Health Assessment of Female and Male Genitalia
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
Specimen collection equipment
Items needed for collecting specimens, including drapes, speculum, gloves, water-soluble lubricant, sterile cotton swabs, glass slides, wooden or plastic spatula, cervical brush devices, cytologic fixative, and culture plates or media.
Lithotomy position
Positioning of the patient for examination with legs apart and supported.
Mons pubis inspection
Expected findings include smooth and clean skin; unexpected findings may include improper hygiene.
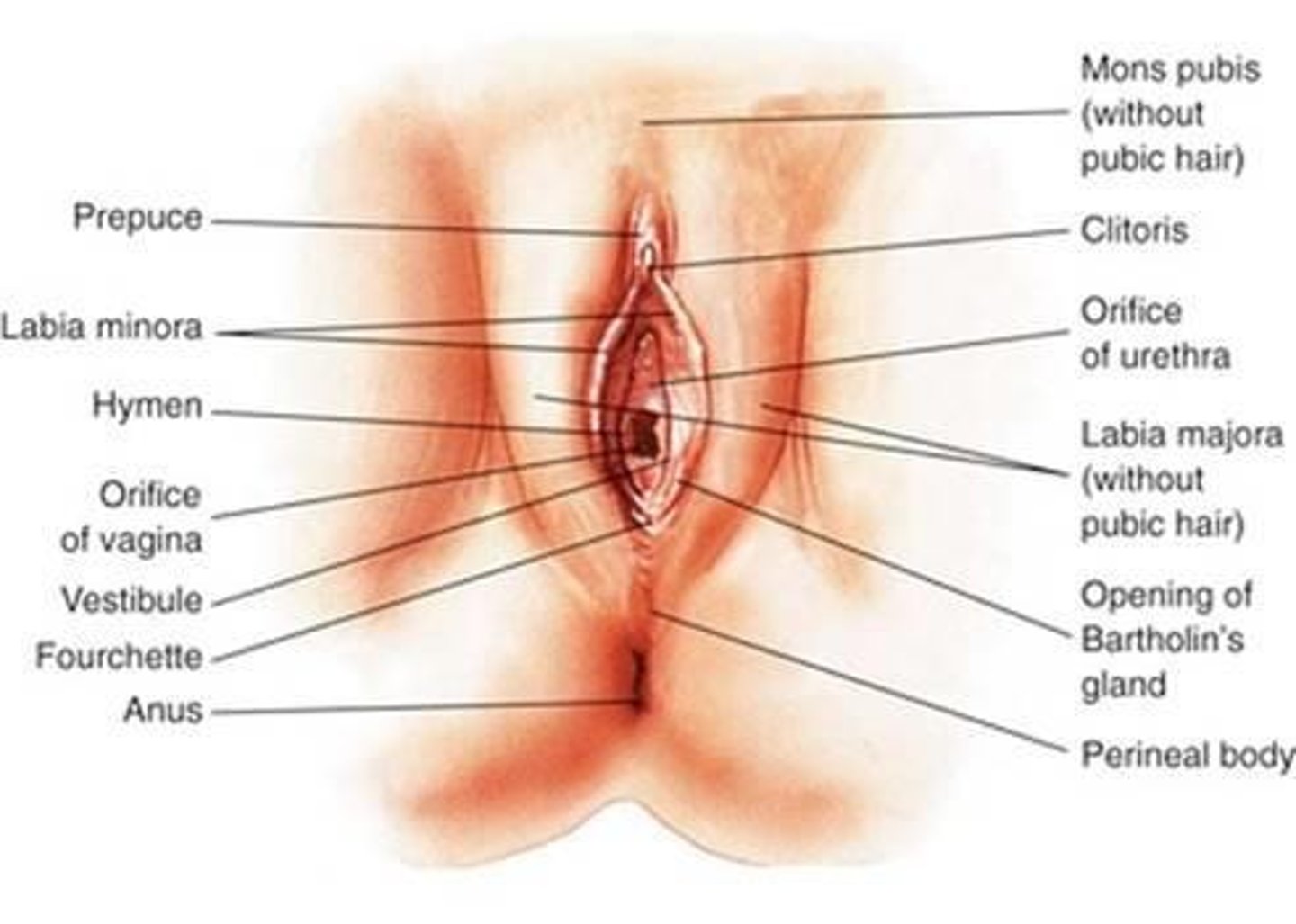
Pubic hair inspection
Expected findings include regularly distributed female pubic hair; unexpected findings may include nits or lice.
Labia majora inspection
Expected findings include gaping or closed, dry or moist, shriveled or full, soft and homogeneous tissue, usually symmetric; unexpected findings may include swelling, redness, tenderness, discoloration, varicosities, obvious stretching, or signs of trauma or scarring.
Labia minora inspection
Expected findings include moist, dark pink inner surface, soft and homogeneous tissue; unexpected findings may include tenderness, inflammation, irritation, excoriation, caking of discharge, discoloration, ulcers, vesicles, irregularities, or nodules.
Clitoris inspection
Expected length is 2 cm or less and diameter is 0.5 cm; unexpected findings may include enlargement, atrophy, inflammation, or adhesions.
Urethral meatus inspection
Expected findings include a slit or irregular opening close to or in vaginal introitus, usually midline; unexpected findings may include discharge, polyps, caruncles, fistulas, lesions, irritation, inflammation, or dilation.
Vaginal introitus inspection
Expected findings include a thin vertical slit or large orifice with irregular edges, moist tissue; unexpected findings may include swelling, discoloration, discharge, lesions, fistulas, or fissures.
Milk Skene glands
Expected findings include no discharge or tenderness; unexpected findings may include discharge or tenderness.
Bartholin glands palpation
Expected findings include no swelling; unexpected findings may include swelling, tenderness, masses, heat, fluctuation, or discharge.
Vaginal muscle tone test
Expected findings include fairly tight squeezing by some nulliparous women, less so by some multiparous women; unexpected findings may include protrusion of cervix or uterus.
Cervix location
Expected findings include midline cervix that may point horizontally, anteriorly, or posteriorly; unexpected findings may include deviation to right or left.
Bulging and urinary incontinence inspection
Expected findings include no bulging; unexpected findings may include bulging of anterior or posterior wall, or urinary incontinence.
Perineum palpation
Expected findings include smooth perineum surface, generally thick and smooth in a nulliparous woman, thinner and rigid in a multiparous woman.
Perineum surface
Smooth—generally thick and smooth in a nulliparous woman, thinner and rigid in a multiparous woman. Possible episiotomy scarring in women who have borne children.
Tenderness
Inflammation, fistulas, lesions, or growths.
Skin characteristics
Skin darkly pigmented and possibly coarse.
Scarring
Lesions, inflammation, fissures, lumps, skin tags, or excoriation.
Speculum examination
If you touched the perineum or anal skin while examining the external genitalia, change gloves before beginning internal examination.
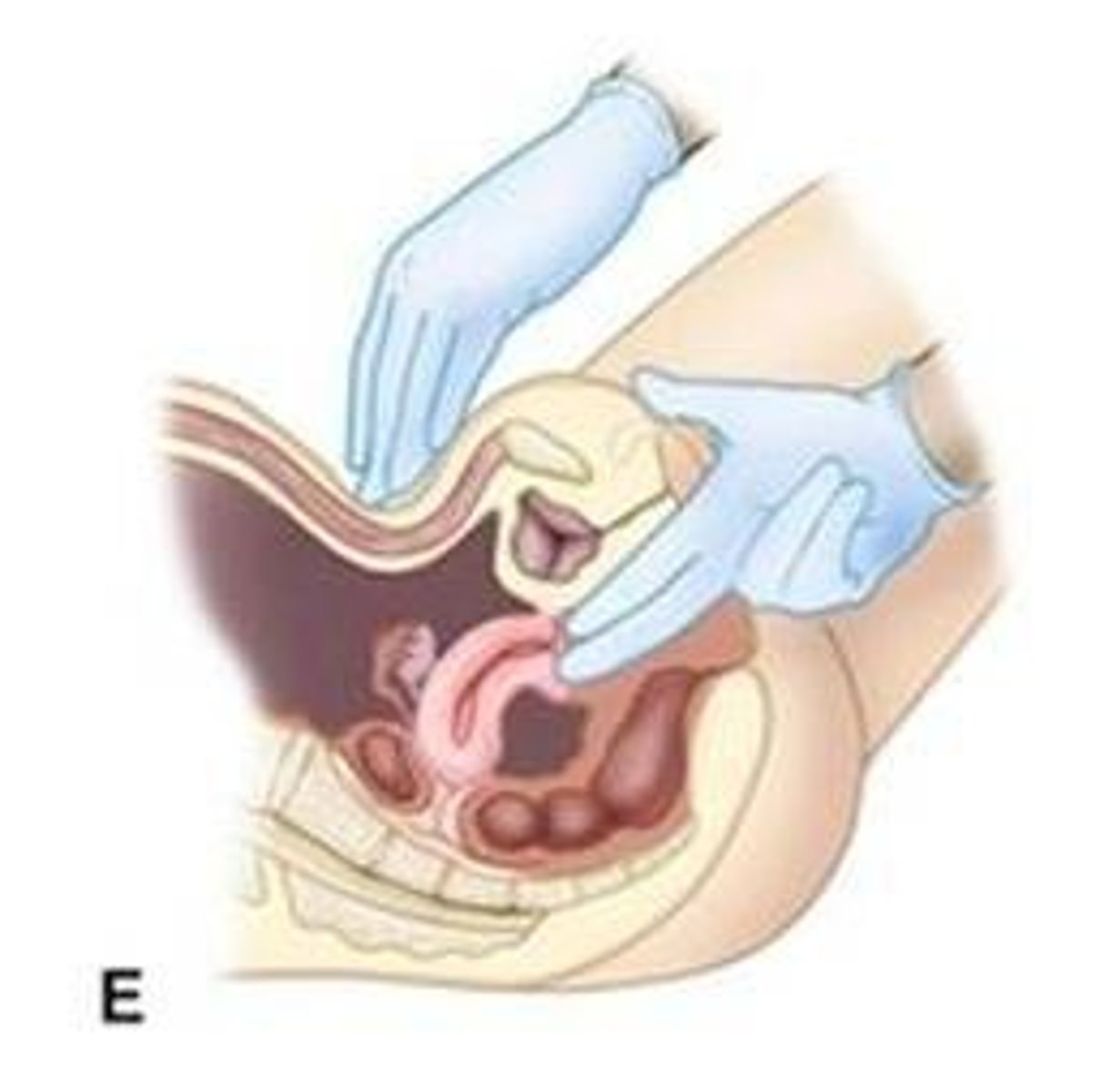
Lubrication
Lubricate speculum and gloved fingers with water or water-soluble gel lubricant. Water is preferred if obtaining a Pap smear.
Speculum insertion
Insert speculum along path of least resistance, often slightly downward, avoiding trauma to urethra and vaginal walls.
Cervix color
Evenly distributed pink. Symmetric, circumscribed erythema around os can be expected.
Cervix position
In midline, horizontal or pointing anteriorly or posteriorly. Protruding into vagina 1 to 3 cm.
Cervix size
3 cm in diameter.
Cervix shape
Uniform.
Cervix surface characteristics
Surface smooth. Possible symmetric, reddened circle around os (squamocolumnar epithelium). Possible small, white, or yellow, raised round areas on cervix (nabothian cysts).
Discharge characteristics
Odorless, creamy or clear, thick, thin, or stringy (often heavier at midcycle or immediately before menstruation).
Size and shape of os
Nulliparous woman: Small, round, oval. Multiparous woman: Usually a horizontal slit or irregular and stellate.
Vaginal wall inspection
Vaginal wall color same pink as cervix or lighter; moist, smooth or rugated; and homogeneous.
Vaginal secretions
Thin, clear or cloudy, odorless secretions.
Unexpected cervix color
Bluish, pale, or reddened cervix (especially if patchy or with irregular borders).
Unexpected cervix position
Deviation to right or left. Protrusion into vagina greater than 1 to 3 cm.
Unexpected cervix size
Larger than 3 cm.
Unexpected cervix shape
Distorted.
Unexpected cervix surface characteristics
Friable tissue, red patchy areas, granular areas, or white patches.
Unexpected discharge characteristics
Odorous and white to yellow, green, or gray.
Unexpected size and shape of os
Slit resulting from trauma from induced abortion, difficult removal of intrauterine device (IUD), or sexual abuse.
Unexpected vaginal wall characteristics
Reddened patches, lesions, pallor, cracks, bleeding, nodules, swelling. Secretions that are profuse; thick, curdy, or frothy; gray, green, or yellow; or malodorous.
Vaginal Smears and Cultures
Vaginal specimens are obtained while the speculum is in place in the vagina but after the cervix and its surrounding tissue have been inspected.
Papanicolaou (Pap) smear
A test for cervical cancer that involves collecting cells from the cervix.
Standard precautions
Guidelines to prevent the transmission of infections during the collection of human secretions.
Palpate vaginal wall
To feel the vaginal wall while inserting fingers into the vagina.
Expected findings of vaginal wall palpation
Smooth and homogeneous.
Unexpected findings of vaginal wall palpation
Tenderness, lesions, cysts, nodules, masses, or growths.
Palpate cervix
Locate cervix with palmar surface of fingers, feel end, and run fingers around circumference to feel fornices.
Expected size, shape, length of cervix
Consistent with speculum examination.
Expected consistency of cervix
Firm in nonpregnant woman; softer in pregnant woman.
Unexpected consistency of cervix
Nodules, hardness, or roughness.
Expected position of cervix
In midline horizontal or pointing anteriorly or posteriorly, protruding into vagina 1 to 3 cm.
Unexpected position of cervix
Deviation to right or left, protrusion into vagina greater than 1 to 3 cm.
Mobility of cervix
Grasp cervix gently between fingers and move from side to side.
Expected mobility of cervix
1 to 2 cm movement in each direction, minimal discomfort.
Unexpected mobility of cervix
Pain on movement ('cervical motion tenderness').
Palpate uterus
Place palmar surface of outside hand on abdominal midline, halfway between umbilicus and symphysis pubis, and place intravaginal fingers in anterior fornix.
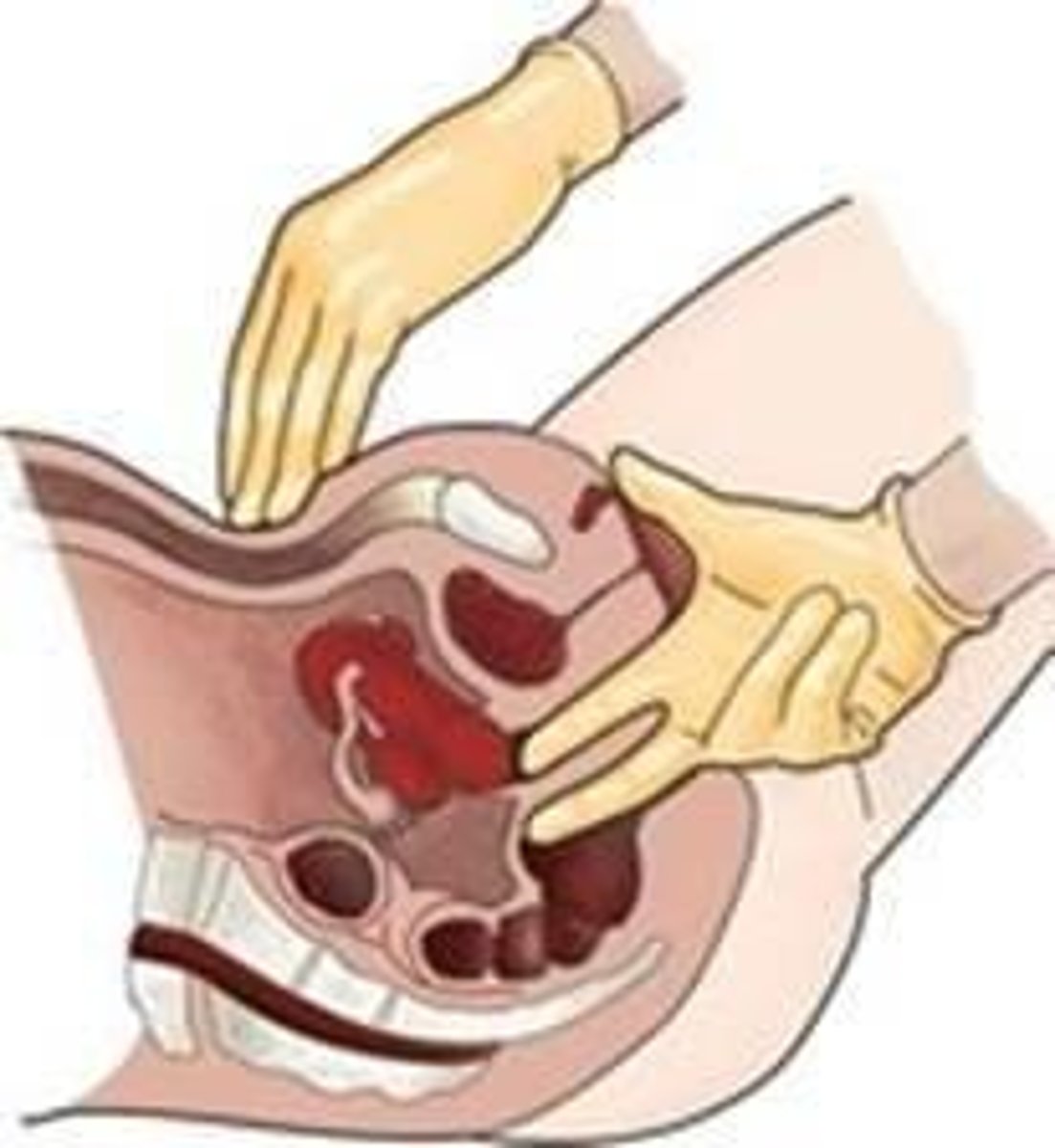
Expected location and position of uterus
In midline, horizontal, or pointing anteriorly or posteriorly, protruding into vagina 1 to 3 cm.
Unexpected location and position of uterus
Deviation to right or left, protrusion into vagina greater than 1 to 3 cm.
Size, shape, contour of uterus
Expected: Pear-shaped and 5.5 to 8 cm long (larger in all dimensions in multiparous women), contour rounded and, in nonpregnant women, walls firm and smooth.
Unexpected size, shape, contour of uterus
Larger than expected or interrupted contour or smoothness.
Mobility of uterus
Expected: Mobile in anteroposterior plane.
Unexpected mobility of uterus
Fixed uterus or tenderness on movement.
Palpate ovaries
Place fingers of outside hand on lower right quadrant. With intravaginal hand facing up, place both fingers in right lateral fornix.
Palpate ovaries
If palpable, ovaries should feel firm, smooth, slightly to moderately tender.
Palpate ovaries - Unexpected findings
Marked tenderness or nodularity. Palpable fallopian tubes.
Ovaries size
About 3 × 2 × 1 cm.
Ovaries size - Unexpected findings
Enlargement.
Ovaries shape
Ovoid.
Palpate adnexal areas
Adnexa difficult to palpate.
Palpate adnexal areas - Unexpected findings
Masses and tenderness. If adnexal masses are found, characterize by size, shape, location, consistency, tenderness.
Internal genitalia - Rectovaginal examination
This examination may be uncomfortable for the patient.
Assess sphincter tone
Even sphincter tightening.
Assess sphincter tone - Unexpected findings
Extremely tight, lax, or absent sphincter.
Palpate anterior rectal wall
Smooth and uninterrupted.
Palpate anterior rectal wall - Unexpected findings
Masses, polyps, nodules, strictures, irregularities, tenderness.
Palpate posterior aspect of uterus
Consistent with bimanual examination regarding location, position, size, shape, contour.
Palpate posterior aspect of uterus - Unexpected findings
Tenderness.
Palpate posterior rectal wall
Smooth and uninterrupted.
Palpate posterior rectal wall - Unexpected findings
Masses, polyps, nodules, strictures, irregularities, tenderness.
Note characteristics of feces
Light to dark brown.
Note characteristics of feces - Unexpected findings
Blood.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Symptoms occur 5 to 7 days before menses (luteal phase) and subside with onset of menses.
Endometriosis
Diagnosis confirmed by laparoscopy.
Condylomata acuminata (genital warts)
Flesh-colored, whitish pink to reddish brown, discrete, soft growths on labia, vestibule or perianal area.
Genital herpes
Small, red vesicles in genital area.
Vaginal infections
Subjective Data: Vaginal discharge, possibly accompanied by urinary symptoms. Sometimes asymptomatic.
Cervical carcinoma
Subjective Data: Often asymptomatic; sometimes vaginal bleeding. Objective Data: Hard granular surface at or near cervical os. Lesion can evolve to form extensive, irregular, easily bleeding cauliflower growth. Precancerous and early cancer changes detected by Pap smear, not by physical examination.
Uterine bleeding
Associated with various conditions including cervical carcinoma and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Subjective Data: Painful intercourse, painful urination, irregular menstrual bleeding, pain in the right upper abdomen. Objective Data: Acute PID: Very tender bilateral adnexal areas. Chronic PID: Bilateral tender, irregular, fairly fixed adnexal areas.
Ovarian cancer
Subjective Data: Persistent and unexplained vague gastrointestinal symptoms such as generalized abdominal discomfort and/or pain, gas, indigestion, pressure, swelling, bloating, cramps or feeling of fullness even after a light meal. Objective Data: May have no physical findings; on bimanual examination an enlarged ovary in premenopausal woman or a palpable ovary in postmenopausal women.
Midcycle spotting
Common Causes: Midcycle estradiol fluctuation associated with ovulation.
Delayed menstruation
Common Causes: Anovulation or threatened abortion with excessive bleeding.
Frequent bleeding
Common Causes: Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB), anovulation.
Profuse menstrual bleeding
Common Causes: Endometrial polyps, DUB, adenomyosis, submucous leiomyomas, intrauterine device.
Intermenstrual or irregular bleeding
Common Causes: Endometrial polyps, DUB, uterine or cervical cancer, oral contraceptives.
Postmenopausal bleeding
Common Causes: Endometrial hyperplasia, estrogen therapy, endometrial cancer.
Pediatric Variations
Examination techniques and expected findings in infants and children regarding genitalia.
Inspect external genitalia
Examine infant using the frog-leg position. EXPECTED: Genitalia of newborn reflect influence of maternal hormones. Labia majora and minora may be swollen, with labia minora often more prominent.
Inspect clitoris
EXPECTED: The clitoris of a term infant is usually covered by labia minora and may appear relatively large.
Inspect urethral meatus and vaginal opening
Inspect for discharge in infants and children. EXPECTED: Mucoid whitish discharge is frequently seen during newborn period and sometimes as late as 4 weeks after birth. Discharge may be mixed with blood.
Unexpected discharge in children
UNEXPECTED: Mucoid discharge from irritation by diapers or powder; any discharge in children.