2.3 - Glutamate and Aspartate
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
neurotransmitter
chemical released at synapse by a neuron that specifically affects postsynaptic cell
hormones
postsynaptic cell released into bloodstream to act on distant targets
Autocoids
acts on tissue from which it was released
neuroactive peptides
short polymers of aa’s; synthesized from genes (ex: endorphins)
small-molecule transmitters
charged molecules, derived from substrates of metabolism regulated at one key enzymatic step
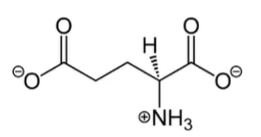
glutamate
- most abundant excitatory aa NT in CNS
- key compound in cellular metabolism
glutamate synthesis (TCA cycle)
oxidative deamination of alpha-ketoglutarate
glutamate breakdown/deanimation (TCA cycle)
via glutamate dehydrogenase → alpha-ketoglutarate
glutamine synthetase
enzyme used for glutamate synthesis in glia cell
glutaminase
enzyme used for glutamate breakdown in neurons
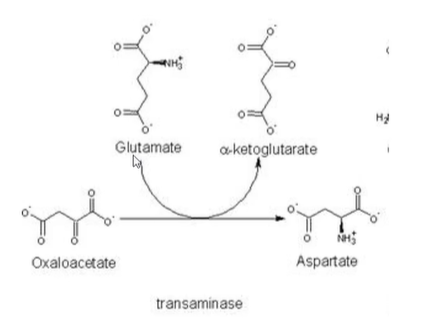
aspartate
excitatory aa NT that is the conjugate base of L-aspartic acid
aspartate synthesis
transamination of oxaloacetate
N-methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) and AMPA
mimic glutamate as a NT by binding to a subset of glutamate receptors
reuptake transporters
help glutamate and aspartate cross BBB and membranes
excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)
- Unique class of active transport reuptake transporters with five protein subtypes found in neurons and glia.
- Function to remove glutamate or aspartate from the synapse.
- Transport occurs by coupling the influx of the negatively charged amino acid with Na⁺ moving down its electrochemical gradient.
vesicles
highly concentrate small molecule NTs that make ready for quick release in synapse
Vesicular transporter (VGLUT)
- 3 subtypes; 12-transmembrane spanning proteins
- catalyzed uptake of charged NT into vesicles
- ATP-dependent H+ pump creates pH gradient
- swaps 2H+ for charged NT, driving into vesicle against [gradient]
false transmitters
NT analogs + packages the same, but show decreased efficacy
glutamate receptors
Kainate, NMDA, AMPA, Metabotropic
Kainate
- ion channel (Na+ in, K+ out)
- excitatory and desensitizes neurons
- found in spinal cord (pain signal)
NMDA
- ion channel (Ca2+, Na+ in; K+ out)
- complex regulation
- Mg2+ blocks, requires depolarization opening modulated
- acts ac coincidence detectors (activation and recent or not)
NMDA locations
hippocampus, neocortex, etc.
AMPA
- ion channel (Na+ in, K+ out)
- excitatory, and very fast
- learning and memory
Metabotropic Glutamate receptors
- 8 types; linked to Gi or Gq proteins
- inhibitory effects → slower, but long duration
ionotropic glutamate receptors
5 subunit pentamer
Group I Metabotropic (mGluR)
slow excitatory receptors
Group II and III mGluRs
slow inhibitory receptors
mGluRs
7 transmembrane proteins (GPCR)
synaptic plasticity
long-term potentiation changes synaptic strength w/ INCREASE stimulation
long-term potentiation
basis for learning and memory formation; cognition
reuptake
Synaptic activity of glutamate is terminated by ______.
fate of glutamate after uptake
- glial cells → metabolized (via glutamine synthetase)
- presynaptic → recycled back into vesicles
Glutamate roles
brain development, motor control, and pain
brain development (ref. Glu)
regulates growth cones and promotes synaptogenesis (neuron contact)
motor control (ref. Glu)
initiates and sets speed of locomotion
mesencephalic locomotor region (MLR)
- stimulates reticulospinal pathway → ↑ signaling and locomotion
pain
NMDA-R in A-delta and C fibers the basis for fast transmissions of nociception
Epilepsy (ref. Glu)
excess glutamate-mediated excitation and depolarization in foci area correlated to seizures
oxidative stress and excitotoxicity
- excess extracellular Glu increases NMDA signaling = ↑ intracellular Ca2+
- ↑ Ca2+ promotes overactivity = ↑ toxicity (peroxide and free radicals)
Mechanisms of cell death (ref. Epilepsy)
- mitochondria damage from ↑ Ca2+
- promotion of apoptotic transcription factor
NMDA receptor antagonists
reduce neuronal cell death
Ketamine and PCP
- NMDA receptor antagonist
- analgesics, hallucinogens
- disrupt motor control, memory, cognition