Lecture 10: Environmental challenges and solutions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Identify the range and environmental consequences of major industrial and natural disasters
What is an example of industrial coal disaster and its solutions?
Mine Spoil Tip Collapse: The spillage/slip of the waste rock and soil removed during coal mining
Solutions:
regulation
revegetation/reclamation
understanding of controlling factors
→ physical, hydraulic and mechanical characteristics
→ climatic conditions
→ slope geometry
What is the famous Coal tip disaster?
1966 Aberfan coal tip
avalanche of black slurry which wiped out every building in its path, including the Pant Glas Junior school
144 lives were lost, including 116 children between the ages of 7 and 10
Oil disaster example: Alaska
Exxon-Valdez Spillage 1989
11 million gallons (125 olympic sized pools) over 800km coastline
400,000 seabirds and 4000 otters dead
$1b fines, $100m research costs
Result: 1990 Oil Pollution Act (US) e.g. double hulled oil tankers
Oil disaster example: Gulf of Mexico
Deepwater Horizon Blow out
11 people killed
780million litres (300 olympic swimming pools)
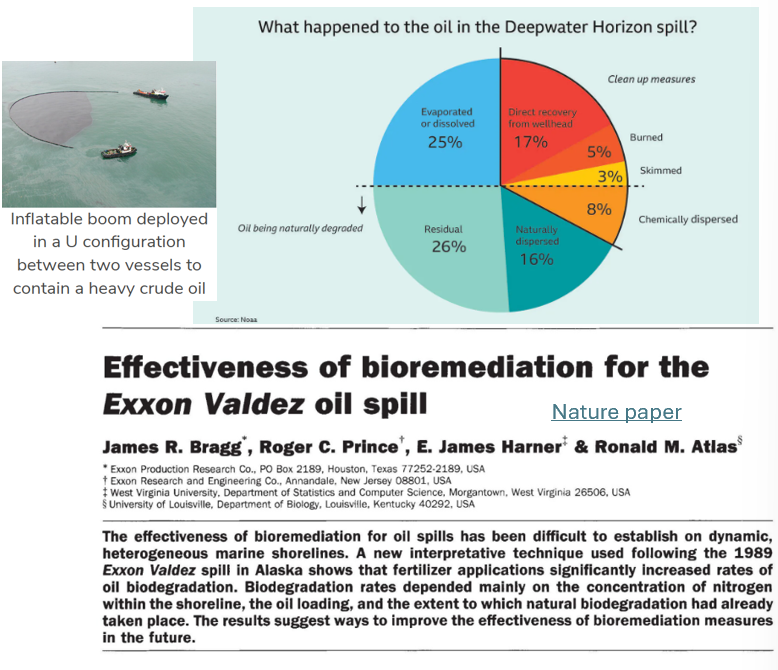
Oil spill solutions
soaking up using:
→ textiles, graphene, magnets, hair/furinflatable booms
skimming
→ Vacuuming the surface/scoopingdispersants
→ breaks oil into smaller droplets
→ sinks or degrades momre easilyNatural attenuation
→ Evaporation, bioremediation
Nuclear disasters: Japan
Fukishima Daiichi accident 2011:
earthquake triggered a 15m tsunami which disabled the power supply and cooling of 3 reactors
level 7 on the international nuclear and radiological event scale due to high radioactive releases over days 4-6
after 2 weeks they were stable again
the main ongoing task was to prevent release of radioactive materials, particularly in contaminated water
no deaths or cases of radiation sickness
Nuclear disasters: Ukraine
Chernobyl 1986:
flawed reactor design and lack of safety culture
steam explosion and fires released 5% reactor core e.g. Sr, Cs and I
30 immediate deaths, in 2005 the UN predicted a further 4,000 deaths from radiation exposure
new safe confinement structure (NSC) was completed in 2017
sealed buildings allows remote dismantling of 1986 structure and removal of the contaminated materials
What are the long term effects of chernobyl?
Chernobyl Exclusion Zone (CEZ) covers 2,800 square km of thick forests
This zone represents the third-largest nature reserve in mainland Europe
Haven for wildlife such as lynx, bison, deer and other animals
accidental dna iconic experiment in rewilding
Chernobyl today
2019: NPP started processing the liquid radioactive waste plant - during the first week 2,755kg of liquid radioactive waste was successfully processed
2025: Chernobyl gets go ahead for solid radioactive waste processing (WNN: World Nuclear News)
Hydroelectric power disasters
Displacement of people due to flooding
River systems:
many systems support unique endemic species that are highly adapted to specific flow conditions
altering these environments can lead to extinction or genetic bottlenecks
e.g. the Yangtze River Dolphin is functionally extinct with damming contributiong to habitat loss and population fragmentation
Balbina:
7 species of endemic fish wiped out in brazilian amazon hydroelectric dam area
creation of the dam in the amazon has flooded ~2,400km² rainforest
biodiversity loss + isolation of species on artificial islands
transformed fast flowing river to static environments
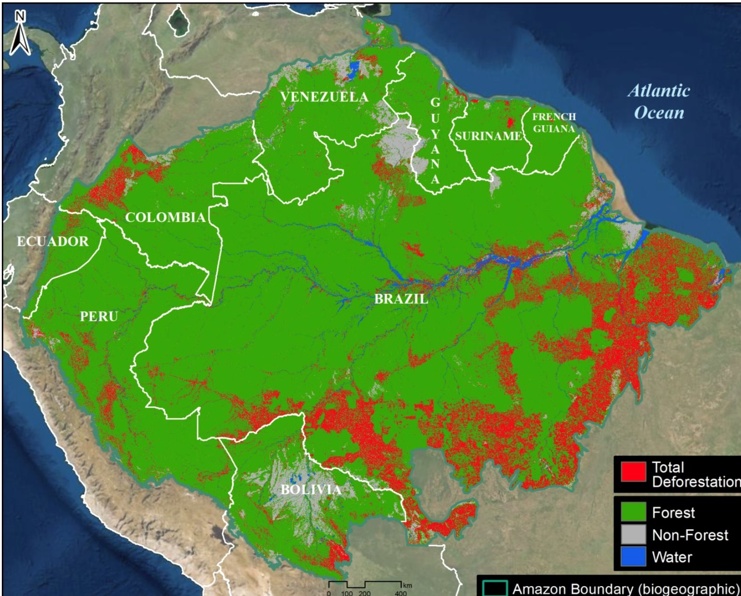
Deforestation: Amazon rainforest
~50,000 species become extinct each year due to deforestation
60M indigenous people worldwide depend on forests for their livlehoods
deforestation accounts for ~10% of global emissions
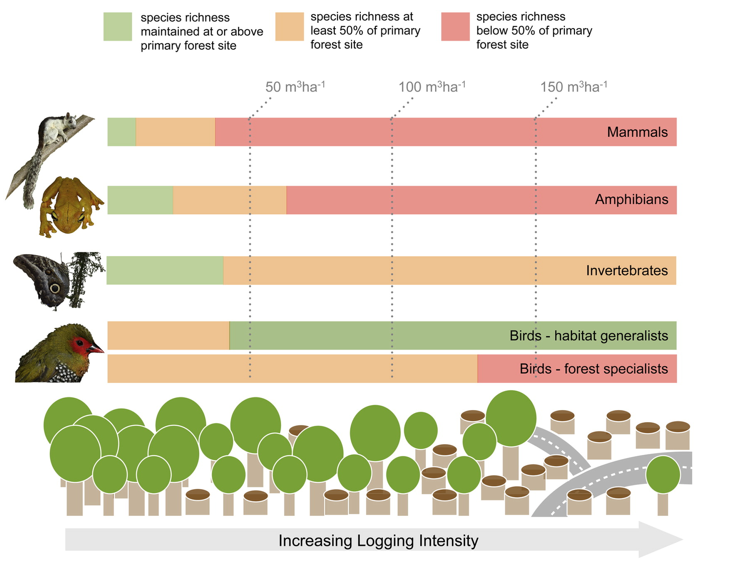
What are the tipping points of biodiversity in relation to deforestation?
organism richness decreases with logging intensity
increases in bird species richness are caused by the influx of habitat generalists
logging intensity of 38m³/ha would halve mammal richness
63m³/ha would halve amphibian richness
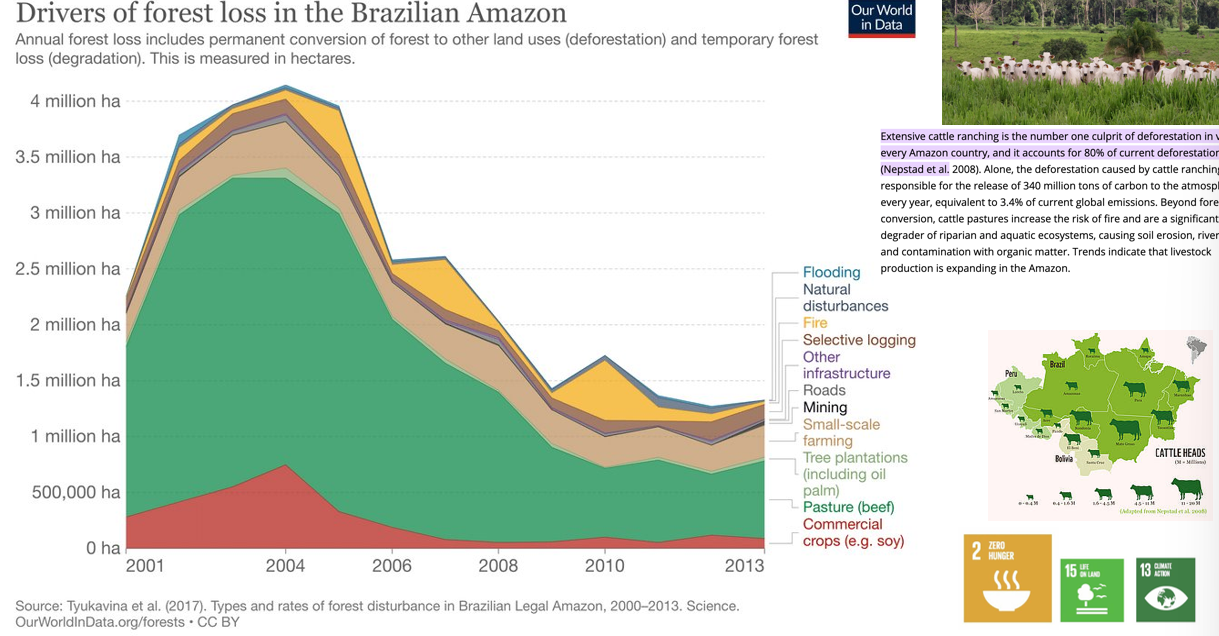
What are the key drivers of forest loss in the Amazon?
CATTLE FIELDS
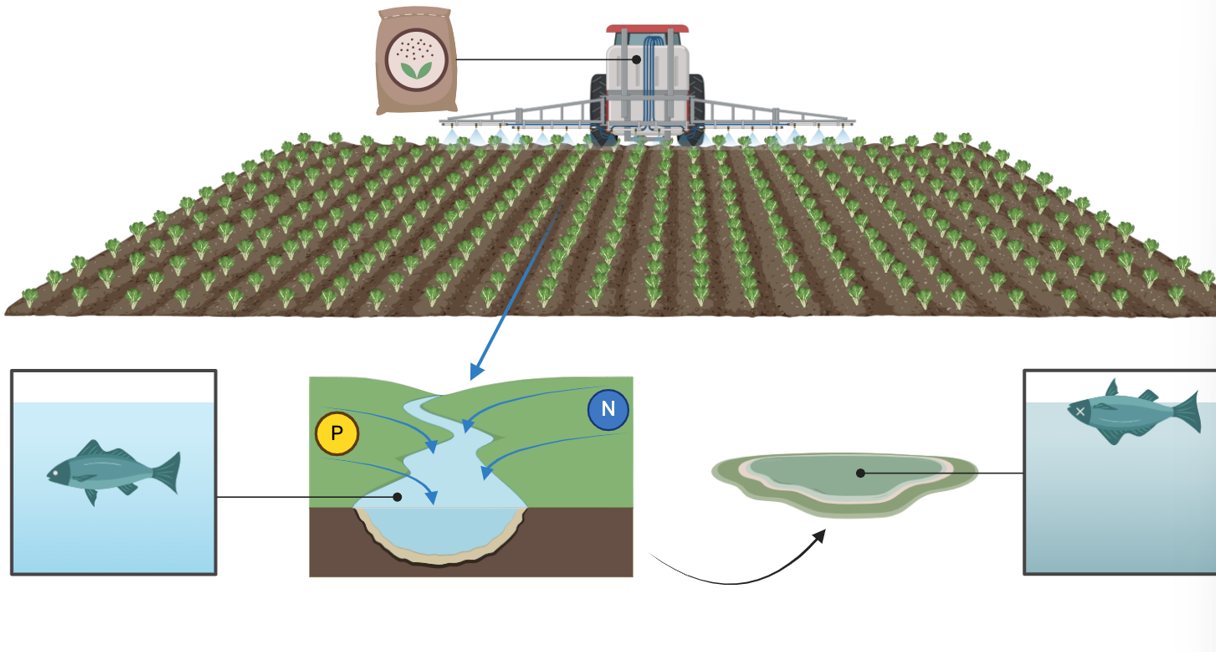
What is eutrophication?
Process by which a body of water becomes overly enriched with nutrients (N and P), often due to runoff from agriculture and sewage
Effects:
excessive algae growth
oxygen depletion (hypoxia)
death of aquatic life
poor water quality and bad odors
Worlds largest hypoxic zone:
Gulf of Mexico dead zone
harm to shrimping industry and kills fish
Effects of mining and its remediation strategies
Effect: open cast ecosystem destruction
Remediation: Land reclamation e.g. China Clay Pit - Eden Project, UK
Effect: Underground mine collapse
→ e.g. Lily gold mine, Barberton South Africa - 3 fatalities
Effect: Acid Mine Drainage - occurs at abandoned mine sites, forms iron oxides and contaminates water which affects water quality
→ e.g. Rio Tinto, Spain - long term water and soil contamination
Remediation: limestone neutralization, constructed wetlands, anoxic limestone drains, and active chemical treatments to raise pH and reduce metal toxicity.
Effect: Dam failure
→ e.g. Minas Gerais, Brazil 2019 - 270 fatalities, 12m m³ iron ore tailings - severely affected quality of water in Paraopeba River
Effect: Processing
→ e.g. Ajka Alumina plant, Hungary 2010 - 700,000m³ of highly caustic red mud slurry , 10 fatalities, contaminated several towns
Arsenic in drinking water
3 in 10 people globally lack access to safely managed drinking water

Lecture summary
