C2 Global Atmospheric Circulation
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Why are tropics warmer?
Distance of the atmosphere which insolation has to travel through
Lower latitudes: radiation travels a shorter distance through the atmosphere, less insolation is lost, hence they receive greater concentration of incoming energy
Higher latitudes: radiation travels a longer distance through the atmosphere, more energy is lost through absorption, reflection and scattering, hence they receive lower concentration of incoming energy
Surface area and angle of incidence
Lower latitudes: angle of incidence of insolation and Earth’s surface is higher, resulting in amount of incoming energy to be spread over a smaller area of the earth
Higher latitudes: angle of incidence of insolation and Earth’s surface is lower, resulting in amount of incoming energy to be spread over a larger area of the earth
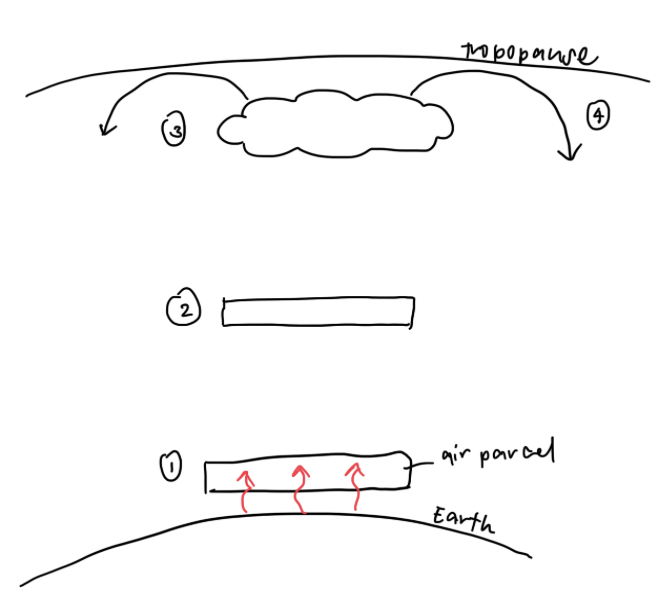
Rising Limb of Hadley
Due to transfer of heat from earth’s surface to air parcel above, air parcel is warmer than surrounding air, causing it to expand, lower in density and rise
As it rises, it continues to undergo further expansion and adiabatic cooling (where temperature decreases due to expansion)
Potential to hold water vapour decreases, relative humidity increases, air parcel becomes saturated and condensation occurs forming clouds
When it reaches the tropopause, it will diverge polewards and start to cool
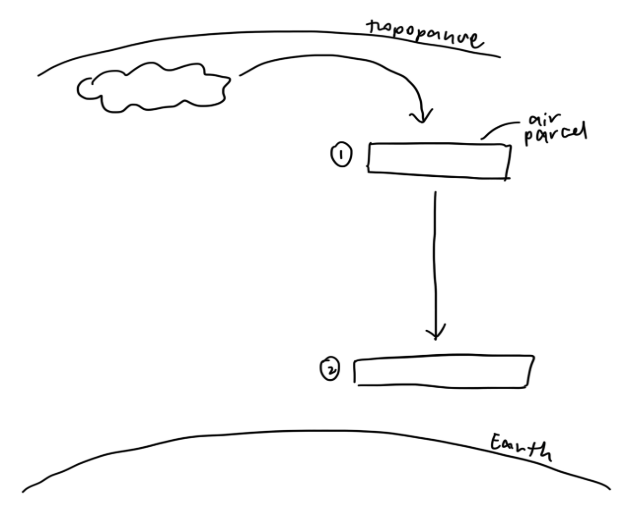
Descending Limb of Hadley
Temperature of cooled air parcel is lower than surroundings, contracts and increases in density, causing it to sink, resulting in stable atmospheric conditions
Undergoes adiabatic warming (gain in temperature due to compression), the maximum amount of water vapour it can hold increases. Subsiding air parcel is relatively dry and hence saturation is seldom reached, resulting in lack of cloud cover and little precipitation at descending limb
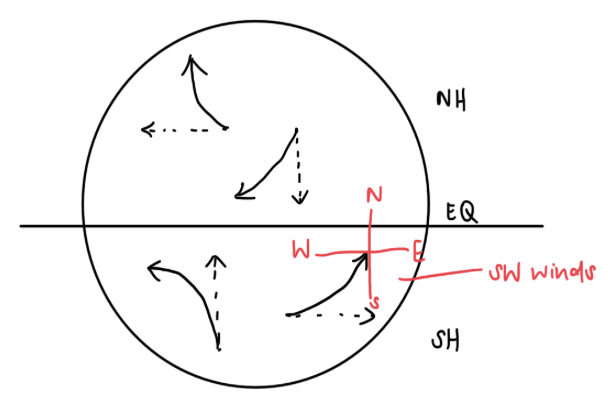
Coriolis Effect
Due to Earth’s rotation, it produces the coriolis effect
NORTHERN HEM: deflects to the right
SOUTHERN HEM: deflects to the left
Trade Winds
Ascending limb becomes an area of low pressure as air parcel rises
Descending limb becomes an area of high pressure as air parcel sinks
Creates a pressure gradient force, causing air to move from area of high pressure to low pressure, forming trade winds
Due to deflection of winds because of Coriolis Effect, NE and SE trade winds are formed
Trade winds converge at the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
ITCZ
Characteristics:
Towering cumulonimbus clouds and intense rainfall
Intense heating
Shifting
July: pressure belt shifts northwards due to overhead sun at Tropic of Cancer
January: pressure belt shifts southwards due to overhead sun at Tropic of Capricorn
Shape of ITCZ: not uniformly straight due to differential rates of heating