Gross Anatomy - Head and Neck
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
c. Angular artery
What is the concluding branch of #14?
a. Premasseteric artery
b. Inferior labial artery
c. Angular artery
d. Lateral nasal artery
d. Elevation of the upper lip and dilatation of the nares
Which action is primarily associated with contraction of #4?
a. Elevation of the upper lip
b. Narrowing of the nares
c. Elevation of the upper lip and narrowing of the nares
d. Elevation of the upper lip and dilatation of the nares
c. CN V3
#15 is primarily innvervated by?
a. CN VII
b. CN V1
c. CN V3
d. CN IX
c. Parotid Duct
Which anatomical structure passes through #13 to reach the oral cavity?
a. Facial Nerve
b. Temporal artery
c. Parotid Duct
d. Submandibular Duct
b. Submandibular nodes
Which lymph nodes primarily receive the lymphatic drainage from #10?
a. Parotid nodes
b. Submandibular nodes
c. Submental nodes
d. Cervical nodes
a. Draws down medial eyebrows
Contraction of #1 causes what action?
a. Draws down medial eyebrows
b. Elevation of upper eyelid
c. Flares the nostrils
d. Compress nostrils
b. Maxillary bone above incisor teeth
What is the origin of #9?
a. Upper part of the frontal process of the maxillary bone
b. Maxillary bone above incisor teeth
c. Skin around the lips
d. Skin at the angle of the mouth
a. Muscle #10
Which muscle raises and protrudes the lower lip?
a. Muscle #10
b. Muscle #5
c. Muscle #3
d. Muscle #11
c. Muscle #9
Which muscle is a sphincter muscle surrounding the lips?
a. Muscle #12
b. Muscle #5
c. Muscle #9
d. Muscle #7
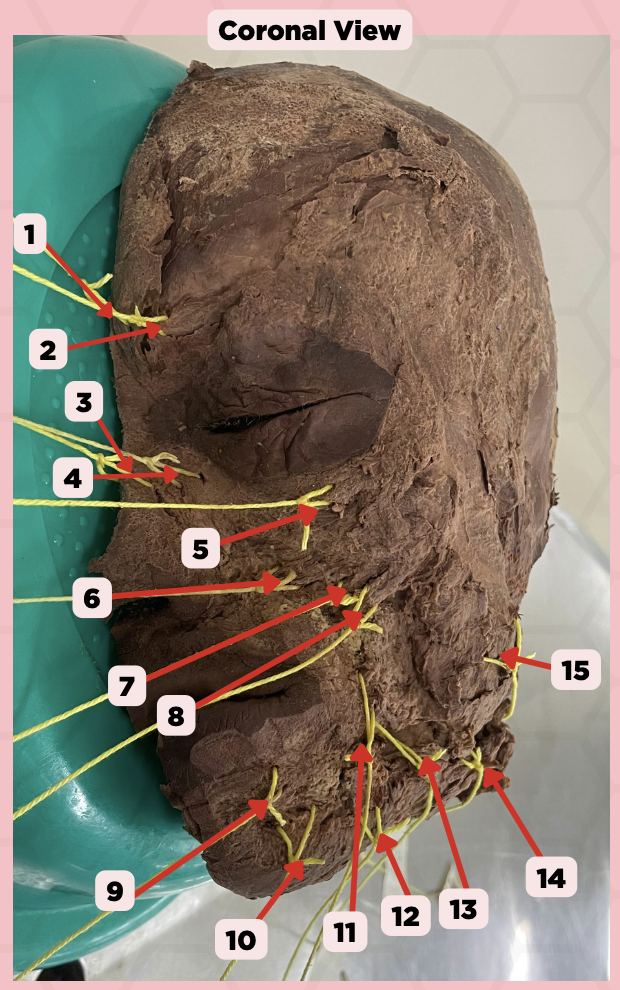
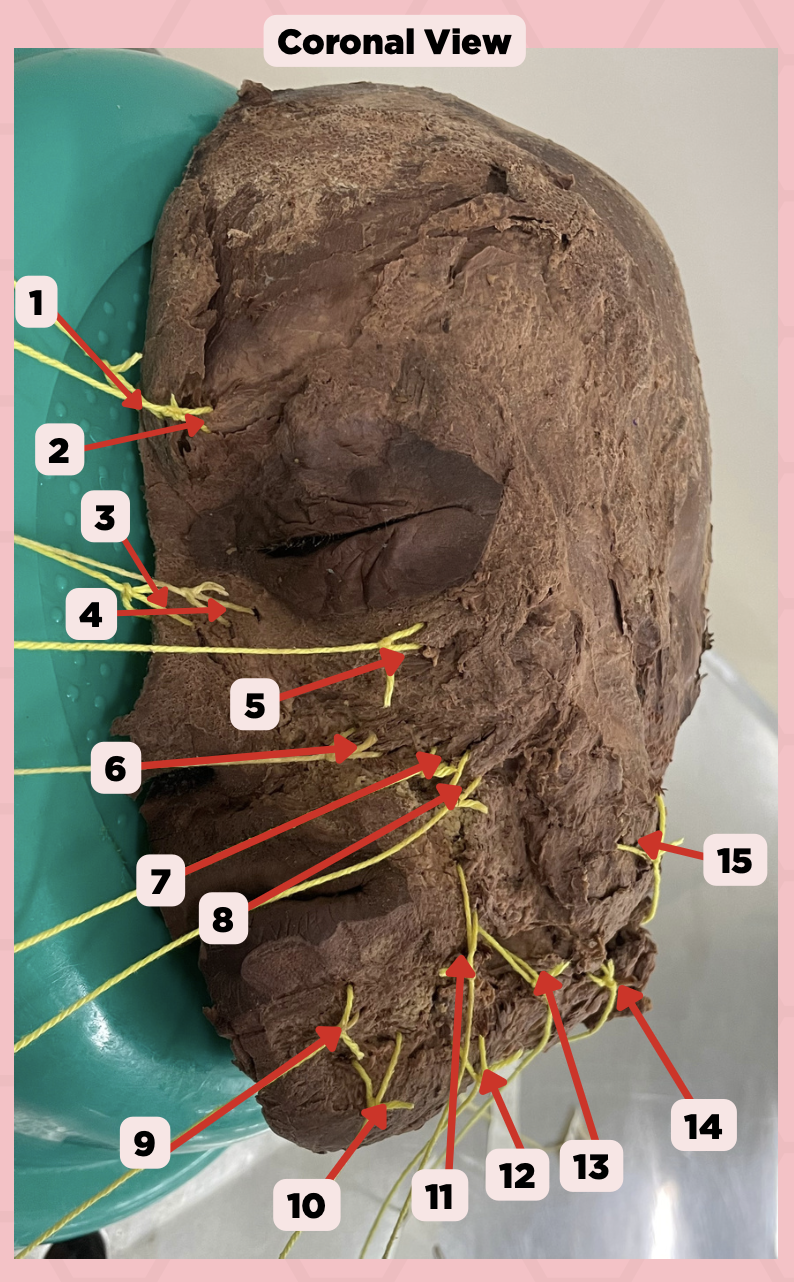
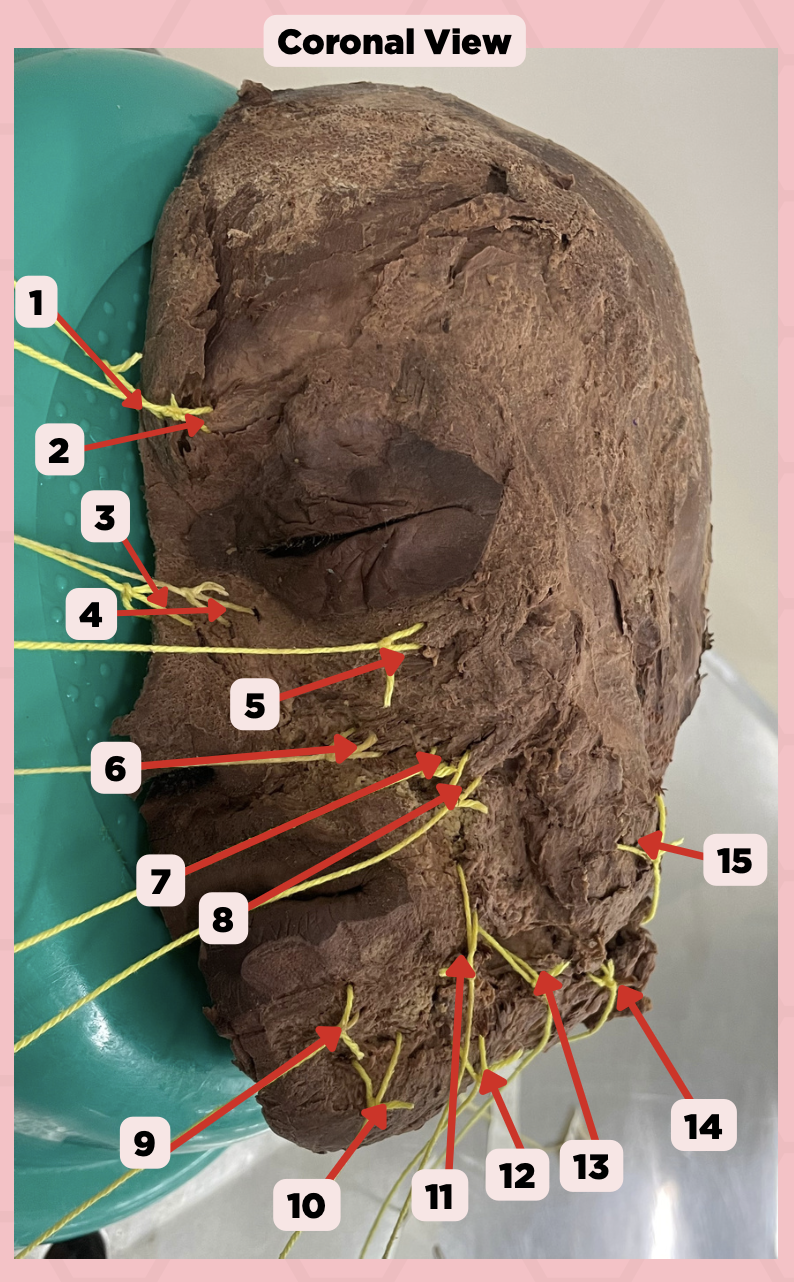
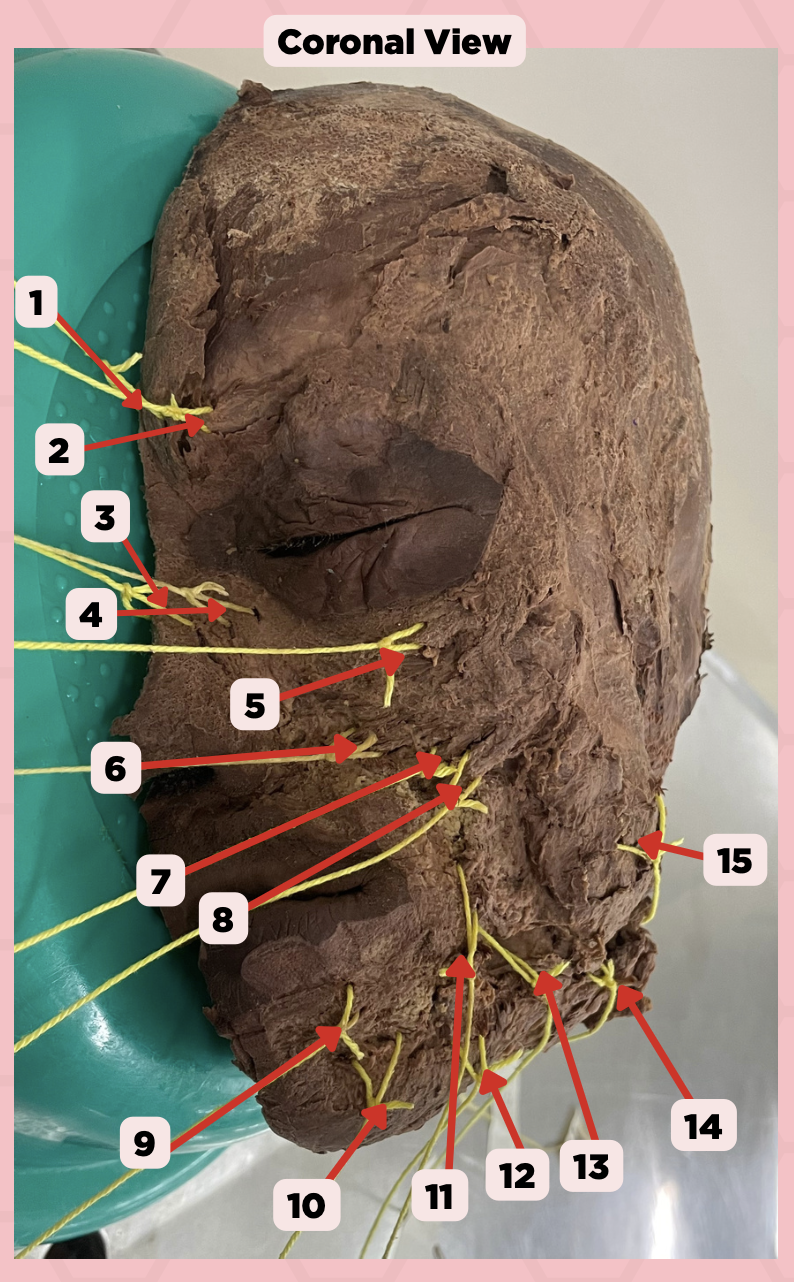
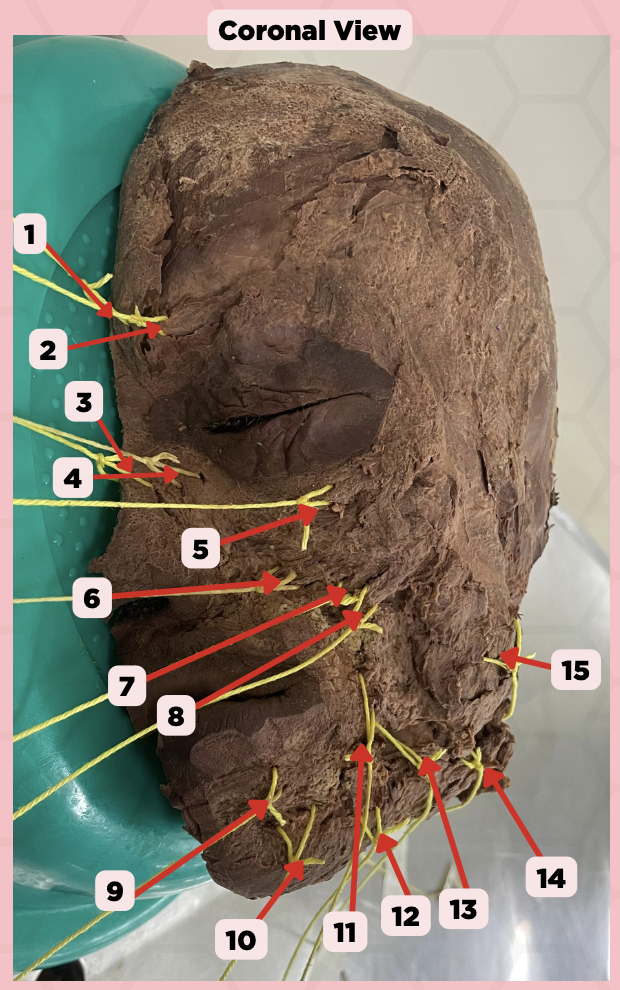
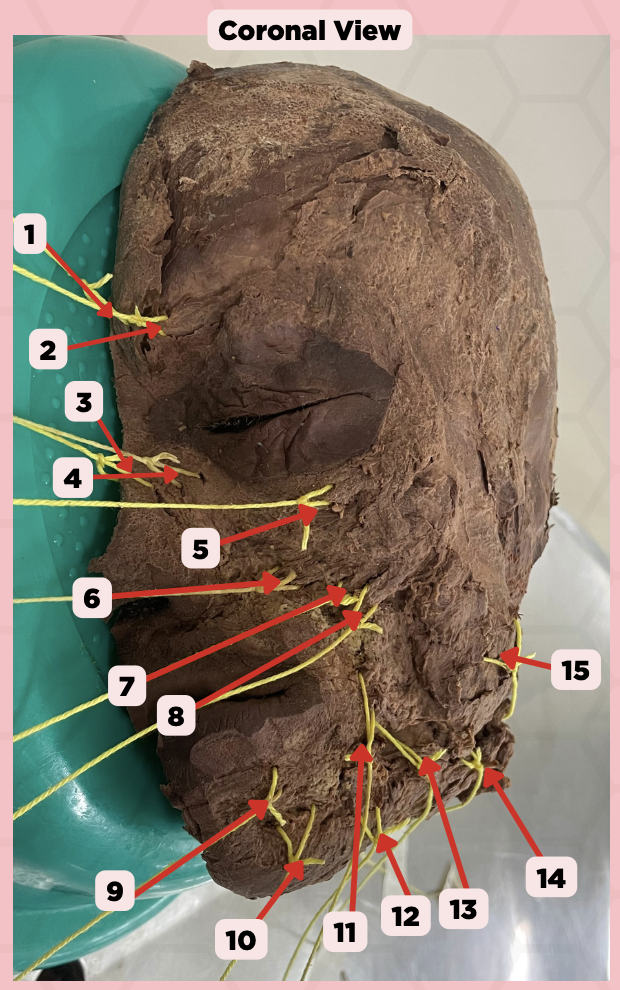
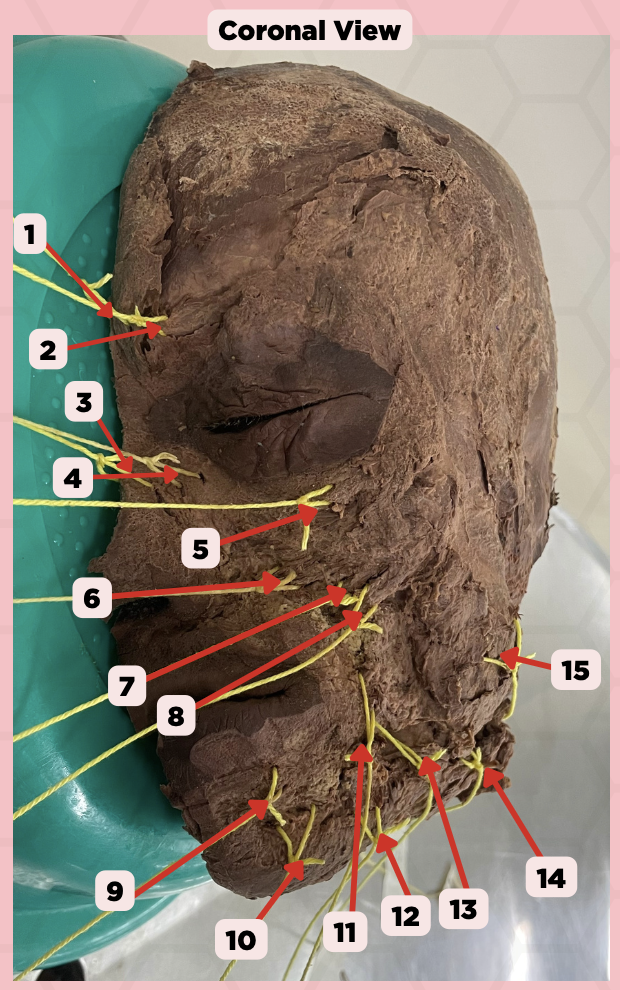
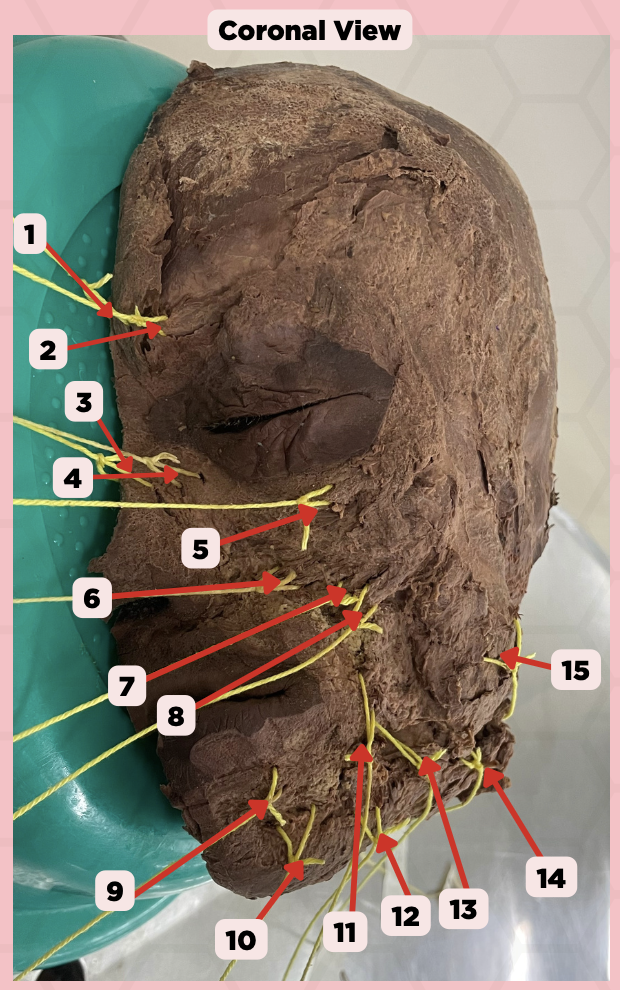
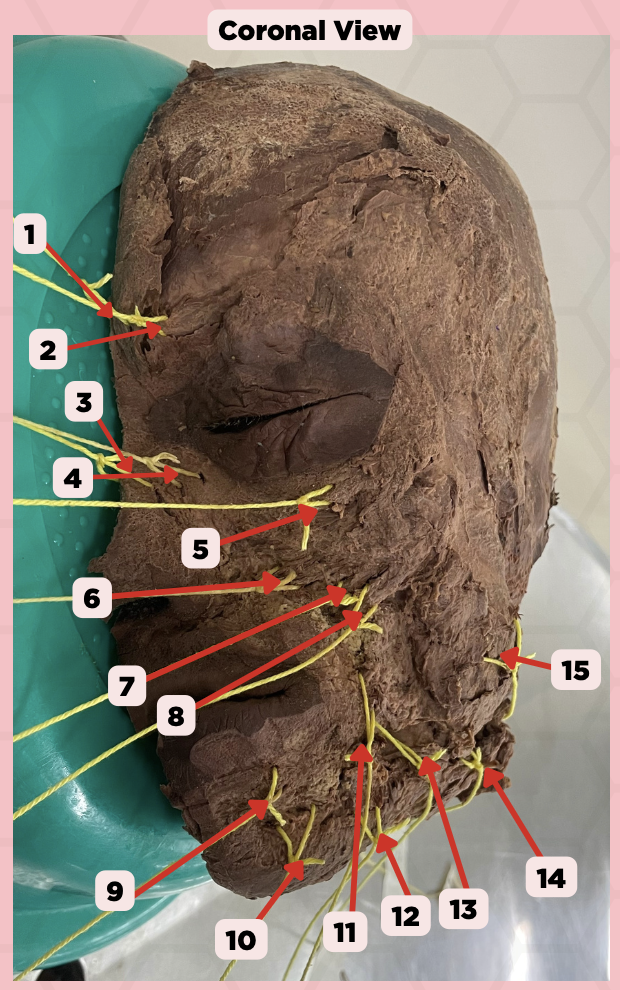
Procerus
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
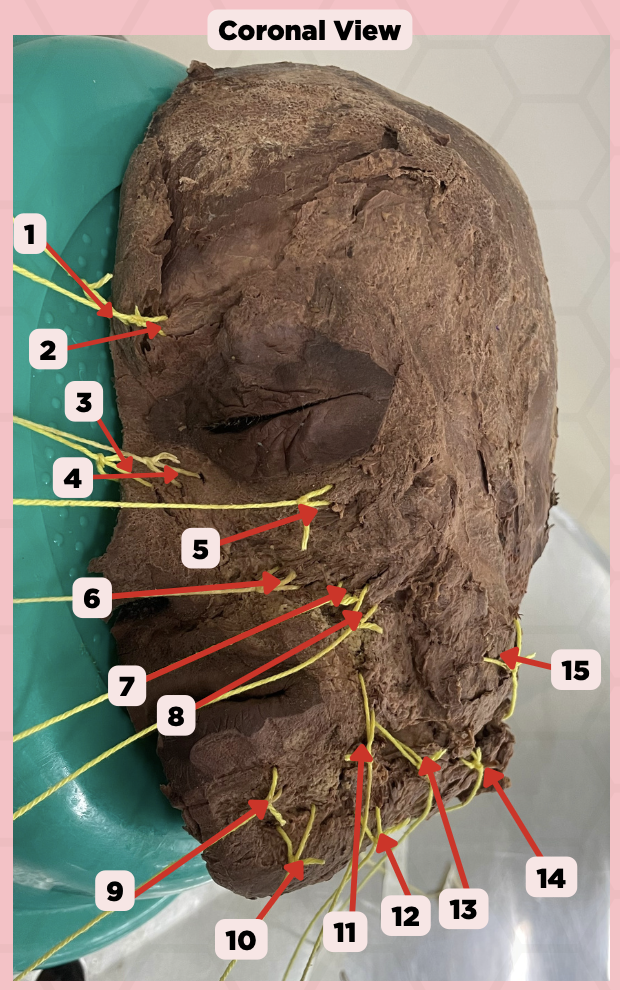
Corrugator Supercilii
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
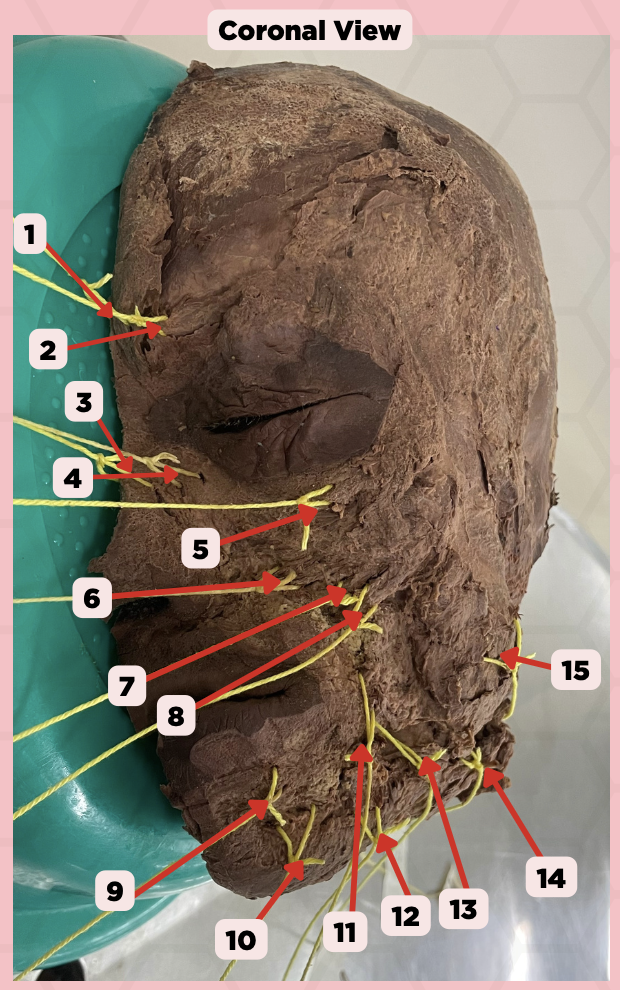
Nasalis
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
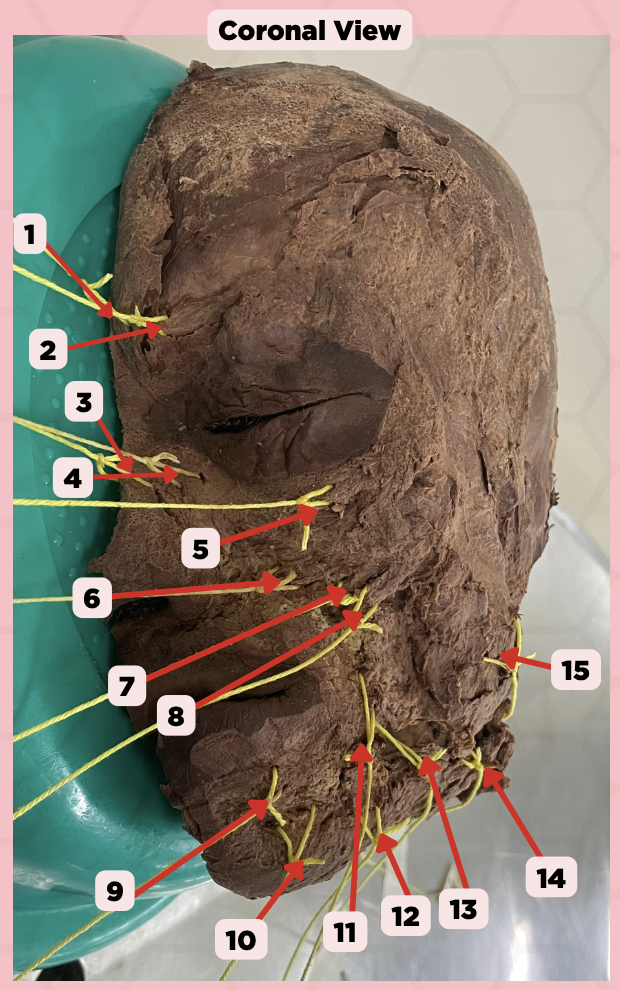
Levator Labii Superioris Alaque Nasi
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
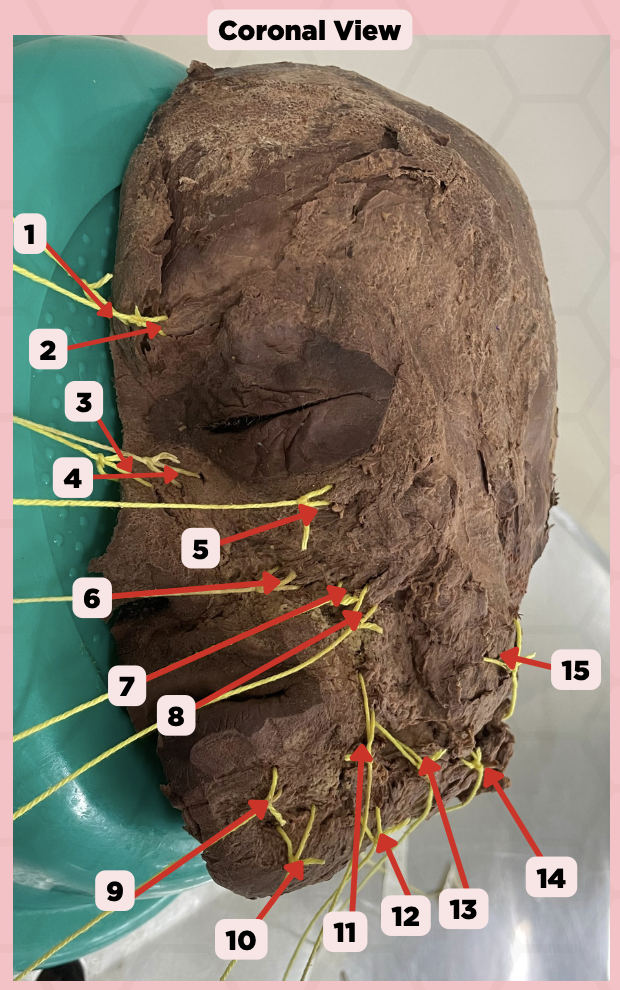
Orbicularis Oculi
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
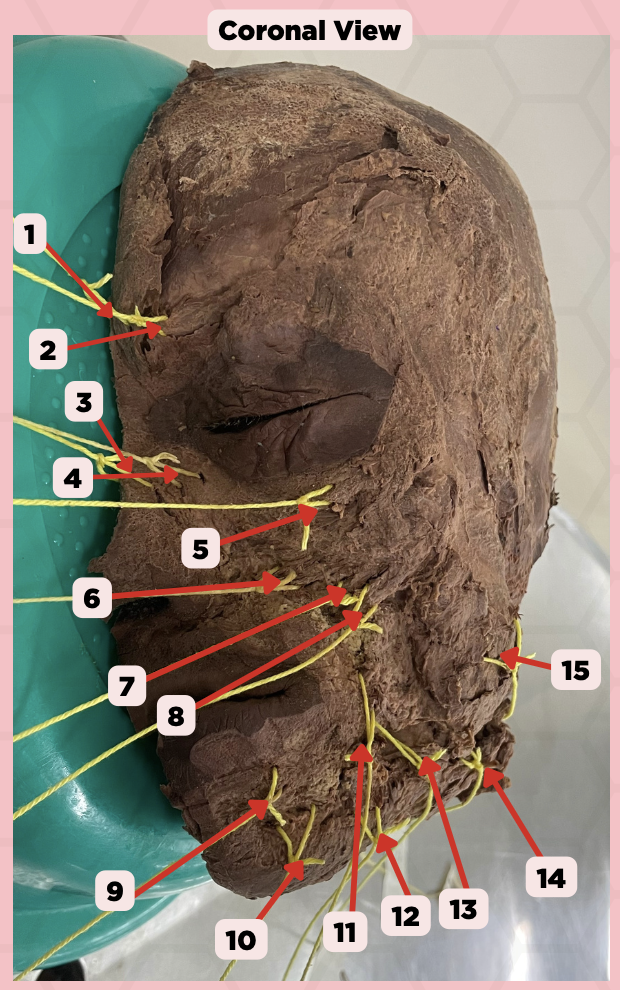
Levator Labii Superioris
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
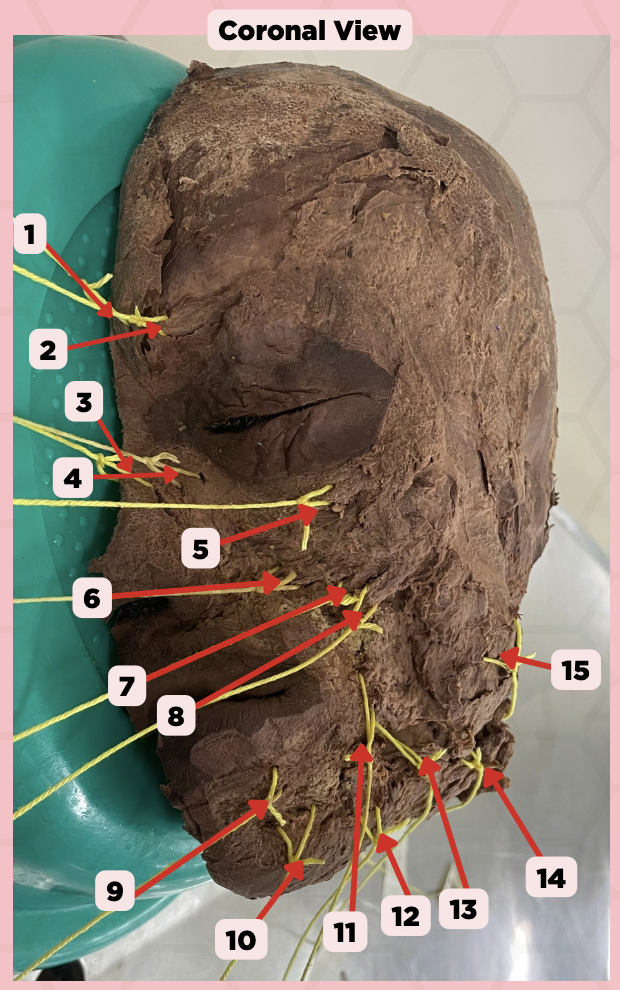
Zygomaticus Minor
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
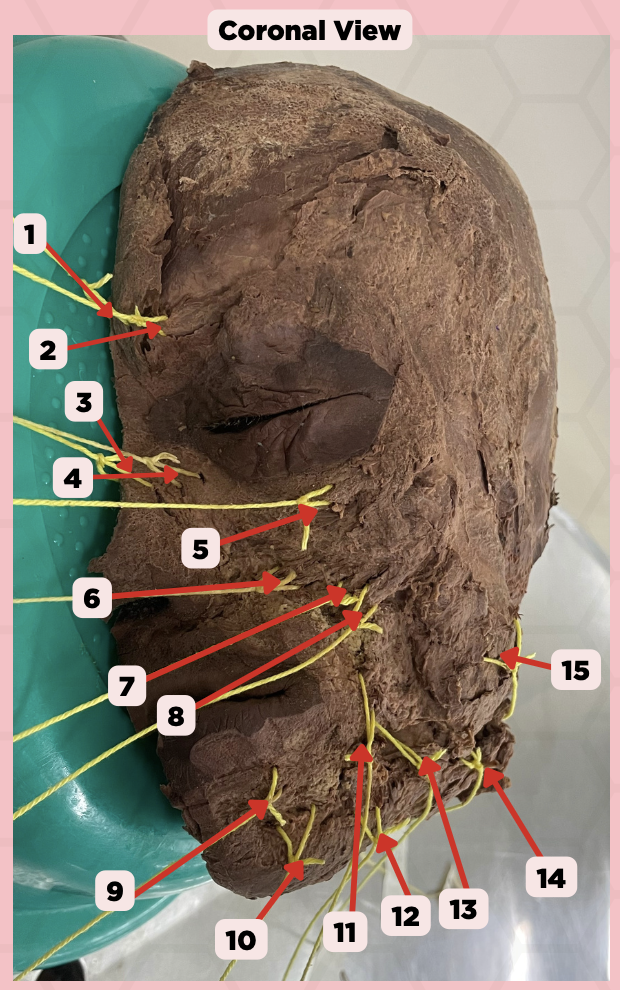
Zygomaticus Major
Identify the structure labeled as 8.
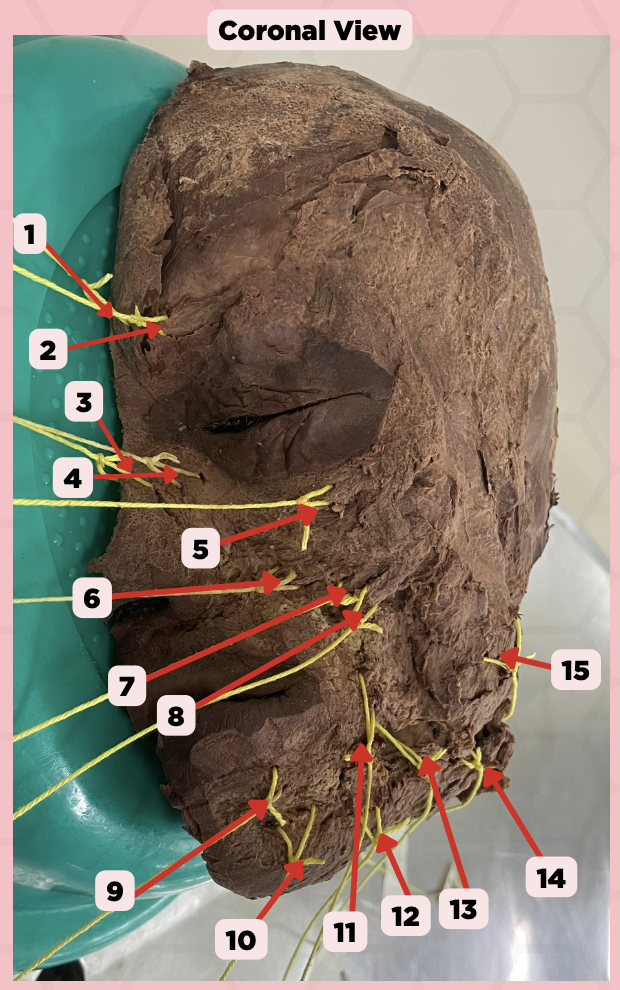
Orbicularis Oris
Identify the structure labeled as 9.
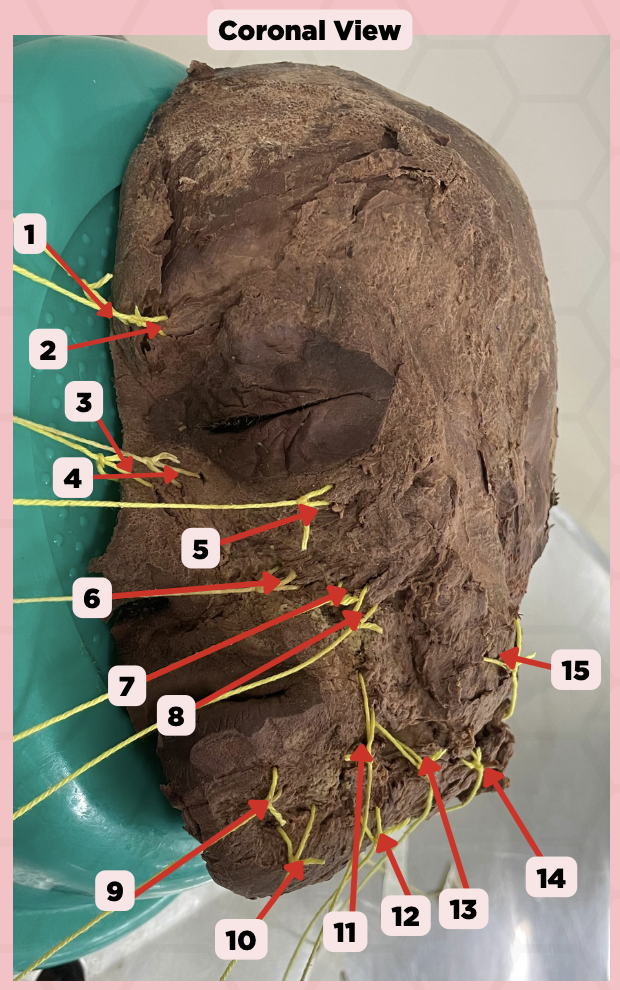
Mentalis
Identify the structure labeled as 10.
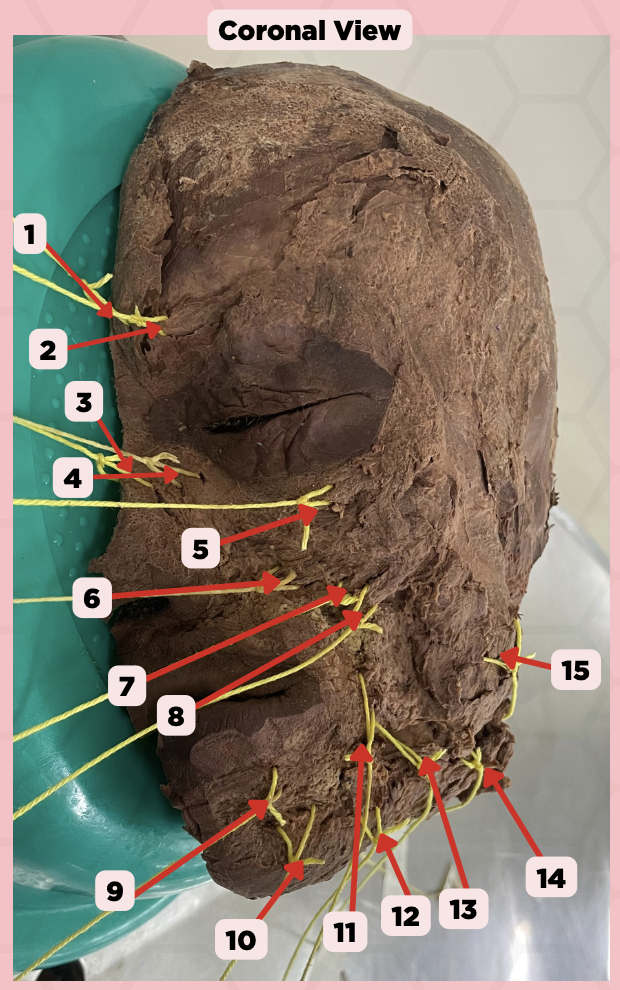
Risorius
Identify the structure labeled as 11.
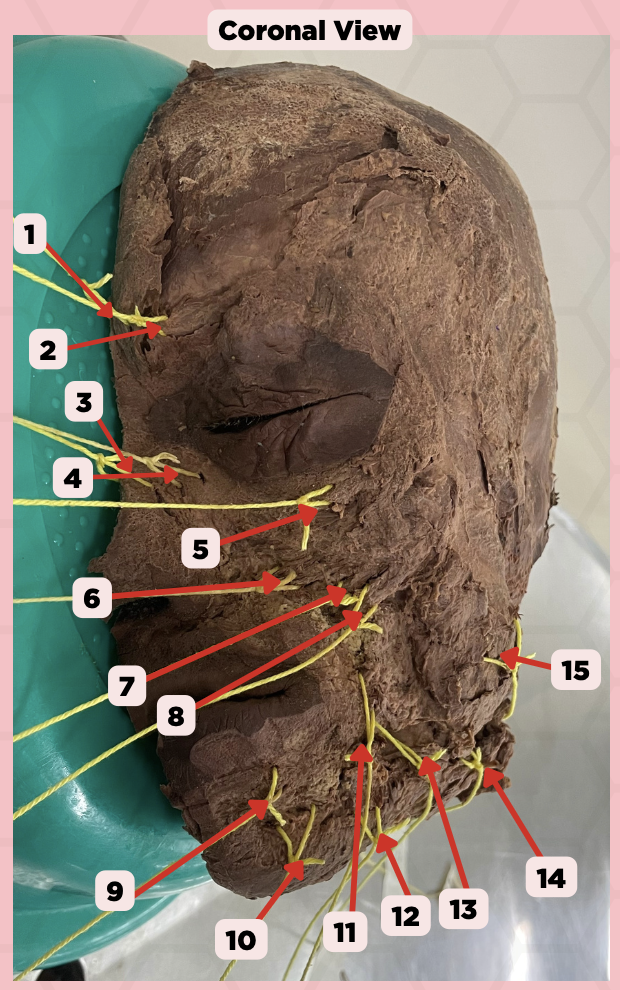
Depressor Anguli Oris
Identify the structure labeled as 12.
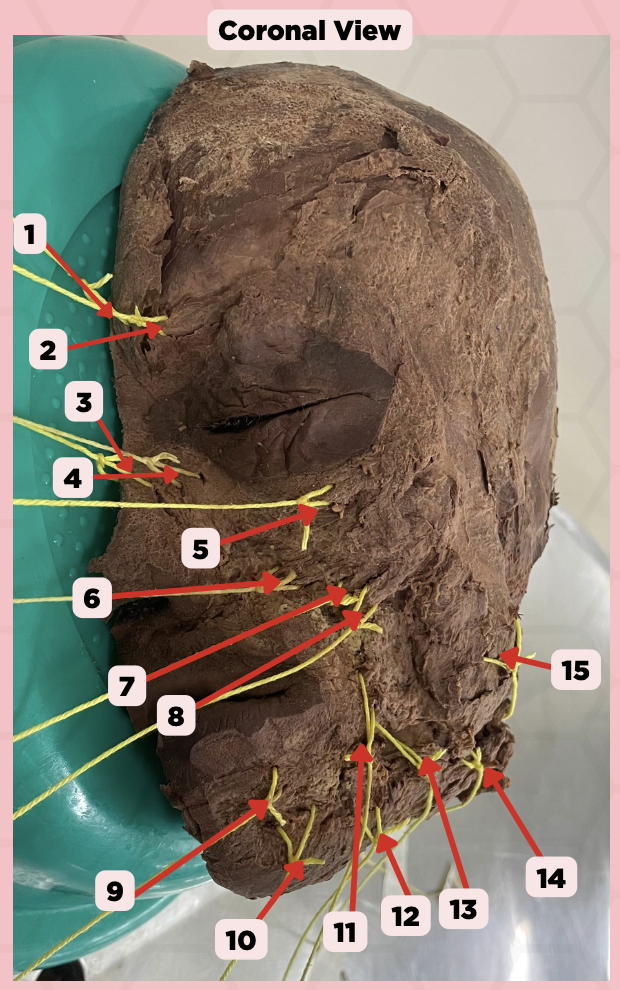
Buccinator
Identify the structure labeled as 13.
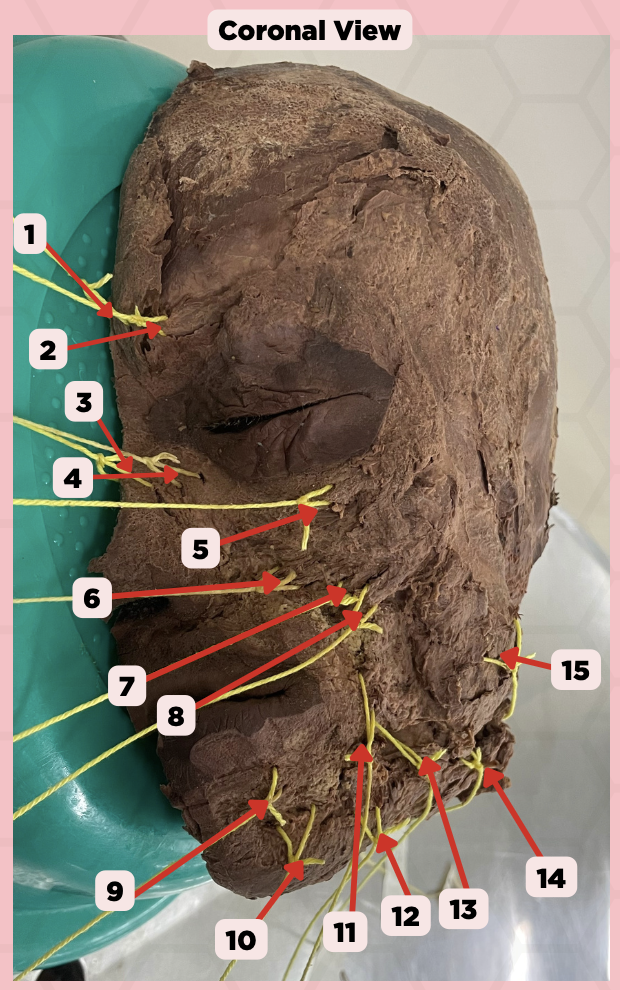
Facial Artery
Identify the structure labeled as 14.
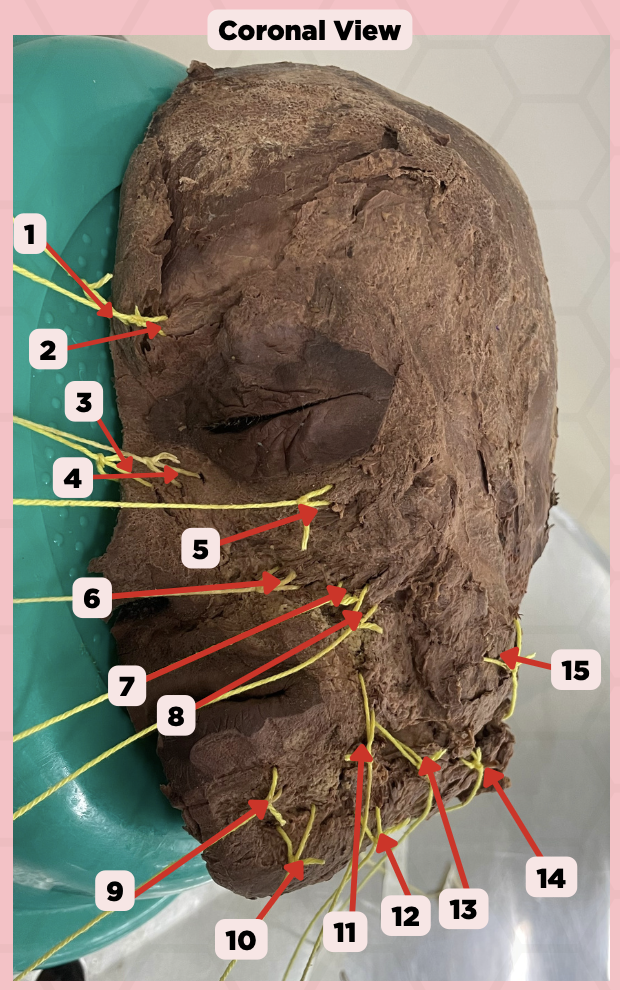
Masseter
Identify the structure labeled as 15.
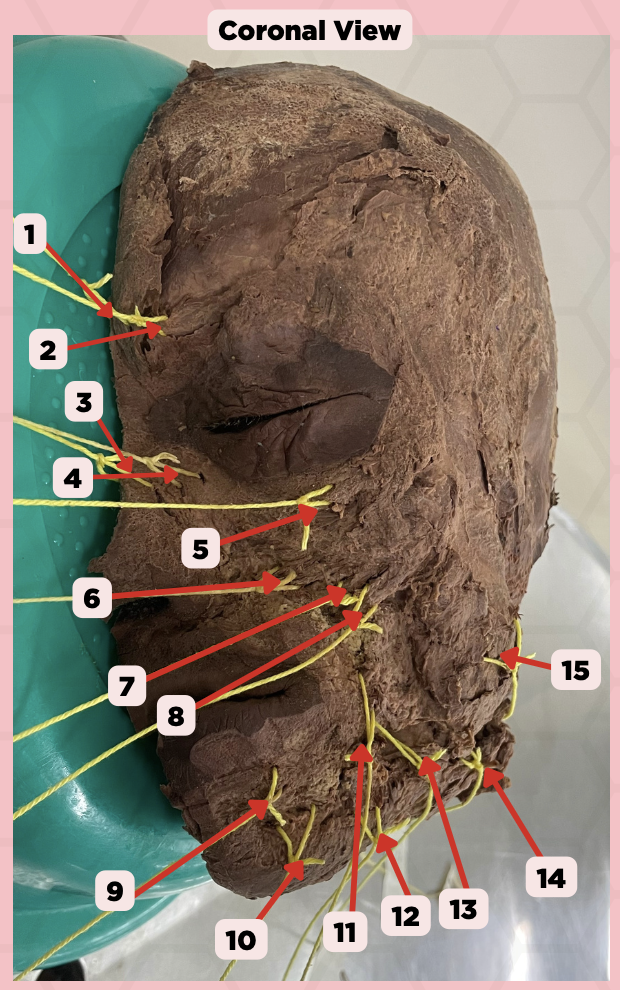
External Carotid Artery
The following arteries of the scalp comes from what major artery: Superior Thyroid, Ascending Pharyngeal, Lingual, Facial, Occipital, Posterior Auricular, Superficial Temporal, Maxillary
Internal Jugular Vein (Superior bulb)
The following veins of the scalp comes from what major vein: Inferior Petrosal, Occipital, Pharyngeal, Common Facial, Lingual, Superior Thyroid, Inferior Thyroid
Subclavian Artery
The following arteries of the face comes from what major artery: Vertebral, Internal Thoracic, Thyrocervical Trunk, Costocervical Trunk, Dorsal Scapular
External Carotid Artery
The following arteries of the face comes from what major artery: Facial Artery (Lateral Nasal, Superior Labial, Inferior Labial), Maxillary (Masseteric)
Internal Jugular Vein
The following veins of the face comes from what major vein: Common Facial, Facial (Angular, Supratrochlear, Supraorbital)
C. Internal Thoracic Artery
Which vessel originate from the subclavian artery?
A. Internal Carotid Artery
B. External Carotid Artery
C. Internal Thoracic Artery
D. External Thoracic Artery
A. Suprasternal Vein
The facial vein collects blood from these structures, EXCEPT for?
A. Suprasternal Vein
B. Angular Vein
C. Supratrochlear Vein
D. Supraorbital Vein
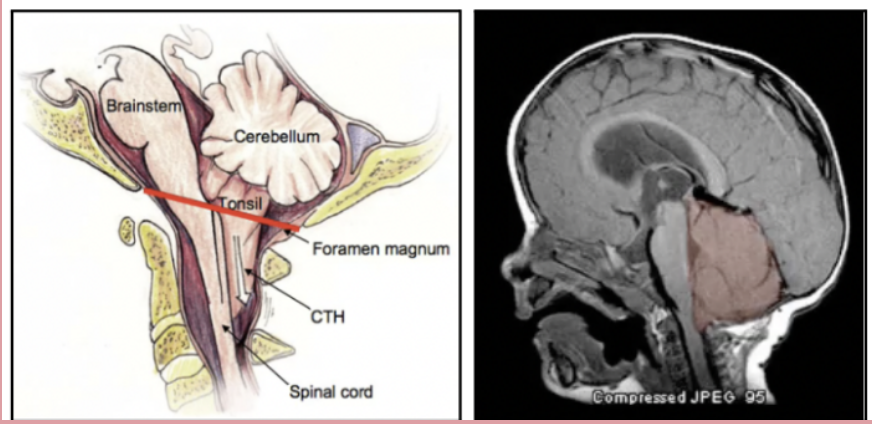
Cerebellar Tonssilar Herniation
Cerebellum herniates down through the foramen magnum which is produced by an increased intracranial pressure. This results in the compression of the pons and medulla and can result to death by cause of cardiopulmonary arrest. Manifestations: Pupil constriction, impaired arousal, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, Decorticate (Flexor) Posturing, Coma, and extremely poor prognosisFro
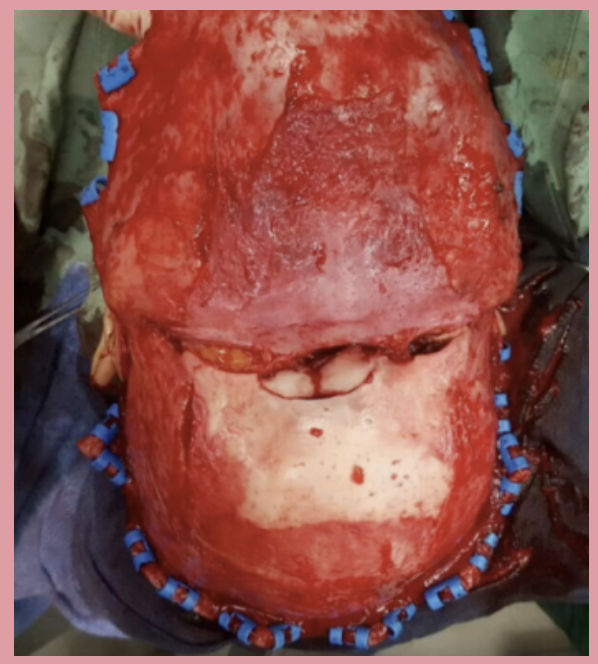
Frontal Bone Fracture
Intraoperative photo showing the scalp peeled back to reveal a what tye of fracture. The blue clips lining the edge of the cut scalp are necessary in order to prevent bleeding from the rich blood supply.
C. Improvement in respiratory function
Which of the following is NOT a potential consequence of cerebellar tonsillar herniation?
A. Compression of the pons and medulla
B. Increase in intracranial pressure
C. Improvement in respiratory function
D. Cardiopulmonary arrest
C. Aponeurotic layer
In which layer of the scalp is the frontal bone located?
A. Skin
B. Connective tissue
C. Aponeurotic layer
D. Loose areolar tissue
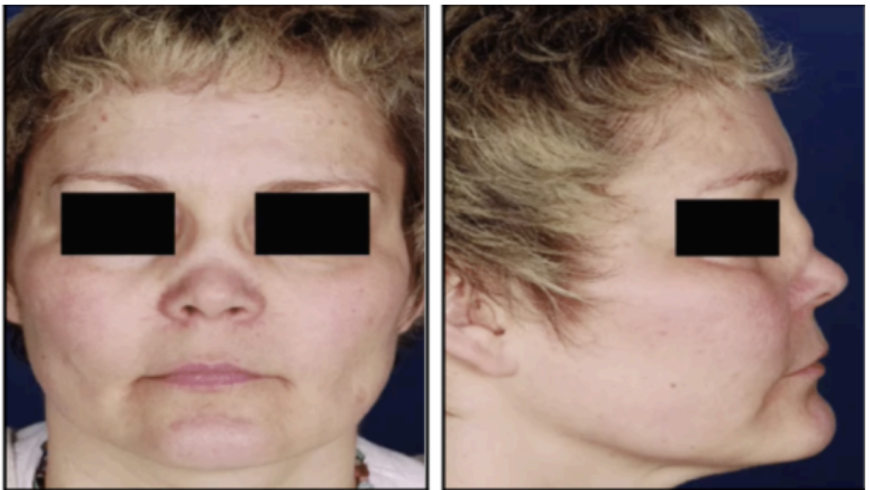
Saddle Nose Deformity
Presence of hematoma between the septal cartilage and perichondrium causes a result in destruction of septum, resulting in this deformity
B. Infections in the area cannot travel past the neck
The insertion of the occipitofrontalis into the occipital bones means that
A. Black eyes become more common in occurence
B. Infections in the area cannot travel past the neck
C. Scalp infections can spread to the eyes and nose
D. None of the choices given
B. Blood vessels within the surrounding perichondrium
What supplies the septal cartilage with oxygen and nutrients
A. Basilar artery
B. Blood vessels within the surrounding perichondrium
C. Axial arteries
D. Premasseteric artery
Glabellar Wrinkles
Corrugator supercilli. Located between the eyes. Draws eyebrows inferiorly/medially as in frowning causing vertical wrinkles superomedially to eye.
Smile Lines
Wrinkles found in Risorius Muscle, Zygomaticus Major
A.Cranial Nerve VII
What is the nerve supply of the corrugator supercilli and the risorius muscle?
A.Cranial Nerve VII
B. Cranial Nerve V
C.Cranial Nerve IX
D. Cranial Nerve X
A. Dynamic lines
Botulinum Toxin is used for?
A. Dynamic lines
B. Static lines
C. Tension lines
D. Trago labia line
Bell’s Palsy
Injuries to CN VII (Facial) may come from untreated ear infections, iatrogenic injuries from surgery, temporal bone fractures. This can result to?
d. Sudden onset of facial droop
Which of the following is a common symptom of an injury to the CN VII?
a. Blurred vision
b. Difficulty swallowing
c. Loss of taste sensation
d. Sudden onset of facial droop
d. i, ii, ii, iv, and v
The Kiesselbachs plexus/area is located on the anterior septum of the nose is made up of which blood vessels?
i. Anterior ethmoidal, Posterior ethmoidal
ii. Sphenopalatine
iii. Greater palatine
iv. Superior labial
v. Opthalmic artery
a. i, ii, iii, and iv
b. i, ii, and iii
c. i, iii, and iv
d. i, ii, ii, iv, and v
c. Kiesselbach’s Plexus
The nose is supplied by the Internal Carotid Artery as well as the External Carotid Artery. The latter splits into the Facial and Maxillary Artery, while the former into the Opthalmic Artery. What is the structure wherein the branches each converge at?
a. Cavernous Sinus
b. Semilunar Hiatus
c. Kiesselbach’s Plexus
d. Lamina Papyracea
Internal Carotid Artery
The following arteries of the nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses comes from what major artery: Opthalmic Artery, Anterior and Posterior Ethmoidal, Kiesselbach’s Plexus (Little’s Area)
External Carotid Artery
The following arteries of the nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses comes from what major artery: Facial Artery, Maxillary Artery
Internal Jugular Vein
The following veins of the nose, nasal cavity, and paranasal sinuses comes from what major vein: Common Facial Vein (Facial, Maxillary, Pterygoid venous plexus), Tributaries of Cavernous Sinus (Superior Opthalamic, Ethmoidal)
c. Nasal Turbinate
These structures located along the lateral walls of the nasal cavity play a role in warming and humidifying inspired air and regulates nasal airflow.
a. Nasal Conchae
b. Nasal Mucosa
c. Nasal Turbinate
d. Nasal Meatus
b. Caldwell view, grayish
A patient is suspected to have frontal sinusitis. What radiographic view should you utilize to confirm this diagnosis, and what would you expect the appearance of the sinuses to be?
a. Water’s view, black
b. Caldwell view, grayish
c. Water’s view, grayish
d. Caldwell view, black
d. Water’s view - Ethmoid sinus
Which of the following is INCORRECTLY paired?
a. Water’s view - Maxillary sinus
b. Caldwell view - Frontal sinus
c. Lateral view - Sphenoid sinus
d. Water’s view - Ethmoid sinus
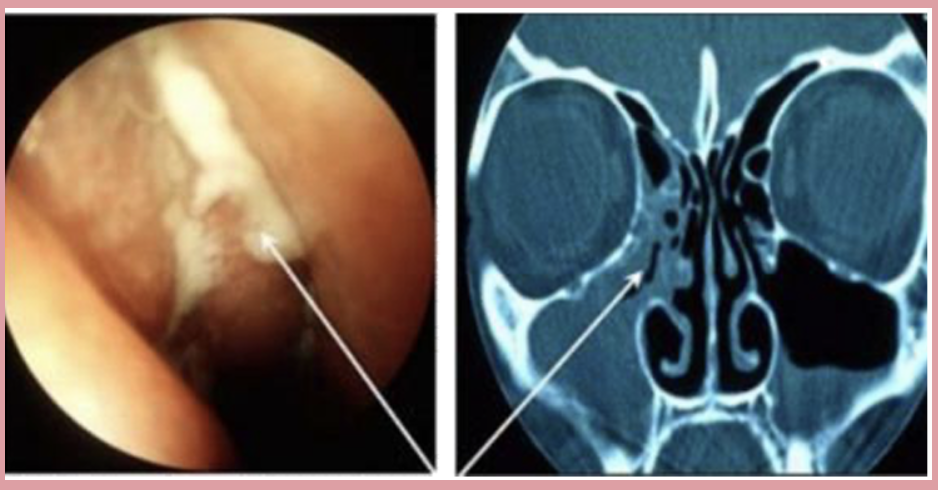
Sinusitis
CT scan showing the discharge coming out of the middle meatus and the pus within the maxillary sinus and that of the ethmoid sinuses more pronounced at the right side of the px.
b. Middle Meatus
What is the sinus drainage that drains the anterior and middle ethmoidal sinus, frontal sinus, and maxillary sinus?
a. Superior Meatus
b. Middle Meatus
c. Inferior Meatus
a. Caldwell-Luc’s
A patient with sinusitis will undergo an operation that involves irreversibly removing damaged mucosa from the maxillary sinus. What is this operation called?
a. Caldwell-Luc’s
b. Ohngren’s
c. Water’s
d. Sphenoid Surgery
A. Purulent mucoid discharge at the middle meatus
A patient with maxillary and frontal and ethmoidal sinus pain, fever and foul muco purulent rhinorrhea consults you. What will be a likely finding during your PE intranasally?
A. Purulent mucoid discharge at the middle meatus
B. Hyperacusis
C. Epiphora
D. Clear watery nasal discharge
c. Lamina papyracea
Extensive bleeding occurred while a patient was undergoing an endoscopic intranasal surgery. The surgeon notes hematoma located at the medial canthal area of the patient’s left eye. What structure may have been damaged?
a. Cribriform plate
b. Nasal Concha
c. Lamina papyracea
c. Concha Bullosa
When sinuses are hazy and turbinate/s are hyperaerated with a deviated nasal septum, what is the common finding for this patient?
a. Nasal Conchae
b. Ethmoid Bulla
c. Concha Bullosa
d. Sinusitis
c. Nasal Septum
What is the structure located in the midline of the nose that is comprised of flat cartilage anteriorly and bone posteriorly?
a. Middle Turbinate
b. Semilunar Hiatus
c. Nasal Septum
d. Nasal Meatus
c. Ethmoid sinus
A tumor in which sinus is most likely to encroach on the orbit as shown in the image?
a. Frontal sinus
b. Maxillary sinus
c. Ethmoid sinus
d. Sphenoid sinus
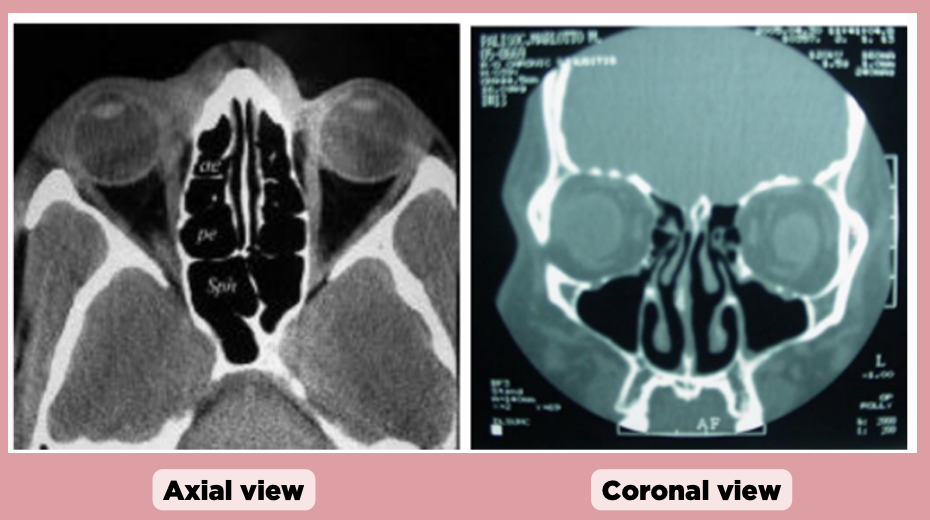
d. Ethmoid sinus
In the coronal view, which sinus is primarily visible and centrally located?
a. Sphenoid sinus
b. Frontal sinus
c. Maxillary sinus
d. Ethmoid sinus
b. A line connecting the medial canthus to the angle of the mandible
What anatomical landmark is used to define Ohngren's line?
a. A line connecting the infraorbital foramen to the angle of the mandible
b. A line connecting the medial canthus to the angle of the mandible
c. A line connecting the medial canthus to the maxillary second molar
d. A line connecting the lateral canthus to the angle of the mandible
b. A poor prognosis due to the tumor growing cranially towards the CNS
A malignancy located in the supra-structure region as defined by Ohngren's line is associated with?
a. A better prognosis due to the tumor moving away from the CNS
b. A poor prognosis due to the tumor growing cranially towards the CNS
c. No difference in prognosis compared to the infra-structure
d. Better prognosis due to better surgical accessibility
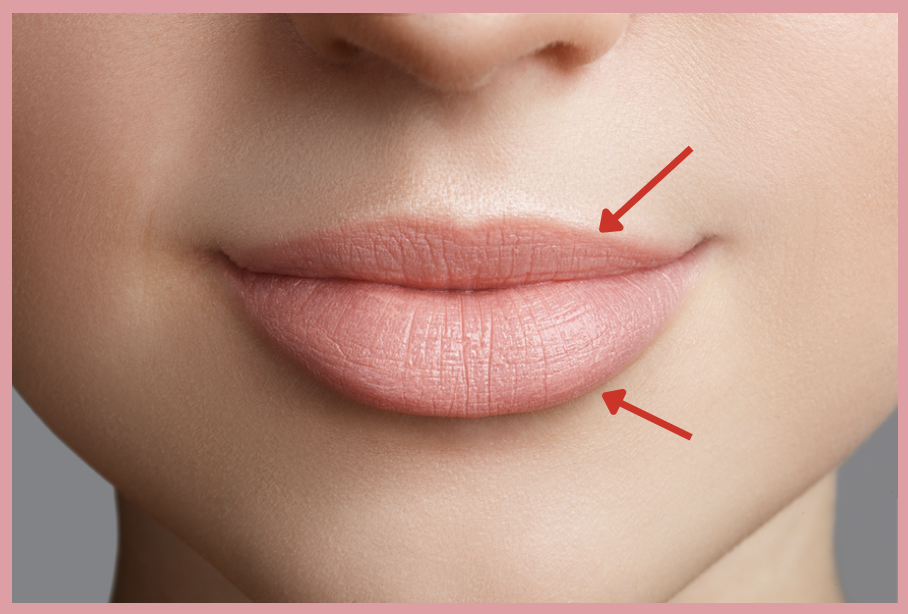
d. Vermillion border
This is the term of the pointed structures which marks the transition between skin and mucus membrane of the lips?
a. Oral commissure
b. Mentolabial sulcus
c. Philtral ridge
d. Vermillion border
The following muscles are innervated by the zygomatic and buccal
branch of the facial nerve EXCEPT:
a. Levator labii superioris
b. Risorius
c. Mentalis
d. Zygomaticus minor
a. Infraorbital nerve
Nerve which innervates the upper lip
a. Infraorbital nerve
b. Lingual nerve
c. Buccal nerve
d. Inferior alveolar nerve
External Carotid Arteries → Facial Artery
Trace the arterial supply of the lips.
Superior Labial Vein / Inferior Labial Vein → Facial Vein → Internal Jugular Vein
Trace the venous drainage of the lips.
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) → Maxillary Division (V2) → Infraorbital Nerve
Trace the innervation of the upper lip.
Trigeminal nerve (CN V) → Mandibular division (V3) → Mental nerve
Trace the innervation of the lower lip.
Cleft lip
A condition that arises due to a problem in the embryological development of the lip during gestation. Proper correction recreates a complete orbicularis muscular sling for better cosmesis and functional result
d. 32
How many permanent teeth does a normal young adult have?
a. 27
b. 28
c. 30
d. 32
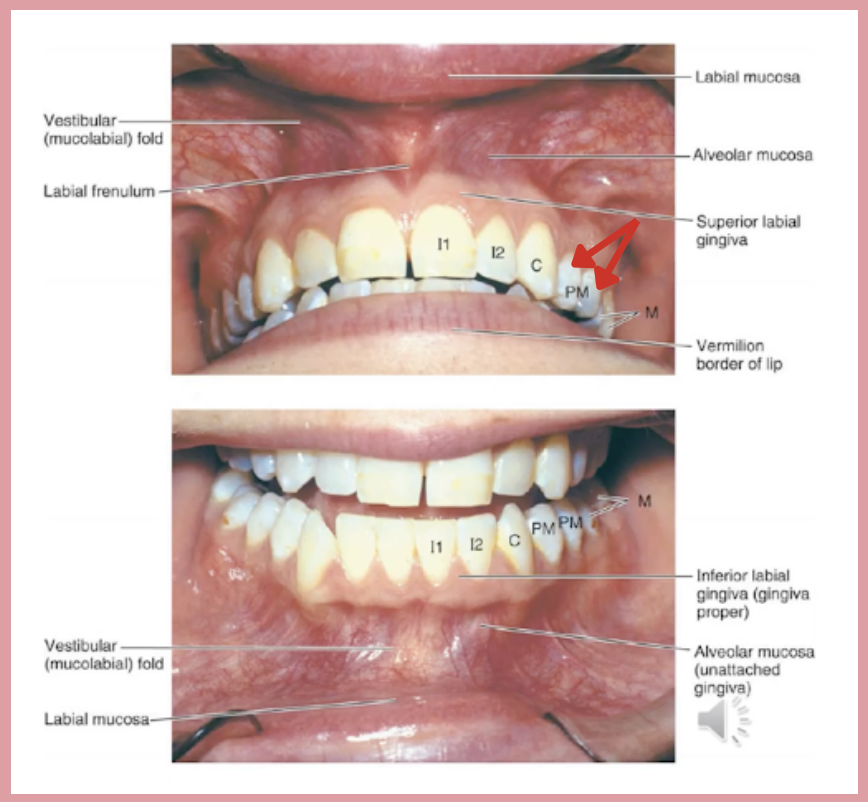
b. Middle superior alveolar branch
Teeth pointed by the red arrow is innervated by which nerve?
a. Posterior superior alveolar branch
b. Middle superior alveolar branch
c. Anterior superior alveolar branch
c. Submandibular nodes
The gingiva and teeth drain to which set of lymphatic nodes?
a. Lateral cervical nodes
b. Retropharyngeal nodes
c. Submandibular nodes
d. Submental nodes
Anterior superior alveolar, Middle superior alveolar artery
What is the arterial supply of the maxillary gingiva and teeth?
Greater palatine artery
What is the arterial supply of the lingual maxillary gingiva?
Inferior alveolar artery
What is the arterial supply of the mandibular gingiva and teeth?
Superior alveolar vein, Palatine vein
What is the venous drainage of the maxillary gingiva?
Mental vein
What is the venous drainage of the mandibular gingiva?
Infraorbital nerve, Anterior superior alveolar branch, Middle superior alveolar branch, Posterior superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the buccal side of maxillary gingiva?
Nasopalatine nerve, Greater palatine nerve
What is the innervation of the lingual side of maxillary gingiva?
Buccal nerve, Mental nerve
What is the innervation of the buccal side of mandibular gingiva?
Lingual nerve, Nerve to mylohyoid muscle
What is the innervation of the lingual side of mandibular gingiva?
Anterior superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the incisors and canines of maxillary teeth?
Middle superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the premolars and parts of the first molar of maxillary teeth?
Posterior superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the remaining parts of maxillary molar?
Posterior superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the incisors and canines of mandibular teeth?
Posterior superior alveolar branch
What is the innervation of the remaining mandibular teeth?
c. 3rd upper molar
The Greater palatine foramen is located opposite which area in the buccal mucosa?
a. 3rd lower molar
b. 2nd lower molar
c. 3rd upper molar
d. 2nd upper molar
c. Tensor Veli Palatini, Levator Veli Palatini, Musculus Uvulae
Cleft palate can cause problems in the insertion of various muscles:
a. Palatopharyngeus, Tensor Veli Palatini, Levator Veli Palatini
b. Palatoglossus, Tensor Veli Palatini, Levator Veli Palatini,
c. Tensor Veli Palatini, Levator Veli Palatini, Musculus Uvulae
d. Palatoglossus, Palatopharyngeus, Musculus Uvulae
a. Fauces
The palatine tonsils can be located in this landmark:
a. Fauces
b. Transverse palatine fold
c. Floor of the mouth
d. Palatine raphe
Greater ascending palatine artery
What is the arterial supply of the hard palate?
Palatine vein
What is the venous drainage of the hard palate?
Lesser palatine artery
What is the arterial supply of the soft palate?
Palatine vein
What is the venous drainage of the soft palate?
Greater palatine nerve, Nasopalatine nerve
What is the innervation of the hard palate?
Lesser palatine nerve
What is the innervation of the soft palate?
a. Cranial nerve X
Which of the following cranial nerves supply the palatoglossus?
a. Cranial nerve X
b. Cranial nerve IX
c. Cranial nerve V
d. Cranial nerve VII
c. Transverse Muscle
Which of the following intrinsic muscles elongates the tongue?
a. Superior Longitudinal Lingual Muscle
b. Inferior Longitudinal Lingual Muscle
c. Transverse Muscle
d. Vertical Muscle
d. Frenulum
The ventral portion of the tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth by which anatomic structure?
a. Sulcus terminalis
b. Foramen cecum
c. Circumvallate papillae
d. Frenulum