(c) (i) the importance of photosynthetic pigments in photosynthesis (ii) practical investigations using thin layer chromatography (TLC) to separate photosynthetic pigments
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To include reference to light harvesting systems and photosystems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
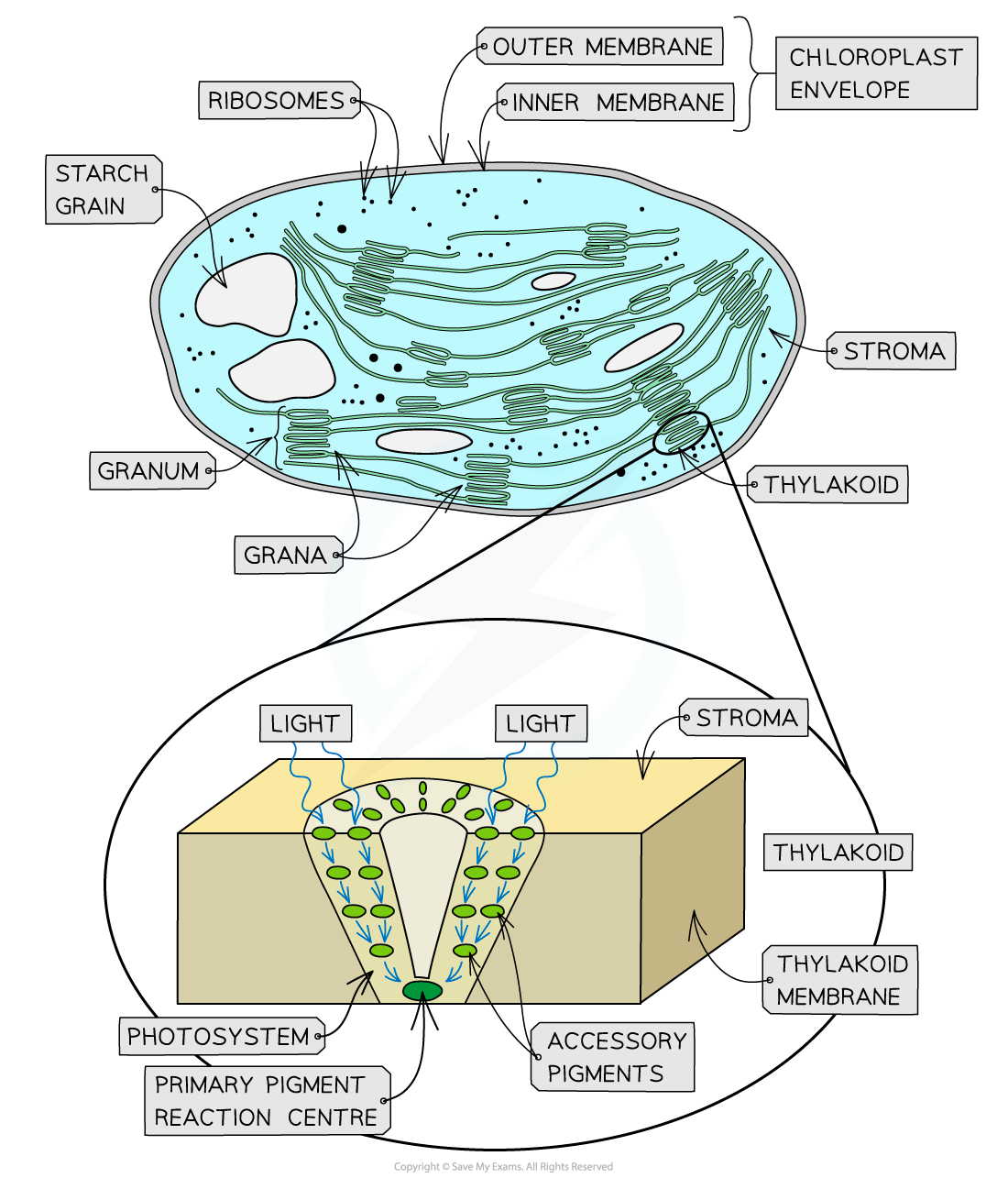
Photosynthetic pigments
Are within the thylakoid membranes, which absorb different wavelengths of light
two types of pigments: chlorophylls and carotenoids
Chlorophylls absorb wavelengths in the blue-violet and red regions of the light spectrum
They reflect green light, causing plants to appear green
Carotenoids absorb wavelengths of light mainly in the blue-violet region of the spectrum
Pigment group | Name of pigment | Colour of pigment |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Pigment group | Name of pigment | Colour of pigment |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a Chlorophyll b | Blue-green Yellow-green |
| β carotene Xanthophyll | Orange Yellow |
Photosystems
are pigment molecules that are attached to proteins that are arranged in light-harvesting clusters
the different pigment molecules are arranged in funnel-like structures in the thylakoid membrane (each pigment molecule passes energy down to the next pigment molecule in the cluster until it reaches the primary pigment reaction centre)
There are two different photosystems, each with a specific form of chlorophyll a
Photosystem 1 (PSI), often referred to as P700
The chlorophyll a in this system has a maximum absorption of light at 700nm
Photosystem 2 (PSII), often referred to as P680
The chlorophyll a in this system has a maximum absorption of light at 680nm
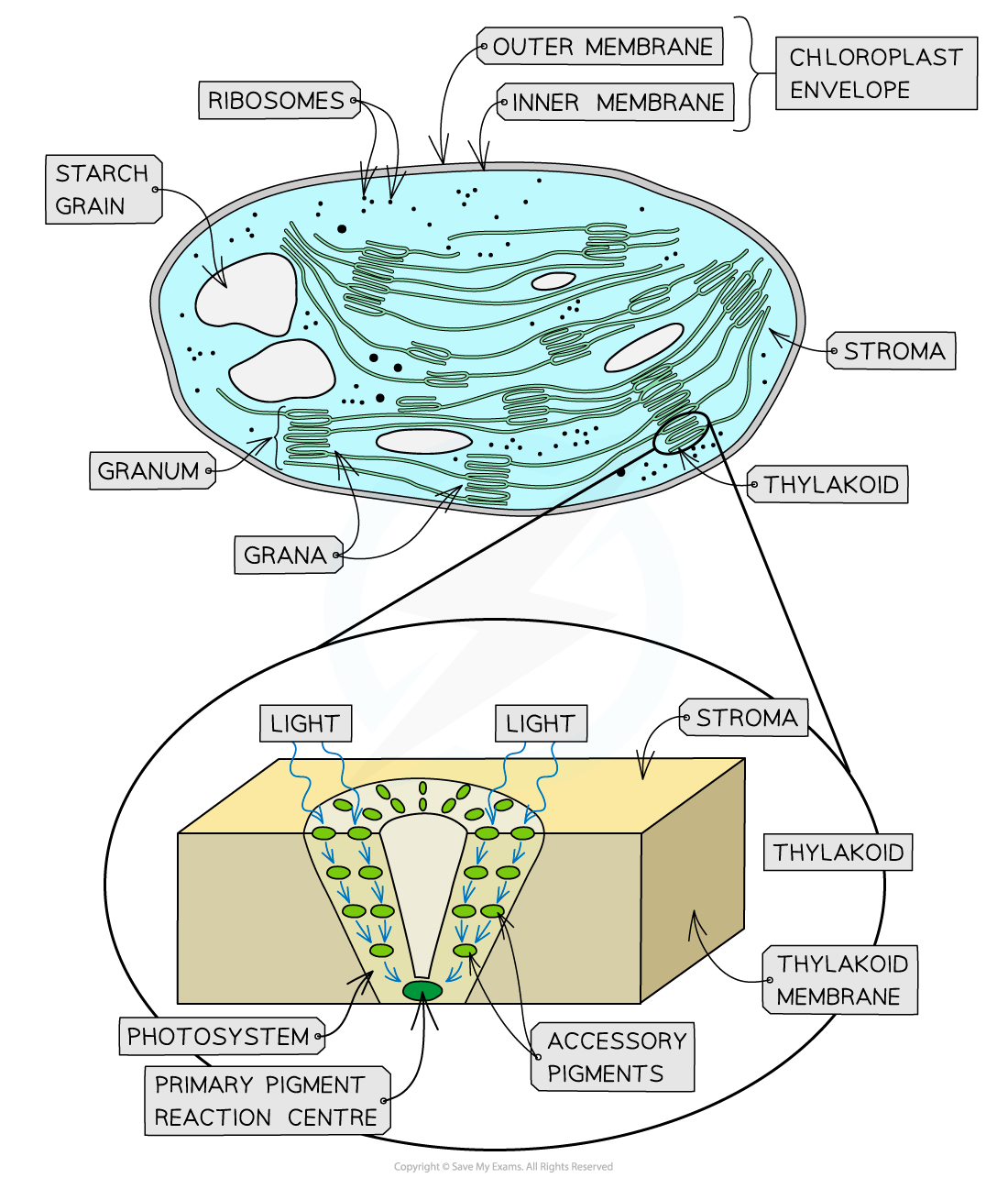
Photosynthetic pigments
a photosystem contains two types of photosynthetic pigments
primary pigments : are reaction centres where electrons are exited during the light-dependent reaction - in most chloroplasts the primary pigment is chlorophyll a
Accessory pigments: make up light harvesting systems. These surround reaction centres and transfer light energy to them to boost the energy available for electron excitement to take place