Abx requiring monitoring and Abx resistance
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is selective toxicity for antibiotics?
Ideal compound will kill/inhibit growth of pathogenic cells but have no effect on host cells - no Abx currently exists that does this
When might agents that are more toxic to humans be needed to be used?
Treat resistant or difficult bacteria e.g., Klebsella, ESBLs or MRSA
What is ESBL?
extended spectrum beta lactamase producing organisms
What are some antibiotics that require therapeutic drug monitoring?
Gentamicin, vancomycin, teicoplanin, Amikacin, tobramycin, chloramphenicol IV
What is gentamicin?
Aminoglycoside used to treat serious gram negative infections - HAP, urosepsis and intra-abdominal sepsis
What can gentamicin be used alongside to treat infective endocarditis?
Ampicillin or vancomycin - rapid bactericidal activity provides synergistic benefit
What is infective endocarditis?
Serious infection of hearts inner lining (endocardium) or valves
What is the clinical value of Gentamicin?
Able to rapidly kill bacteria in severe sepsis and broad spectrum against aerobic gram negative bacteria
What factors have dosing implications in gentamicin?
Kidney excretion and highly hydrophobic so not distributed into fatty tissue
What are the side effects of gentamicin?
Associated with nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, as well as vomiting, nausea, allergic reactions or rashes
How do the side effects of gentamicin present?
Rising creatinine, hearing loss, tinnitus or balance disturbance and risk increases with prolonged courses
What may increase the risk of renal damage when using gentamicin?
Use with other nephrotoxic agents e.g., amphotericin, ciclosporin, tacrolimus or contrast medium
What can increase the risk of ototoxicity when using gentamicin?
Use with loop diuretics e.g., furosemide
Why should gentamicin be generally avoided in pregnancy (unless risk > benefit)?
Can cause fetal ototoxicity
What are the contraindications and cautions of gentamicin?
CI in severe renal impairment where monitoring isn’t feasible, cautioned when prescribing with other renally clearly/ototoxic drugs
What can prevent the risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in gentamicin?
Dose according to IDEAL body weight of the patient and monitor the plasma concentration of gentamicin closely to ensure accumulation does not occur
What is the traditional method of administering and monitoring gentamicin?
Multiple daily dosing regimen - monitor peak levels around half an hour after administration and trough levels before administration - used for infections of heart
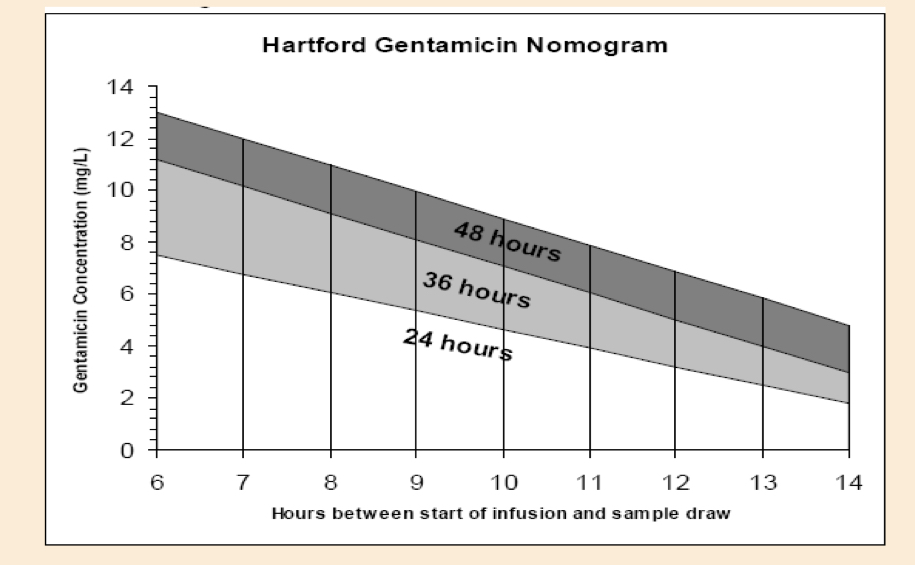
What is an alternative way of adminstering gentamicin?
Once daily dosing schedule using Hartford nomogram
What is the Hartford regimen for dosing gentamicin?
Consistent dose of 7mg/kg gentamicin calculated from lower value of ideal body weight/actual body weight - plasma concentration then measured 6-14 hours after initial dose to determine interval
What does the Hartford Nomogram ultimately determine?
Whether the patient should receive gentamicin every 24, 36 or 48 hours
Why is antimicrobial resistance a problem?
Infections become more difficult to treat and increase cost, duration and morbidity of illness
What are some examples of inappropriate Abx use which may encourage resistance?
Antibacterials used for viruses, longer/shorter duration of treatment than necessary, using broad spectrum Abx necessarily, single agent use when should be used in combination to reduce resistance risk, incorrect doses, inappropriate route
How much of human Abx use and agricultural use is unnecessary?
20-50% humans, 40-80% agricultural questionable
What factors can affect clinical resistance?
Precise location of infection, drug distribution in body fluids and state of patients immune system
What is intrinsic resistance of microorganisms?
Inherent resistance - already there
What is acquired resistance in microorganisms?
Microorganism develops resistance via genetic elements
How can resistant microorganisms share their DNA with other bacteria?
Conjugation (plasmid transfer between cells), transduction (DNA transfer by a bacteriophage) and transformation (uptake of DNA when cells break down)
What are some examples of methods of acquired resistance to antimicrobial?
Enzymes that inactive antibacterial before it binds to bacteria e.g., beta-lactamases inactivating penicillins
Reduced ability of antibacterial to permeate bacterial cell wall - aminoglycosides inactive against anaerobic bacteria
Active removal of antibacterial form e.g., tetracyclines in E. coli
Mutation at binding site of antibacterial
New synthesis pathways
What is klebsiella penumoniae responsible for as a gram negative bacteria?
Urinary, respiratory tract and bloodstream infections
What are the 3 main recommendations for antimicrobial resistance?
ensuring widespread recognition that it is a major threat to public health
Increase in emphasis on professional development of prescribers in antibiotic prescribing
Government must educate the public about proper use of antimicrobial
What is the antimicrobial prescribing and stewardship competencies?
Document by ARHAI (antimicrobial resistance and healthcare associated infection committee) about knowledge, skills and behaviours that IPs must demonstrate to support effective antimicrobial stewardship
What key messages can be spread in community to reduce inappropriate prescribing?
Don’t prescribing for viral sore throats, self limiting conditions e.g., simple coughs and colds, limit prescribing for uncomplicated cystitis to 3 days for fit women, limit prescribing Abx over the telephone
What is hospital guideline for antimicrobial prescribing?
Abx should be prescribed with as narrow of a spectrum as possible, should review every 48 hours after initial prescription, as short a course as possible, switch from IV to oral ASAP, reduce routine use of Abx for surgical prophylaxis to a minimum, shouldn’t be started immediately in all suspected infections