HS 200 Exam #2
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Chance Seedling (Cultivar Type)
Happened to grow by itself, no intervention
Discovered, then developed
No difference in botanical nomenclature between this and genetic mutations
Variant Plant
Variation of a straight species
Self-perpetuating
Characteristics that last thru generations; no humans involved to continue bringing out that specific trait
Come True from Seed (Species + Variety)
Grow up to look just like their parents
Genetic Mutation (Cultivar Type)
Occurs on an individual plant in a particular location, causes a genetic change (in genotype)
Discovered, then developed
No difference in botanical nomenclature between this and chance seedlings
Hybrid (Cultivar Type)
Just developed, NOT discovered; someone had the idea first
Genotype vs Phenotype
DNA vs Appearance
Cuttings
Pieces of a plant that’s treated a certain way in order to grow the parts that are missing
Grafting
Surgically connect one genome to another; they don’t mesh, they continue to grow as their respective genotypes
Trees (Ornamental)
Exposed trunks with canopy
Allee (Ornamental)
Trees that run along both sides of a path/road/etc
Shrubs (Ornamental)
Multi-stemmed with branches to the ground
Vines (Ornamental)
Climbs on something vertical
Ground Covers (Ornamental)
Grows along the ground
Evergreen (Winter Appearance)
Plants that retain each year’s set of leaves for 3-5 years
Deciduous (Winter Appearance)
Loses all of its leaves every autumn (more born in spring)
Woody (Growth Kind)
Tissue comprised of hard, permanent tissue called wood
Herbaceous (Growth Kind)
Soft, tender, and succulent tissue that’s not permanent (cold often damages/destroys this tissue)
Tropical (Temp Tolerance)
Will not tolerate freezing temps and below, often injured by cold → ex: tomatoes, orchids
First Frost Free Date (FFFD)
The date after which the chance of frost decreases; Raleigh, April 15th
Last Frost Free Date (LFFD)
The date after which the chance of frost increases; Raleigh, Oct 31
Subtropical (Temp Tolerance)
Tolerate short periods of freezing but not for prolonged periods of time (hours) → ex: citrus
Temperate (Temp Tolerance)
Tolerate long periods of freezing and below for prolonged periods of time (days) → ex: apples, pears, cherries, oaks, maples, hollies
Annual (Length of Life)
Any plant that lives for one growing season
AKA “bedding plants”
often killed by freezing temps
plant 2-4 weeks after FFFD
Registered Trademark Names
Name given to a plant that’s used to mark the plant or a group of similar plants → ex: apple
Not a patent
Little TM = trademark vs Little R = registered trademark
Scientific Cultivar Name vs Registered Trademark Name
Cercis canadensis ‘JN2’
“The Rising Sun(TM)” Redbud
Biennial
Completes life cycle in two years
First year = vegetative growth / second year = reproductive growth
ex → Carrots and Queen Anne’s Lace, Daucus carota, are the same genus
Foxglove, Digitalis
Perennial
Plants that live for 3 years or more
Woody vs herbaceous perennials
Volunteers
Annuals that “appear” to act like perennials
The plants idle but have set seed that is able to “overwinter” and germinate in the next season
Temperate Plant Hardiness Scale
Based on the average annual minimum winter temperature
Zone ratings = the lowest temps a plant can survive compared to the USDA chart
Divided into 10 degree Fahrenheit zones
Roots (Vegetative Organ)
Function: Absorption, anchorage, transportation of nutrients, storage
#1 Absorbing organ; absorbing roots grow in the top foot of soil (12”)
Not all roots do every function; certain ones for certain things
Primary Root
The first root to emerge from the seed
Secondary Root
Any root that emerges from a primary root or another secondary root
Adventitious Root
Roots arising from abnormal places; roots coming from other adventitious roots
Some plants can have just adventitious roots and be perfectly fine
Tap Root
Large swollen primary root “easily recognized” → carrot
All ____ roots are primary roots but not all primary roots are ____ roots
Tuberous Root
Large swollen secondary root
Typically a storage organ → ex: sweet potatoes
Aerial Roots
Roots often growing above ground
Often adventitious but not always
Epiphyte
Plants that grow on other plants; 100% aerial roots
Absorbing water/nutrition from the air, only using host plant as supportive structure; NOT PARASITIC
Can accidentally kill other plants due to being overbearing and blocking the sun
Ex: Orchids and Bald Cypress
Stems
Functions: Storage, transportation of nutrients, support, food production
Prostrate Stem
Stems that run along the ground
Stolon
Type of Prostrate stem; runs along the ground and produces a plantlet at the tip
Ex: Strawberries, spider plants → Chlorophytum comosum
Rhizome
Type of Prostrate stem that runs below ground and produces a plantlet at the tip
Ex: snake plant, iris, turf grass → Polygonatum odoratum ‘Variegatum’ = Variegated Solomon’s Seal → Seemannia nematanthodes ‘Evita’
Tuber Stem
Large swollen underground stem
ex: Irish (white) potato, tuberous begonia
Potatoes are the seeds themselves, the eyes can be cut with their own chunks and planted to grow more potatoes
Crown (Stem)
Area where the stem meets the root
Growing center of the plant, rosette of leaves (kind of a wagon wheel shape)
How do you distinguish roots from stems?
Stems have nodes and internodes, but roots do not
Roots can have adventitious buds, but it won’t have the set system
Nodes
Where leaves and buds come from on a stem
Internodes
The space between nodes
Leaves
Leaf = blade + petiole
Functions: Food production, storage → #1 food producing organ
Simple Leaf
One blade + petiole
Bud is always the indicator of where the leaf begins
Difference between simple and compound leaves is where the bud is located
Compound Leaf
Leaflets + petiole
Needle-Like Leaves
Found on some conifers, often in fascicles
Fascicle
The bundle of needles on a conifer tree → ex: loblolly pines have three needles per ____
Scale-Like Leaves
Found on some conifers
Awl-Like Leaves
Found on some conifers
What two factors causes plant failure and what increases due to this?
Poor light relations (sugar production)
Soil issues (water and nutrition)
Results in increased maintenance and plant replacement
What is necessary for plant growth?
Water: Hydration, photosynthesis
Nutrients: Health, compound
Sugar (Glucose): Building blocks and fuel, “the 2 by 4 of growth”
Chemical Energy: Energy to grow
Dry Weight
The measurement of the weight of the plant without any water in it
96% dry weight = sun, 4% dry weight = soil (both equally important)
Make-Up of Plants and Full Sun
Made of tissues containing water, sugars, nutrients, and other compounds
Full sun = 6 hours of unimpeded sunlight at minimum, any less is partial
Absorption (Plant Growth Process)
Primary function of the roots
Water + nutrition absorbed differently
Dependent on good soil building practices
Needs water AND oxygen
Water Absorption
Solute concentration (salts dissolved in solution)
Osmosis occurs to maintain the same amount of solute concentration
Water absorption is a passive process within the plant; requires no use of energy
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
Passive Reaction/Process
A reaction that requires no use of energy
Fertilizer Burn
The phenomenon in which too much fertilizer in the soil solution raises the solute concentration to the point where the water in the roots exits the roots and no new water can get into the plant, leading to the leaves drying out and dying.
How to fix fertilizer burn?
Add water in order to lower the solute concentration; unfortunately that also causes leaching of nutrients
Nutrient Absorption; CMT and AT
Carrier Molecule Theory: Nutrient-specific molecules responsible for nutrient uptake
We KNOW that these molecules must burn energy in order for the nutrients to be taken up
Active Transport: Any biological process that requires an expenditure of energy
Translocation
The movement of material from one location to another
Water and nutrients → up → xylem
Sugars → down and up → phloem
Vascular tissue, veins
Photosynthesis Equation
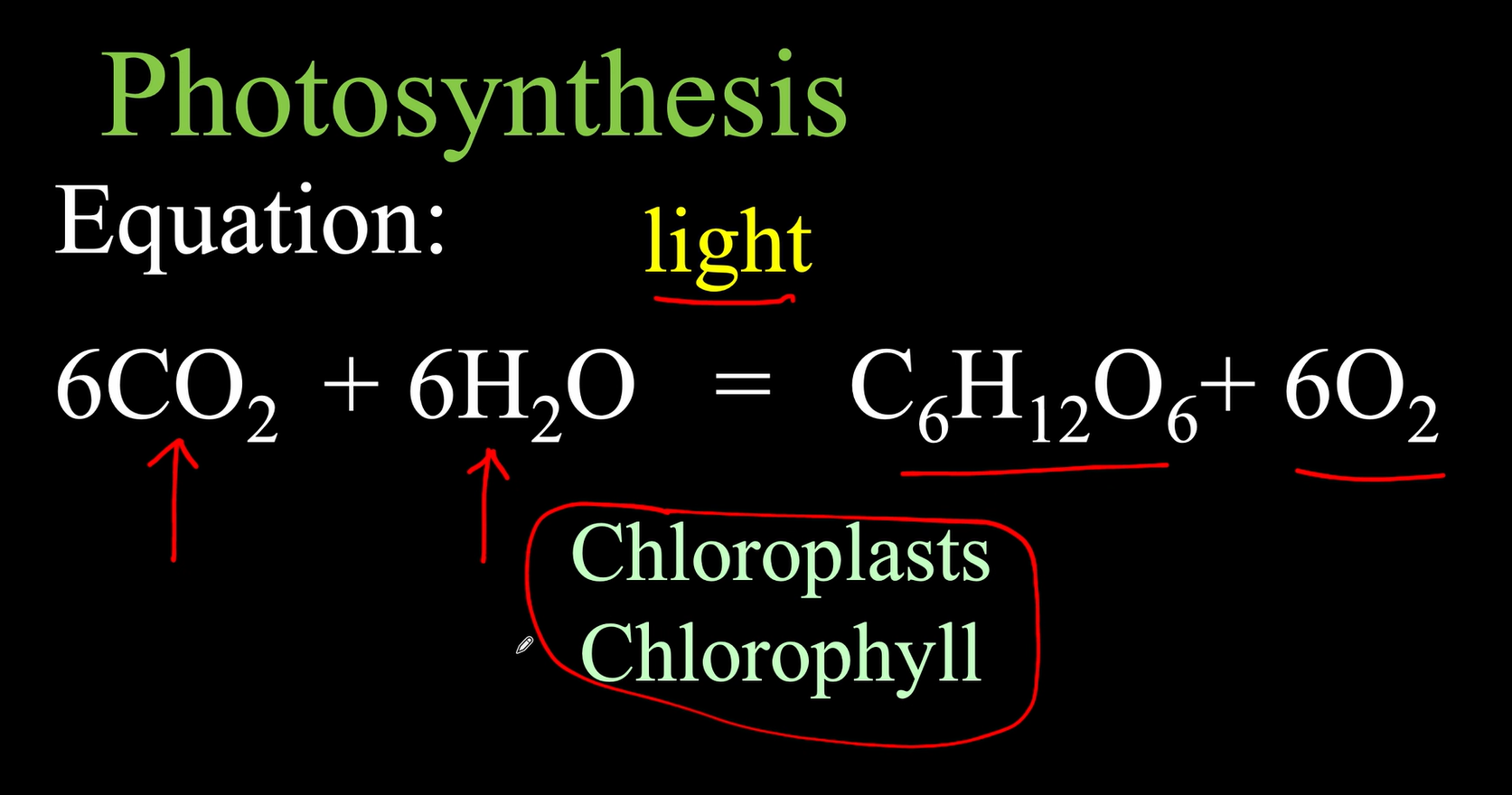
Chlorosis
Yellowing of the leaves that indicates a lack of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Light sensitive; plants stimulated to produce chlorophyll when they’re in the light
High light intensities will destroy chlorophyll, there’s often
Dynamic molecule, breaks down over time if not replenished → needs to be produced regularly
What Factors Affect the Rate of Photosynthesis
Light intensity
Light duration
Water availability
Nutrient availabilty
Chlorophyll concentration
Temperature
Science of Foliage Color
Typically plants with multicolored or variegated leaves require higher light intensities than their green leafed straight species counterparts
Transpiration
Process where water is absorbed by the roots, translocated through the plant, and evaporated through the leaves
99% of the water absorbed into the plant exits thru transpiration, the other 1% is part of the ingredients of photosynthesis
Transpiration and photosynthesis are positively connected to each other (buddies)
Full cells are turgid; turgidity = amount of water in the cell
Factors that Affect the Rate of Transpiration
Temperature
Relative Humidity
Air Movement
Stomata/Stomate
Organelle of Transpiration (guard cell)
When enough water, they open vs when not enough water, closes to cut off transpiration (photosynthesis rate also goes down)
Potassium is the nutrient that regulates the opening and closing; a lack of potassium also causes leaf margin burn
What Happens to Glucose?
Stored
Used as building blocks
Biochemical synthesis; making hormones, proteins, etc.
Burned for energy
Respiration
Sugars are burned to yield chemical energy (ATP)
Converting sun energy into food energy
Temperature regulates the rate
Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + chemical energy
Typically 3 photosynthetic units to 1 respiration unit
Continues without sunlight, temp dictates how much respiration occurs during the night
If plant is making equal to what it burns, it will die
Balance of Plant Growth
Light if often the most limiting factor
Anthocyanin: reds, purples, blues → function of glucose, so higher concentration when you have more sugar to spare
How do Plants Partition Sugar?
Vegetative growth (roots, stems, leaves) and Reproductive growth (flowers, fruits, seeds)
If there isn’t enough sugar for both, the default is vegetative growth to keep the plant alive
If there isn’t enough for both but the plant thinks its in danger of dying, the sugar is then pushed to reproduction for continuation of the species and the plant will die after fruiting and flowering