IV Fluid Therapy
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What type of solution is the first line choice for fluid resuscitation?
crystalloids
contain water-soluble electrolytes
What is a hypotonic solution?
contains less e- than the plasma
What is a hypertonic solution?
contains more e- than plasma
What is an isotonic solution?
contains the same amount of e- as the plasma
What is diffusion?
the movement of things from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower
What is the direction of osmotic water movement in an isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solution?
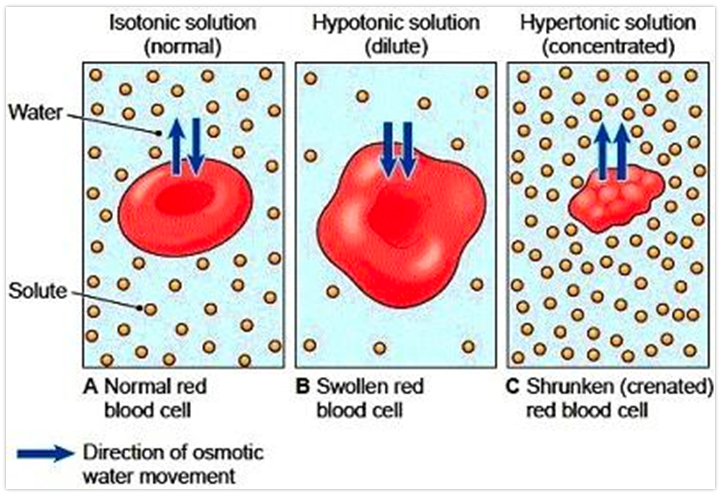
What is the purpose of an isotonic solution?
increase ECF volume d/t
replaces plasma volume, does not cause shifts
What are risks of an isotonic solution?
fluid volume overload
What are three examples of an isotonic solution?
lactated ringers (LR)
normal saline (NS)
D5W
What are common uses of an isotonic solution?
blood loss
surgery
dehydration
fluid loss that has been loss extracellularly
What is the difference between LR and NS?
LR matches our plasma makeup better and contains more types of e-
caution for other imbalances
NS has more Na
Describe the shift of water in cells caused by HYPOtonic crystalloids.
shifts water from ECF to ICF compartment → out of the blood into the cells and tissue spaces
ICF ← ECF
What are common uses for HYPOtonic crystalloids?
DKA
hypernatremia
What are risks for HYPOtonic crystalloids?
hemolysis
Describe the shift in cells caused by HYERtonic crystalloids.
increases extracellular volume and decreases intracellular volume → out of the cells and into blood
ICF → ECF
What are common uses for HYPERtonic crystalloids?
increased ICP
hyponatremia
What are risks for HYPERtonic crystalloids?
hypervolemia
What are colloid solutions?
contain large insoluble molecules, generally proteins
How do colloid solutions function?
these large molecules do not easily cross the capillary wall, colloids remain in the intravascular space longer than crystalloids, so less volume is needed for the same effect, reducing the risk for fluid overload
What is the benefit of colloids?
can have volume replacement w/ less volume
What is a risk of colloid solutions?
allergic reactions (similar to a blood product)
What are IV therapy complications?
circulatory overload
pulmonary edema
increased ICP
electrolyte/glucose disturbance
important to have the correct IV solution to minimize complications