jobs
Seasonal Unemployment
Unemployment due to the demand for labor in certain industries changing on a seasonal basis
Underemployment
Refers to people of working age who have part time jobs/jobs that don’t make full use of their skills
NRU
Natural Rate of Unemployment
At Ypot, UR=NRU
All unemployment except cyclical combined
Costs of Unemployment BIC(GDP)
Crime
Social cost, quality of life of citizens ⬇
Loss of GDP
Inefficient allocation of resources
Consumers spend less, C component of GDP ⬇
Government Burdens
Less spending by consumers
Less income received by households
Therefore consumption tax + income tax revenue ⬇
Therefore government has to spend more budget on unemployment benefits
Increase in Income Inequality
Typically low-income households are affected the greatest by unemployment
Limitations of UR Figure (UP)
Does not include Underemployment/Discouraged Workers/Underground Economy
Still an inefficient allocation of resources
Hence UR tends to be underreported
Doesn’t account for different population groups
Women UR > Men UR
UR differs for different races, genders, ages etc.
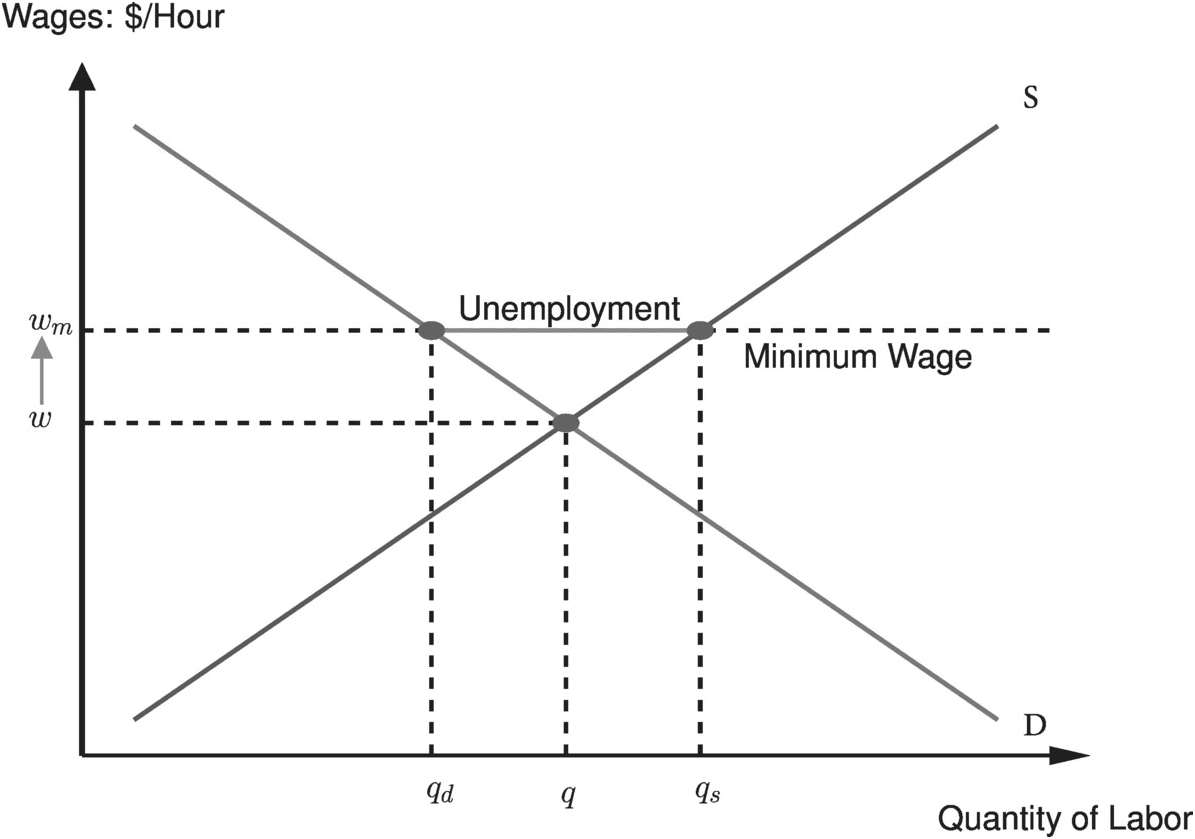
Minimum Wage Labor Market