DNA + RNA - Structure, Function, Processes
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid; composed of nucleotides
where/when does dna replication end?
when there’s dna damage
at telomeres (in eukaryotes) - at the very ends of linear chromosomes, replication requires special mechanisms involving an enzyme to fully replicate the ends
origins of replication
sequences of DNA where replication starts
What type of point mutation causes translation to be terminated prematurely, resulting in a shorter polypeptide than was encoded by the normal gene?
nonsense mutation
inversion mutation
type of chromosomal mutation where a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end. This occurs when a piece of DNA breaks at two points within the chromosome and then reattaches in the opposite orientation.
prions
misfolded versions of a protein that are infectious and cause brain diseases
Components of a Nucleotide
Sugar-phosphate (backbone)
Nitrogenous base
Functions of DNA
Controls cell activities (protein synthesis)
Cell replication through mitosis
Undergo mutations for genetic diversity (evolution)
Typically rare, recessive, random
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA fragments synthesized on the lagging strand during replication, later joined by DNA ligase.
Leading strand
The continuously synthesized DNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction toward the replication fork.
Lagging strand
The discontinuously synthesized DNA strand built in short Okazaki fragments away from the replication fork. (5’ to 3’ direction)
DNA polymerase
The enzyme that adds nucleotides to a growing DNA strand and proofreads for errors during replication.
helicase
The enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds at the replication fork.
single stranded binding proteins
bind to single-stranded DNA to stabilize it and prevent it from re-annealing or forming secondary structures during replication.
Topoisomerase
relieves the supercoiling and tension in the DNA ahead of the replication fork by cutting and rejoining DNA strands.
transcription
Synthesis of RNA from a DNA template where the code in the DNA is converted into a complementary DNA code
Occurs in the nucleus
translation
process by which a cell converts the information encoded in mRNA into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein.
occurs in cytoplasm and on the rough ER: ribosomes read mRNA in codons —> tRNA bring corresponding amino acids to build polypeptide chain —> key steps of translation are: initiation, elongation, termination
wobble pairing
phenomenon in translation where non-standard base pairs form between the 3rd codon position of mRNA and the corresponding anticodon in tRNA. This allows some tRNAs to pair with multiple codons, increasing translation efficiency.
ex: (G) can pair with (U) in the tRNA anticodon
what direction does DNA polymerase synthesize a strand of DNA?
can only add nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction. This means it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the new DNA strand as it builds.
If the template strand is: 3' - A T G C - 5' DNA polymerase will read it 3' to 5' and add the complementary nucleotides to the growing strand: 5' - T A C G - 3'
RNA Polymerase
enzyme that synthesizes RNA by reading a DNA template during the process of transcription. It unwinds the DNA locally and builds a complementary RNA strand using the DNA sequence as a guide
tRNA (transfer RNA)
small RNA molecule that helps decode mRNA into a protein by carrying specific amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Each tRNA matches to a codon on the mRNA using its anticodon
found in the cytoplasm
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
structural and functional component of ribosomes. It helps align mRNA and tRNA and catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds during protein synthesis.
formed in the nucleolus
purines
double ringed nitrogenous base
adenine and guanine
“AG is pure” (silver is pure)
“AG” —> two letters = double ringed
pyrimidines
single-ringed nitrogenous base
cytosine, thymine, guanine
“CUT the Py”
mRNA
single-stranded RNA molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it serves as a template for assembling a protein.
Steps of Protein Synthesis
Transcription (in the nucleus)
DNA —> mRNA. RNA polymerase builds mRNA, introns are removed, and a cap/tail are added
Translation (cytoplasm)
Ribosome reads mRNA, tRNA delivers amino acids, and a polypeptide is built. Process ends at a stop codon
After these steps, the polypeptide folds into a functional protein; modifications may occur
Start codon
AUG
Purines always match with a...
Pyrimidine (Adenine pairs with Thymine, Guanine pairs with Cytosine in DNA).
Chromosome
threadlike structure made of DNA and proteins that carries genetic information. Humans typically have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) in each cell.
Chromatin
complex of DNA and histone proteins found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
histone proteins
Proteins around which DNA winds to form chromatin. They help package DNA into a compact structure and play a role in gene regulation.
Sugar-Phosphate Backbone
structural framework of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), made up of alternating sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA) and phosphate groups. It provides structural stability to the nucleic acid chain.
Primase and its role
enzyme that synthesizes RNA primers during DNA replication
provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin synthesizing the new DNA strand.
topoisomerase vs. single-stranded binding proteins (SSBs)
Topoisomerase: enzyme that prevents DNA from supercoiling by creating temporary cuts in the DNA strand to relieve tension
SSBs: Proteins that bind to single-stranded DNA to keep it from re-annealing or degrading during replication.
supercoiling and topoisomerase
Supercoiling: overwinding or underwinding of the DNA double helix, causing tension.
Role of topoisomerase: prevents supercoiling by cutting and rejoining DNA strands, allowing the DNA to unwind without becoming too tangled
why does primase have to be replaced?
Primase adds RNA primers to initiate DNA replication, but these primers are later replaced by DNA nucleotides.
RNA primers are short-lived, and DNA polymerase cannot start replication without them, but they are not part of the final DNA sequence, so they need to be replaced with DNA.
when does dna replication occur?
occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle, before a cell divides (either mitosis or meiosis).
where does replication occur?
ccurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells (since they lack a nucleus)
small ribosomal subunit
binds to mRNA and decodes its sequence. It ensures the correct pairing between the codons on the mRNA and the anticodons of tRNA during translation
large ribosomal subunit
catalyzes the formation of peptide bond sbetween amino acids, enabling the elongation of the polypeptide chain. It contains sites for tRNA binding and facilitates the assembly of proteins
Anticodons
sequence of three nucleotides in tRNA that is complementary to a codon in mRNA. The anticodon allows the tRNA to match with the correct codon during translation to ensure the proper amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
example: if the mRNA codon is AUG, the tRNA anticodon would be UAC
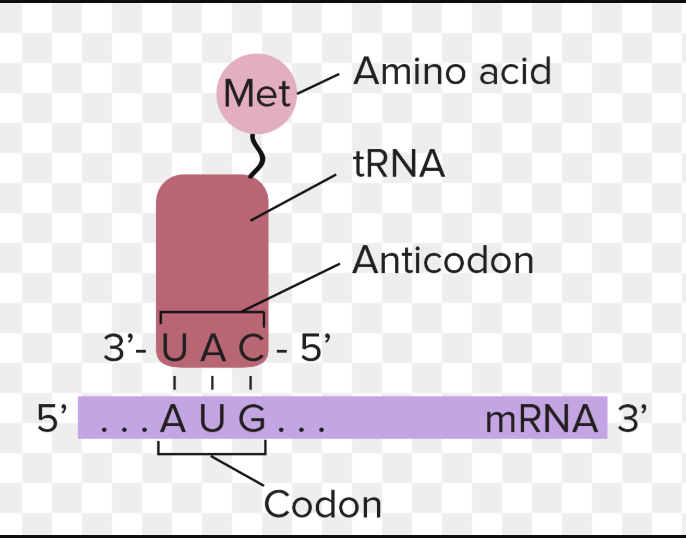
both RNA polymerase and DNA polymerase synthesize their respective strands in what direction?
5' to 3' direction

What is the first step in transcription initiation?
Transcription factors bind to the promoter region of DNA.
What is the promoter in transcription?
a specific sequence of DNA that signals the start of a gene and where RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription.
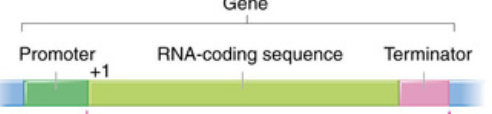
What role do transcription factors play in transcription?
proteins that help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter region of the gene to initiate transcription
they do this by binding to the TATA box
function of RNA polymerase in transcription
the enzyme that synthesizes RNA by reading the DNA template strand and adding complementary RNA nucleotides.
How does DNA unwind during transcription?
RNA polymerase unwinds a small section of the DNA double helix to expose the template strand for RNA synthesis.
why is it beneficial that multiple triplets can code for the same amino acid?
minimizes errors due to mutations
TATA box
type of promoter sequence (recognition site) that specifies where transcription begins
found in core promoter region of genes in many eukaryotes
about 25-30 bases before the actual start of the gene
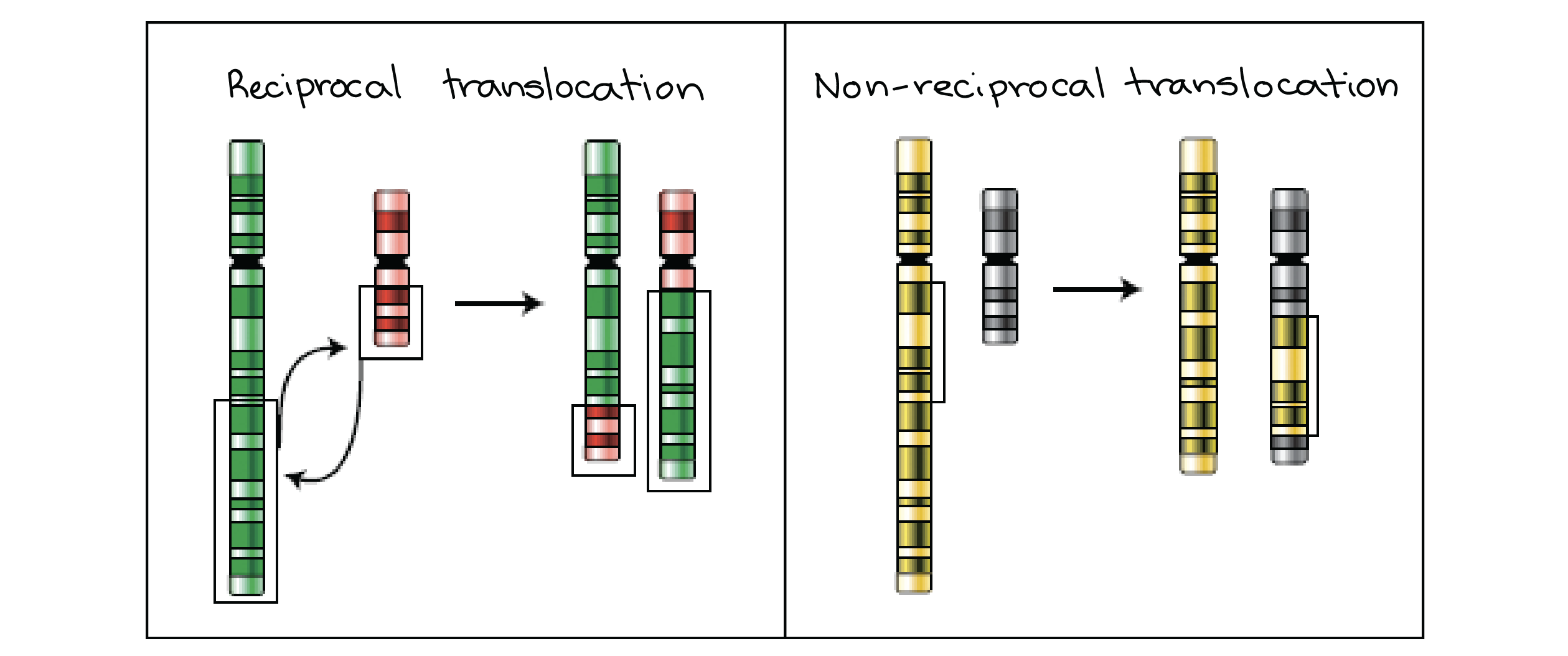
translocation mutation
a piece of one chromosome gets attached to another chromosome.
introns
regions of a gene that doesn’t code for a protein
exons
regions of a gene that actually codes for a protein
RNA splicing
removing introns and splicing the exons together
polyA tail
sequence of adenine nucleotides added to the 3’ end of a pre-mRNA molecule during RNA processing in eukaryotic cells
5’ cap
modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of the pre-mRNA and serves various essential functions.
restriction enzymes
enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences called recognition sites. These enzymes are naturally found in bacteria, where they serve as a defense mechanism against viruses by breaking down foreign DNA.
plasmid
small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecules that are separate from the chromosomal DNA of an organism. They are commonly found in bacteria and sometimes in eukaryotic cells.
can replicate independently and often carry genes that provide advantages, such as antibiotic resistance.
sticky ends
short + single-stranded overhangs of DNA that result when a DNA molecule is cut by certain restriction enzymes at specific recognition sites.
these overhangs can easily pair with complementary sticky ends on another DNA molecule, making them useful in molecular cloning and genetic engineering for joining DNA fragments.
vector DNA
DNA piece that can be modified to accommodate a piece of foreign DNA
recombinant DNA
DNA that contains DNA from 2 other sources —> DNA is inserted into that of another organism
process of recombinant DNA
gene is removed from existing chromosome (removed using special restriction enzymes)
bacterial plasmid is opened and gene is inserted
enzyme ligase is used to seal gene into plasmid
plasmid now contains rDNA
transgenic plants
insertion of foreign genes into crops plants for beneficial characteristics
transgenic animals
insertion fo genes into the eggs/embryos of animals
mutation
change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene
telomeres
repetitive sequences of non-coding DNA found at the ends of linear chromosomes in eukayrotic cells
act like a buffer zone
frame shift mutations
insertions or deletions of nucleotides in DNA —> results in a drastically altered protein (possibly non-functional)
point mutations
changing a single nucleotide (changes a specific codon)
silent mutation
a changed codon still codes for the same amino acid
nonsense mutation
substitution occurs early on in protein chain → malfunctioning protein
missense mutation
substitution of a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence.
leads to a change in the codon, which codes for a different amino acid. results in a change in the protein structure.
can be benign and do not signficiantly impair protein function
mutagens + examples
environmental:
substances in the environment = mutations to DNA
radiation:
radioactive substances, X-rays or UV radiation
chemical:
cigarette smoke, pesticides, pollutants
somatic mutations
occurs in body cells → not reproductive cells, cannot be inheritable
germinal mutations
mutation occurs in reproductive cells (heritable) - can lead to evolutionary changes
PCR
method to amplify specific DNA sequences using repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension. Requires DNA template, primers, Taq polymerase, and nucleotides.
oncogenes
mutated or overexpressed forms of proto-oncogenes that drive uncontrolled cell growth and division, leading to cancer.
tumor suppressor genes
genes that encode proteins responsible for processes like cell growth/differentiation/apoptosis
If deactivated, can lead to uncontrolled growth
act like “brakes” for the cell cycle
carcinogens
substances, agents, or exposures that can lead to cancer by causing DNA damage or disrupting normal cellular processes. They can be chemical (e.g., tobacco smoke), physical (e.g., UV radiation), or biological (e.g., certain viruses).
Vascularisation (angiogenesis)
new blood vessels are formed near cancerous tissue
Bring nutrients/O2 to cancerous cells and carry away wastes
Metastasis
Tumour becomes malignant
Cells break away and travel to other areas of the body through blood vessels/lymphatic vessels
proto oncogenes
normal genes that play a crucial role in regulating cell growth, division, and survival. When mutated or abnormally expressed, they can become oncogenes, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and potentially causing cancer.
growth factors
signaling proteins that stimulate cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and survival. They bind to specific receptors on the cell surface to activate signaling pathways that regulate cellular processes.
signaling proteins
molecules that facilitate communication between cells or within a cell by transmitting signals to regulate biological processes.
heterochromatin
Tightly packed form of chromatin.
Transcriptionally inactive due to its condensed structure.
Found in regions like centromeres and telomeres.
Helps maintain genome stability and regulate gene expression
Euchromatin
Loosely packed form of chromatin.
Transcriptionally active and accessible to RNA polymerase.
Contains most genes and is involved in active gene expression.
retrovirus
type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades
after invading a host cell’s cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome
reverse transcriptase
enzyme that converts retroviral RNA to DNA, which can be integrated into the host cell’s genome
the enzyme is encoded by the RETROVIRUS and brought along with the virus when it infects a host cell (not pre-existing in host cell)
the role of initiators in the development of a cancerous tumour
substances/factors that can cause mutations in the DNA of a cell
can affect proto-oncogenes, tumour suppressor genes, or DNA repair genes
mutation usually is irreversible and permanent
cell that undergoes mutation may not be immediately cancerous but is more susceptible to further changes that could lead to tumour formation
the role of promoters in the development of a cancerous tumour
can accelerate/promote the growth of cells that have been initiated/mutated, but don’t cause mutations themselves
ex: hormones like estrogen or carcinogens can make someone more likely to develop cancer
neoplasia
provess of abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells, which can form a tumour
anaplasia
loss of structuarl and functional differentiation of cells, characteristic feature of MALIGNANT tumours
anaplastic tumours are aggressive and invade nearby tissues, often metastasize
3 types of cancer
carcinoma (epithelial tissue)
sarcoma (connective tissues)
leukemia (blood forming tissues)
How do tumor suppressor genes differ from proto-oncogenes?
Tumor suppressor genes: produce proteins that help prevent uncontrolled cell division and tumor formation. When these genes are mutated or inactivated, they can lead to cancer
Proto-oncogenes: These genes are normal genes that promote cell growth and division. However, when mutated or overexpressed, they can become oncogenes
uses for rDNA technology
transgenic plants (enhancing crops)
transgenic animals (insertion of genes —> embryos/eggs of animals
What are the stages in the development of cancer, and what roles do initiators, promoters, and neoplasia/anaplasia play?
Initiation: Genetic mutations occur in a cell’s DNA, often due to environmental factors (e.g., chemicals, radiation). These mutations are called initiators and can make a cell abnormal but not cancerous.
Promotion: Additional factors (called promoters) stimulate the growth of the mutated cells, leading to abnormal cell division, though the cells are still not fully cancerous.
Progression: The abnormal cells accumulate more mutations, becoming more aggressive and capable of forming a tumor. This stage involves neoplasia, where the cells start to proliferate uncontrollably.
Metastasis: Cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. Anaplasia refers to the loss of cellular differentiation, making the cancer cells more primitive and harder to identify.