Hearing and balance
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
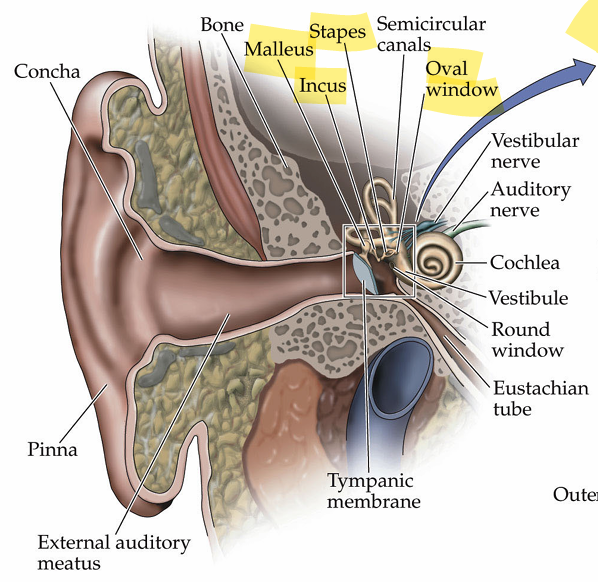
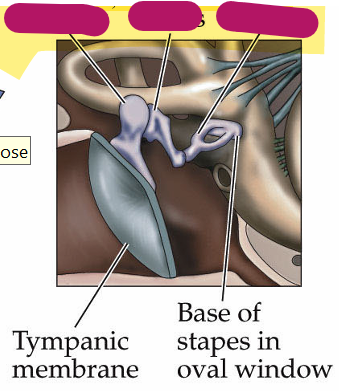
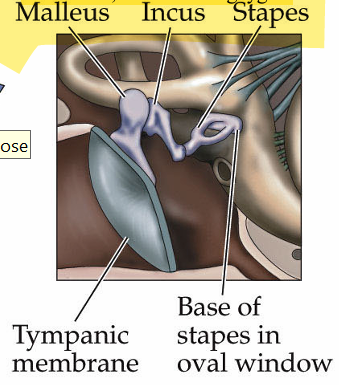
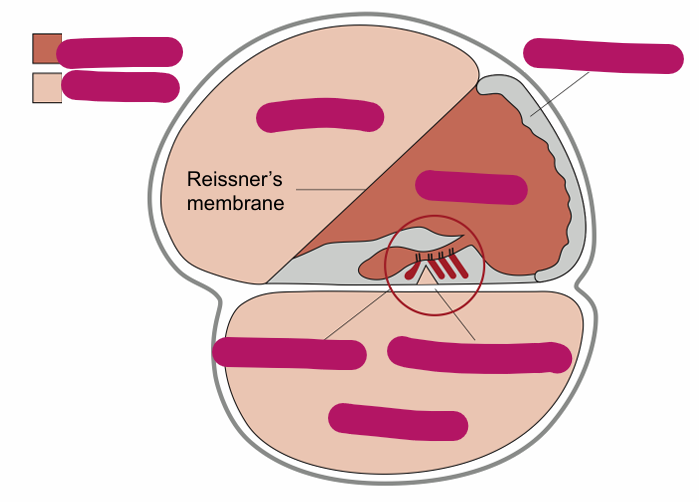
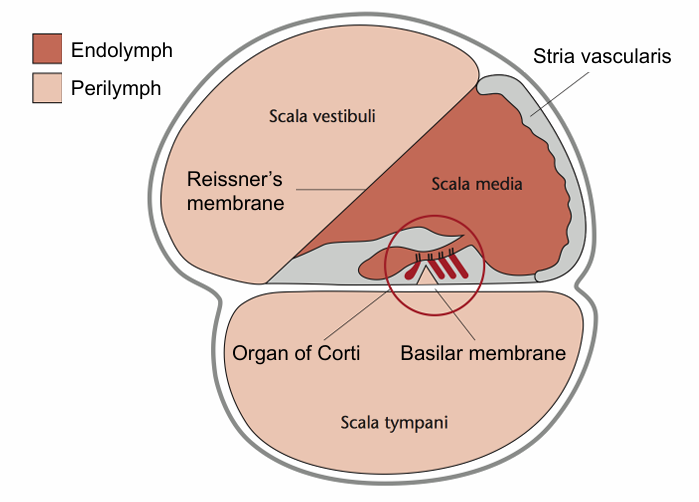
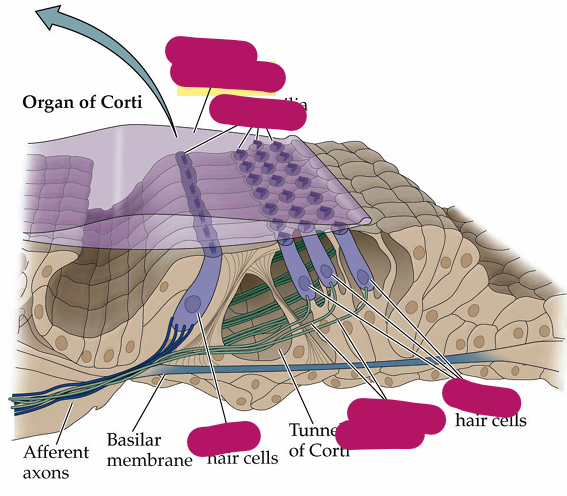
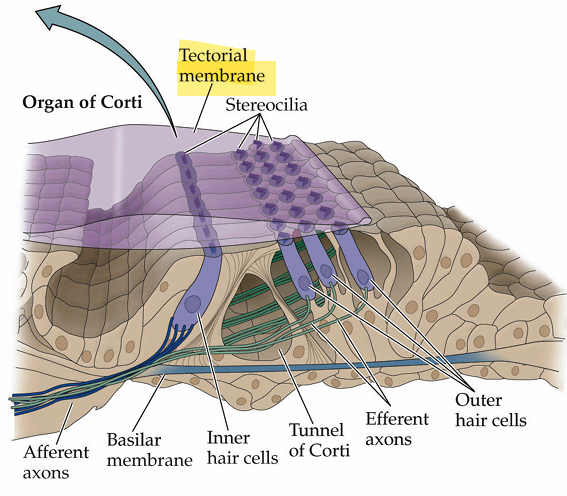
Base of basilar membrane is tuned for which frequencies
high
apex is tuned for which frequencies
low frequencies
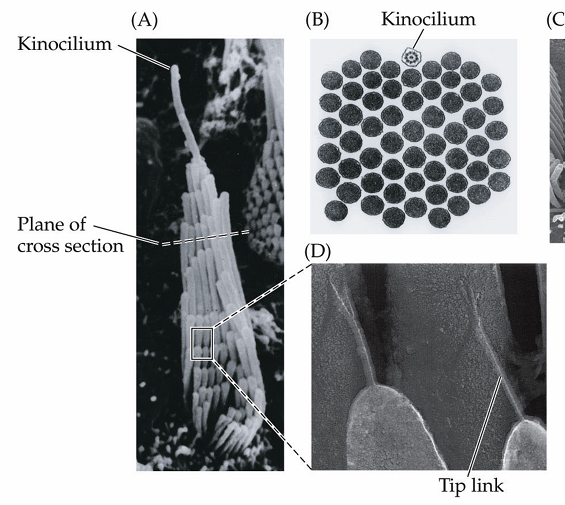
Difference between kinocilium and stereocilia
Stereocilia make up the hair bundle, kinocilium is one longer protrusion
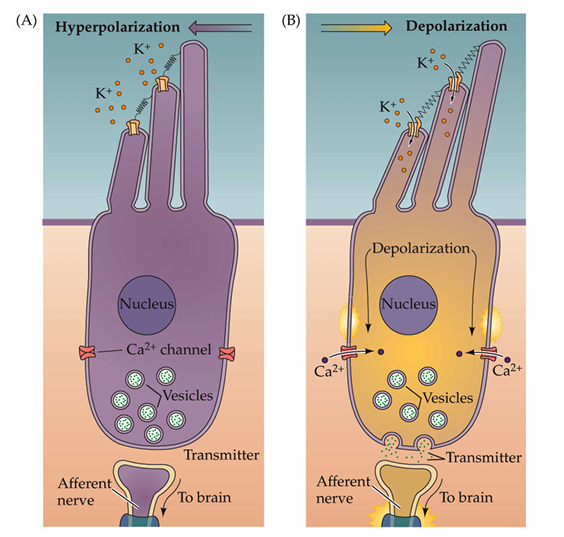
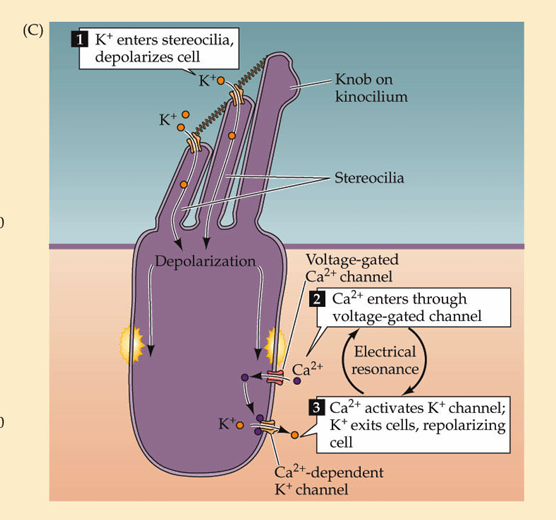
What happens during depolarization of hair cells
K+ flows into the hair cell, opens Ca2+ channels, triggers release of neurotransmitters
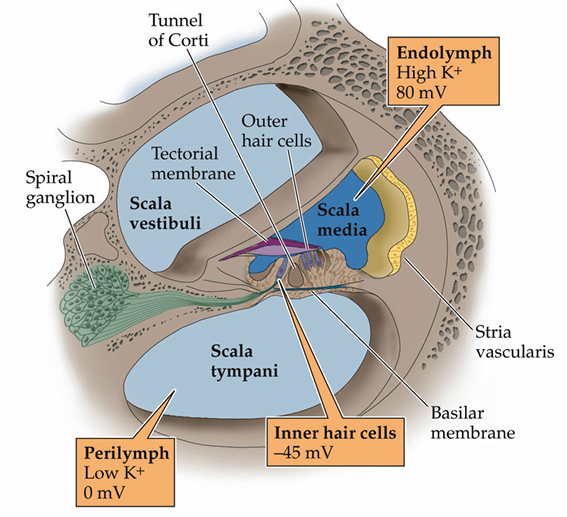
Endolymph, inner hair cell and perilymph membrane potential
Which principle is used for high frequencies
Place principle
Which principle is used at low frequencies
phase locking
How do we localize sound at low frequencies
by the time difference (phase difference)
How do we localize sound at high frequencies
Via intensity
Major auditory pathway
Auditory nerve travels to
The signal is then relayed to
Finally it reaches
Auditory nerve travels to cochlear nucleus
The signal is then relayed to inferior colliculus
Finally it reaches primary auditory complex
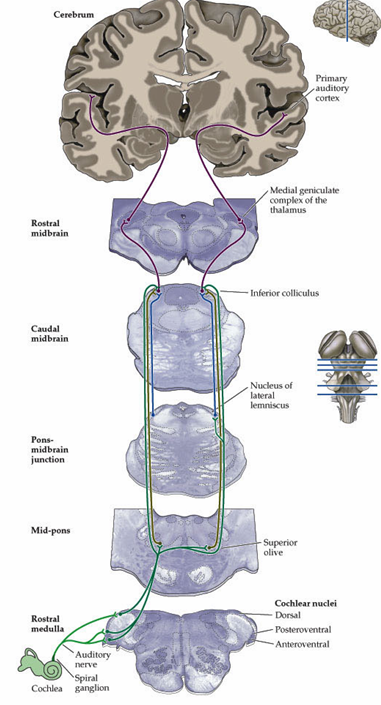
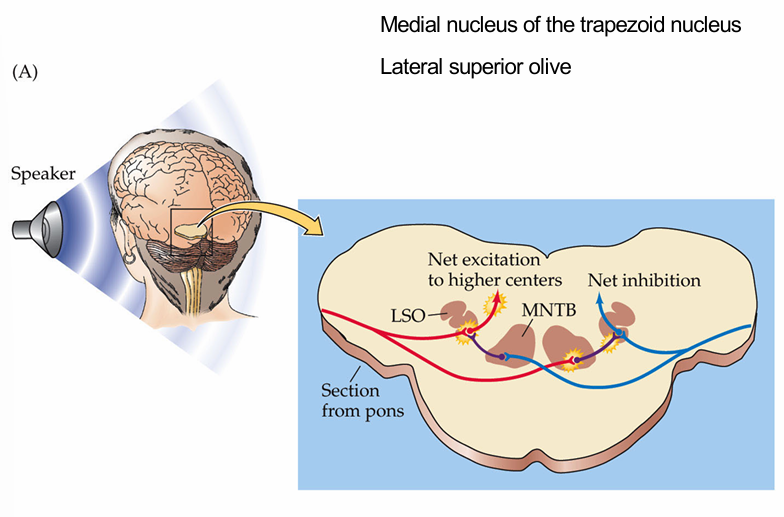
What happens at the superior olivary complex
A neuron crosses the midline at the olivary complex and reaches the inferior colliculi
What does the superior olivary pathway help with
discriminating the direction of the speaker
Which structures are involved in this process [2]
Medial nucleus of the trapezoid nucleus (MNTB)
lateral superior olive (LSO)
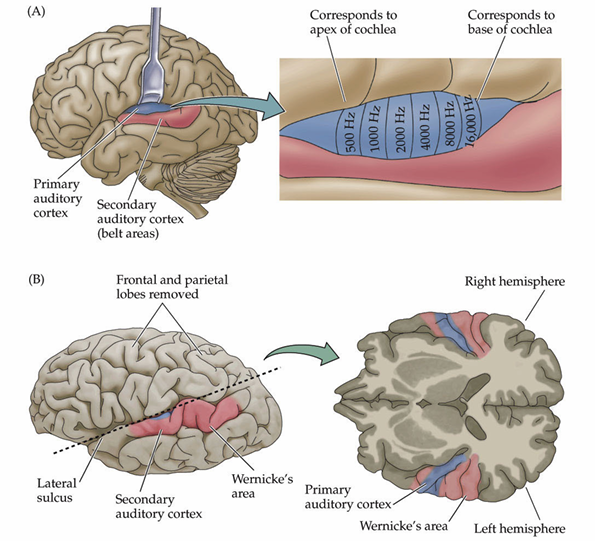
Primary auditory cortex is also called
Broadmann’s area
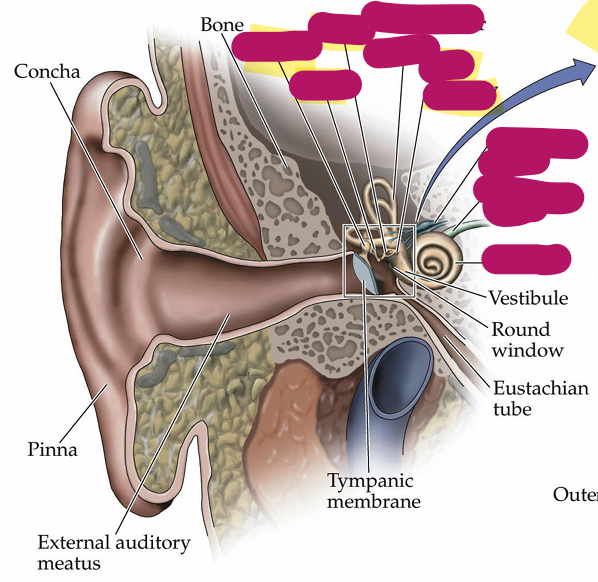
Vestibular system is responsible for
balance
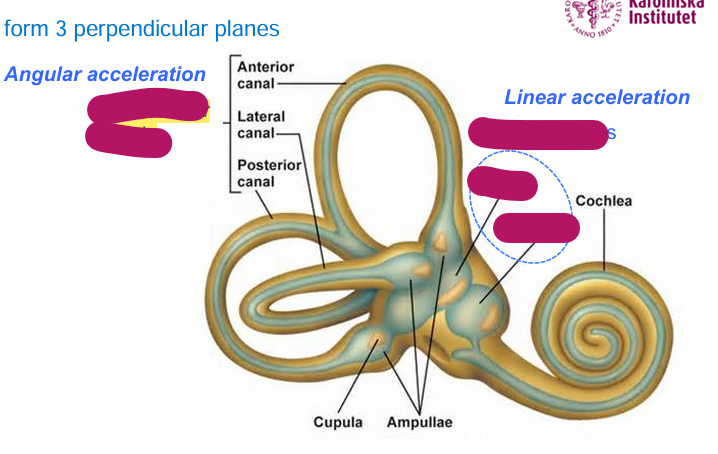
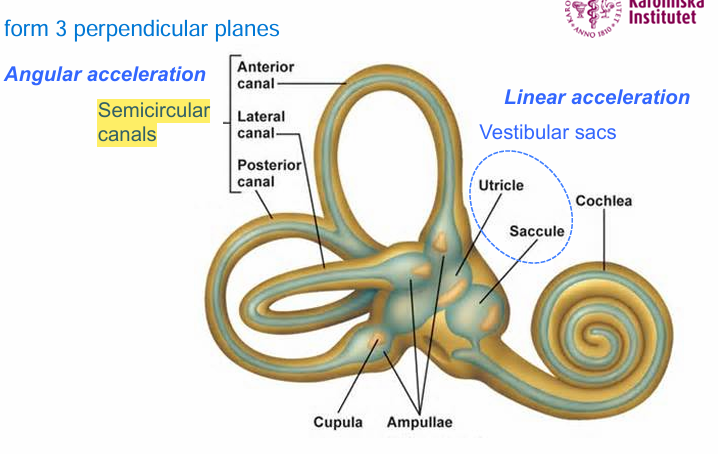
Angular acceleration occurs in
semicircular canals
Linear acceleration occurs in
vestibular sacs
Vestibular sacs are composed of
utricle and saccule
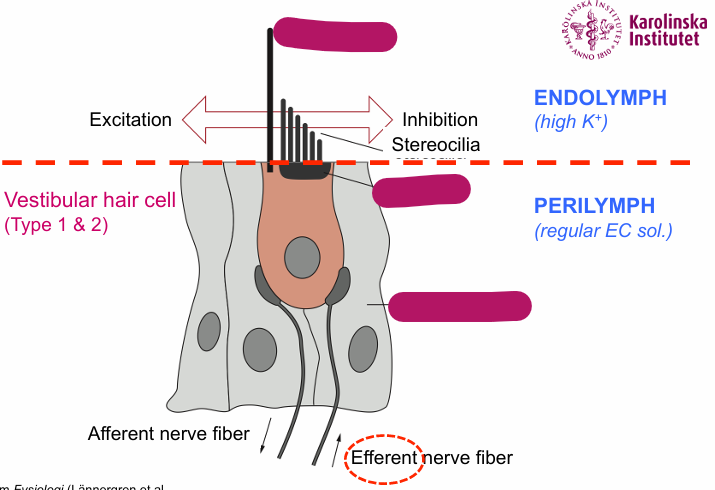
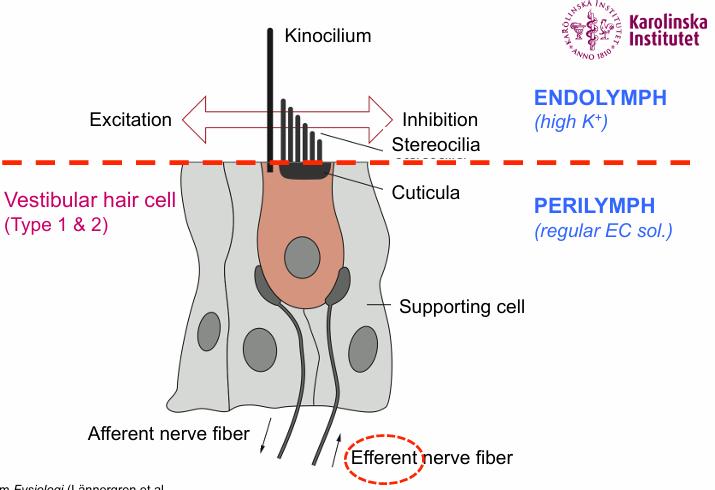
How do vestibular cells move
With gating-springs
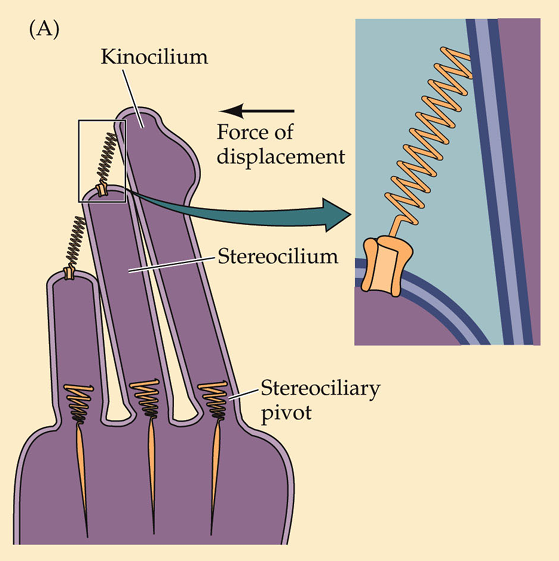
Depolarization in stereocilia causes
K+ influx and Ca2+ entry into the cell
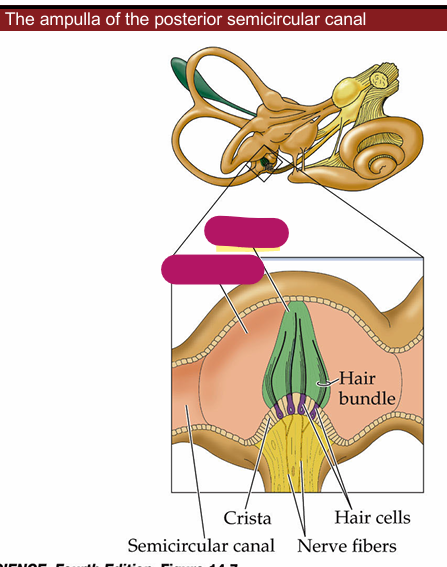
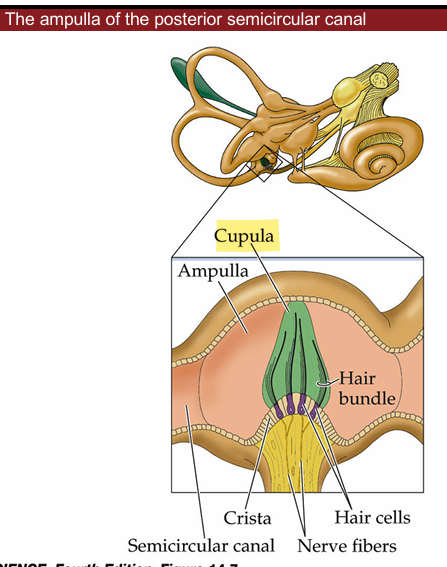
Sensory organs of semicircular canals
Ampullae which contains Cupula inside
What happens in response to rotation?
Endolymph flows in due to inertial forces
Results in depolarization, transmitter release, synaptic activation
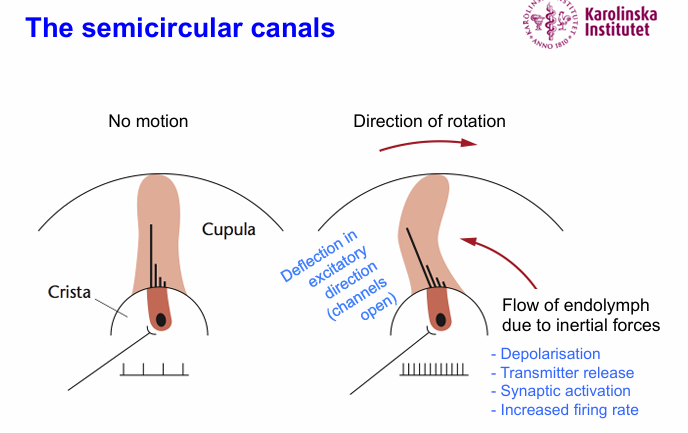
Rotation to the right and left - effect on firing frequency
Left - decreased firing rate
Right - increased firing rate
What mediates the linear acceleration in utricle and saccule
Otoliths
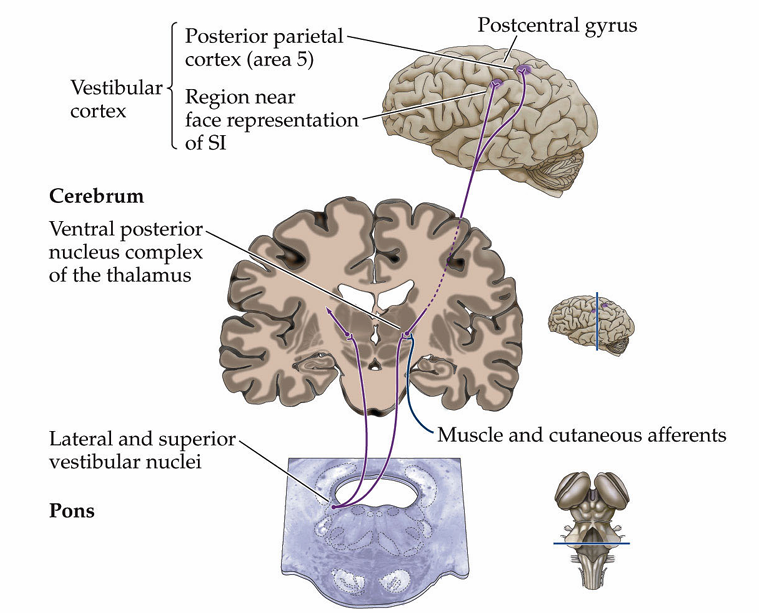
The efferent nerve relays signals via (vestibulo-occular reflex)
medial vestibular nuclei
Where does it further connect to [5]
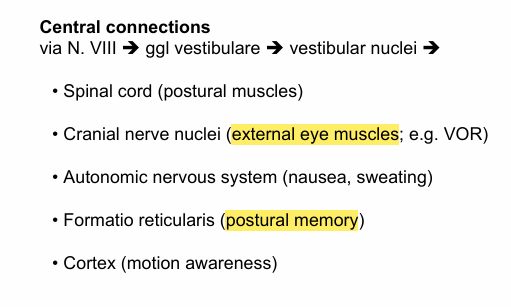
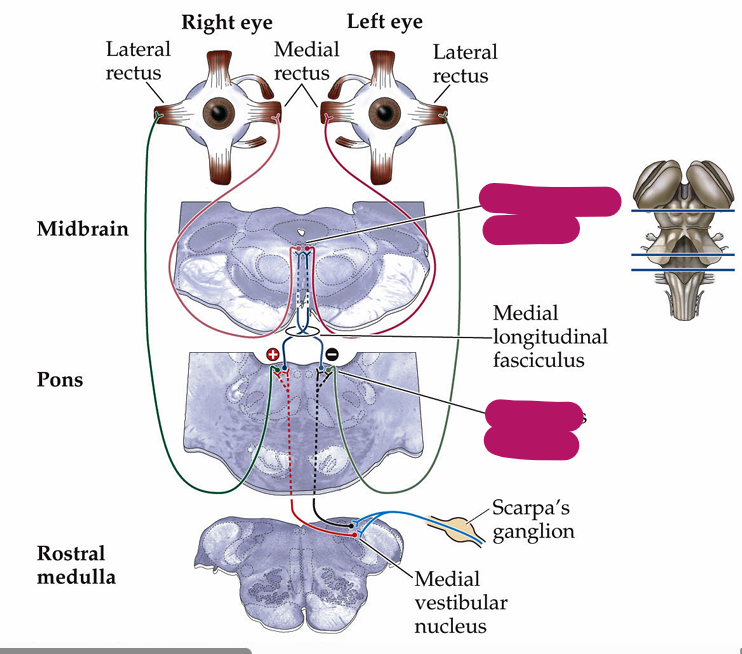
Efferent nerve projects via (thalamocortical pathway)
lateral and superior vestibular nuclei