History and Science of Dental Implants
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are potential reasons for missing teeth?
- Carious loss
- Endodontic failure
- Periodontal disease
- Trauma
- Congenitally absent
Why would we replace missing teeth?
- Aesthetic improvement
- Avoid social stigma associated w/ tooth loss
- Improve func
- Improve speech
- Space maintenance
What are the otions for an edentulous space?
- No tx
- Ortho closure
- Removable partial denture (RPD)
- Fixed bridge: RBB or conventional
- Dental implant
What are indications for RPDs?
- Long edentulous spans
- Multiple missing teeth on both sides of arch
- Transition to complete dentures
- Interim/immediate prosthesis
- Growing pt e.g. hypodontia
What are potential advantages for RPDs?
- Cheap
- Easy to construct
- Easy to modify
- Good aesthetics
What are potential disadvantages for RPDs?
- > plaque accumulation
- Increased gingival inflammation
- Candidiasis
- Increase in caries/root caries
Indications for fixed bridges:
Conventional (U) RBB (L)
- Short edentulous spans (1-2 missing teeth)
- Replacement of existing bridge
- Crowned or sound abutment tooth?
What are the advantages of RBBs?
- Fixed restoration
- Minimal preparation
- Good aesthetic
What are the disadvantages of RBBs?
- Bond failure
- Greying of abutment tooth
What are the advantages of conventional bridges?
- Fixed restoration
- Good aesthetics
What are the disadvantages of conventional bridges?
- Destructive
- Catastrophic failure
- Diff maintenance
Define: Dental implant (Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms)
prosthetic device made of synthetic material(s) implanted into the oral tissues beneath the mucosal &/or periosteal layer, & on/within
the bone to provide retention & support for a dental prosthesis
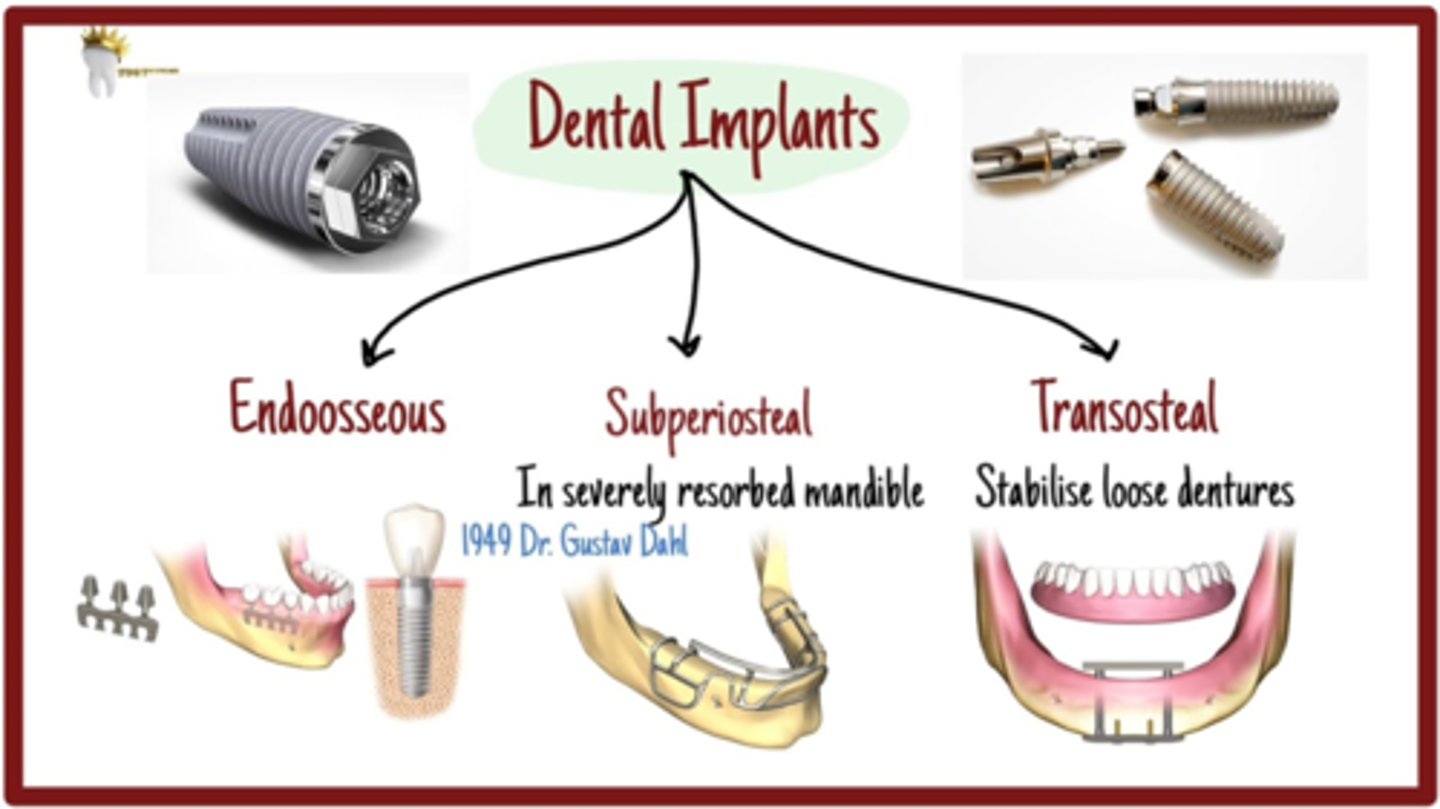
What are the three types of dental implants (anchorage)?
- Endosteal (within bone)
- Periosteal (sits on jaw)
- Transosteal (through bone)
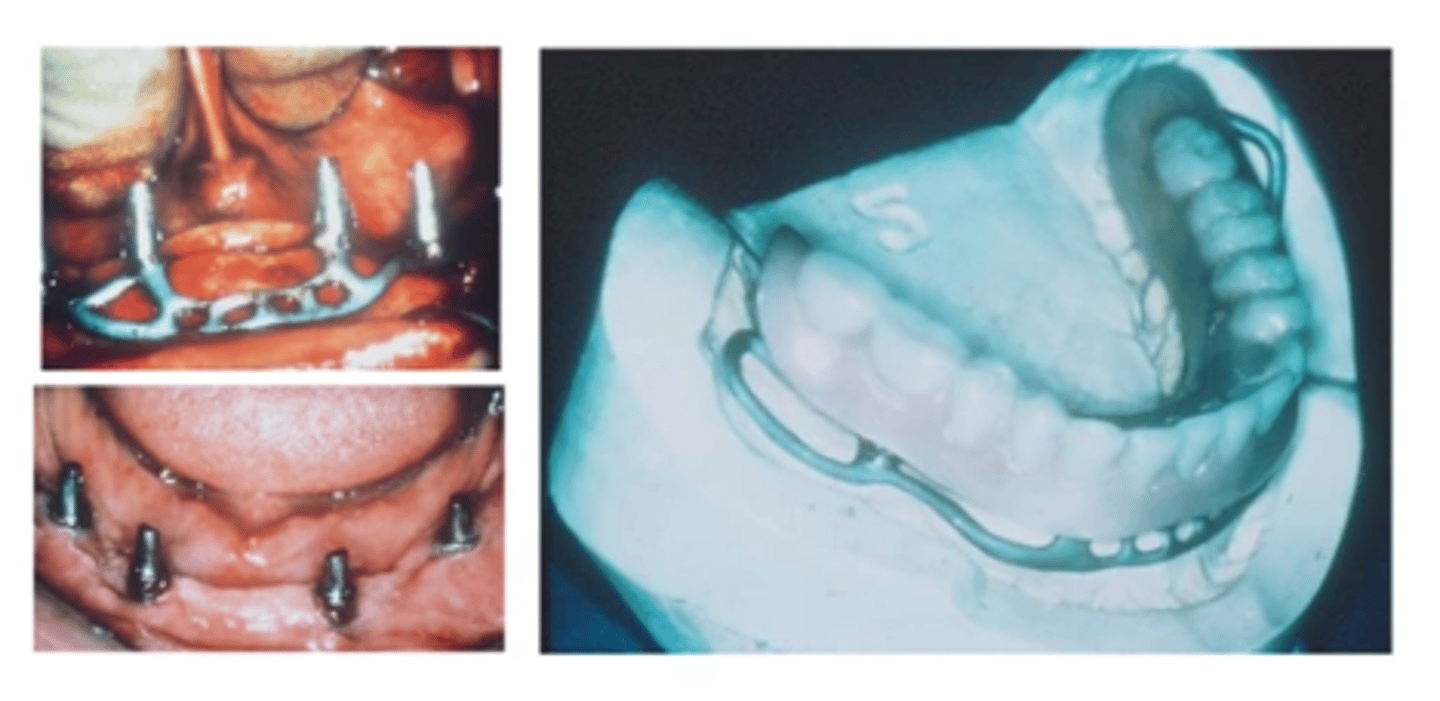
Periosteal Implant
- Metal implant framework rests directly on top of the bone, underlying the periosteum
- Provides attachment posts which extend through the gingival tissue for prosthesis anchorage
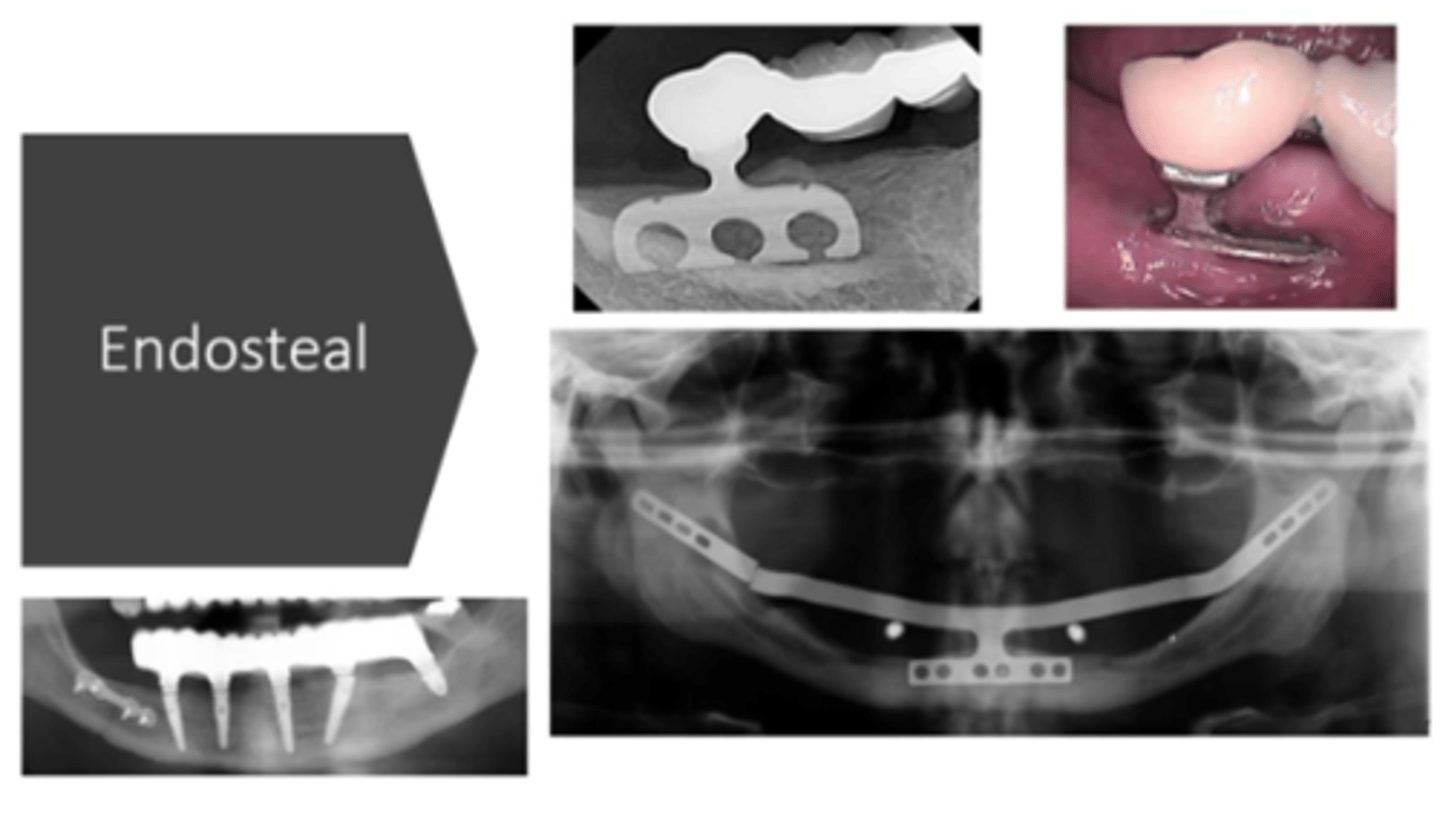
Endosteal Implant
- Contemporary dental implant
- Surgically placed in the bone & can be used to replace a single tooth/multiple teeth
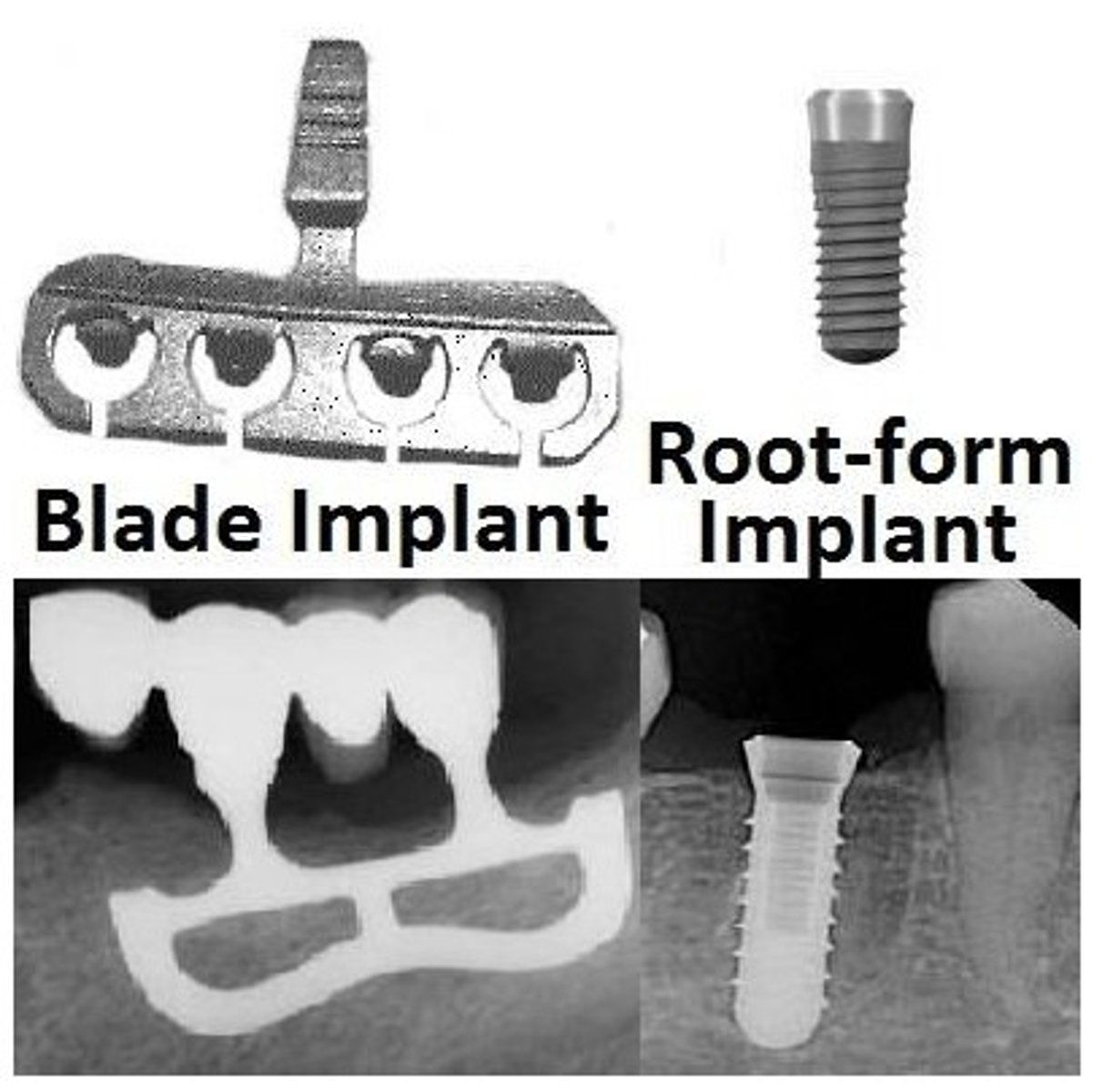
in pic: root form, blade, ramus frame
Transosteal Implant
- Large plate stabilised on the inferior border of the mandibular bone w/ posts extending through the gingiva;
- Used to anchor prostheses in diff situations
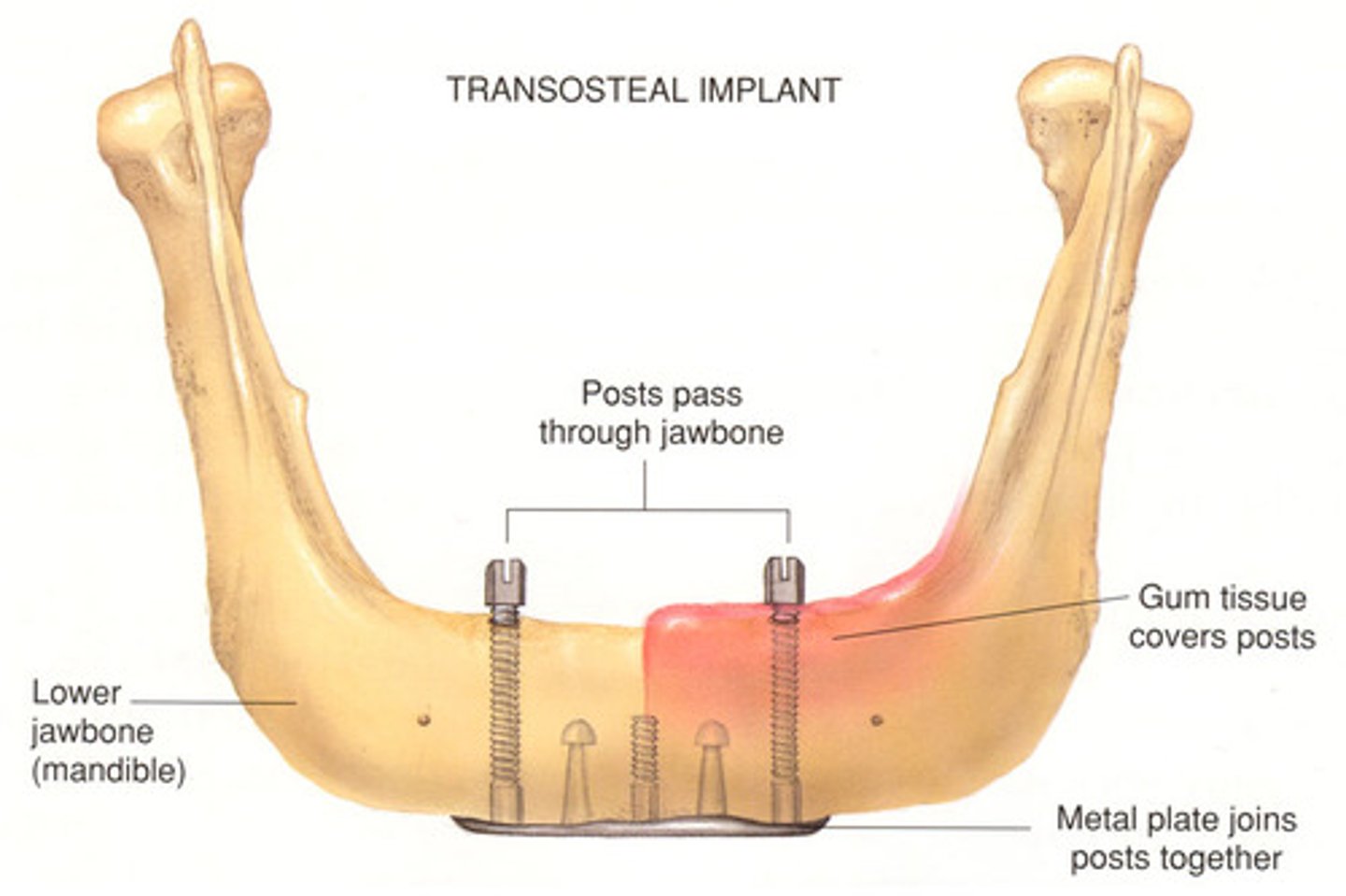
DIAGRAM: Dental implant - Blade
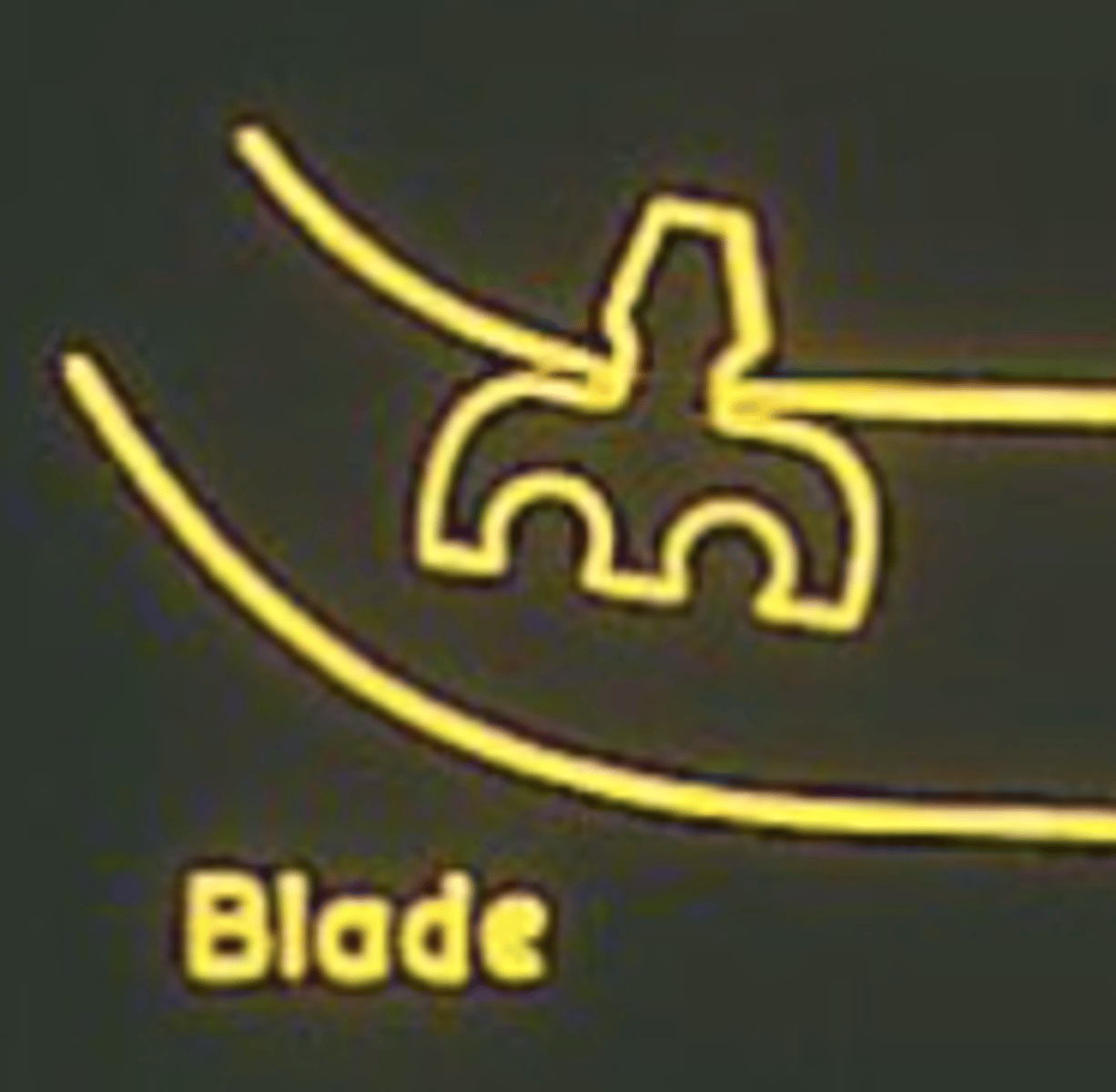

DIAGRAM: Dental implant - Root Form
What is osseointegration?
- "Direct structural & func connection b/t ordered, living bone & the surface of a load-bearing implant"
- Process of introducing certain metals, such as titanium, into living bone & forming a biocompatible bond w/ living bone
What is the process of osseointegration in implants?
1. Haemostasis: coagulum resorbed
2. Inflammatory reaction: angiogenesis, granulation tissue forms
3. Bone resorption through osteoclastic action
4. Release of growth factors
5. Attraction by chemotaxis of osteoprogenitor cells to the site
6. Osteoprogenitor (precursor) cells differentiate into osteoblasts
7. Bone deposition at the implant surface
What are the advantages to dental implants?
- Fixed restoration
- Tooth for tooth replacement
- Maintains alveolar bone
- Improves denture retention/support
- No preparation of
abutment teeth
- Good aesthetics
How could you deal with a patient who has gone out of the country for dental treatment? implants, veneers etc...
- as a HC prof, can only deal w/ pain & infection
- repairs etc... to go back to where had in the first place
- can take out, but no options for replacment
- NHS will not maintain
What are the disadvantages to dental implants?
- Surgical procedure
- Technique sensitive
- High cost
- Significant maintenance requirements
- Relies on availability of bone stock
- Contraindicated for various comorbidities
What are most commonly used contemporary dental implants?
root-form endosseous implants
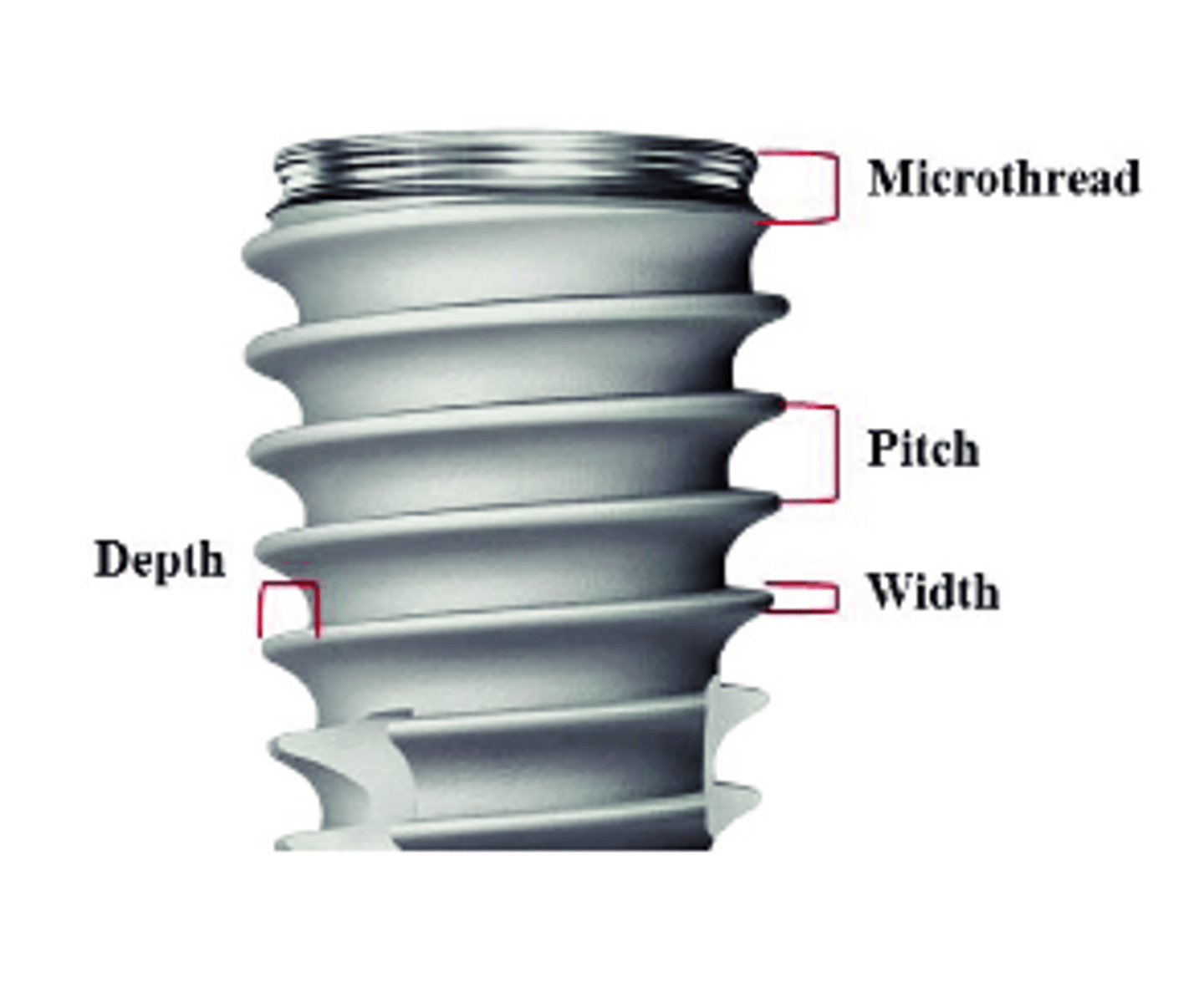
Variations in implant design...
- Shape
- Length
- Diameter
- Surface topography
Variations in implant design: Shape
- Parallel cylindrical
- Tapered cylindrical
- Thread design: shape, pitch, depth/width
Variations in implant design: Length
Usually choose one similar to root you are replacing (13-15mm standard)
Variations in implant design: Diameter
- 3.5mm standard
- 3mm not usually recommended for high load bearing areas
- Mini-implant: atrophic mandible, v small diameter
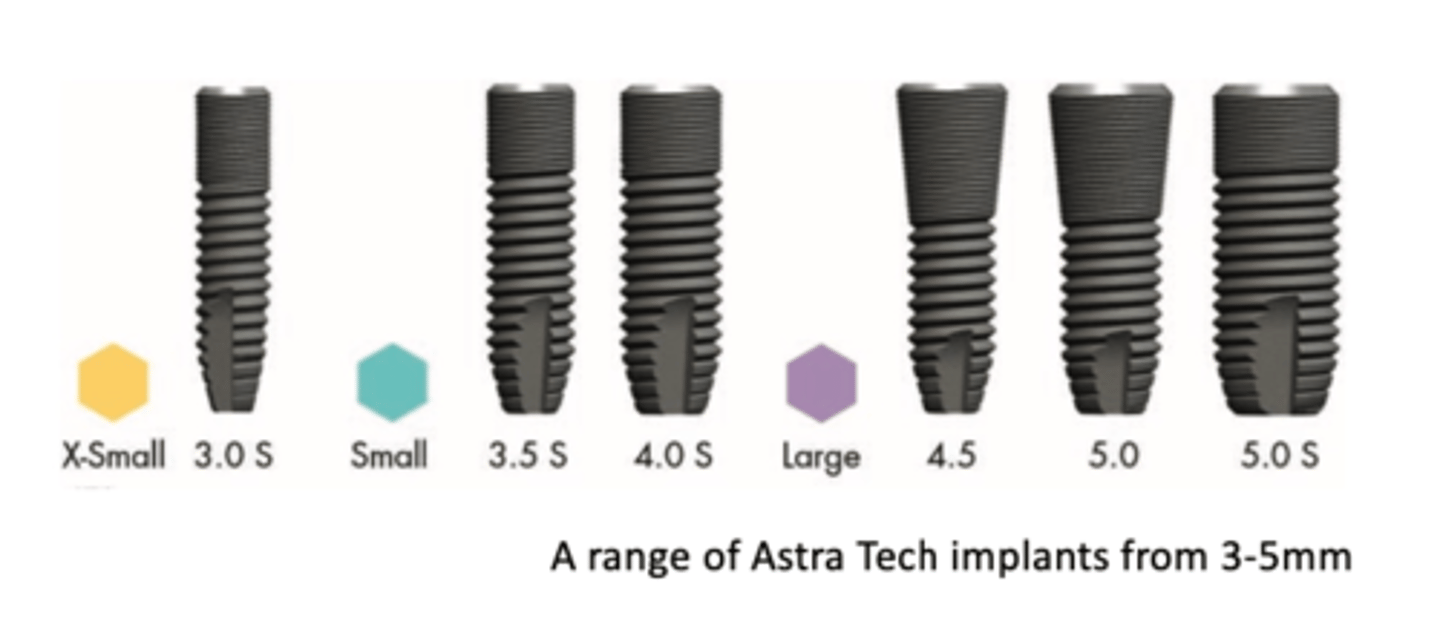
NDI
narrow dental implant ≤3.5mm
What are the three different categories of NDIs?
1 - <2.5mm
2 - 2.5-<3.3mm
3 - 3.3-3.5mm
Variations in implant design: Surface topography
- Surface roughness
- Surface coatings
- Surface preparation: sandblasted/air abraded w/ titanium oxides (‘moderately rough’)

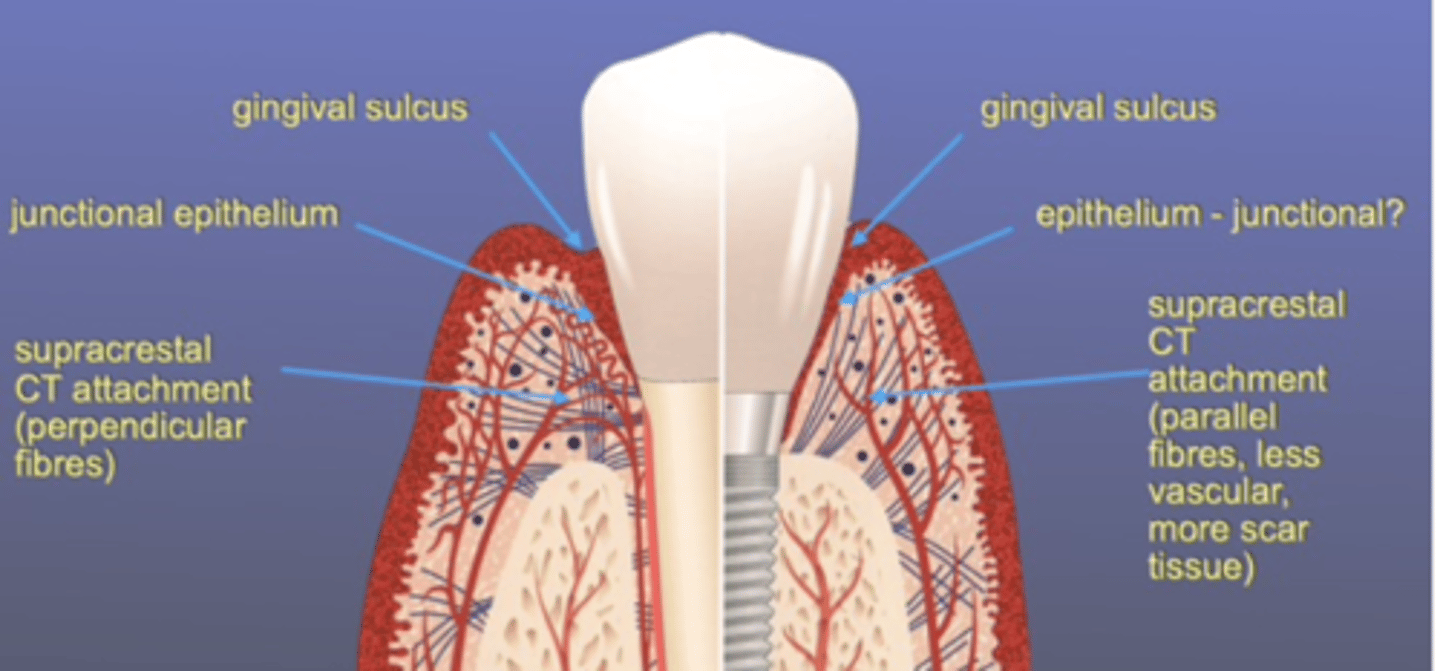
Soft tissue response consideration to implants:
Fibres are parallel & perpendicular so BL can be slower than in implants (bacteria can penetrate implant sulcus much easier bc it goes straight down)
implant - epithelial tissue attachment (less robust than CT)